SendFar AP-8110 User manual

A
Outdoor
Wireless Access Point
User’s Manual
Before operating the unit, please read this manual thoroughly, and
retain it for future reference.
i
■
Contents
CHAPTER 1. HARDWARE INSTALLATION ........................................... 1
1.1 BEFORE YOU START ............................................................................. 1
1.2 LOCATE THE ACCESS POINT AND INLINE POWER INJECTOR PORTS.......... 2
1.3 INSTALLING THE ANTENNAS ................................................................... 3
1.4 INSTALLING THE CONSOLE PORT CABLE................................................. 3
1.5 CONNECTING THE POWER SUPPLY AND ETHERNET CABLE ....................... 4
1.6 OUTDOOR INSTALLATION ....................................................................... 5
CHAPTER 2. NETWORK TOPOLOGIES................................................. 6
2.1 WIRELESS ACCESS BRIDGE................................................................... 7
2.2 WIRELESS ACCESS ROUTER WITH PPPOE ETHERNET CONNECTION ....... 8
2.3 WIRELESS ACCESS ROUTER WITH DYNAMIC IP ETHERNET CONNECTION.. 9
2.4 WIRELESS ACCESS ROUTER WITH STATIC IP ETHERNET CONNECTION... 10
CHAPTER 3. WEB ACCESS.................................................................. 11
CHAPTER 4. CONFIGURATION............................................................ 15
4.1 INTRODUCTION ................................................................................... 15
4.1.1 Basic Configuration Steps........................................................... 15
4.2 SYSTEM SETUP................................................................................... 16
AFTER THAT, CLICK FINISH AT THE BOTTOM OF THIS PAGE TO COMPLETE THE
MODIFICATION OF THIS PAGE. ......................................................................... 20
AFTER THAT, CLICK FINISH AT THE BOTTOM OF THIS PAGE TO COMPLETE THE
MODIFICATION OF THIS PAGE.TCP/IP PROTOCOL CONFIGURE ......................... 20
TCP/IP PROTOCOL CONFIGURE .................................................................... 21
4.2.1 Virtual Server Mapping................................................................ 21
4.3 CONFIGURE DHCP SERVER ................................................................ 23
4.3.1 General DHCP Server Parameter............................................... 24
4.3.2 Fixed Host Entries ....................................................................... 24
4.4 CONFIGURE SNMP............................................................................. 26
4.4.1 Configure Community Pool ......................................................... 26
4.4.2 Configure Trap Host Pool............................................................ 27
4.5 CONFIGURE WIRELESS RELATED PARAMETERS..................................... 29
4.6 SECURITY........................................................................................... 31
4.6.1 IEEE 802.1x Access Control ....................................................... 31
4.6.2 MAC based Access Control ........................................................ 32
4.7 UTILITY............................................................................................... 33

ii
4.7.1 Software Upgrade ....................................................................... 33
4.7.2 Administration.............................................................................. 34
CHAPTER 5. STATUS MONITOR.......................................................... 35
5.1 SYSTEM INFORMATION ........................................................................ 36
5.2 DHCP INFORMATION .......................................................................... 37
5.3 STATION INFORMATION........................................................................ 38
5.4 STATISTIC INFORMATION ..................................................................... 39
CHAPTER 6. SPECIFICATIONS ............................................................ 40
CHAPTER 7. DEFAULT SETTINGS ...................................................... 42
7.1 GENERAL CONFIGURATION .................................................................. 42
7.1.1 System......................................................................................... 42
7.1.2 Virtual Server Mapping................................................................ 43
7.1.3 DHCP .......................................................................................... 44
7.1.4 SNMP .......................................................................................... 45
7.1.5 Wireless LAN............................................................................... 47
7.2 UTILITY............................................................................................... 48
7.2.1 Software Upgrade ....................................................................... 48
7.2.2 Administration.............................................................................. 48
CHAPTER 8. REGULATORY COMPLIANCE INFORMATION ............. 49
1
Chapter 1. Hardware Installation
This chapter describes the procedures for installing the SendFar Outdoor
Access Point.
1.1 Before You Start
After unpacking the system, make sure the following items are present and
in good condition.
1. Access Point
2. Inline Power Injector
3. AC Power Cord
4. MIL-C-5015 style RS232 Console Port Cable
5. Grounding Wire
6. Cross over Ethernet Cable
7. Two rubber dipole antenna
7. 30M MIL-C-5015 style Ethernet Cable
8. Mast Mounting Kit
10. Wall Mounting Kit
11. User’s Manual Disk
12. Simple Spanner
2
3
4
5
6
8
9
10
11
12
7

