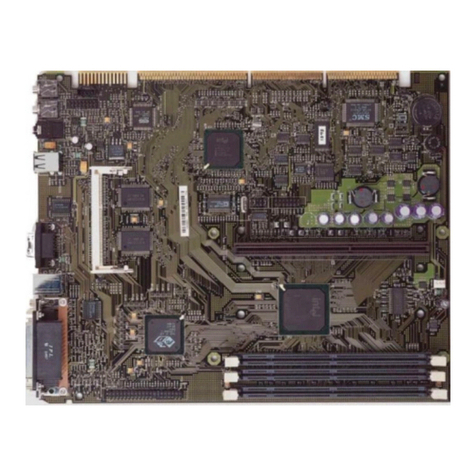
trimond HN440 ATX User manual

TRIMOND™ HN440 ATX
MOTHERBOARD USER'S GUIDE
www.trimond.com

Trademarks mentioned within this document are the
properties of their respective owners. Details available on
request.
Information contained in this document is subject to change
without notice and does not represent a commitment on the
part of Mitsubishi Electric.
No part of this manual may be reproduced or transmitted in
any form or by any means electronic or mechanical including
photocopying and recording, for any purpose, without the
express written permission of the publishers.
Published by:
Mitsubishi Electric Motherboard Division
3500 Parkside
Birmingham Business Park
Birmingham, England
B37 7YS
Copyright
Mitsubishi Electric UK 1999

HN440 USER’S GUIDE
Safety & Regulatory Notices 3
SAFETY & REGULATORY NOTICES
Battery
This product contains a lithium battery.
Do not use a metal or other conductive tool to remove the
battery. If a short-circuit is made between its positive and
negative terminals the battery may explode.
Replace a discharged battery with one of the same type;
another type may explode or ignite. Follow the instructions
contained in this User’s Guide to replace the battery. Dispose
of a discharged battery promptly and in accordance with the
battery manufacturer’s recommended instructions. Do not
recharge, disassemble or incinerate the discharged battery.
Keep away from children.
Thermal interface material
Thermal interface materials used between a heatsink and the
processor can cause skin irritation and stain clothing. Avoid
prolonged or repeated contact with skin. Wash thoroughly
with soap and water after handling. Avoid contact with eyes
and inhalation of fumes. Do not ingest.
Anti-static precautions
Warning
Static electricity can cause permanent damage to electronic
components. You should be aware of this risk, and take
precautions against the discharge of static electricity.
This product is at risk from static discharge because the
electronic components of the motherboard are exposed.
Memory modules and replacement processors are examples
of electrostatic sensitive devices (ESSDs).
All work that involves contact with the HN440 motherboard
should be done in an area completely free of static electricity.
We recommend using a Special Handling Area (SHA) as
defined by European Standard EN 100015-1: 1992. This
means that working surfaces, floor coverings and chairs must
be connected to a common earth reference point, and you
HN440 USER’S GUIDE
4 Safety & Regulatory Notices
should wear an earthed wrist strap and anti-static clothing. It
is also a good idea to use an ionizer or humidifier to remove
static from the air.
Handle static-sensitive items with extreme care. Hold
components only by their edges, avoiding their electrical
contacts. In general, do not handle static-sensitive items
unnecessarily.
Keep all conductive material, and food and drink, away from
your work area and the motherboard.
Legalities
This product complies with the relevant clauses of the
following European Directives (and all subsequent
amendments):
Low Voltage Directive 73/23/EEC
EMC Directive 89/336/EEC
CE Marking Directive 93/68/EEC
Important
This product, when supplied, complies with the CE Marking
Directive and its legal requirements. Use only parts tested
and approved by Mitsubishi Electric’s Motherboard Division.
Standards
Safety
This product complies with the American Safety Standard
UL1950.
Electro-magnetic Compatibility
This product complies with the following European EMC
standards:
Emissions EN55022 Class B
Immunity EN50082-2
This product also complies with the following American
EMC standard: FCC Class B
HN440 USER’S GUIDE
Safety & Regulatory Notices 5
FCC Compliance Statement
Note: This equipment has been tested and found to comply
with the limits for a Class B digital device, pursuant to part 15
of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide
reasonable protection against harmful interference in a
residential installation. This equipment generates, uses and
can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and
used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful
interference to radio communications. However, there is no
guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular
installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference
to radio or television reception, which can be determined by
turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to
try to correct the interference by one or more of the following
measures:
Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
Increase the separation between the equipment and
receiver.
Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit
different to that to which the receiver is connected.
Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV
technician for help.
Important
You are cautioned that any change or modification to the
product not expressly approved by the manufacturer could
void the approvals held by this product.

