1. Overview
The 8051 project board is desi ned for teachin how to develop a dedicated microcontroller project
usin c codin . The project board is based on the SuperFlash SST89E51RD microcontroller. The
MCU has 64kB code memory with extra 1024 bytes RAM. This memory size is very suitable for c
codin . In addition, the board also provides the 7-se ment display, LCD display, keypad, the analo
to di ital converter and USB port.
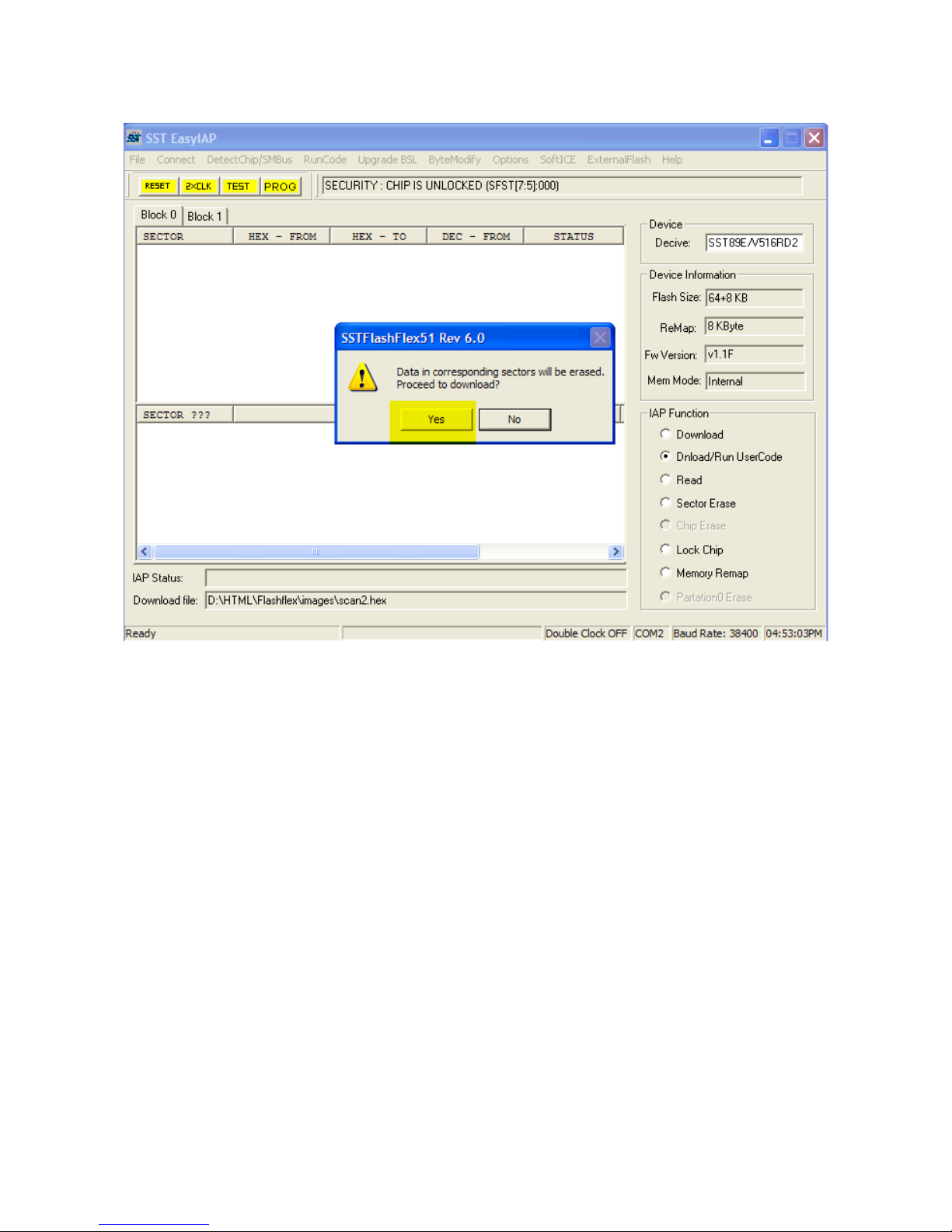
The MCU has bootloader firmware. We can pro ram the code memory without the need of external
pro rammer. Only the micro USB cable will be needed.
While developin the code with PC, the 8051 project board ets the power from USB port directly.
The micro USB port allows many power sources, e. ., power bank, cheap cell-phone AC adapter.
The example c pro rams demonstrate how to write c code to control the display, UART, keypad.
8051
2 channel ADC SST89E516RD 4-digit 7-segment
display
4 Tact s itches
UART
USB
64kB