1-Aug-2012
Table of Contents
1INTRODUCTION.................................................................................................................................. 3
1.1 ZYNQ BANK PIN ASSIGNMENTS ...................................................................................................... 5
2FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION............................................................................................................ 6
2.1 EPP................................................................................................................................................. 6
2.2 MEMORY......................................................................................................................................... 6
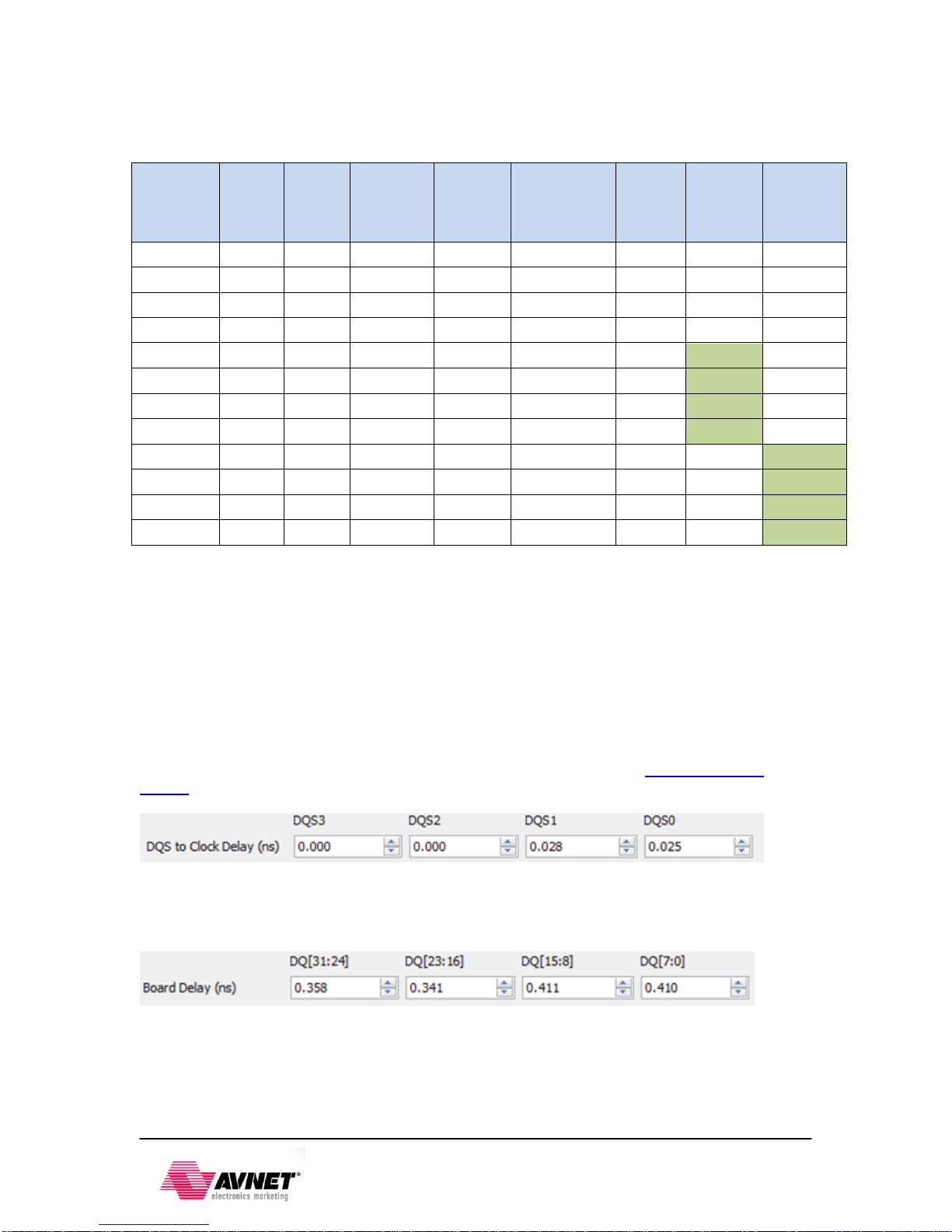
2.2.1 DDR3...................................................................................................................................... 6
2.2.2 SPI Flash ................................................................................................................................ 9
2.2.3 SD Card Interface..................................................................................................................11
2.3 USB ...............................................................................................................................................12
2.3.1 USB OTG...............................................................................................................................12
2.3.2 USB-to-UART Bridge ............................................................................................................12
2.3.3 USB-JTAG.............................................................................................................................13
2.3.4 USB circuit protection...........................................................................................................14
2.4 DISPLAY AND AUDIO......................................................................................................................14
2.4.1 HDMI Output.........................................................................................................................14
2.4.2 VGA Connector......................................................................................................................17
2.4.3 I2S Audio Codec....................................................................................................................18
2.4.4 OLED.....................................................................................................................................19
2.5 CLOCK SOURCES.............................................................................................................................19
2.6 RESET SOURCES .............................................................................................................................19
2.6.1 Power
‐
on Reset (PS_POR_B)................................................................................................19
2.6.2 Program Push Button Switch.................................................................................................20
2.6.3 Processor Subsystem Reset....................................................................................................20
