trimond IN440 Micro-ATX User manual

164831UG January 1999
User Guide
IN440 Micro-ATX Motherboard
www.trimond.com

MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC MOTHERBOARD DIVISION PAGE 2 OF 47
Document History
1.0 First release February 99
Trademarks mentioned within this document are the properties of their respective
owners. Details available on request.
Information contained in this document is subject to change without notice and does not
represent a commitment on the part of Mitsubishi Electric Motherboard Division.
No part of this manual may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means
electronic or mechanical including photocopying and recording, for any purpose, without
the express written permission of the publishers.
Published by:
Mitsubishi Electric
Motherboard Division
3500 Parkside
Birmingham Business Park
Birmingham, England
B37 7YS

MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC MOTHERBOARD DIVISION PAGE 3 OF 47
This product contains a lithium battery.
Do not use a metal or other conductive implement to remove the battery. If a short-circuit is
made between its positive and negative terminals the battery may explode.
Replace a discharged battery with one of the same type; another type may explode or ignite.
Follow the instructions contained in section 3 of this document to replace the battery. Dispose of
a discharged battery promptly and in accordance with the battery manufacturer’s recommended
instructions. Do not recharge, disassemble or incinerate the discharged battery. Keep discharged
batteries away from children.
Warning
Static electricity can cause permanent damage to electronic components. You should be
aware of this risk, and take precautions against the discharge of static electricity.
This product is at risk from static discharge because the electronic components of the
motherboard are exposed. Memory modules and replacement processors are examples of
electrostatic sensitive devices (ESSDs).
All work that involves contact with the IN440 Micro-ATX Motherboard should be done in an
area completely free of static electricity. We recommend using a Special Handling Area (SHA)
as defined by EN 100015-1: 1992. This means that working surfaces, floor coverings and chairs
must be connected to a common earth reference point, and you should wear an earthed wrist
strap and anti-static clothing. It is also a good idea to use an ionizer or humidifier to remove
static from the air.
Handle static-sensitive items with extreme care. Hold add-on components only by their edges,
avoiding their electrical contacts. In general, do not handle static-sensitive items unnecessarily.
Keep all conductive material, and food and drink, away from your work area and the IN440
MICRO ATX Motherboard.
This product complies with the relevant clauses of the following European Directives (and all
subsequent amendments):
Low Voltage Directive 73/23/EEC
EMC Directive 89/336/EEC
CE Marking Directive 93/68/EEC
Important
This product, when supplied, complies with the CE Marking Directive and its strict legal
requirements. Use only parts tested and approved by Mitsubishi Electric Motherboard
Division.

MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC MOTHERBOARD DIVISION PAGE 4 OF 47
This product complies with the American Safety Standard UL1950.
This product complies with the following European EMC standards:
Emissions EN50022 Class B
Immunity EN50082-1 Class B
This product also complies with the following American EMC standard:
FCC Class B
Note: This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital
device, pursuant to part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable
protection against harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates,
uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the
instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is no
guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause
harmful interference, which can be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is
encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the following measures:
Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different to that which the receiver is
connected.
Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
Important
You are cautioned that any change or modification to the product not expressly approved by
the manufacturer could void the approvals held by this product.

MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC MOTHERBOARD DIVISION PAGE 5 OF 47
1 OVERVIEW..........................................................................................................................................7
MOTHERBOARD FEATURES..........................................................................................................................8
CONFIGURATION OPTIONS...........................................................................................................................9
Build-time................................................................................................................................................9
User Configurable ..................................................................................................................................9
BLOCK DIAGRAM ......................................................................................................................................10
2 INSTALLATION GUIDE..................................................................................................................11
CONNECTOR, HEADER, SLOT IDENTIFICATION DIAGRAM .......................................................11
CONNECTOR, HEADER, SLOT, IDENTICATION TABLE................................................................12
3 UPGRADING THE MOTHERBOARD...........................................................................................14
ADDING MORE MEMORY............................................................................................................................14
Fitting and removing DIMMs...............................................................................................................14
Fitting a DIMM.....................................................................................................................................15
Removing a DIMM................................................................................................................................ 15
THE PROCESSOR ASSEMBLY.......................................................................................................................15
To fit a new processor...........................................................................................................................16
REPLACING THE BATTERY FOR THE CONFIGURATION CMOS..................................................................... 17
4 ELECTRONICS .................................................................................................................................18
PROCESSOR................................................................................................................................................18
CORE LOGIC ..............................................................................................................................................18
Concurrency..........................................................................................................................................19
LEVEL 2 CACHE.........................................................................................................................................19
MEMORY ...................................................................................................................................................19
DIMM....................................................................................................................................................19
BIOS......................................................................................................................................................19
VIDEO........................................................................................................................................................ 20
AUDIO........................................................................................................................................................20
ESS Solo 1.............................................................................................................................................20
REAL TIME CLOCK ....................................................................................................................................21
STANDARD I/O ..........................................................................................................................................21
Keyboard and Mouse............................................................................................................................ 21
Floppy Disk Interface ...........................................................................................................................21
Serial Ports........................................................................................................................................... 21
Parallel Port.........................................................................................................................................21
ADDITIONAL I/O........................................................................................................................................21
IDE Disk Controller..............................................................................................................................21
Universal Serial Bus (USB) ..................................................................................................................21
SECURITY ..................................................................................................................................................21
MOTHERBOARD POWER.............................................................................................................................22
Processor Power...................................................................................................................................22
Battery...................................................................................................................................................22
POWER MANAGEMENT ..............................................................................................................................22
Standby Switch......................................................................................................................................22
Behaviour After AC-Disconnect............................................................................................................22
Sleep State Indication ...........................................................................................................................22
SYSTEM MANAGEMENT.............................................................................................................................23
Heceta II System Monitor .....................................................................................................................23
FAN CONTROL ........................................................................................................................................... 23

MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC MOTHERBOARD DIVISION PAGE 6 OF 47
EXPANSION SLOTS.....................................................................................................................................23
Industry Standard Architecture (ISA) ...................................................................................................23
Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI)...........................................................................................23
Accelerated Graphics Port (AGP)........................................................................................................24
BUS RESOURCE UTILISATION ....................................................................................................................25
ISA DMA Channels............................................................................................................................... 25
ISA Interrupts........................................................................................................................................ 25
PCI Interrupts.......................................................................................................................................26
PCI Device Selection (motherboard devices) .......................................................................................26
PCI Arbitration.....................................................................................................................................26
5 BIOS SETUP & POST .......................................................................................................................27
BIOS SETUP ..............................................................................................................................................27
Control keys..........................................................................................................................................27
Getting help in BIOS Setup...................................................................................................................28
Reserving ISA legacy resources............................................................................................................ 28
MULTI-BOOT FACILITY ..............................................................................................................................28
POWER-ON SELF-TEST................................................................................................................................29
Recoverable POST errors.....................................................................................................................29
Terminal POST errors and beep codes.................................................................................................30
6 ELECTRICAL....................................................................................................................................37
POWER REQUIREMENTS............................................................................................................................. 37
PCB...........................................................................................................................................................37
7 CONNECTOR ASSIGNMENTS.......................................................................................................38
Keyboard and Mouse (PS/2 Mini-DIN) ................................................................................................ 38
Serial Port 1 and Serial Port 2 (9 way D-type).....................................................................................38
Parallel Port (25 way D-type) ..............................................................................................................39
USB Ports 0 and 1 ................................................................................................................................40
Line Input and Output (3.5mm stereo jack)..........................................................................................40
Microphone Input (3.5mm stereo jack).................................................................................................40
Processor and System Fan (3 way header with locking ramp).............................................................40
Internal CD audio (4 way green ATAPI header)..................................................................................41
Internal LINE in (4 way natural colour ATAPI header).......................................................................41
Internal telephony (4 way black ATAPI header)...................................................................................41
Chassis Intrusion Switch (2 pin single row 0.1” header).....................................................................41
MIDI/Joystick (15 way D-Type)............................................................................................................42
Floppy Disk (34 way dual row 0.1” header) ........................................................................................43
Primary and Secondary IDE Disk (40 way dual row 0.1” header)......................................................44
Front panel connectors (single row 0.1” header).................................................................................45
8 GLOSSARY..........................................................................................................................................46

MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC MOTHERBOARD DIVISION PAGE 7 OF 47
IN440 MICRO ATX is a Pentium® II/III processor-based ATX profile motherboard.
The design of IN440 MICRO ATX is based around the following components.
Intel Celeron™, Pentium® II or Pentium®III processor in Slot 1.
Intel 440ZX-100 host bridge and system controller.
Intel PIIX4e ISA bridge and peripheral and power management controller.
SMSC 37C677 I/O Combo.
ESS Solo 1 PCI audio controller (build option).
The Celeron™, Pentium® II and Pentium®III processors are all based on the P6 micro-
architecture and include MMX technology. Two package styles are available – cartridge (slot 1)
pin-grid array (socket 370). IN440 requires the cartridge versions. All three cartridge variations
are supported – SEPP (Celeron™), SECC (Pentium® II) and SECC2 (Pentium® II and Pentium®
III).
The 440ZX North bridge connects the processor to the SDRAM main memory, an AGP port and
PCI bus interface. The device is housed in a 492-pin BGA package.
The PIIX4e provides the PCI to ISA bus bridge and contains the system’s RTC, the IDE
interfaces, the DMA and Interrupt Controllers. The PIIX4e also provides ACPI support, a SMbus
controller and all the general purpose I/O ports used on the IN440 MICRO ATX motherboard.
The PIIX4e device is packaged in a 324 pin BGA.

MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC MOTHERBOARD DIVISION PAGE 8 OF 47
Form factor ATX, 9.6" wide x 7.8" deep. ATX 2.01 compliant.
Processor Slot 1 with the VRM8.2 regulator on motherboard.
Accepts Slot 1 Celeron™, Pentium® II and Pentium® III processors
Core logic Intel 440ZX & PIIX4e
Cache L2 cache included on processor module.
Memory –
RAM Memory sockets accept 168 pin un-buffered PC100 SDRAM modules.
66MHz Bus speed Processors can use PC66 or PC100 SDRAM modules.
100MHz Bus speed Processors can only use PC100 SDRAM modules.
2 DIMM sockets accept 64-bit modules.
Memory –
Flash ROM 2Mb flash ROM. Includes BIOS, Setup-in-ROM, USB, DMI, 120MB
floppy etc.
Buses 1 ISA/PCI bus master slot
2 PCI bus master slots
1 AGP 2X slot
VGA AGP 2X slot
Audio –
controller Active speaker support only (external). Internal mono speaker and PCB
mounted ‘beeper’. ESS Solo 1 CODEC.
Hard Disk &
CD-ROM Dual UltraDMA33 interfaces for hard disk and CD-ROM.
Floppy Disk 720kB, 1.2MB (3-mode), 1.44MB 3½ drives, 1.2MB 5¼ drives.
Support for 120MB drives via ATA port.
Parallel Port IEEE 1284 (ECP & standard) on 25-way D-type
Serial Ports Dual 16550s. Two 9-way D-types on rear edge of motherboard.
USB Two ports.
Keyboard &
Mouse PS/2-style connectors.
Security Chassis intrusion detection.
Power
Management Green and deep green via system management mode.
ACPI compatible.
Requires logic-controlled PSU.
Standby option with wake-up on interrupt, serial port activity or button.
System
Management Hardware monitoring (Voltage, temperature and fan monitor) via optional
Heceta II device.
Plug & Play PC97 and PC98 compliant
Battery back-
up On-board lithium coin cell with 5 years typical life.
PCB 4-layer Micro-ATX form-factor.
All components on top side

MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC MOTHERBOARD DIVISION PAGE 9 OF 47
The following items can be configured at build-time and cannot be modified by the user.
Audio with MIDI/joystick support
Heceta II system monitor.
Please contact Mitsubishi Electric Motherboard Division to determine available configurations.
The user can configure the following items.
Processor (Intel boxed products)
Main memory DIMMs
Processor speed (core/bus ratio)
BIOS ROM write enable
Audio enable/disable
Hard or soft switch power supply

MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC MOTHERBOARD DIVISION PAGE 10 OF 47
Super I/O
FDC37C677
IC25
COM1, PL10 COM2, PL10 Keyboard, PL1 Mouse, PL1
DMI
AD9240
IC1 ISA
SLOT
PL26
PCI SLOTS
PL23,24,25
Midi/Joys,
PL16
CD In, PL12
Line In 1, PL16
IN440 Block Diagram v1.0
Parallel Port, PL10
Line In 2, PL11
Floppy, PL13
TELEPHONE
PL17
CLK BUFF.
ICW W149
IC4
CLK synth
ICW W149
IC4
ISA BUS
PCI BUS
CPU
SLOT 1
IC7
SYSTEM
BUS
CORE
CHIPSET
443ZX
IC9
AGP BUS
AGP CONN.
PL21 MEM BUS SDIMM
MODULES
MM1-2
AUDIO CODEC
SOLO 1
IC16
Mic In, PL23
Line Out, PL16 PCI-ISA BRIDGE
PIIX4E
IC22
BIOS ROM
,IC24
Dual USB,
PL5 Prim. IDE, PL15
Sec. IDE, PL14

MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC MOTHERBOARD DIVISION PAGE 11 OF 47
Warning
Static electricity can cause permanent damage to electronic components. You should be
aware of this risk, and take precautions against the discharge of static electricity.
B
A
PL7
1
PL8
PL6 PL15 PL14 PL13 PL20 PL19
PL4
MM2
MM1
PL3
PL2
J1
PL21 PL23 PL24 PL25 PL26
PL18
PL22
D
G
PL17PL12
PL11
2
CEFH
J
PL9

MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC MOTHERBOARD DIVISION PAGE 12 OF 47
1 Slot 1 connector PL13 Floppy Drive Header PL26 ISA Connector
2 Lithium cell (CR2032) PL14 IDE Secondary Header
MM1
MM2 SDRAM socket PL15 IDE Primary Header J1 Processor Speed
Jumpers
PL2 System Fan Power PL17 ATAPI Audio LINE in
(natural) A Keyboard/Mouse
PL3 Processor Fan Power PL18 Audio Volume Header B USB (Dual)
PL4 Hard switch power supply
jumper PL19 BIOS Write Protect C Serial Port COM 1
PL6 Configuration memory
clear jumper PL20 Wake on LAN Header D Parallel Port
PL7 Intrusion Detect connector PL21 AGP Connector E Serial port COM 2
PL8 Power connector PL22 PCI Audio Disable Jumper F Line Output
PL9 Front Panel Connector PL23 PCI Slot 1 Connector G Microphone Input
PL11 ATAPI Telephony (black) PL24 PCI Slot 2 Connector H Line Input
PL12 ATAPI CD audio in (green) PL25 PCI Slot 3 Connector J MIDI & Joystick
! " #
The processor operating frequency is a multiple of the bus speed, 66 or
100MHz. This jumper block sets the multiple. Note many processors
have a fixed multiple and therefore the jumper setting is ignored.
X – Jumper fitted
X X 3.5 233 350
X X X 4.0 266 400
X X 4.5 300 450
X X 5.0 333 500
X 5.5 366 550
X X X 6.0 400 600
$%& & '(( ! " '((#
1-2 Enable audio CODEC
2-3 Disable audio CODEC
A B C D
Motherboard
Audio Disabled
Motherboard
Audio Enabled

MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC MOTHERBOARD DIVISION PAGE 13 OF 47
)$ & ' * ! " ' *#
1-2 Disable BIOS updates
2-3 Enable BIOS updates
" !+$# +, '- ! "
'-#
(Ensure AC is disconnected from the power supply before moving this jumper)
1-2 Normal operation
2-3 Clear CMOS
(Jumper must be returned to normal position before power-on)
. / / , ' ! " '#
Link 1-2 and 3-4 when 5V standby rail is not available
BIOS Updates
Disabled BIOS Updates
Enabled
Clear CMOSNormal Operation

MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC MOTHERBOARD DIVISION PAGE 14 OF 47
Caution
Care must be taken in the purchase of upgrade parts to ensure both compatibility with the
system and the compliance with appropriate approvals and certification, e.g. CE marking
within Europe. Using non-approved parts may invalidate your warranty and system approvals.
Upgrading the motherboard is not difficult, but if you do not feel confident about the work
involved, you may wish to have your supplier or service organisation complete it for you.
Warning
Never carry out any work inside the computer with AC power applied. Turn off the computer
and unplug all power cords before starting work.
The motherboard has two DIMM (Dual Inline Memory Module) sockets, each of which accepts
modules of up to 128 Mbytes, in any combination. The slot furthest from the processor (MM2)
should be used first.
DIMM specification
The memory modules must meet the PC66 (66MHz processors) or PC100 (100MHz
processors) specification.
!
Read all of these instructions through carefully before you start work.
Turn off the computer and unplug all power cords. Take suitable anti-static precautions and
remove the system cover. Leave the DIMM in the anti-static packaging until the last possible
moment and when you do take the DIMM out of its packaging, hold it by its ends and avoid
touching the metal contacts.
Follow the diagrams and simple instructions on the following pages to insert each DIMM.
"/
After you have fitted new modules, check that the system recognises all the memory. If not,
check that you have:
Correctly fitted the DIMMs in their slots.
Installed DIMMs of the correct type.
It may be necessary to refit the original memory to check if there is a problem with your new
modules.

MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC MOTHERBOARD DIVISION PAGE 15 OF 47
!
Do not use excessive force. If the module will not fit easily, remove it and start again.
The DIMM is inserted vertically and held in place by the clips at each end.
" !
Do not use excessive force. If the module will not come free easily, check that the holding clips
are clear of the module ends.
Press the tabs on both of the socket’s end clips at the same time. This releases the DIMM and
lifts it partly out of the socket.
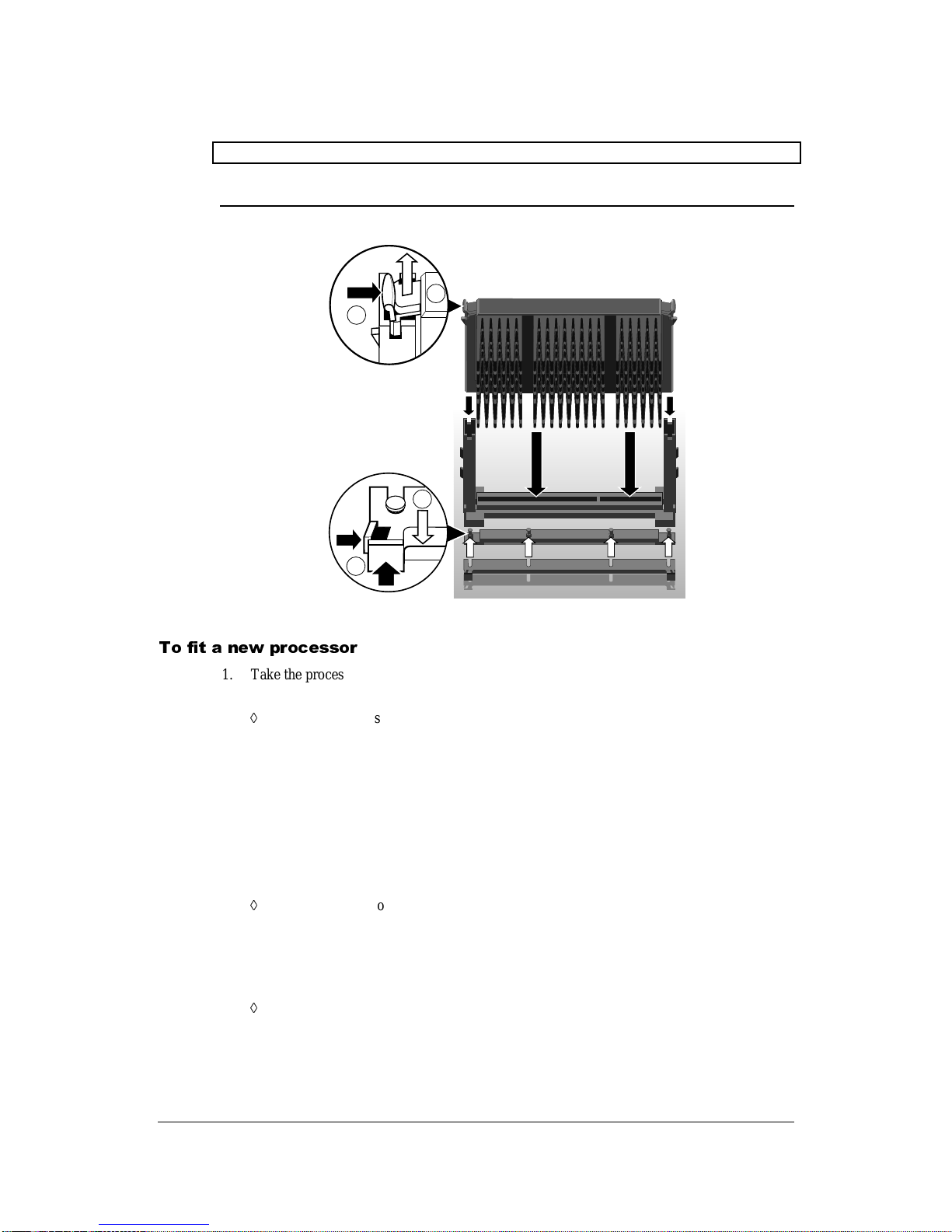
0 1 2
1. Turn off the computer and unplug all power cords. Take suitable anti-static precautions and
remove the system cover.
2. If the system was in use just before starting this procedure, the processor may be hot, wait
until it cools.
3. If there are any expansion cards fitted that obstruct access to the processor, you may have to
remove them.
4. See ‘A’ in the illustration. Carefully squeeze together the grips at both ends (1) of the
heatsink support bracket (2) and slide it away.
Some designs of heatsink do not have this bracket fitted.
5. See ‘B’ in the illustration. Press in the clips (1) at both ends of the top of the processor body
to depress the retaining pins out of the vertical supports. Then lift the processor body (2) out
of the socket.
MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC MOTHERBOARD DIVISION PAGE 16 OF 47
Caution
Handle the processor with care, by the body only. Avoid touching the connector at the
bottom. Store in an antistatic container.
A
1
2
12
B
# $
1. Take the processor out of its anti-static packaging. Hold the processor by its edges, or its
heatsink and avoid touching the edge connector.
The upgrade processor and the socket are keyed to ensure that the processor is installed in
the correct orientation. It will only fit into the socket one way.
2. Slide the processor into the vertical guides and down into the socket, making sure that it is
correctly aligned and that you do not bend or otherwise damage the supports. Do not use
excessive force.
3. Apply just enough pressure to overcome the resistance offered by the socket. Ensure that
the retaining pins snap into the sockets on the end supports.
4. Refit the heatsink support, making sure that it is correctly and fully seated on the pins. It
should snap into place.
This bracket may not be fitted with some heatsink designs, or may not be needed with the
new processor.
5. The upgrade or overdrive processor may have its own cooling fan built into the heatsink.
This will have a power lead that will need to be connected to the processor fan power
(marked ‘CPU FAN’ (PL2) on the motherboard, see installation guide).
If the fan has only a two-pin connection, ensure it is connected to pins 1 and 2.
6. Now adjust the processor multiplier speed jumpers on the motherboard (see installation
guide) in conjunction with the new processor’s data sheet.

MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC MOTHERBOARD DIVISION PAGE 17 OF 47
Warning
The processor requires continuous airflow.
7. Return to their original position any expansion cards that had been removed earlier, then
refit and secure the system cover.
The computer keeps a record of its current hardware configuration in a CMOS memory chip,
which is sustained by a small battery. This battery has a life of up to 5 years. If you find that you
have to reconfigure the computer every time you turn it on, or the date and time seem to be
dramatically incorrect, the battery is probably failing and needs to be replaced.
The battery is a 3-volt lithium type (CR2032 or equivalent) typically used in calculators, watches
and other small, battery-powered electronic items.
Read carefully the following instructions before commencing work.
1. Turn off the computer and unplug all power cords.
Warning
Do not use a metal or other conductive tool to remove the battery. If a short-circuit is
accidentally made between its positive and negative terminals, it may cause the battery to
explode.
2. Using a non-conductive tool, release the latch that holds the battery in place. The battery
will pop up allowing you to lift it out of the holder.
3. Taking care not to touch the top or bottom surface of the new battery, pick up the
replacement with the positive (+) terminal upwards and press the battery into the holder
using a non-conductive implement.
4. Dispose of the old battery in accordance with the battery manufacturer’s instructions.
When you next turn on the computer you will have to run the BIOS Setup utility to enter the
hardware configuration.

MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC MOTHERBOARD DIVISION PAGE 18 OF 47
The IN440 MICRO ATX motherboard accepts the following Celeron™, Pentium® II and
Pentium® III processors operating at a bus speed of 66 or 100MHz.
233 3.5 66
266 4.0 66
300 4.5 66
333 5.0 66
350 3.5 100
366 5.5 100
400 6.0/4.0 66/100
450 4.5 100
500 5.0 100
The processor core voltages are generated by switched-mode regulators on the motherboard to
the Intel VRM8.2 specification. The design meets the 66MHz and 100MHz Slot 1 flexible
motherboard recommendations and supports boxed products (processors), including a CPU fan
supply.
The core logic is based around the Intel 440ZX PCI AGP Controller (PAC) and the PIIX4e
multi-function ISA bridge. The features of each are summarised below.
.
Slot1 host bridge
DRAM controller supporting SDRAM main memory
PCI 2.1 compliant
AGP compliant target
Virtual PCI to PCI bridge to support AGP bus
Packaged in a 492 Pin BGA
+" )
PCI to ISA bridge
Dual UltraDMA33 IDE controller
ISA system peripherals (timers, DMA etc.)
Dual USB controller (12Mbps or 1.5Mbps)

MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC MOTHERBOARD DIVISION PAGE 19 OF 47
SMbus controller (motherboard management)
Real-time clock
ACPI power management logic
Packaged in a 324 pin BGA
The two IDE interfaces are completely independent and can operate concurrently. Both can also
be configured as a PCI bus master.
The major busses (processor, memory, PCI and AGP) all operate independently to achieve a
high degree of concurrency. Most CPU-DRAM and AGP-DRAM transfers can occur
concurrently with PCI transfers and so consume no PCI bus bandwidth.
The second level cache is contained within the processor module. There is no provision for a
third level cache. Cache size is determined by the type of CPU fitted, refer to your CPU
manufacturer for this information.
!
There are two DIMM sockets on the motherboards that accept 168-pin un-buffered SDRAM
modules to the Intel PC SDRAM un-buffered memory module specification. PC100 modules are
required when using processors with a 100MHz bus. Either PC66 or PC100 modules may be
used with 66MHz bus processors. All modules must support SPD (serial presence detect) to
allow the BIOS to determine the memory configuration and set up the chipset optimally. These
modules contain a small EEPROM that describes the module capabilities in detail - including
speed, capacity and organisation. EDO modules are not supported.
64-bit modules.
2 or 4 bank organisation
Asymmetric or symmetric memory addressing.
Single or double-sided modules.
!%
The BIOS is contained in a flash ROM device soldered directly to the motherboard and includes
the code listed below. The motherboard will automatically perform a BIOS recovery operation if
it detects a valid recovery disk during the boot sequence. An override jumper that prevents all
writes (recovery or update) provides update protection. The BIOS ROM is accessed as a single
linear region in the memory space from 4GB-128kB (0FFFE0000 - 0FFFFFFFFh) and copied at
the top of ISA memory (0E0000 - 0FFFFFh).
Core motherboard BIOS
USB
DMI
Setup-in-ROM
Intel microcode update support and code

MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC MOTHERBOARD DIVISION PAGE 20 OF 47
Power and system management code
The IN440 MICRO ATX motherboard requires a video card fitted to one of the expansion slots.
This may be an ISA, PCI or AGP product. The AGP expansion slot supports 1X and 2X modes
of operation (66MHz and 133MHz effective speed) and usually provides the best performance.
The optional audio subsystem is based around an ESS Solo1 PCI CODEC. When not fitted, the
standard PC beep function remains.
&
SoundBlaster™ Pro register-level compatible
PCI bus interface
Internal FM synthesiser
Dual DMA support with FIFO & full duplex operation
Programmable power management
Joystick and MPU-401 compatible MIDI interfaces
5 channel input mixer
One power amplifier is used - a National Semiconductor LM4880 ’Boomer’ to drive the LINE-
out jack socket and the optional internal speaker. The microphone input provides power to
enable condenser microphones to be used.
!
CODEC LINE Rear line input jack socket
CODEC AUXA Internal CD input (ATAPI connector)
CODEC AUXB Internal auxiliary LINE input (ATAPI connector)
CODEC MIC Rear microphone jack socket
CODEC Mono In Internal telephony input (ATAPI connector)
The following audio connectors are supported.
Rear 3.5mm jack microphone input with phantom power
Rear 3.5mm jack LINE in
Rear 3.5mm jack LINE out (also suitable for 32 ohm headphones)
Internal CD-ROM stereo audio on 4-pin ATAPI connector
Internal stereo LINE input on 4-pin ATAPI connector
Internal telephony connection (mono input and output) on 4-pin ATAPI connector
Table of contents
Other trimond Motherboard manuals