2
1.2 Locate the Access Point and Inline Power
Injector Ports
zSpecial Ethernet port 1 for connecting the MIL-C-5015 style Ethernet
Cable
zSpecial serial port 2 for connecting the MIL-C-5015 style RS-232
console port cable
zGrounding port 3.
zSpecial N-Type connector 4 for connecting the antenna or RF cable.
zPower & Data output port 5 for connecting the other of the MIL-C-
5015 style Ethernet Cable
zData input port 6 for connecting the Ethernet Cable to a Hub Switch
Router or a PC.
3
1.3 Installing the Antennas
Step 1: With the unit powered off, attach the dipole antenna to the antenna
connector as shown in Figure 1.3.
NOTE: Do not over-tighten; finger tight is sufficient. Position the antenna
vertically for best omni-directional signal reception.
Figure 1.3.
Before installing your WLAN system, we recommend that you test the
Access Point using the dipole antenna included in your package. Once
testing is completed, install your Access Point for use with the appropriate
antenna for your application.
1.4 Installing the Console Port Cable
Step 2: Attach the Console Port cable to the Serial Port. Attach the other
cable end to the Serial Port on a PC running a terminal emulation program,

4
and set the terminal to 15200 Baud, No-Parity, 8 data bits, 1 Stop bit, and
ANSI compatible.
NOTE: This connection is required for setting up initial configuration
information.
After configuration is completed, this cable may be removed until additional
configuration is required via the Serial Port.
1.5 Connecting the power supply and Ethernet
cable
Step 3 Plug the female end of the power cord into the Inline Power Injector,
and then plug the male end of the power cord into a power outlet or power
strip. The Power LED on the front of the Inline Power Injector will light up.
Step 4 Run the cross over Ethernet cable (included in your package) from
Data Input Port (on the front of the Inline Power Injector) to the Ethernet
Port on the PC we mentioned above.
NOTE: This connection is required for setting up initial configuration
information. After configuration is completed, this cable will be removed,
and then you should run an Ethernet cable from Data Input Port (on the
front of the Inline Power Injector) to the LAN connection (such as a hub or
concentrator).
Step 5 Plug the MIL-C-5015 style Ethernet connector into the Special
Ethernet port on the back of the access point.
Step 6 Plug the RJ-45 Ethernet connector (the other end of the Special
Ethernet cable) into the Power & Data Output Port on the front of the Inline
Power Injector. When the Access Point receives power over the Ethernet
cable, the Access Point will start its boot sequence and the Active LED on
the front of the Inline Power Injector will light up.
5
1.6 Outdoor Installation
Outdoor Access Point device can be mounted on the side of a
building or mounted to an mast as shown in following:
A wall (side) mount allows for mounting the Outdoor AP on the side of
a building. This will provide a convenient mounting location when the
roof overhang is not excessive and/or the location is high enough to
provide a clear line of sight.
Grounding
A safety grounding system is necessary to protect your outdoor
installation from lightning strikes and the build-up of static electricity.
So direct grounding of the antenna mast, Outdoor AP and
Surge Arrester is very important. And so mounting the Outdoor AP on
the antenna mast, you have to connect the Outdoor AP to the same
grounding system with the AC wall outlet.
The grounding system must comply with the National Electrical Code
and safety standards that apply in your country. Always check with a
qualified electrician if you are in doubt as to whether your outdoor
installation is properly grounded.

6
Chapter 2. Network Topologies
This chapter describes several main types of installations commonly
implemented using the Outdoor Wireless Access Point (OWAP). This is
by no means intended to be an exhaustive list of all possible configurations,
but rather shows examples of some of the more common implementations
(as shown in following figuration).
The OWAP can perform in router or bridge modes. In a wireless topology,
all communication between network stations is done through a centralized
Access Point. To show some possibilities of wireless topologies, the
following examples are provided:
1. Wireless Access Bridge
2. Wireless Access Router with PPPoE Ethernet connection
3. Wireless Access Router with dynamic IP address Ethernet
4. Wireless Access Router with static IP address Ethernet
7
2.1 Wireless Access Bridge
1. Set the OWAP as a bridge (bridge IP address is 192.168.2.1).
2. Set Wireless parameters on OWAP: Channel (1) and SSID
(wireless)
3. Set Wireless parameters on client stations PC1, PC2 and PC3:
SSID (wireless).
4. Left side stations are transparent to the right side network.
5. DHCP server assigns IP address to PC1, PC2 and PC3.