2.7 USER I/O........................................................................................................................................20
2.7.1 User Push Buttons .................................................................................................................20
2.7.2 User DIP Switches.................................................................................................................20
2.7.3 User LEDs .............................................................................................................................21
2.8 10/100/1000 ETHERNET PHY ........................................................................................................21
2.9 EXPANSION HEADERS ....................................................................................................................22
2.9.1 LPC FMC Connector.............................................................................................................22
2.9.2 Digilent Pmod™ Compatible Headers (2x6).........................................................................23
2.9.3 Agile Mixed Signaling (AMS) Connector, J2.........................................................................24
2.10 CONFIGURATION MODES................................................................................................................27
2.10.1 JTAG......................................................................................................................................28
2.11 POWER ...........................................................................................................................................29
2.11.1 Primary Power Input.............................................................................................................29
2.11.2 On/Off Switch ........................................................................................................................29
2.11.3 Regulators..............................................................................................................................29
2.11.4 Sequencing.............................................................................................................................30
2.11.5 Power Good LED ..................................................................................................................31
2.11.6 Power Estimation ..................................................................................................................31
2.11.7 Testing ...................................................................................................................................31
2.11.8 Probes....................................................................................................................................32
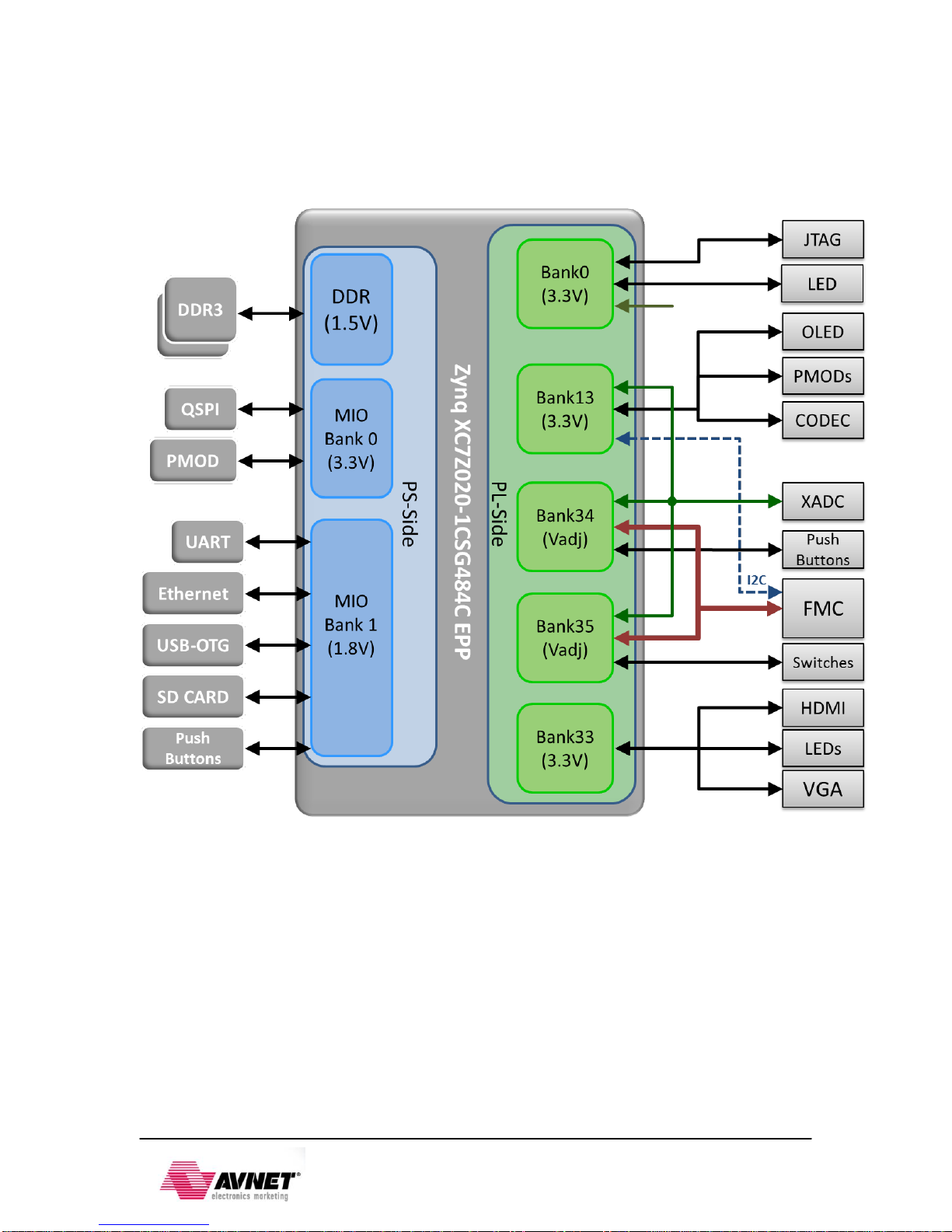
3ZYNQ EPP BANKS..............................................................................................................................33
3.1 ZYNQ EPP BANK VOLTAGES..........................................................................................................34
4JUMPER SETTINGS............................................................................................................................35
5MECHANICAL ....................................................................................................................................37