Actron SunPro CP7678 User manual

Index
Safety Precautions ....................................... 2
Vehicle Service Information ......................... 3
Visual Inspection ..........................................3
Warranty .....................................................72
1. Multimeter Basic Functions
Functions and Display Definitions............ 4
Setting the Range..................................... 6
Battery and Fuse Replacement ...............7
Measuring DC Voltage .............................8
Measuring Resistance.............................. 8
Measuring DC Current .............................9
Testing for Continuity .............................10
Testing Diodes........................................10
Measuring Engine RPM (TACH)............ 11
Measuring Dwell ..................................... 12
Measuring Duty Cycle ............................12
2. Automotive Testing with the CP7678
General Testing ......................................13
- Testing Fuses ......................................13
- Testing Switches..................................13
- Testing Solenoids and Relays.............14 1
CP7678
®
by
®
Digital Multimeter
OPERATING
INSTRUCTIONS
Starting / Charging System Testing ...........15
- No Load Battery Test...........................15
- Engine Off Battery Current Draw ........ 16
- Cranking Voltage/Battery Load Test ... 17
- Voltage Drops ......................................18
- Charging System Voltage Test............ 19
Ignition System Testing.............................. 20
- Ignition Coil Testing .............................20
- Ignition System Wires..........................22
- Hall Effect Sensors/Switches ..............23
- Magnetic Pick-Up Coils .......................24
- Reluctance Sensors .............................24
- Ignition Coil Switching Action ..............25
Fuel System Testing...................................26
- Testing GM C-3 Mixture Control
Solenoid Dwell ....................................26
- Measuring Fuel Injector Resistance....27
Testing Engine Sensors .............................28
- Oxygen (O2) Type Sensors..................28
- Temperature Type Sensors................. 30
- Position Type Sensors –
Throttle and EGR Valve Position,
Vane Air Flow ......................................31
- Manifold Absolute Pressure
(MAP)
and
Barometric Pressure
(BARO)
Sensors ..... 32
- Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensors ..............34
250V MAX
15A MAX
FUSED
COM
DC
15A
AUTO POWER OFF
CP7678
®
OFF
200
20
2
DC V
200
m
20M
200
K
20K
2K 200 8CYL6CYL TACH
X10
5CYL
4CYL
8CYL
6CYL
5CYL
4CYL
DWELL
DUTY
CYCLE
%
OHMS
°
20
15
A
20V

SAFETY GUIDELINES
TO PREVENT ACCIDENTS THAT COULD RESULT IN SERIOUS INJURY
AND/OR DAMAGE TO YOUR VEHICLE OR TEST EQUIPMENT, CAREFULLY
FOLLOW THESE SAFETY RULES AND TEST PROCEDURES
2
• Always wear approved eye protection.
• Always operate the vehicle in a well ventilated area. Do not inhale exhaust gases – they are
very poisonous!
• Always keep yourself, tools and test equipment away from all moving or hot engine parts.
• Always make sure the vehicle is in park (Automatic transmission) or neutral (manual
transmission) and that the parking brake is firmly set. Block the drive wheels.
• Never lay tools on vehicle battery. You may short the terminals together causing harm to
yourself, the tools or the battery.
• Never smoke or have open flames near vehicle. Vapors from gasoline and charging battery
are highly flammable and explosive.
• Never leave vehicle unattended while running tests.
• Always keep a fire extinguisher suitable for gasoline/electrical/chemical fires handy.
• Always use extreme caution when working around the ignition coil, distributor cap, ignition
wires, and spark plugs. These components contain High Voltage when the engine is
running.
• Always turn ignition key OFF when connecting or disconnecting electrical components,
unless otherwise instructed.
• Always follow vehicle manufacturer’s warnings, cautions and service procedures.
CAUTION:
Somevehiclesareequippedwithsafetyairbags.You
must
followvehicleservicemanualcautions
whenworkingaroundtheairbagcomponentsorwiring.Ifthecautionsarenotfollowed,theairbag
may open up unexpectedly, resulting in personal injury. Note that the air bag can still open up
severalminutesafterthe ignition key isoff(oreven if the vehiclebatteryisdisconnected) because
of a special energy reserve module.