8
2.2 Wireless Access Router with PPPoE
Ethernet connection
1. Set the OWAP as a Router (Wireless Interface IP is 192.168.1.1,
Ethernet Interface IP is 192.168.2.1, must turn on NAT on Ethernet
Interface, default route is 0.0.0.0).
2. Choose the PPPoE connection mode and specify that your
personal ISP provided PPPoE Username and PPPoE Password to
enable ADSL broadband access.
3. Set Wireless parameters on OWAP: Channel (1) and SSID
(wireless)
4. Turn on DHCP server on the OWAP and assign IP address to PC1,
PC2 and PC3.
5. Set Wireless parameters on client stations PC1, PC2 and PC3:
SSID (wireless).
9
2.3 Wireless Access Router with dynamic IP
Ethernet connection
1. Set the OWAP as a Router (Wireless Interface IP is 192.168.1.1, must
turn on NAT on Ethernet Interface).
2. Enable DHCP client on the Ethernet Interface of the OWAP (This
OWAP will got IP / Gateway / DNS from the DHCP server).
3. Set Wireless parameters on the OWAP: Channel (1) and SSID
(wireless)
4. Turn on DHCP server on the OWAP and assign IP address to PC1,
PC2 and PC3.
6. Set Wireless parameters on client stations PC1, PC2 and PC3:
SSID (wireless).

10
2.4 Wireless Access Router with static IP
Ethernet connection
1. Set the OWAP as a Router (Wireless Interface IP is 192.168.1.1,
Ethernet Interface IP is 192.1682.1, must turn on NAT on Ethernet
Interface, default route is 192.168.2.254).
2. Set Wireless parameters on OWAP: Channel (1) and SSID
(wireless)
3. Turn on DHCP server on the OWAP and assign IP address to PC1,
PC2 and PC3.
4. Set Wireless parameters on client stations PC1, PC2 and PC3:
SSID (wireless).
11
Chapter 3. Web Access
Web Connection
The SendFar Wireless Access Point (OWAP) supports access to the
configuration system through the use of an HTTP Interface (web browser).
Before configuring the OWAP, you need to know the IP Address assigned
to the unit.
When shipped from the factory, the IP Address (192.168.2.1) was assigned
to the OWAP by default. To start a web connection use:
http://192.168.2.1/
Identify the IP Address assigned to the unit
However, the IP Address may be changed and you cannot connect the unit
using the default IP Address. In this case, you must identify the OWAP IP
Address before configuration. To identify the IP Address, you can use the
Serial Port to gain access the current network status. To start a Serial Port
connection:
1. Attach a serial data (RS-232) cable to the Serial Port Adapter.
Connect the other cable end to a terminal or a PC running a terminal
emulation program. Use a 9-pin female to 9-pin female NULL Modem
cable.
2. Set the terminal to 115200 Baud, No-Parity, 8 data bits, 1 Stop bit,
and ANSI compatible.
Note: Running a terminal emulation program on your PC, such as
HyperTerminal, and then set the following connection properties:
zClick the Start icon > Program > Accessories >
Communication > Terminal.
zCreate a new connection file, and then select a Com Port
<COM1, COM2, etc., depending on your PC> with 115200bps /
8-bits / 1-stop.
zClick the properties icon in the Tool Bar > setting > select
Emulation terminal VT100 > ok.