HN440 USER’S GUIDE
6 Contents
CONTENTS
OVERVIEW 7
Item checklist 8
Key features 8
Motherboard layout diagram 10
Motherboard block diagram 12
INSTALLATION 13
Installation steps 14
Jumper settings 15
System memory (DIMMs) 17
Processor 19
Expansion cards 23
Internal connectors 26
External connectors 31
Connecting to AC power 32
Replacing the motherboard battery 34
BIOS SETUP 35
USING THE SUPPORT CD 39
GLOSSARY 40

HN440 USER’S GUIDE
Overview 7
OVERVIEW
The name Mitsubishi Electric is known the world over for
quality, reliability and dependability. The Trimond™ HN440
“Hornet” ATX motherboard from Mitsubishi Electric
Motherboard Division continues this tradition, combining
innovative design with high-quality components.
The HN440 is an ATX profile motherboard designed around
the use of Intel Celeron™, Pentium®II and Pentium®III
processors. All three package variations are supported – SEPP
(Celeron™), SECC (Pentium® II) and SECC2 (Pentium® II
and Pentium®III).
The motherboard is intended for use with a logic-controlled
“soft-switch” Power Supply Unit (PSU). Such a PSU is
needed for certain features of the motherboard, such as Wake-
on-LAN and power-saving Suspend and Standby modes.
The HN440 has the following major build options:
Intel 440ZX or 440BX chipset
Audio system with joystick/MIDI support (440BX only)
Heceta II System Monitor
Note
The number of memory (DIMM) sockets is affected by these
build choices. Builds with 440ZX have two DIMM sockets;
builds with 440BX have three DIMM sockets.

HN440 USER’S GUIDE
8 Overview
Item checklist
Check that your package is complete. If you discover
damaged or missing items, contact your Trimond™ supplier.
HN440 motherboard
HN440 User’s Guide (this book)
Support CD with BIOS and drivers
Ribbon cable for 3.5- and 5.25-inch diskette drives
Ribbon cable for master and slave IDE drives
Key features
Advanced processor support: Intel Pentium®III,
Pentium®II and Celeron™ processors at 233 MHz and above
in a Slot 1 connector with a Universal Retention Mechanism.
ATX form-factor: ATX 2.01 compliant (12.0 x 7.5 inches)
with standard fixing holes.
Intel AGPset: Either Intel 440ZX or 440BX PCI AGP
Controller (build option) plus PIIX4e Multifunction ISA
Bridge.
PC100 Memory Support: Either two (440ZX) or three
(440BX) DIMM sockets supporting Intel PC100/66-
compliant SDRAMs. PC100 modules are required when using
processors with a 100 MHz bus. Either PC66 or PC100
modules may be used with 66 MHz bus processors. See page
17 for more information.
Optional Audio: Available only for 440BX-based
motherboards. ESS Solo-1 PCI codec, Sound Blaster Pro
register-compatible. Features internal FM synthesiser, five-
channel input mixer and MPU401-compatible MIDI interface.
Supports external line-in, line-out and microphone
connectors. Supports internal CD-ROM stereo, line-in and
telephony (voice mail) via 4-pin ATAPI connectors.