All information, illustrations and specifications contained in this manual are based on the latest
information available from industry sources at the time of publication. No warranty (expressed
orimplied) canbe made for its accuracy or completeness, nor isany responsibilityassumed by
Actron Manufacturing Co. or anyone connected with it for loss or damages suffered through
relianceonanyinformationcontainedinthismanualormisuseofaccompanyingproduct.Actron
Manufacturing Co. reserves the right to make changes at any time to this manual or accompa-
nying product without obligation to notify any person or organization of such changes.

3
Vehicle Service Manual – Sources For Service Information
The following is a list of sources to obtain vehicle service information for your specific vehicle.
• Contact your local Automotive Dealership Parts Department.
• Contact local retail auto parts stores for aftermarket vehicle service information.
• Contact your local library. Libraries often allow you to check-out automotive service manuals.
Do a Thorough Visual Inspection
Do a thorough visual and “hands-on” underhood inspection before starting any diagnostic
procedure! You can find the cause of many problems by just looking, thereby saving yourself a
lot of time.
• Has the vehicle been serviced recently?
Sometimes things get reconnected in the
wrong place, or not at all.
• Don’t take shortcuts. Inspect hoses and
wiring which may be difficult to see due
to location.
• Inspect the air cleaner and ductwork for
defects.
• Check sensors and actuators for
damage.
• Inspect ignition wires for:
- Damaged terminals.
- Split or cracked spark plug boots
- Splits, cuts or breaks in the ignition
wires and insulation.
• Inspect all vacuum hoses for:
- Correct routing. Refer to vehicle service
manual, or Vehicle Emission Control
Information(VECI) decal located in the
engine compartment.
- Pinches and kinks.
- Splits, cuts or breaks.
• Inspect wiring for:
- Contact with sharp edges.
- Contact with hot surfaces, such as
exhaust manifolds.
- Pinched, burned or chafed insulation.
- Proper routing and connections.
• Check electrical connectors for:
- Corrosion on pins.
- Bent or damaged pins.
- Contacts not properly seated in housing.
- Bad wire crimps to terminals.
250V MAX
15A MAX
FUSED
COM
DC
15A
AUTO POWER OFF
CP7678
®
OFF
200
20
2
DC V
200
m
20M
200
K
20K
2K 200 8CYL6CYL
TACH
X10
5CYL
4CYL
8CYL
6CYL
5CYL
4CYL
DWELL
DUTY
CYCLE
