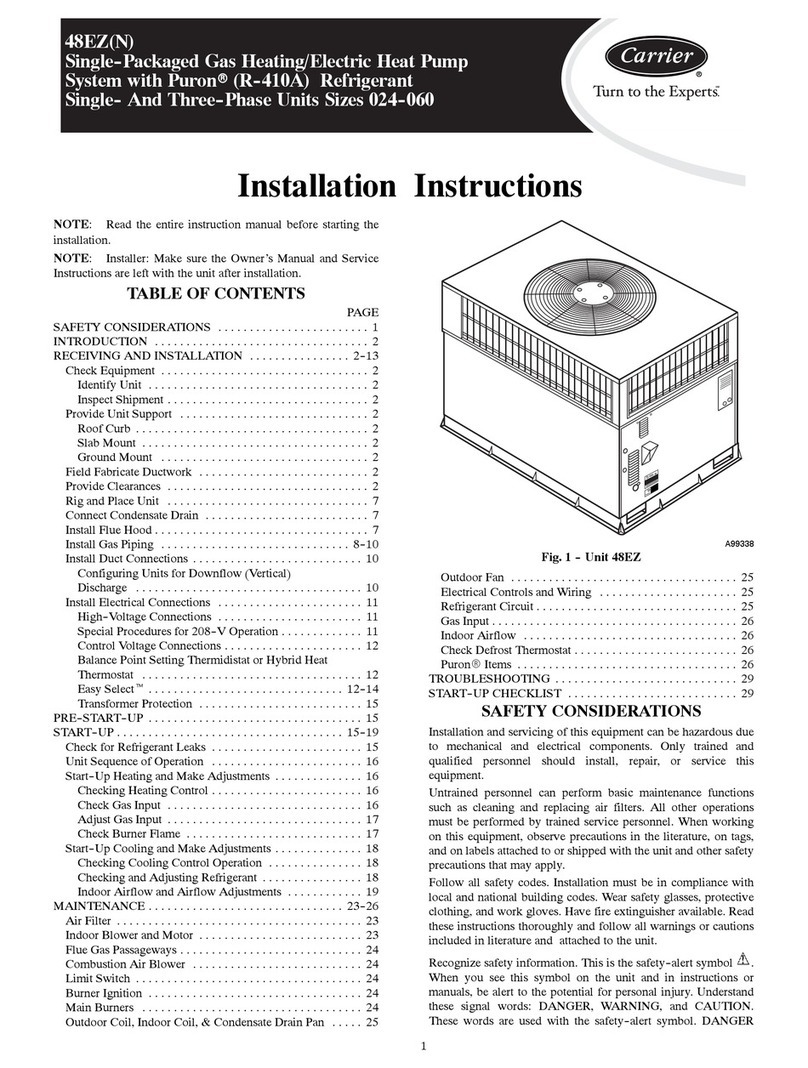
8
Eubank Wall Mount Heat Pump I&O Manual
05/2023 Rev.2
Ventilation Options
Optional - Ventilation Configuration C: The economizer is a regulated damper system with controls.
The damper regulates the circulation of outside air into the enclosure (when the outdoor air conditions
are suitable) to reduce the need for mechanical cooling, save energy, and extend compressor life.
Depending upon the options selected, the damper responds to the enthalpy of the outdoor air. On a call
for cooling from a space thermostat, it operates as follows:
When the enthalpy of the outdoor air is below the set point, the outdoor air damper is proportionally open
(and return air damper is proportionally closed) to maintain between 50°F and 56°F (10°C to 13°C) at
the mixed/discharge air sensor. Integral pressure relief allows the indoor air to exit the shelter through
the air conditioner.
When the enthalpy of the outdoor air is above the set point, the outdoor air damper closes to its minimum
position. A call for cooling from the space thermostat brings on mechanical cooling.
Optional - Ventilation Configuration D: Motorized, two position damper (open and closed) capable
of 0 to 450 cfm (maximum of 40% of rated airflow) of outside air; includes pressure relief. A 24-volt
actuated motor controls the damper from an external input such as: a time clock, CO2 sensor, energy
management system or manual switch.
Hot Gas Reheat (HGR) Dehumidification Mode (Special Option “G”)
When the HGR is in the dehumidification mode, the hot gas reheat (HGR) coil is energized. The cooled,
dehumidified air exits the evaporator coil and is blown through the HGR coil. This coil is sized to the
sensible capacity of the unit. The heat in the HGR coil is transferred to the air stream. The use of the HGR
coil allows the indoor humidity of the classroom to be maintained at or below a certain set humidity set
point without over cooling the classroom. These units can not add humidity to the classroom.
The operation of the HGR coil is controlled by a humidity controller. If the humidity rises above the set
point on the controller and the temperature in the classroom is satisfied, both mechanical cooling and
the HGR coil operate to temper the air and lower the humidity. If the temperature in the classroom rises
above or falls below the set point of thermostat and the unit is operating in the dehumidification mode,
the need for cooling or heating will override the call for dehumidification and the HGR coil is disengaged
until the thermostat is satisfied. This assures the classroom temperature is maintained as first priority
and humidity control is second.
The humidity controller or BAS control is required for proper operation of the HGR coil.
Optional - Ventilation Configuration H: GreenWheel®ERV
The GreenWheel® ERV is a total energy (both sensible and latent) wheel that reduces both construction
and operating cost while ventilating the classroom to ASHRAE 62-1999 requirements. The use of the
GreenWheel ERV reduces the energy load of the outside air. Exhausting stale, inside air keeps indoor
pollutants and harmful gases to a minimum. The GreenWheel ERV has been tested and certified according
to ARI Standard 1060.
How It Works
During the summer, cool dry air from the classroom is exhausted through the GreenWheel® ERV to the
outside. As the air passes through the rotating wheel, the desiccant becomes cooler and drier. Simultaneously,
hot humid air is being pulled across the rotating wheel. The cool, dry desiccant absorbs moisture and
heat from the incoming air. The cooler, drier air is mixed with the return air from the classroom and
distributed throughout the room.
In the winter, warm moist air is exhausted through the GreenWheel® ERV to the outside. As the air passes
through the rotating wheel, the desiccant becomes warmer and absorbs moisture. Simultaneously, cold
dry air is being pulled across the rotating wheel. The cold, dry air absorbs heat and moisture from the
desiccant. The warmed air is mixed with the return air from the classroom and distributed throughout
the room.