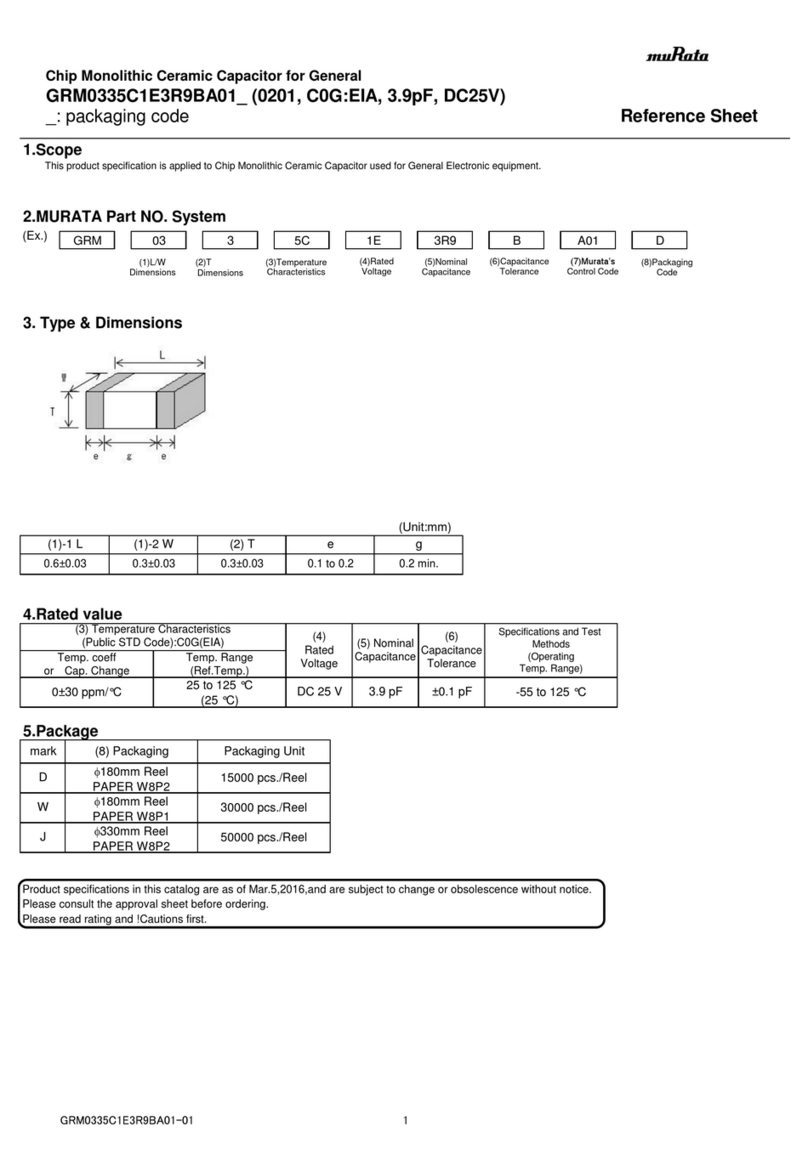
Copyright 2012 by American Control Electronics® - All rights reserved. No part of this document may be
reproduced or retransmied in any form without wrien permission from American Control Electronics®.
The informaon and technical data in this document are subject to change without noce. American
Control Electronics®makes no warranty of any kind with respect to this material, including, but not
limited to, the implied warranes of its merchantability and fitness for a given purpose. American
Control Electronics®assumes no responsibility for any errors that may appear in this document
and makes no commitment to update or to keep current the informaon in this document.
QSG-0018 rev 0
Calibration
Minimum Speed (MIN SPD): The MIN SPD seng determines the minimum motor speed when the
speed adjust potenometer is set for minimum speed. It is factory set for zero speed. To calibrate the
MIN SPD:
1. Set the MIN SPD trim pot full CCW.
2. Set the speed adjust potenometer for minimum speed.
3. Adjust the MIN SPD trim pot unl the desired minimum speed is reached or is just at the
3. threshold of rotaon.