%
OHMS
°
20
15
A
20V
4
2
Alligator Clip Adapters
Some multimeter tests and measurements are more easily done
using alligator clips instead of test prods. For these tests, push
the crimp end of the alligator clip onto the test prod. If the crimp
onthealligatorclip becomes loose, thenremovethealligator clip
from the test prod and re-crimp using a pair of pliers.
Section 1. Multimeter Basic Functions
DigitalmultimetersorDMMshavemanyspecialfeaturesandfunctions.Thissectiondefinesthese
features and functions, and explains how to use these functions to make various measurements.
1
11
3
5
4
6
7
8
9
10
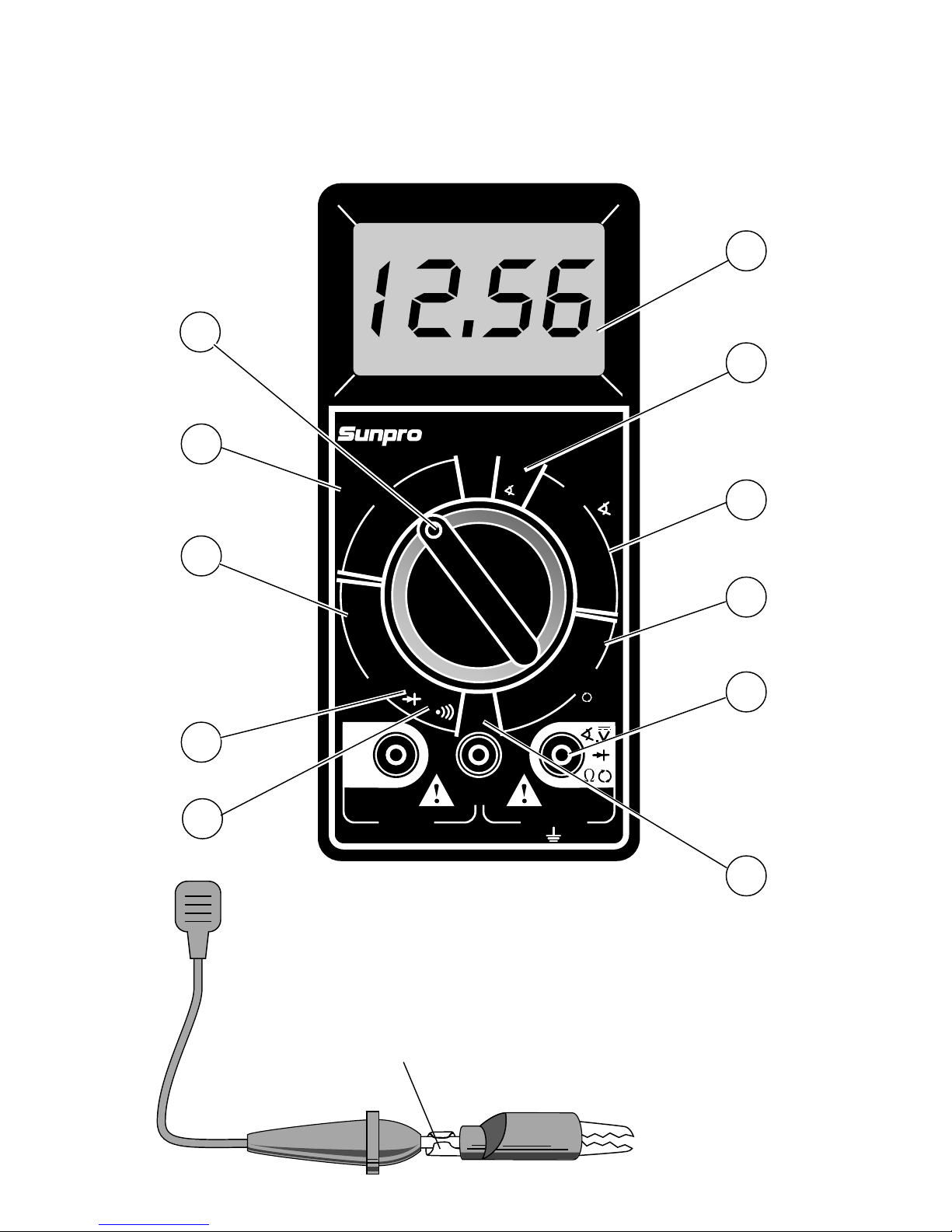
Functions and Display Definitions
1. ROTARY SWITCH
Switch is rotated to turn multimeter ON/
OFF and select a function.
2. DC VOLTS
This function is used for measuring DC
(Direct Current) Voltages in the range of 0
to 200V.
3. OHMS
This function is used for measuring the
resistance of a component in an electrical
circuit in the range of 0.1Ωto 20MΩ. (Ωis
the electrical symbol for Ohms)
4. DIODE CHECK
This function is used to check whether a
diode is good or bad.
5. CONTINUITY TESTS
It is also used for fast continuity checks of
wires and terminals. An audible tone will
sound if a wire and terminal are good.
6. DC AMPS
This function is used for measuring DC
(Direct Current) Amps in the range of 0 to
15A.
7. TEST LEAD JACKS
BLACK Test Lead is always
inserted in the COM jack.
RED Test Lead is inserted in
the jack corresponding to the
multimeter rotary switch set-
ting.
8. TACH
Thisfunctionisusedformeasuringengine
speed (RPM).
9. DWELL
ThisfunctionisusedformeasuringDWELL
on distributor ignition systems, and sole-
noids.
10.DUTY CYCLE
This function is used for measuring DUTY
CYCLE on relays, solenoids, and other
ON/OFF types of devices.
11.DISPLAY
Used to display all measurements and
multimeter information.
Low Battery – If this symbol
appears in the lower left corner
of the display, then replace the
internal 9V battery. (See Fuse
and Battery replacement on
page 7.)
Overrange Indication – If “1”
or “-1” appears on the left side
of the display, then the multim-
eter is set to a range that is too
small for the present measure-
ment being taken. Increase the
range until this disappears. If it
does not disappear after all the
ranges for a particular function have been
tried,thenthevaluebeingmeasuredistoo
large for the multimeter to measure. (See
Setting the Range on page 6.)