HN440 USER’S GUIDE
Overview 9
Peripheral ports: Two serial ports. One parallel port with bi-
directional, EPP 1.9 and ECP (IEE1284) capability. Dual
Universal Serial Bus (USB) ports. PS/2-style mouse and
keyboard ports.
UltraDMA/33 IDE: The PIIX4e incorporates a dual IDE
Controller. Two motherboard connectors allow two devices
on each of two channels. Supports UltraDMA/33, Polled IO
Modes 3 and 4, and Bus Master IDE DMA Mode 2. Supports
Enhanced IDE and ATAPI devices.
Advanced Configuration & Power Interface: The PIIX4e
supports ACPI. Compatible with Microsoft/Intel PC97 and
PC98 Plug and Play standards. Support for a logic-controlled
“soft-switch” Power Supply Unit (PSU). Supports power-
saving Suspend and Standby modes.
PCI & ISA Expansion Slots: One ISA slot, one shared
ISA/PCI slot and three PCI slots.
AGP 2X Slot: Supports either Accelerated Graphics Port 1X
(66 MHz) or 2X (133 MHz) modes. (There is no on-board
video controller.)
Wake-on-LAN: Motherboard connector for input from
network cards that support Wake-on-LAN technology.
System Management: Desktop Management Interface
(DMI) support in BIOS. Heceta II System Monitor (build
option) supports monitoring of fans, power rails (+12 V,
+5 V, +3.3 V, CPU Core, -12 V and 2.5 V), motherboard
surface temperature, and chassis intrusion.
Battery back-up: On-board lithium coin cell with 5 years
typical life.
Concurrent busses: The major busses (processor, memory,
PCI and AGP) all operate independently to achieve a high
degree of concurrency. Most CPU-DRAM and AGP-DRAM
transfers can occur concurrently with PCI transfers and so
consume no PCI bus bandwidth.

HN440 USER’S GUIDE
10 Overview
Motherboard layout diagram
CD E
F
B
A
22
4
J
GHI
18
21
20
19
1 2 5
36789
11 10
12
13
17 16 15
23
14