12
3. Reboot or turn on your OWAP
4. When the OWAP is powered up, the “Current Network Status” will be
displayed.
Figure 3-1 Current Network Status
Web Access Procedure
Once you identify the IP Address assigned to your OWAP, use your web
browser to configure the OWAP through the HTTP Interface.
The following procedure explains how to configure each item.
1. Open your browser and enter the IP Address
2. Press ENTER and the OWAP Login screen appear.
13
Figure 3-2 Login Screen
3. Enter
root in the User Name and the Password fields. And then the
web configuration user interface screen appears.
Figure 3-3 Web User Interface
Web Configuration Structure
The web configuration user interface be grouped in a tree structure, and
contains the following settings or information:
▽ General Configuration
● System
● TCP/IP
-Virtual Server
-DHCP
-SNMP
● Wireless
● Security
-802.1x Access Control

14
-MAC Filter
▽ Running Status
● System Info
● DHCP Info
● Station Info
● Statistic Info
▽ Utility
● Software Upgrade
● Administration
Move through the tree by clicking on an icon to expand or collapse the tree.
The nodes on the tree represent web pages that allow you to view and
modify the parameters.
Figure 3-4 Web Configuration Structure
15
Chapter 4. Configuration
4.1 Introduction
What you Need to Know
Since each network is unique, the OWAP must be configured to operate in
your network environment. Before configuring the OWAP, you need to
know the role of the OWAP on your network.
The OWAP can be configured into four operation modes:
1. Wireless Access Bridge
2. Wireless Router with PPPoE Client Ethernet connection
3. Wireless Router with DHCP Client Ethernet connection
4. Wireless Router with Static IP Ethernet connection
4.1.1 Basic Configuration Steps
Modify the Default Settings and Apply the New
This section will describe a 5-step configuration to setup your Outdoor
Wireless Access Point (OWAP) workable.
1. Select an operation mode for your OWAP on the web page “/General
Config/System/”, and click FINISH to refresh this page.
2. Modify the factory-set default parameters on the web page “/General
Config/System/”page, and click FINISH to save your changes.
3. Modify the factory-set default parameters on the web page “/General
Config/Wireless/”page, and click FINISH to save your changes.
4. (Optional) Modify others parameters on the web page “/General
Config/”page, and click FINISH to save your changes.
5. Move on page “/Utility/Administration/”, select the Save then Restart
and then click FINISH to take effect the previous configuration
changes.

16
4.2 System Setup
When setting up a SendFar Wireless Access Router (OWAP), you must
decide which operation mode that your OWAP works. This feature is
available in the “/General Config/System/” page.
Figure 4-1 & 4-2 show the “General Configuration – System Setup”
page.
Figure 4-1 General Configuration – System Setup-1
17
Figure 4-2 General Configuration – System Setup-2
Host Information
- Host Name. The Host Name is not an essential setting, but it helps
identify the device in network. Use this setting to assign a name to the
device.
Operation Mode
The First Thing You Have To Do
Select an operation mode, and click FINISH to refresh this page.
Wireless Access Bridge
Select the Wireless Access Bridge mode. And then set the corresponding
parameters.
- Bridge IP Address. Use this setting to assign or change the bridge’s IP
address.

18
- Bridge Subnet Mask. Enter an IP subnet mask to identify the sub
network so the IP address can be recognized on the LAN.
Default Route IP
- IP Address. Enter the default Gateway IP Address.
After that, click FINISH at the bottom of this page to complete the
modification of this page.
Wireless Router with PPPoE Client Ethernet connection
If you are an ADSL subscriber, you need to specify that you personal ISP
PPPoE Username and Password to enable ADSL broadband access.
- PPPoE User Name. This setting allows you to enter the user name that
your ISP assigns to your account.
- PPPoE Password. Enter the password that your ISP assigns to your
account.
- Password Confirm. Enter the PPPoE Password once more again.
Wireless Interface Address
- IP Address. Use this setting to assign or change the wireless interface’s
IP address.
- Subnet Mask. Enter an IP subnet mask to identify the sub network so the
IP address can be recognized on the WLAN.
Ethernet Interface Address
- IP Address. Use this setting to assign or change the Ethernet interface’s
IP address
- Subnet Mask. Enter an IP subnet mask to identify the sub network so the
IP address can be recognized on the WAN.
NAPT performs on which interface?
There are three interfaces. You can select one to use or select "None"
to disable it.
19
Default Route IP
- IP Address. Enter the default Gateway IP Address.
DNS Server IP
- Primary DNS Server IP. Enter the Primary Domain Name Server IP
Address.
- Secondary DNS Server IP. Enter the Secondary Domain Name Server
IP Address.
After that, click FINISH at the bottom of this page to complete the
modification of this page.
Wireless Router with DHCP Client Ethernet connection
Wireless Interface Address
- IP Address. Use this setting to assign or change the wireless interface’s
IP address.
- Subnet Mask. Enter an IP subnet mask to identify the sub network so the
IP address can be recognized on the WLAN.
NAPT performs on which interface?
There are three interfaces. You can select one to use or select "None"
to disable it.
Default Route IP
- IP Address. Enter the default Gateway IP Address.
DNS Server IP
- Primary DNS Server IP. Enter the Primary Domain Name Server IP
Address.
- Secondary DNS Server IP. Enter the Secondary Domain Name Server
IP Address.

