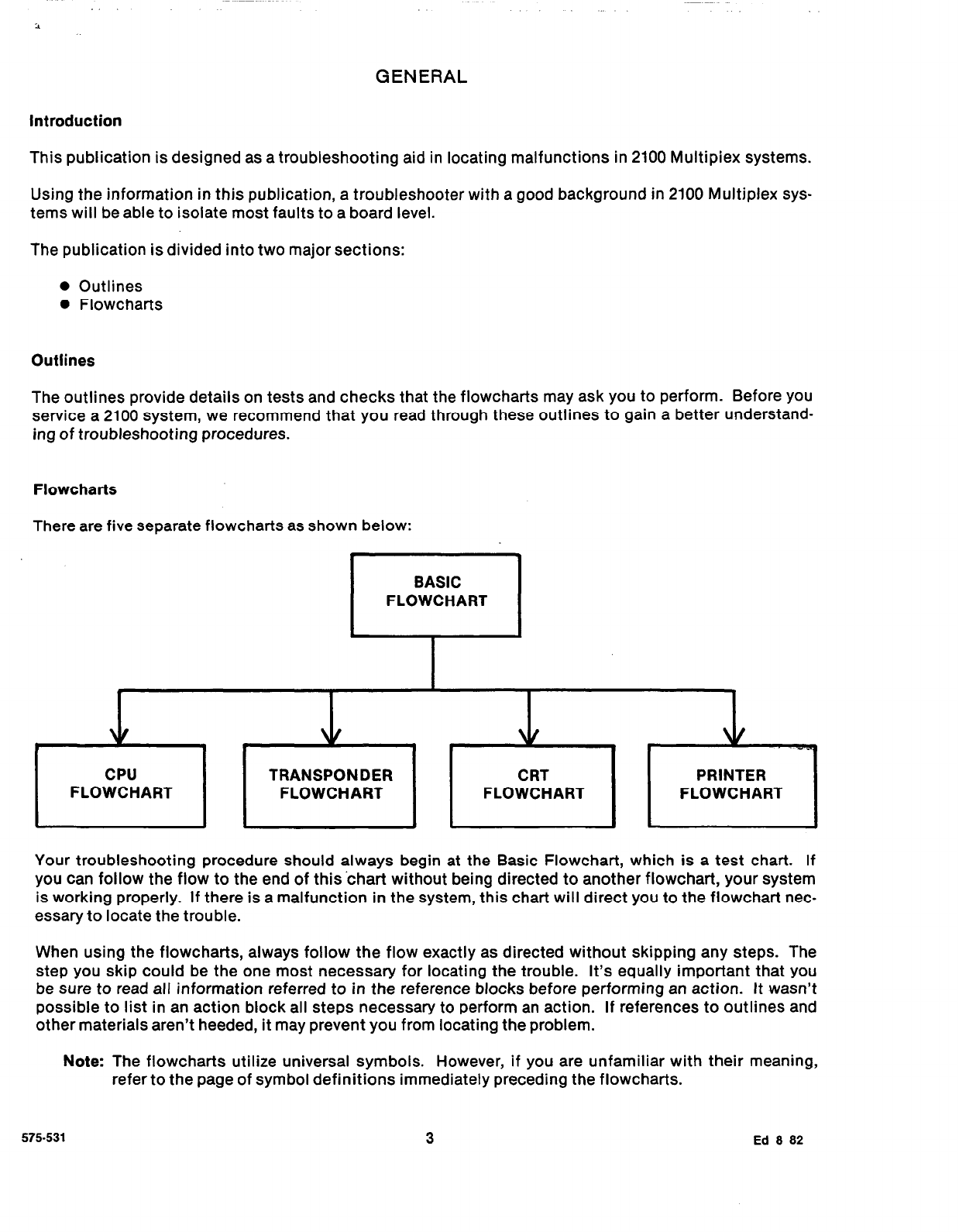
CPU Outline
1. The Central Processing Unit (CPU)is located in the pedestal of the central console. It consists of the
console’s motherboard and all of the PC boards housed in the motherboard rack. Access is obtained
by pulling off the two snap covers of the pedestal, exposing the cover of the CPU card file. Remove
this cover (six screws) to gain access to the PCboards.
2. Disconnect power when replacing PC boards by performing the two following steps:
a. Disconnect battery by removing one of the battery connectors (front of pedestal).
b. Open both AC circuit breakers inside back door.
Carefully remove and replace PC boards so that motherboard connector pins will not be damaged.