Automatic Power Off
Themultimeterwillautomaticallyturnitselfoff
after approximately thirty (30) minutes if the
rotary switch has not been rotated. Momen-
tarily change the rotary switch position to
restore normal operation.
Zero Adjustment
The multimeter will automatically zero on the
Volts, Amps and RPM functions.
Automatic Polarity Sensing
The multimeter display will show a minus (-)
sign on the DC Volts and DC Amps functions
when test lead hook-up is reversed.
5
Always connect TEST LEADS to the multi-
meter before connecting them to the cir-
cuit under test!!
COM
DC VOLTS
OHMS
DIODES
CONTINUITY
15
A
TACH
DWELL
DUTY CYCLE
DC AMPS

250V MAX
15A MAX
FUSED
COM
DC
15A
AUTO POWER OFF
CP7678
®
OFF
200
20
2
DC V
200
m
20M
200
K
20K
2K 200 8CYL6CYL
TACH
X10
5CYL
4CYL
8CYL
6CYL
5CYL
4CYL
DWELL
DUTY
CYCLE
%
OHMS
°
20 M
15
A
250V MAX
15A MAX
FUSED
COM
DC
15A
AUTO POWER OFF
CP7678
®
OFF
200
20
2
DC V
200
m
20M
200
K
20K
2K 200 8CYL6CYL TACH
X10
5CYL
4CYL
8CYL
6CYL
5CYL
4CYL
DWELL
DUTY
CYCLE
%
OHMS
°
2
15
A
250V MAX
15A MAX
FUSED
COM
DC
15A
AUTO POWER OFF
CP7678
®
OFF
200
20
2
DC V
200
m
20M
200
K
20K
2K 200 8CYL6CYL
TACH
X10
5CYL
4CYL
8CYL
6CYL
5CYL
4CYL
DWELL
DUTY
CYCLE
%
OHMS
°
20
15
A
Setting the Range
Two of the most commonly asked questions
aboutdigitalmultimetersareWhatdoesRange
mean? and How do I know what Range the