HN440 USER’S GUIDE
Overview 11
1 Main Power
2 Diskette drive connector
3 Front panel header strip
4 Primary IDE connector
5 Secondary IDE connector
6 Processor speed jumpers
[J1]
7 CMOS memory clear
jumper [PL1]
8 Lithium cell (CR2032)
9 BIOS write-protect jumper
[PL6]
10 ISA expansion slots
11 PCI expansion slots
12 Network card “Wake-on-
LAN” connector
13 Audio disable jumper &
digital volume control
[PL24]
14 AGP slot
15 ATAPI CD audio in
16 ATAPI audio line-in
17 ATAPI telephony
18 Slot 1 processor socket
19 Chassis intrusion switch
connector [PL14]
20 Processor fan connector
[PL15]
21 Chassis fan connector
[PL11]
22 DIMMs sockets (build-
dependent)
23 Hard switch power supply
jumper (Not supported)
A Keyboard
B Mouse
C USB (Dual)
D Serial port 1
E Serial port 2
F Parallel port
G Line output
H Line input
I Microphone input
J MIDI & joystick
HN440 USER’S GUIDE
12 Overview
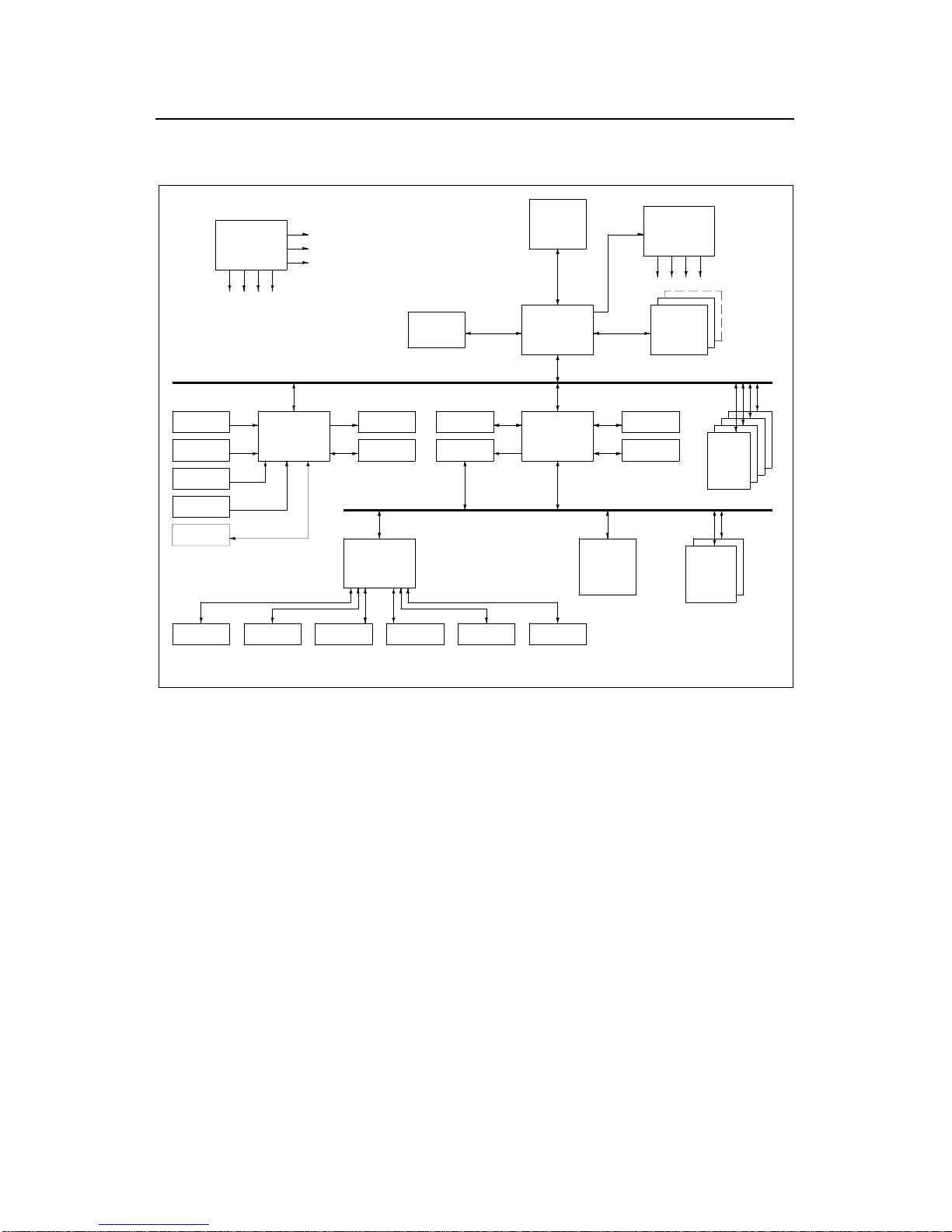
Motherboard block diagram
AGP CONN.
PL10
HN440 Block Diagram v2.0
CLK Synth.
ICS9148-10
IC10
PCI BUS
BIOS, U1BIOS, U1
Dual USB, PL28
AGP BUS
SYSTEM BUS
CPU
SLOT1
IC18
MEM BUS
CLK BUFF.
ICS9179-12
IC12
CLK BUFF.
ICS9179-12
IC12
CORE CHIPSET
443BX/ZX
IC13
DIMM Module
SDRAM
MM1-3
Telephony, PL22
Parallel Port, PL27 Floppy, PL3 COM1, PL27 COM2, PL27
Super I/O
FDC37C677
IC25
AUDIO CODEC
SOLO1
IC23
Line In 2, PL21
CD In, PL20
Line In 1, PL26
Mic In, PL26
ISA BUS
Midi/Joys, PL26
Line Out, PL26
Heceta II
IC17
Mouse, PL29Keyboard, PL29
ISA SLOT
PL12,13
PCI-ISA BRIDGE
PIIX4E
IC9 PCI SLOT
PL16-19
Prim. IDE, PL4
Sec. IDE, PL7