Maximum Speed (MAX SPD): The MAX SPD seng determines the maximum motor speed when the
speed adjust potenometer is set for maximum speed. To calibrate the MAX SPD:
1. Set the MAX SPD trim pot full CCW.
2. Set the speed adjust potenometer for maximum speed.
3. Adjust the MAX SPD trim pot unl the desired maximum speed is reached.
Check the MIN SPD and MAX SPD adjustments aer recalibrang to verify that the motor runs at the
desired minimum and maximum speed.
Torque (CURRENT LIMIT): The CURRENT LIMIT seng determines the maximum torque for
accelerang and driving the motor. To calibrate the CURRENT LIMIT:
1. With the power disconnected from the drive, connect a DC ammeter in series with the
1. armature.
2. Set the CURRENT LIMIT trim pot to minimum (full CCW).
3. Set the speed adjust potenometer to maximum speed (full CW).
4. Carefully lock the motor armature. Be sure that the motor is firmly mounted.
5. Apply line power. The motor should be stopped.
6. Slowly adjust the CURRENT LIMIT trim pot CW unl the armature current is 150% of motor
6. rated armature current. Connuous operaon beyond this rang may damage the motor.
7. Turn the speed adjust potenometer CCW.
8. Remove line power.
9. Remove the stall from the motor.
10. Remove the ammeter in series with the motor armature if it is no longer needed.
IR Compensaon (IR COMP): The IR COMP seng determines the degree to which motor speed is
held constant as the motor load changes. To calibrate the IR COMP:
1. Set the IR COMP trim pot full CCW.
2. Increase the speed adjust potenometer unl the motor runs at midspeed without load. A
2. handheld tachometer may be used to measure motor speed.
3. Load the motor armature to its full load armature current rang. The motor should slow down.
4. While keeping the load on the motor, rotate the IR COMP trim pot unl the motor runs at the
4. speed measured in step 2. If the motor oscillates (overcompensaon), the IR COMP trim pot
4. may be set too high (CW). Turn the IR COMP trim pot CCW to stabilize the motor.
5. Unload the motor.
Acceleraon (ACCEL): The ACCEL seng determines the me the motor takes to ramp to a higher
speed. ACCEL is factory set for the shortest acceleraon me (full CCW). To calibrate the ACCEL:
1. Set the speed adjust potenometer for minimum speed.
2. Set the speed adjust potenometer for maximum speed. Measure the me is takes the motor
2. to go from minimum speed to maximum speed.
3. If the me measured in step 2 is not the desired acceleraon me, turn the ACCEL trim pot
3. CW for a longer acceleraon me, or CCW for a shorter acceleraon me. Repeat steps 1
3. through 3 unl the acceleraon me is correct.
Deceleraon (DECEL): The DECEL seng determines the me the motor takes to ramp to a lower
speed. DECEL is factory set for the shortest deceleraon me (full CCW). To calibrate the DECEL:
1. Set the speed adjust potenometer for maximum speed.
2. Set the speed adjust potenometer for minimum speed. Measure the me is takes the motor
2. to go from maximum speed to minimum speed.
3. If the me measured in step 2 is not the desired deceleraon me, turn the DECEL trim pot
3. CW for a longer deceleraon me, or CCW for a shorter deceleraon me. Repeat steps 1
3. through 3 unl the deceleraon me is correct.