3. To check DC voltages for the CPU, measure tham at plug Pl on the motherboard. Access to Pl can
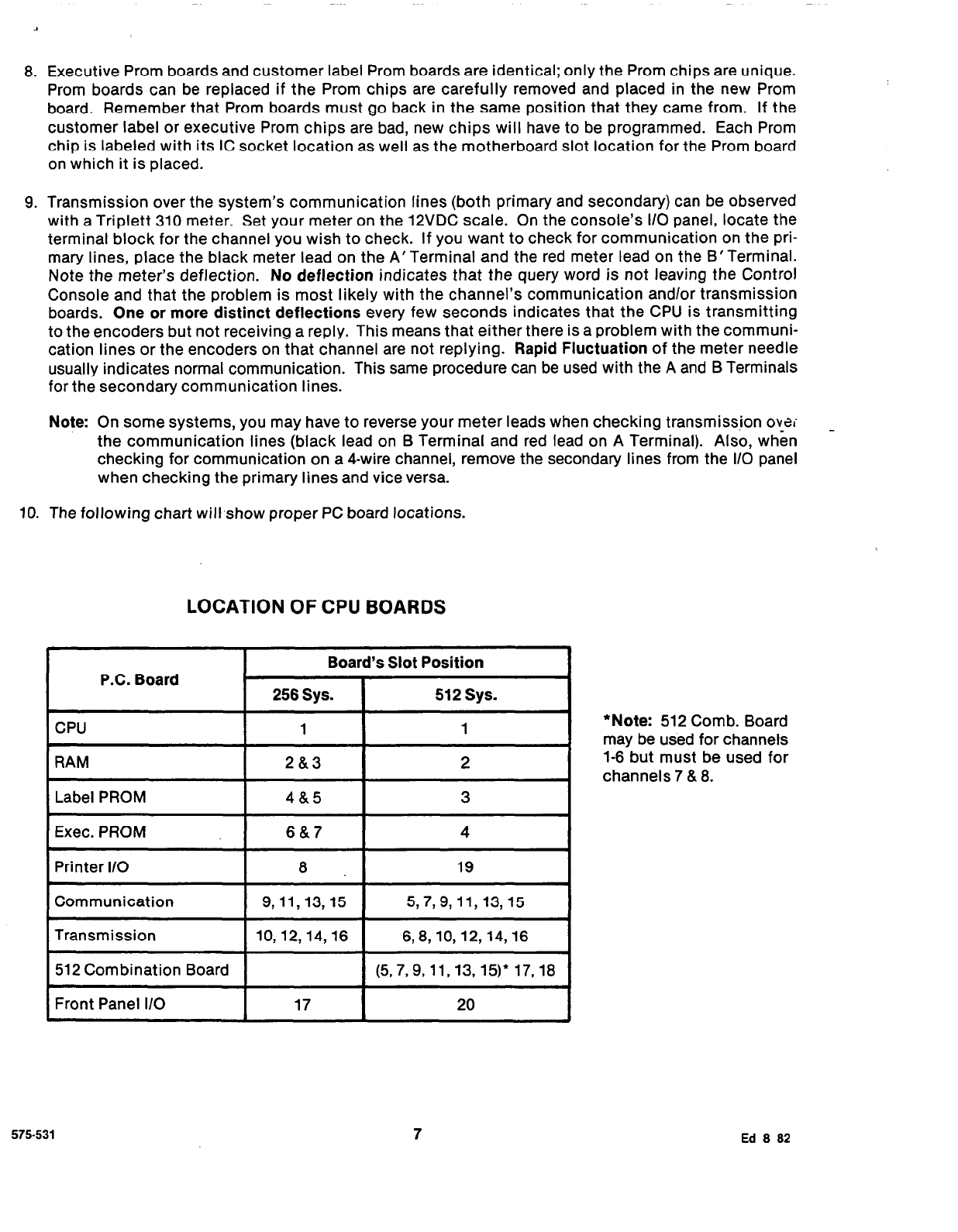
be gained from the back of the console. (Pin 1= +8.5 [z 0.31VDC; Pin 2 = +12 [a 0.31VDC; Pin 3 = GND;
Pin4= -12 [k 0.31VDC). The +5VDC from VRl on the motherboard should also be checked. The +8.5
VDC input to VRI can be checked by putting your meter across capacitor Cl on the motherboard.
The +5VDC can be checked by putting your meter across capacitor C2 on the motherboard. Cl, C2,
and VRl are located on the lower right front of the motherboard.
4. If illumination of the service light is caused by a hang-up in a software routine, it is possible that it
may be reset using the reset switch on the Front Panel PC board. Placing this switch in the down
position will reset the microprocessor and should clear the service light if no serious problem exists.
After the system is reset, return the switch to the up position. (This is a three-position switch: down
for reset, middle for off, up for normal operation.)
5. When checking the motherboard, remove all of the PC boards from the card file. These boards are
subject to
static shock damage
and must be handled carefully. Place them where they will not be
damaged.
Visually inspect
each board as you remove it.
Note:
Make sure all proms on the label and executive prom boards are pressed firmly in their sockets.
If it is obvious that a board has damaged components, replace that board. Be sure that the board’s
markings are clear enough to read and that their location can be identified. (Remember, PROM boards
look alike but contain different PROM chips and therefore must be installed in their proper locations.)
Check the motherboard by performing a close physical inspection of its components. A flashlight
is helpful on this type of inspection.
a. Check connectors Jl through J20 for rolled or bent pins.
b. Check for good solder connections throughout the motherboard.
c. Check cables to and from the.motherboard to ensure that the connectors are good and the cables
are aligned properly.
6. If the CPU has stopped processing information (service light is on) and one of the PC boards is sus-
pected, use the CPU troubleshooting flow chart to determine which board is defective.
Hint:
The CPU will normally operate without a service light when the Printer l/O, Communication,
and Transmission boards are removed. With these boards removed, we can determine whether the
problem is with one or more of these boards or with one or more of the remaining boards.
7. Make sure only defective boards are sent for repair and return. By following the CPU flowchart, you
can systematically determine which board (or boards) are bad. Send a description of the board’s prob-
lem along with the returned board.
Ed 8 82
6
575-531