20
After that, click FINISH at the bottom of this page to complete the
modification of this page.
Wireless Router with static IP Ethernet connection
Wireless Interface Address
- IP Address. Use this setting to assign or change the wireless interface’s
IP address.
- Subnet Mask. Enter an IP subnet mask to identify the sub network so the
IP address can be recognized on the WLAN.
Ethernet Interface Address
- IP Address. Use this setting to assign or change the Ethernet interface’s
IP address
- Subnet Mask. Enter an IP subnet mask to identify the sub network so the
IP address can be recognized on the WAN.
NAPT performs on which interface?
There are three interfaces. You can select one to use or select "None"
to disable it.
Default Route IP
- IP Address. Enter the default Gateway IP Address.
DNS Server IP
- Primary DNS Server IP. Enter the Primary Domain Name Server IP
Address.
- Secondary DNS Server IP. Enter the Secondary Domain Name Server
IP Address.
After that, click FINISH at the bottom of this page to complete the
modification of this page.
21
TCP/IP Protocol Configure
4.2.1 Virtual Server Mapping
Sometimes, the operator can expose the internal servers on the local
intranet to the public Internet. For this, you must create the Virtual Server
Mapping for these invisible internal servers.
Select the “/General Config/ Virtual Server/”, and then the General
Configuration - Virtual Server screen appears. Figure 4-3 show the
current virtual server entry table. (Default Virtual Server Mapping pool is
empty)
Figure 4-3 General Configuration - Virtual Server
1. Click
Add .The Virtual Server Entry Edit page Figure 4-4 appears.
2. To edit the Virtual Server Entry, specify all the entry fields to allow
Internet user to access the Internal servers.
Service Name: Alias name of this internal server, such as FTP.

22
Access Interface: Indicate the translation occurs on which interface
(Wireless interface / Ethernet interface), such as Ethernet.
Protocol: Indicate which protocol (TCP/UDP) you want to translate
from outside to internal server, such as TCP.
Public Access Port number: Indicate which socket port (1 ~ 65535)
you want to translate from outside to internal server, such as 21.
Virtual Server IP address: Specify the private IP address of the
internal server, such as 192.168.1.100.
Virtual Server Port number: Specify the socket port (1 ~ 65535) of the
internal server, such as 21.
3. Click
OK . The Virtual Server Entry Table appears with the entries list.
4. To modify or delete a virtual server entry, click the select button beside
the entry index number and click Modify or Delete .
5. To add another entry to the Virtual Server Mapping Pool, repeat step 1
through step 3.
6. When you have included all the entries you need, click FINISH .
Figure 4-4 Add Virtual Server Entry
23
4.3 Configure DHCP server
Sometimes, the operator want to managing a large TCP/IP network
requires maintaining accurate and up-to-date IP address and domain name
information. In this situation, it needs manually configure and enable the
DHCP server service. Select the “/General Config/ DHCP/”, and then the
General Configuration – DHCP Parameter screen appears. Figure 4-5
shows the general DHCP parameters and the fixed host entry table.
(Default fixed host entry pool is empty).
Figure 4-5 DHCP Parameter