HN440 USER’S GUIDE
Installation 13
INSTALLATION
Because of its standard ATX size and dimensions, the HN440
is capable of being installed in a variety of computer chassis.
For this reason, the installation instructions provided here do
not include any chassis-specific details such as how to mount
the motherboard or install hard disk drives. For these details,
you should consult the documentation supplied with your
chosen chassis, or the chassis manufacturer.
Warning
Always turn of the AC power supply and unplug the AC
power cord before carrying out any work inside the computer
chassis.
Anti-static precautions
Computer motherboards, processors, memory modules and
expansion cards are all vulnerable to static electricity. To
protect them against damage you should follow these
precautions:
Unplug the computer from the AC power supply.
If possible, always wear a grounded wrist-strap.
Otherwise, touch both your hands to a safely grounded
object or to a metal object such as the PSU case before
handling components.
Hold components by their edges and avoid touching any
circuitry, chips, pins or connectors.
Keep components in their anti-static packaging until
required. Place components on static-dissipative pads or
their anti-static packaging when separated from the
system.

HN440 USER’S GUIDE
14 Installation
Installation steps
1. Review jumper settings.
2. Install memory modules.
3. Install the processor.
4. Install expansion cards.
5. Connect internal ribbon cables and leads, and the power
supply.
6. Connect external cables.
7. Connect AC power.

HN440 USER’S GUIDE
Installation 15
Jumper settings
PCI Audio codec Enable PL24 (item 13 on page 10)
This allows you to disable the optional ESS Solo-1 PCI
codec, if fitted.
1-2 Enable audio codec
2-3 Disable audio codec
Motherboard
audio
enabled
Motherboard
audio
disabled
BIOS Programming Enable PL6 (item 9 on page 10)
This allows you to update the BIOS firmware when
necessary.
1-2 Disable BIOS updates
2-3 Enable BIOS updates
BIOS
updates
disabled
BIOS
updates
enabled
Clear CMOS Memory PL1 (item 7 on page 10)
To clear configuration (CMOS) memory: disconnect the AC
power supply, move the jumper to position 2-3 and wait for a
few seconds, then return the jumper to position 1-2. The
jumper must be returned to the Normal position before power
is applied.
1-2 Normal operation
2-3 Clear CMOS
Normal
operation Clear CMOS

HN440 USER’S GUIDE
16 Installation
Processor speed jumpers J1 (item 6 on page 10)
These jumpers set the ratio of the processor’s internal clock
frequency (that is, the processor’s advertised speed), to the
external bus frequency (either 66 MHz or 100 MHz).
Note that many processors have fixed ratios, in which case
these jumper settings are ignored.
A B C D
Processor speed ABCD Ratio Bus frequency
233 MHz o
oo
oo
oo
o3.5 66 MHz
266 MHz o
oo
oo
oo
o4.0 66 MHz
300 MHz o
oo
oo
oo
o4.5 66 MHz
333 MHz o
oo
oo
oo
o5.0 66 MHz
350 MHz o
oo
oo
oo
o3.5 100 MHz
366 MHz o
oo
oo
oo
o5.5 66 MHz
400 MHz o
oo
oo
oo
o6.0 66 MHz
400 MHz o
oo
oo
oo
o4.0 100 MHz
450 MHz o
oo
oo
oo
o4.5 100 MHz
500 MHz o
oo
oo
oo
o5.0 100 MHz
550 MHz o
oo
oo
oo
o5.5 100 MHz
HN440 USER’S GUIDE
Installation 17
System memory (DIMMs)
The number of Dual In-line Memory Module (DIMM)
sockets on the HN440 motherboard depends on whether it is a
440BX or 440ZX build. The BX-build has three sockets, the
ZX-build has two. Also, Error Checking & Correcting (ECC)
is supported only by the BX-build.
The DIMM sockets accept 168-pin, 3.3 Volt, unbuffered
Synchronous Dynamic Random Access Memory (SDRAM)
modules of 16, 32, 64 or 128 MB (see “Choosing your
memory modules” below). The maximum possible total
memory is thus either 384 Mb (BX-build) or 256 Mb (ZX-
build). EDO (Extended Data Output) memory is not
supported.
Error Checking & Correcting (ECC)
To use the 440BX chipset’s ECC feature, you must use 72-bit
DIMM modules and make the proper settings within the
BIOS Setup utility.
Choosing your memory modules
The HN440 may fail to boot if non-compliant memory
modules are fitted. The SDRAM DIMMs must be:
Intel PC100 or PC66 compatible (see below)
168-pin
64-bit wide (72-bit with parity/ECC support)
3.3 Volt
Unbuffered
Non-EDO
PC100 modules are required when using processors with a
100 MHz bus. Either PC66 or PC100 modules may be used
with 66 MHz bus processors.
All modules must support Serial Presence Detect (SPD) to
allow the BIOS to determine the memory configuration.
See the Approved Vendor List (AVL) on the Trimond™
website for details of DIMMs that have been tested with the
HN440.