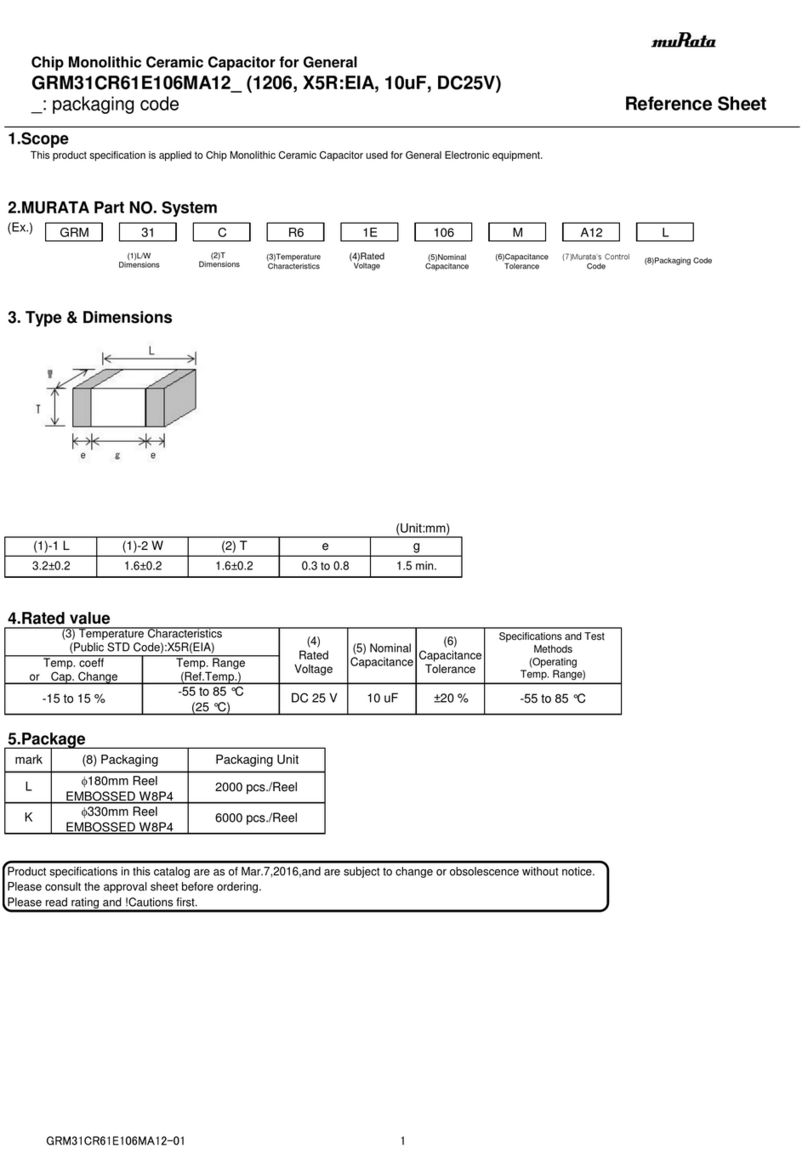
MOTOR
A1 A2
FWD
BRAKE
REV
DYNAMIC
BRAKE
RESISTOR
INHIBIT
Reversing with a Dynamic Brake
A dynamic brake may be used when reversing the motor direcon. Use a three pole, three posion
switch rated for at least the armature voltage rang and 150% of the armature current rang. For the
dynamic brake resistor, use a 40 wa minimum, high power, wirewound resistor. Sizing the dynamic
brake resistor depends on load inera, motor voltage, and braking me. Use a lower-value,
higher-waage dynamic brake resistor to stop a motor more rapidly. Recommended values are 15
ohms for a 130 VDC motor and 30 ohms for 240 VDC motor. The motor must come to a complete stop
before changing direcons.