24
4.3.1 General DHCP Server Parameter
- Trigger DHCP Service. Select Enable to allow the OAP to assign
IP Addresses from IP Pool Table. Select Disable to prevent IP Address
assignment from the OAP
- Default Gateway. Enter the default Gateway IP Address.
- Subnet Mask. Configure the subnet for the client.
- Name Server 1, 2, 3. Configure the DNS servers IP for the client.
- DHCP Start IP address. Enter the starting IP Address for this IP Pool
Table.
- DHCP End IP address. Enter the ending IP Address for this IP Pool
Table.
- Apply Interface. Enable DHCP server service on Wireless or Ethernet
interface.
4.3.2 Fixed Host Entries
Figure 4-5 shows the general DHCP parameters and the fixed host entry
table. (Default fixed host entry pool is empty).
1. Click
Add .The Fixed Host Entry Edit page Figure 4-6 appears.
2. To edit the Fixed Host Entry, specify the Ethernet and Internet Address
fields.
- Ethernet Address. Enter the MAC address for a fixed IP user.
- Internet Address. Assign a fixed IP Address to this special user.
3. Click
OK . The Fixed Host Entry Table appears with the entries list.
4. To modify or delete a fixed host entry, click the select button beside the
entry index number and click Modify or Delete .
25
5. To add another entry to the Fixed Host Mapping Pool, repeat step 1
through step 3.
6. When you have included all the entries you need, click FINISH .
Figure 4-6 Add Fixed Host Entry

26
4.4 Configure SNMP
Click General Config, SNMP, and then the General Configuration – SNMP
Community Parameter screen appears. Figure 4-7 shows the current
SNMP community pool and trap host pool.
Figure 4-7 General Configuration – SNMP Community Parameter
4.4.1 Configure Community Pool
The SNMP Community Pool has five entries.
1. To modify a entry, click the select button beside the entry index
number and then click Modify ,the configuration page Figure 4-8
appears.
2. Specify the Validity, Access Right and Community field.
- Validity. Select Enable or Disable to control this community.
27
- Access Right. Select a command from the pull down menu for this field.
- Community. Enter the password related the Access Right in this field.
3. Click
OK . To refresh the current community pool.
4. To modify another community entry to the current community pool,
repeat step 1 through step 3.
5. When you have modified all the entries you need, click FINISH .
Figure 4-8 Modify SNMP Community Parameter
4.4.2 Configure Trap Host Pool
The Trap Host Pool has five entries.
1. To modify a entry, click the select button beside the entry index
number and click Modify .The configuration page Figure 4-9
appears.

28
2. Specify the Version, IP Address and Community field.
- Version. Select Disable, Version 1 or Version 2 to control this trap host.
- IP Address. Enter the Trap Host IP Address.
- Community. Enter the password in this field.
3. Click
OK . To refresh the current trap host pool.
4. To modify another trap host entry to the current trap host pool, repeat
step 1 through step 3.
5. When you have modified all the entries you need, click FINISH .
Figure 4-9 Modify SNMP Trap Host Parameter
29
4.5 Configure Wireless related parameters
Click General Cofig, Wireless.The Wireless LAN information page Figure
4-10 appears. In here, enter the Channel (default is 1),rts Threshold
(default is 1600), frag Threshold (default is 1600), SSID (default is
wireless) and Station Name (default is ap) that are suitable for your radio
network and then you can clicked radio button to disable WEP or enable
64/128 bit WEP services (default is disable), if WEP is enabled, you must
input corresponded Default Key index and WEP Key and then click
KeyGen to generate the WEP64 & WEP128 key patterns. After that, click
FINISH at the bottom of this page to complete the modification.
Figure 4-10
- Channel. The factory setting is Radio Channel 1 transmitting at 2412 MHz.
The channel set appears on the screen installed on your access. Each
channel covers 22 MHz. The bandwidth for channels 1, 6, and 11 does not
overlap, so you can set up multiple access point in the same vicinity without
causing interference.
- RTS Threshold. This setting determines the packet size at which the

