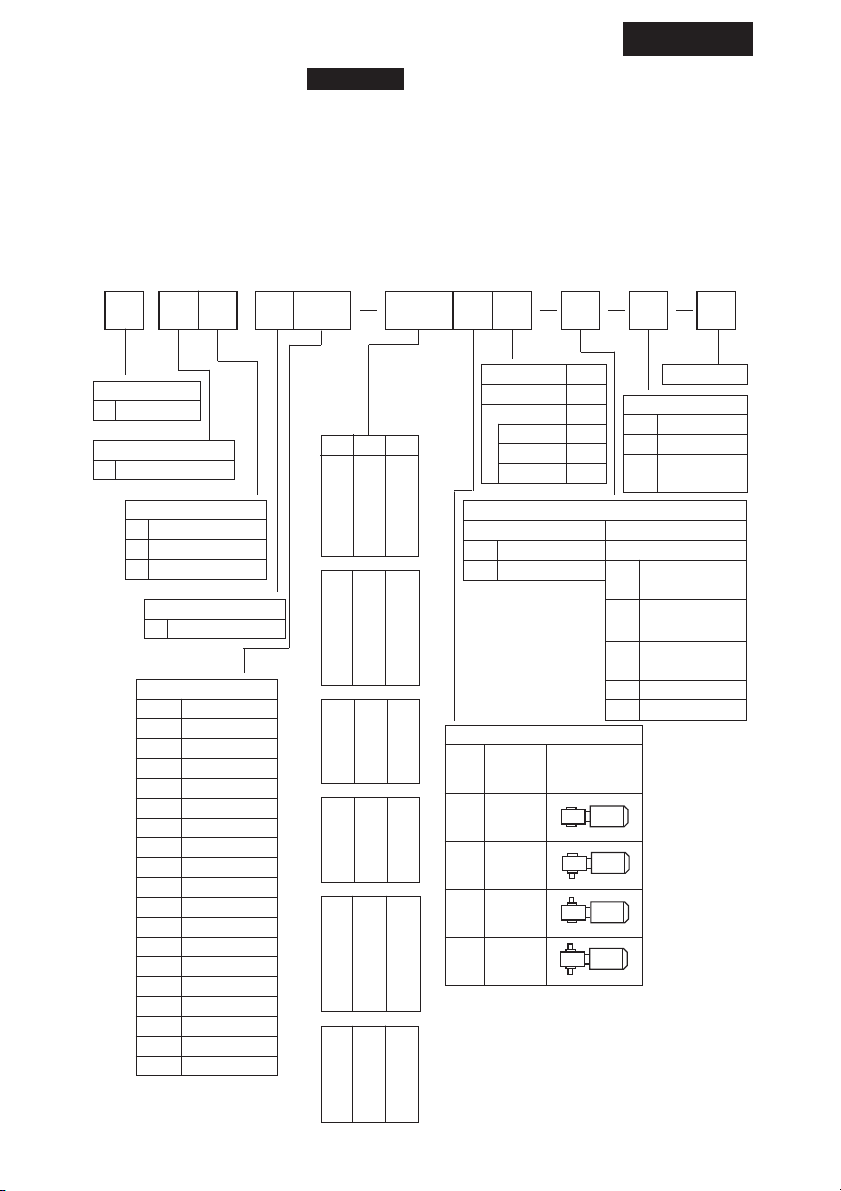
9
4–3) Flange mounting (RNFM series), Foot mounting (RNHM series)
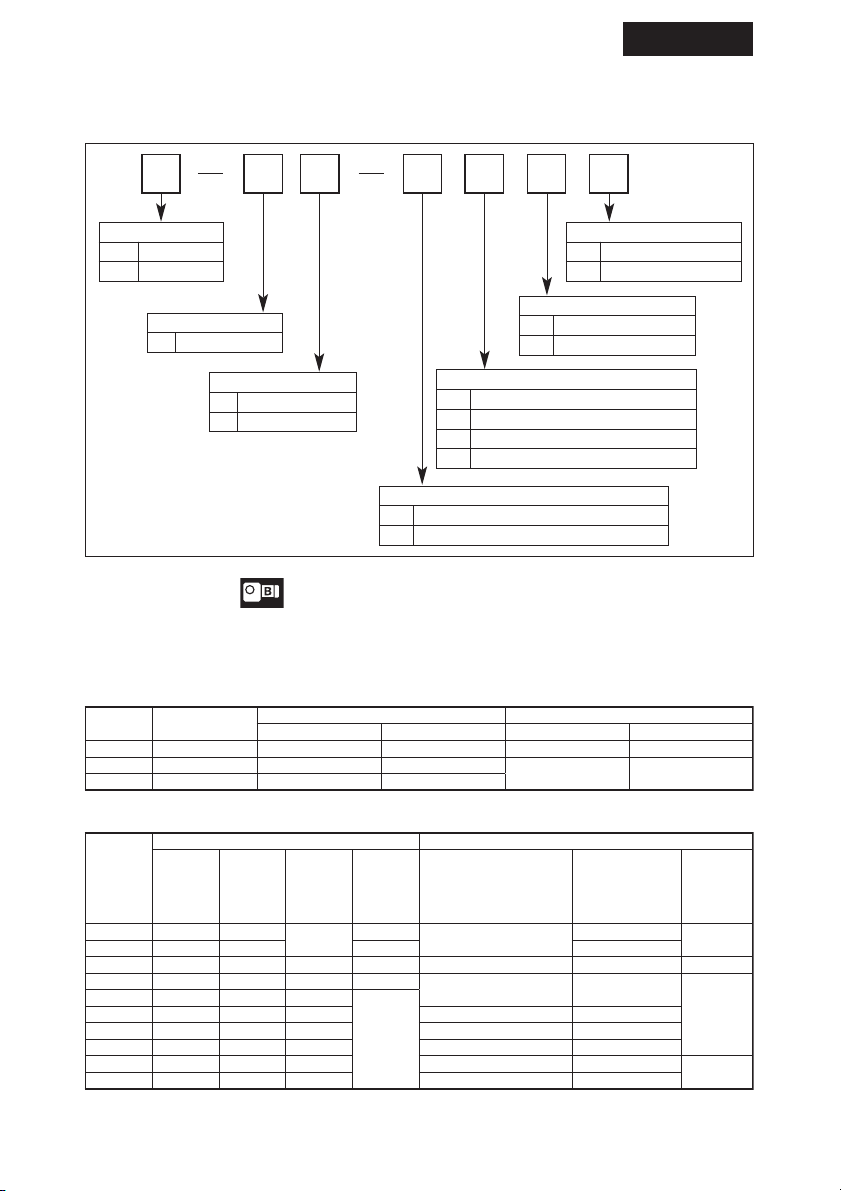
Use bolt shown under Table 2. and refer to 5. coupling with other machines. (P14-18)
Series Frame Size Size of bolt
RNFM
05#, 07#, 15#, 17#, 190# Hexagon socket head bolt M6
01#, 03# Hexagon socket head bolt M5
20#, 23#, 25#, 270#, 1240# Hexagon socket head bolt M8
30#, 33#, 35#, 370#, 1340#
Hexagon socket head bolt M10
40#, 43#, 45#, 470# Hexagon socket head bolt M10
50#, 53#, 54#, 55#, 56#, 1440# Hexagon socket head bolt M12
1540# Hexagon socket head bolt M16
1630#, 1631#, 1640# Hexagon socket head bolt M20
RNHM
20#, 23#, 25#, 190#, 270# Bolt M8
30#, 33#, 35#, 370#, 1340#
Bolt M10
40#, 43#, 45#, 470#, 1440#
Bolt M12
50#, 53#, 54#, 55#, 1540#
Bolt M16
60#, 63#, 64# Bolt M20
Table 2 Bolt Size
4–4) Hollow shaft (RNYM series)
There are (1) Torque arm mounting and (2) Flange and On-bed mounting for Hollow shaft.
(1) Torque arm mounting
(a-1) How to set the shaft (03#, 07#, 17#, 1010#)
Apply molybdenum disulfide grease to the surface of a driven shaft and the inner
surface of a hollow shaft. Then insert the Drive into the driven shaft.
If the fitting is too tight, lightly knock the end face of a hollow output shaft with a
wooden hammer for smooth insertion. Do avoid knocking the casing. We recommend
making a jig shown Fig 2. Using this jig, you can insert the Drive smoothly.
COMMON
4–2) Installation Angle
There is no restriction on the installation angle.
(For outdoor type gearmotors, standard installation angle is horizontal in the axial direction.
Contact us for other axial directions.)
· Units made to special specifications are necessary for installation under conditions other than
the above.
· Units made according to the outdoor, explosion-proof or other specifications can be used
under the specified conditions without any problem.
· Install units where inspection, maintenance, and other such operations can be easily carried
out.
· Install units on a sufficiently rigid base.
4. Installation