multimeter should be set to?
What Does Range mean?
Range refers to the largest value the multim-
etercanmeasurewiththerotaryswitchinthat
position.Ifthemultimeteris settothe20VDC
range, then the highest voltage the multim-
eter can measure is 20V in that range.
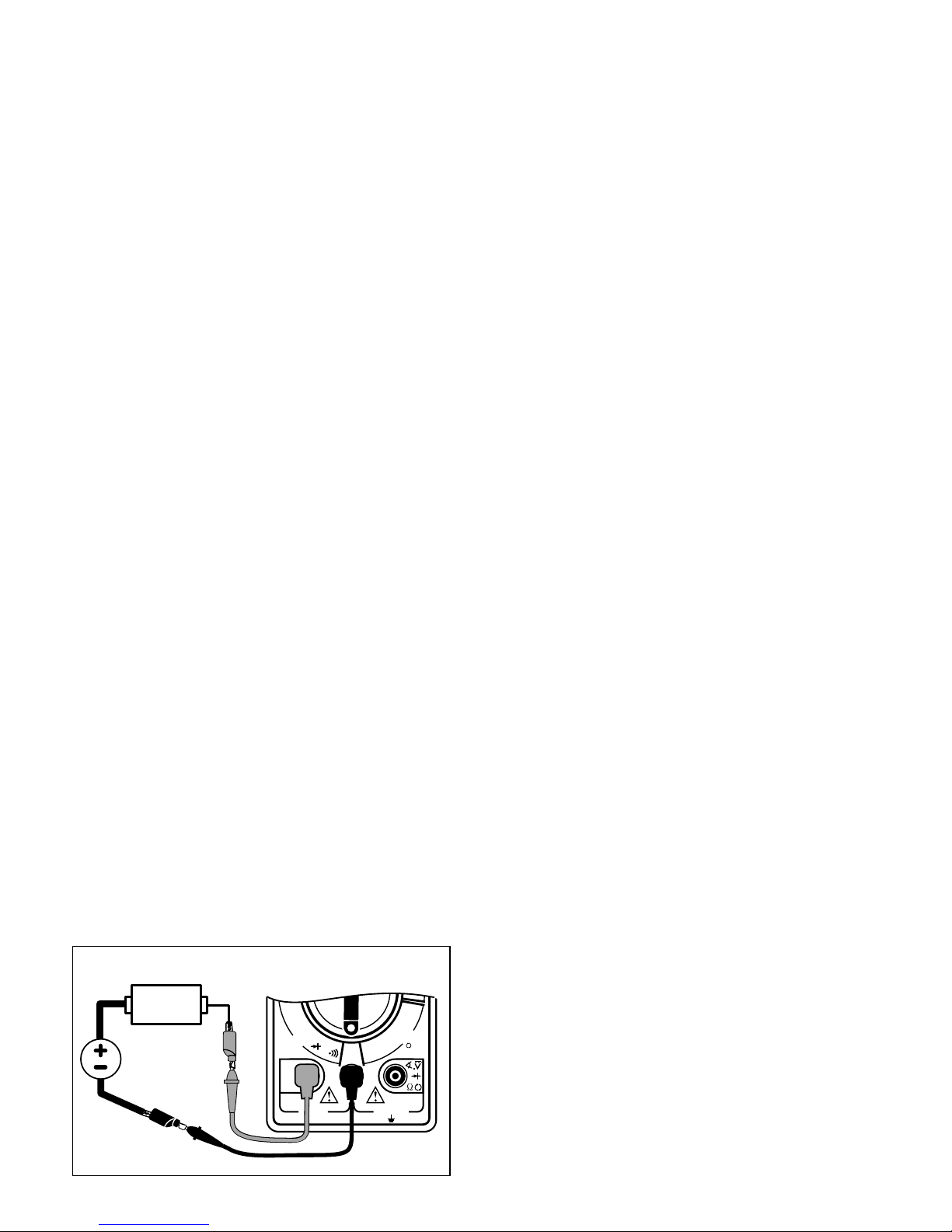
EXAMPLE: Measuring Vehicle Battery Volt-
age (See Fig. 1)
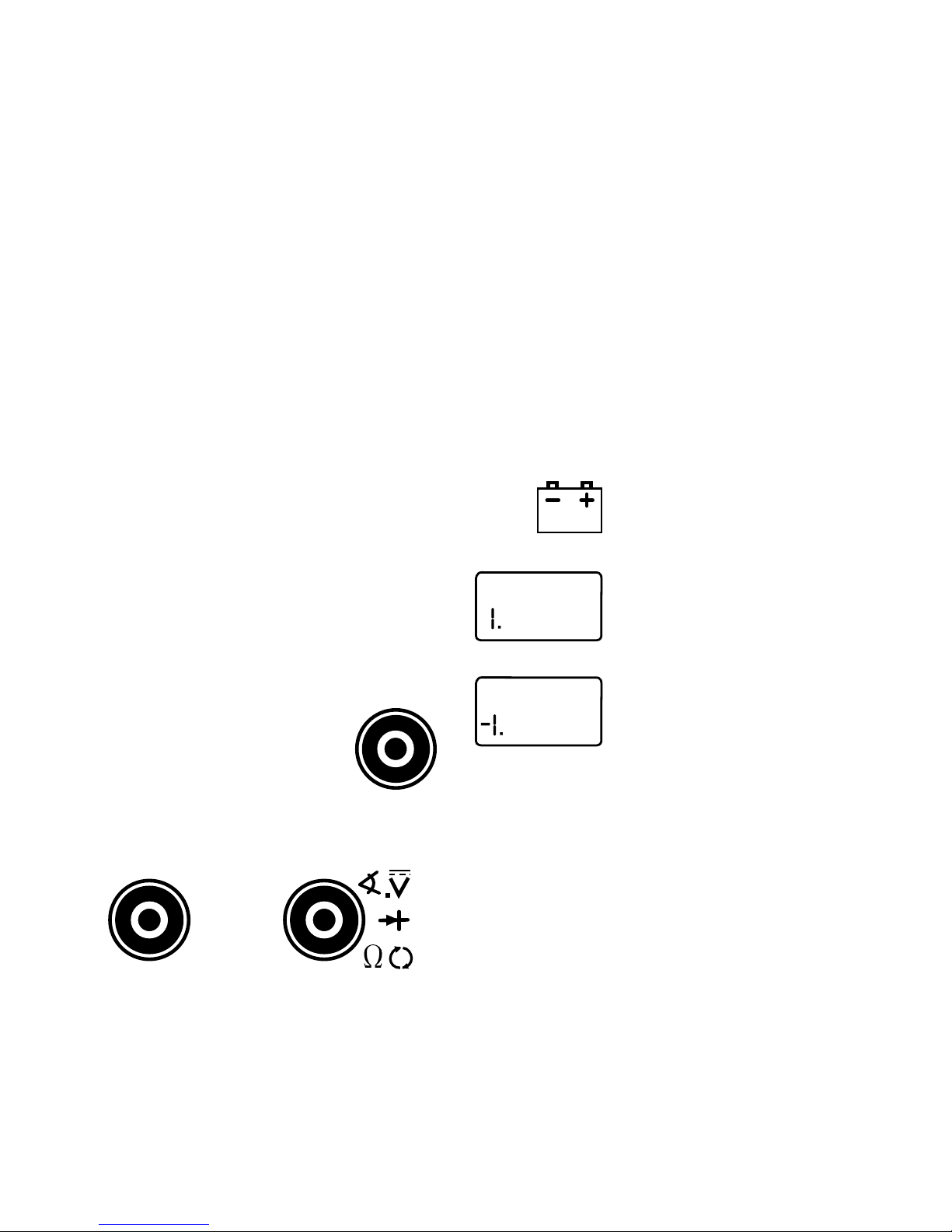
6
Now assume we set the multimeter to the 2V
range. (See Fig. 2)
The multimeter display now shows a “1” and
nothing else. This means the multimeter is
beingoverranged or in other wordsthevalue
being measured is larger than the current
range. The range should be increased until a
valueisshownonthedisplay. If you areinthe
highestrangeandthemultimeterisstillshow-
ingthat itis overranging,then thevalue being
measured is too large for the multimeter to
measure.
How do I know what Range the multimeter
should be set to?
The multimeter should be set in the lowest
possible range without overranging.
EXAMPLE: Measuring an unknown resis-
tance
Let’s assume the multimeter is connected to
anenginecoolantsensorwithunknownresis-
tance. (See Fig. 3)
Fig. 2
Fig. 1
Let’s assume the multimeter is connected to
the battery and set to the 20V range.
The display reads 12.56. This means there is
12.56V across the battery terminals.
Fig. 3