30
bridge issues a request to send (RTS) before sending the packet. A low
RTS Threshold setting can be useful in areas where many client devices
are associating with the access point, or in areas where the clients are far
apart and can detect only the bridge and not each other. Enter a setting
ranging from 0 to 2339 bytes.
- Frag Threshold. This setting determines the size at which packets are
fragmented (sent as several pieces instead of as one block). Enter a setting
ranging from 256 to 2338 bytes. Use a low setting in areas where
communication is poor or where there is a great deal of radio interference.
- SSID. The Service Set ID (SSID) can be any alphanumeric, case-
sensitive entry from two to 32 characters long. This string functions as a
password to joint the radio network.
- Hide SSID. You use this setting to choose whether devices that do not
specify an SSID are allowed to associate with the access point. With Yes
selected, the SSID used by other devices must match exactly the AP’s
SSID.
- Deny Any. You use this setting to choose whether devices that specify
the well define SSID keyword ‘ANY’ or ‘any’ are allowed to associate
with the access point. With Yes selected, the SSID ‘ANY’ or ‘any’ used by
other devices are not allowed to associate with the access point
- Station Name. Enter any alphanumeric, case-sensitive entry.
- WEP Key. Enter 1~15 characters for 64 and 128 bits WEP KEY
encryption, and then click KeyGen to generate the WEP64 & WEP128
key patterns.
- WEP. Disable or enable 64/128 bit WEP services.
- Default Key. Select an encryption key from the pull down menu.
- WEP64 Key1~4 & WEP128 Key1~4. The keys in these fields can be
generated automatically by KeyGen function. For 40-bit encryption, enter
10 hexadecimal digits; for 128-bit encryption, enter 26 hexadecimal digits.
Hexadecimal digits include the numbers 0 through 9 and the letters A
through F. Your 40-bit WEP keys can contain any combination of 10
of these characters; your 128-bit WEP keys can contain any combination of
26 of these characters. The letters are not case-sensitive.
31
4.6 Security
4.6.1 IEEE 802.1x Access Control
You can configure Authenticator on AP:
1. Click General Config,select 802.1x Access Control page, and choice
the IEEE 802.1x services is Enable or Disable (as shown in Figure 4-
11).
Figure 3-11
2. The OWAP supporting authentication which based on two kinds of user
information base, Local User Database or Remote Radius Servers.
You can specify which user database you want to use.
3. You can specify the username/password of an accessible 802.1x
user. All user information entries in the Local User Database are
permitted to connect into the OWAP. You can also click ADD,
DELETE, MODIFY button to maintain this User Information table.
4. Some Radius server implements EAP authentication, like Microsoft
Windows 2000 server or Cisco ACS. To set up the Radius server and
OWAP for authentication, you must specify the Radius server IP

32
address, Share key between OWAP and Radius server,
authentication port and accounting port on this Radius server.
5. Click FINISH at the bottom of this page to complete the modification of
this page.
4.6.2 MAC based Access Control
1. Click Basic Config,select MAC Filter page, and choice the MAC Filter
services is Enable or Disable (as shown in Figure 4-12).
2. You can specify the MAC address of a wireless client station. All MAC
entries in the MAC address table are permitted to connect into the
OWAP. You can also click ADD, DELETE, MODIFY button to maintain
this MAC address table. After that, click FINISH at the bottom of this
page to complete the modification of this page.
Figure 4-12
33
4.7 Utility
4.7.1 Software Upgrade
1. Click Utility,select Software Upgrade page (as shown in Figure 4-
13), and then you can use TFTP to upgrade your AP. In here, you must
specify the TFTP server IP and select which file you want to upgrade it
(Program image, Web image), then click OK button to start the TFTP
upgrade process.
2. If the upgrade process is success, the AP will apply the new settings
and start rebooting right away.
Hint: You must set up a TFTP server and this server must contain one
latest new image.
Figure 4-13

34
4.7.2 Administration
Click Utility,Administration. Figure 4-14 shows the Utility – Administration
page.
Figure 4-14 Utility – Administration
Supervisor Account
Change the supervisor’s user name & password in the Supervisor Account
field, and Click FINISH. To take effect the previous configuration changes.
Apply the New Settings
1. Click Utility,Administration, select the Save then Restart to apply
the new configuration settings.
2. Click FINISH. To take effect the previous configuration changes.
Hint: It takes about 10 seconds, to complete the restart process.
35
Chapter 5. Status Monitor
You can see the system running status and the some information on this
windows. Click the Running Status link on the left window (as shown in
Figure 5-1), you can choose which function that you want to monitor.
Figure 5-1 Running Status