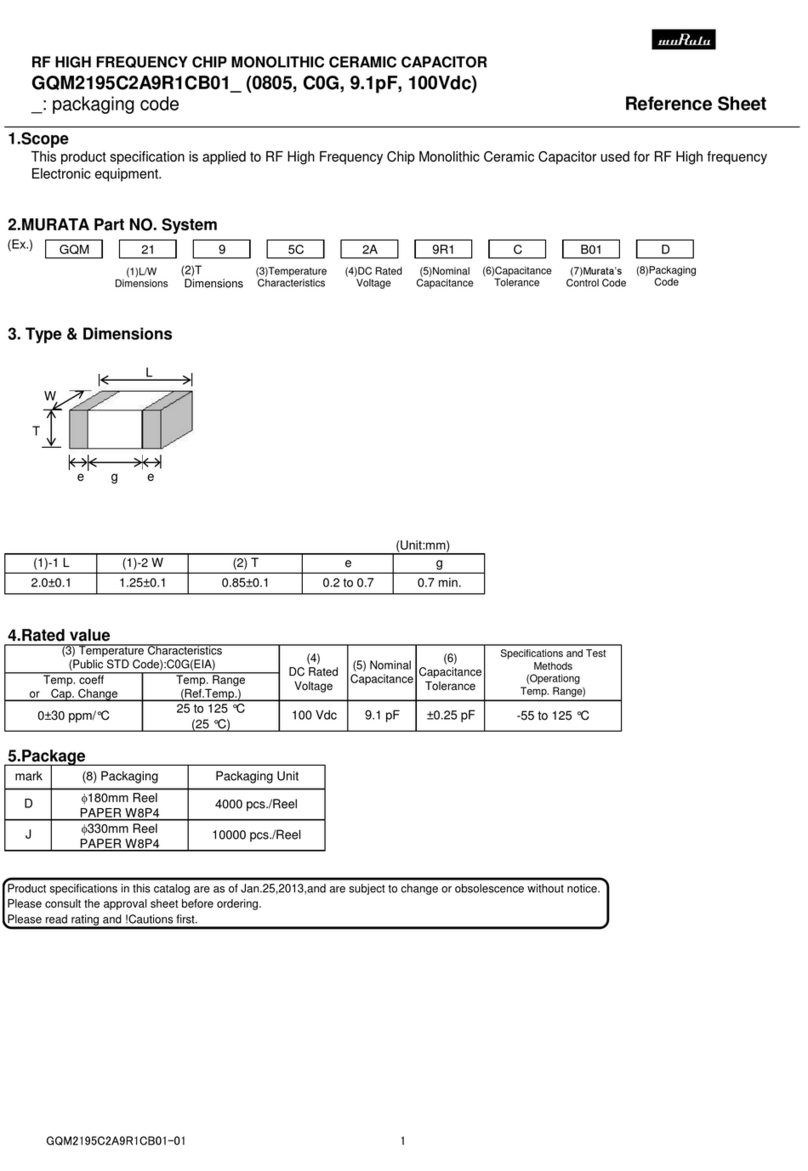
REVERSING
INHIBIT
MOTOR
A2
A1
RUN
BRAKE
DYNAMIC BRAKE
RESISTOR
S3
S2
S1
RUN
DECEL TO
MIN SPEED
10K OHM
SPEED ADJUST
POTENTIOMETER
CW
Decelerate to Minimum Speed
The switch shown below may be used to decelerate a motor to a minimum speed. Closing the switch
between S1 and S2 decelerates the motor from set speed to a minimum speed determined by the MIN
SPD trim pot seng. If the MIN SPD trim pot is set full CCW, the motor decelerates to zero speed when
the switch between S1 and S2 is closed. The DECEL trim pot seng determines the rate at which the
drive decelerates. By opening the switch, the motor accelerates to set speed at a rate determined by
the ACCEL trim pot seng.
Decelerate to Zero Speed (Coast)
See INHIBIT in the CONNECTIONS secon on page 1 for a descripon of wiring and connecon
locaons.
Decelerate to Zero Speed (Dynamic Brake)
Dynamic braking may be used to rapidly stop a motor. For the RUN/BRAKE switch, use a two pole,
two posion switch rated for at least the armature voltage rang and 150% of the armature current
rang. For the dynamic brake resistor, use a 40 wa minimum, high power, wirewound resistor. Sizing
the dynamic brake resistor depends on load inera, motor voltage, and braking me. Use a lower-value,
higher-waage dynamic brake resistor to stop a motor more rapidly. Recommended values are 15
ohms for a 130 VDC motor and 30 ohms for 240 VDC motor.