Start by setting the multimeter to the largest
OHMrange.Thedisplayreads0.0Ωorashort
circuit.
This sensor can’t be shorted so reduce the
range setting until you get a value of resis-
tance.
Atthe 200KΩrange themultimeter measured
a value of 4.0. This means there is 4KΩof
resistance across the engine coolant sensor
terminals. (See Fig. 4)
Red
Black
Red
Black
Black
Red
250V MAX
15A MAX
FUSED
COM
DC
15A
AUTO POWER OFF
CP7678
®
OFF
200
20
2
DC V
200
m
20M
200
K
20K
2K 200 8CYL6CYL
TACH
X10
5CYL
4CYL
8CYL
6CYL
5CYL
4CYL
DWELL
DUTY
CYCLE
%
OHMS
°
20K
15
A
250V MAX
15A MAX
FUSED
COM
DC
15A
AUTO POWER OFF
CP7678
®
OFF
200
20
2
DC V
200
m
20M
200
K
20K
2K 200 8CYL6CYL
TACH
X10
5CYL
4CYL
8CYL
6CYL
5CYL
4CYL
DWELL
DUTY
CYCLE
%
OHMS
°
200K
15
A
250V MAX
15A MAX
FUSED
COM
DC
15A
AUTO POWER OFF
CP7678
®
OFF
200
20
2
DC V
200
m
20M
200
K
20K
2K 200 8CYL6CYL TACH
X10
5CYL
4CYL
8CYL
6CYL
5CYL
4CYL
DWELL
DUTY
CYCLE
%
OHMS
°
2K
15
A
7
Fig. 4
Fig. 5
Ifwechangethemul-
timeter to the 20KΩ
range (See Fig. 5)
the display shows a
valueof3.87KΩ.The
actual value of resis-
tance is 3.87KΩand
not 4KΩthat was
measured in the
200KΩrange.Thisis
very important be-
causeifthemanufac-
turer specifications
say that the sensor
should read 3.8-
3.9KΩat 70°F then
on the 200KΩrange
the sensor would be defective, but at the
20KΩrange it would test good.