36
5.1 System Information
Click Running Status, System Info. Figure 5-2 shows the System
Information page.
Figure 5-2 Running Status – System Info
In this page, you can see the system information and most running
parameters.
General System Information This block displayed the Product Model,
Host Name, Software Version, Build, Boot Code Version, Web Version, AP
Firmware version and System Uptime.
General System Status This block displayed the Operation Mode,
Interface IP/Net mask and brief wireless parameters, if the operator turn on
the DHCP or PPPoE services, you can also see the related information on
here.
Services Information This block displayed which service is turn on or not.
It is includes the NAPT, DHCP server, SNMP, 802.1x access control, MAC
Filter and WEP encryption.
37
5.2 DHCP Information
Click Running Status, DHCP Info. Figure 5-3 shows the DHCP assigned
IP Information page.
Figure 5-2 Running Status – DHCP Info
In this page, you can see the DHCP server assigned table, includes MAC
address, corresponded IP address and IP assigning type (Dynamic or Fix).
Table of contents
Popular Wireless Access Point manuals by other brands

Motorola
Motorola AP-51 Series Product reference guide

Colubris Networks
Colubris Networks CN3000 Administrator's guide

ZyXEL Communications
ZyXEL Communications NWA1100N-CE CloudEnabled quick start guide

Atlantis Land
Atlantis Land I-Fly i I-Fly Wireless Access Point user manual

Acksys
Acksys AirLink V2 Quick installation guide

LevelOne
LevelOne WAP-6121 Quick installation guide

RapidWave
RapidWave RL54-BR-22 Installation guide and user's manual
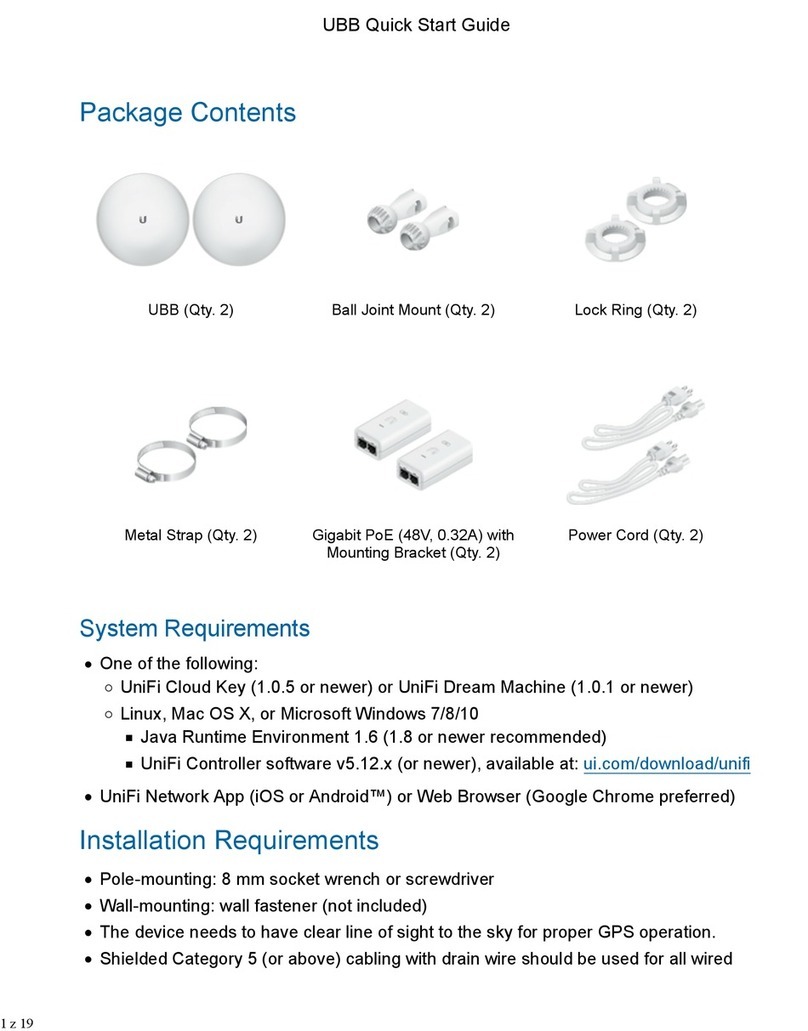
Ubiquiti
Ubiquiti UBB quick start guide

Meru Networks
Meru Networks AP433e installation guide

Ruijie
Ruijie Reyee RG-RAP2200 Hardware installation and reference guide

Grandstream Networks
Grandstream Networks GWN7615 Quick installation guide

HMS
HMS Anybus Wireless Bolt IoT Startup guide