DECELERATING & STOPPING
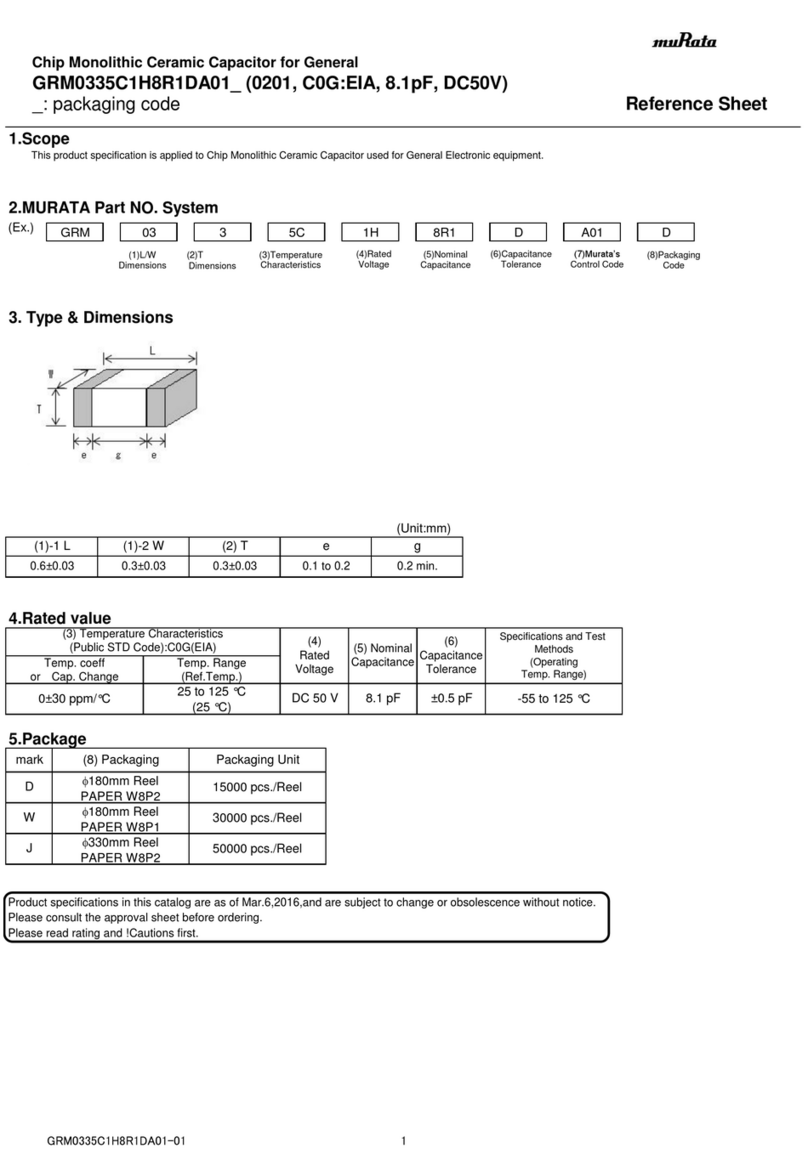
Operation
Current Limit (CURRENT LIMIT): Red LED lights whenever the drive reaches current limit.
Power (POWER): Green LED lights whenever AC line voltage is applied to the drive.
LEDs
IL501
TH501
305Q
IL502
105T
C503
105C
C505
C502
C504
105R
D
IBIHNI T
LIMIT
S3
S2
S1
2L1L 2A 1A
CURRENT
POWER
CURRENT LIMIT
DECEL ACCEL
IR COMP
MAX SPD MIN SPD
Current Limit
LED
Power
LED
Startup
STARTUP
- Verify that no foreign conducve material is present on the printed circuit board.
1. Turn the speed adjust potenometer full counterclockwise (CCW).
2. Apply AC line voltage.
3. Slowly advance the speed adjust potenometer clockwise (CW). The motor slowly accelerates as
the potenometer is turned CW. Connue unl the desired speed is reached.
4. Remove AC line voltage from the drive to coast the motor to a stop.