Now set the multimeter to the 2KΩrange.
(SeeFig. 6)The dis-
play will indicate an
overrange condition
because 3.87KΩis
larger than 2KΩ.
This example shows
that by decreasing
the range you in-
crease the accuracy
of your measure-
ment. When you
change the range,
you change the loca-
tion of the decimal
point. This changes
the accuracy of the
Fig. 6
measurement by either increasing or decreas-
ing the number of digits after the decimal point.
Battery and Fuse
Replacement
Important: A 9 Volt battery must be installed
before using the digital multimeter. (see pro-
cedure below for installation)
Battery Replacement
1. Turn multimeter rotary switch to OFF
position.
2. Remove test leads from multimeter.
3. Remove three screws from back of
multimeter.
4. Remove back cover.
5. Install a new 9 Volt battery.
6. Re-assemble multimeter.
Fuse Replacement
1. Turn multimeter rotary switch to OFF
position.
2. Remove test leads from multimeter.
3. Remove three screws from back of
multimeter.
4. Remove back cover.
5. Remove battery.
6. Remove fuse located on top of
battery clip.
7. Replace fuse with same size and type
as originally installed.
Use a 5mm X 20mm, 15A, 250V, fast blow
fuse.
8. Re-assemble multimeter.
250V MAX
15A MAX
FUSED
COM
DC
15A
200
K
20K
2K 200 8CYL6CYL TACH
X10
5CYL
4CYL
OHMS
15
A
250V MAX
15A MAX
FUSED
COM
DC
15A
AUTO POWER OFF
CP7678
®
OFF
200
20
2
DC V
200
m
20M
200
K
20K
2K 200 8CYL6CYL
TACH
X10
5CYL
4CYL
8CYL
6CYL
5CYL
4CYL
DWELL
DUTY
CYCLE
%
OHMS
°
20V
15
A
8
Measuring DC Voltage
This multimeter can be used to measure DC
voltagesin therange from 0 to 200V. You can
use this multimeter to do any DC voltage
measurementcalledoutinthevehicleservice
manual. The most common applications are
measuring voltage drops, and checking if the
correct voltage arrived at a sensor or a par-
ticular circuit.
crease to the appropriate range as re-
quired.(See Setting theRange on page6)
6. View reading on display - Note range
setting for correct units.
NOTE: 200mV = 0.2V
Measuring Resistance
Resistance is measured in electrical units
called ohms (Ω). The digital multimeter can
measure resistance from 0.1Ωto 20MΩor
(20,000,000 ohms). Infinite resistance is
shown with a “1” on the left side of display
(See Setting the Range on page 6). You can
usethis multimeter to do anyresistance mea-
surement called out in the vehicle service
manual.Testingignitioncoils,sparkplugwires,
and some engine sensors are common uses
for the OHMS (Ω) function.
Fig. 7
To measure DC Voltages (see Fig. 7):
1. Insert BLACK test lead into COM test
lead jack.
2. Insert RED test lead into test
lead jack.
3. Connect RED test lead to positive (+)
side of voltage source.
4. Connect BLACK test lead to negative (-)
side of voltage source.
NOTE: If you don’t know which side is
positive (+) and which side is negative (-),
then arbitrarily connect the RED test lead
to one side and the BLACK to the other.
The multimeter automatically senses po-
larityandwilldisplayaminus(-)signwhen
negativepolarityismeasured.Ifyouswitch
the RED and BLACK test leads, positive
polarity will now be indicated on the dis-
play.Measuringnegativevoltages causes
no harm to the multimeter.
5. Turn multimeter rotary switch to de-
sired voltage range.
If the approximate voltage is unknown,
start at the largest voltage range and de-
Fig. 8
To measure Resistance (see Fig. 8):
1. Turn circuit power OFF.
To get an accurate resistance measure-
ment and avoid possible damage to the
digital multimeter and electrical circuit un-
der test, turn off all electrical power in the
circuitwhere the resistance measurement
is being taken.