HN440 USER’S GUIDE
18 Installation
Installing DIMMs
1. Ensure that the system is turned off and that the AC
power cord is unplugged.
2. Insert the DIMM as shown. The DIMM will only fit one
way round because of the asymmetric notches along the
edge. Use the socket furthest from the processor
(marked MM1) first.
The DIMM is inserted vertically and held in
place by the clips at each end
Removing DIMMS
Press down on the tabs at both ends of the socket at the
same time. This releases the DIMM and lifts it partly out
of the socket.

HN440 USER’S GUIDE
Installation 19
Processor
The HN440 motherboard has a Slot 1 connector for Intel
Celeron™, Pentium®II and Pentium®II processor packages.
All three package variations are supported – SEPP
(Celeron™), SECC (Pentium® II) and SECC2 (Pentium® II
and Pentium®III).
Examples of (from the top) SECC, SECC2 and SEPP processor
packages.
The motherboard uses a Universal Retention Mechanism
(URM) that accepts all supported processors.
To install the processor you must:
Attach the heatsink to the processor package
Insert the processor package into the Slot 1 connector

HN440 USER’S GUIDE
20 Installation
Attaching the heatsink
So-called “boxed” or retail processor packages may already
have a fan heatsink attached. If not, you must obtain one.
There are many different types of heatsink, and the method of
attachment varies according to the manufacturer and the type
of processor package for which it is intended. The following
information is provided only as a general guide — follow
carefully any instructions provided with your particular
heatsink.
The recommended heatsinks are those with integral fans with
three-pin plugs that can be connected to the fan connector on
the motherboard (item 20 on page 10).
In all cases, make sure the heatsink is mounted tightly against
the processor package; otherwise, the processor will overheat.
Most heatsinks have some kind of thermal interface material
applied to assure good heat transfer between the package and
the heatsink. Often, there is a plastic film over the thermal
interface material to protect it during shipping. If so, ensure
that this protective cover is peeled off before attaching the
heatsink.
Warning
Thermal interface materials can cause skin irritation and
stain clothing. Avoid prolonged or repeated contact with skin.
Wash thoroughly with soap and water after handling. Avoid
contact with eyes and inhalation of fumes. Do not ingest.
Celeron™ processor in a SEPP (Single Edge Processor
Package)
The SEPP package has four holes through the substrate by
which you can attach a heatsink. Typically, the heatsink is
secured to the processor side of the SEPP by a heatsink clip
pushed through from the other side of the SEPP.
1. Carefully insert all four legs of the heatsink clip through
the SEPP. Note that the heatsink clip must be on the
back (non-processor) side of the SEPP.
2. If necessary, peel away the protective film from the
thermal interface material on the heatsink.
Table of contents
Other trimond Motherboard manuals
Popular Motherboard manuals by other brands

Colorful
Colorful CVN Z790 GAMING FROZEN V20 installation instructions

Asus
Asus Rambus P3C-L user manual

Gigatrend Technology
Gigatrend Technology Axper XP-K7V400 user manual

Mouser Electronics
Mouser Electronics RIoTboard MCIMX6 SOLO user manual

ASROCK
ASROCK A785GMH 128M - V1.0 user manual

Rosch Computer
Rosch Computer G4V506-P user manual