2. Insert BLACK test lead into COM test
lead jack.
3. Insert RED test lead into test
lead jack.
4. Turn multimeter rotary switch to 200Ω
range.
Touch RED and BLACK multimeter leads
together and view reading on display.
Red
Black
Red Black
Unknown
Resistance
250V MAX
15A MAX
FUSED
COM
DC
15A
20M
200
K
20K
2K 200 8CYL6CYL TACH
X10
5CYL
4CYL
8CYL
OHMS
15
A
9
Displayshouldreadtypically0.2Ωto1.5Ω.
If display reading was greater than 1.5Ω,
check both ends of test leads for bad
connections.Ifbadconnectionsarefound,
replace test leads.
5. Connect RED and BLACK test leads
across component where you want to
measure resistance.
When making resistance measurements,
polarity is not important. The test leads
justhavetobeconnectedacrossthecom-
ponent.
6. Turn multimeter rotary switch to de-
sired OHM range.
If the approximate resistance is unknown,
start at the largest OHM range and de-
crease to the appropriate range as re-
quired.(SeeSettingtheRangeonpage6)
7. View reading on display - Note range
setting for correct units.
NOTE: 2KΩ=2,000Ω;2MΩ=2,000,000Ω
If you want to make precise resistance
measurements,thensubtractthetestlead
resistance found in Step 4 above from the
display reading in Step 7. It is a good idea
to do this for resistance measurements
less than 10Ω.
Measuring DC Current
This multimeter can be used to measure DC
current in the range from 0 to 15A. If the
current you are measuring exceeds 15A, the
internal fuse will blow (see Fuse Replace-
ment on page 7). Unlike voltage and resis-
tance measurements where the multimeter is
connected across the component you are
Fig. 9
testing,current measurements must be made
with the multimeter in series with the compo-
nent. Isolating current drains and short cir-
cuits are some DC Current applications.
To measure DC Current (see Fig. 9):
1. Insert BLACK test lead into COM test
lead jack.
2. InsertREDtest lead into "15A"testlead
jack.
3. Disconnect or electrically open circuit
where you want to measure current.
This is done by:
• Disconnecting wiring harness.
• Disconnecting wire from screw-on type
terminal.
• Unsolder lead from component if work-
ing on printed circuit boards.
• Cut wire if there is no other possible way
to open electrical circuit.
4. Connect RED test lead to one side of
disconnected circuit.
5. Connect BLACK test lead to remaining
side of disconnected circuit.
6. Turn multimeter rotary switch to 15A
DC position.
7. View reading on display.
If minus (-) sign appears on display, then
reverse RED and BLACK test leads.
Black
Red
Electrical
Device
DC
Voltage
Source

15A MAX
FUSED
COM
DC
15A
20M
200
K
20K
2K 200 8CYL6CYL
TACH
X10
5CYL
4CYL
8CYL
OHMS
15
A
250V MAX
250V MAX
15A MAX
FUSED
COM
DC
15A
20M
200
K
20K
2K 200 8CYL6CYL
TACH
X10
5CYL
4CYL
8CYL
OHMS
15
A
10
Testing for Continuity
Continuity is a quick way to do a resistance
test to determine if a circuit is open or closed.
The multimeter will beep when the circuit is
closedorshorted,soyoudon’thavetolookat
the display. Continuity checks are usually
done when checking for blown fuses, switch
operation, and open or shorted wires.
Testing Diodes
Adiodeisanelectricalcomponentthat allows
current to only flow in one direction. When a
positive voltage, generally greater than 0.7V,
is applied to the anode of a diode, the diode
will turn on and allow current to flow. If this
same voltage is applied to the cathode, the
diode would remain off and no current would
flow. Therefore, in order to test a diode, you
mustcheckitinbothdirections(i.e. anode-to-
cathode, and cathode-to-anode). Diodes are
typically found in alternators on automobiles.
Performing Diode Test (see Fig. 11):
1. Insert BLACK test lead into COM test
lead jack.
2. Insert RED test lead into test
lead jack.
3. Turn multimeter rotary switch to 2K
diodefunction.Nobeeperondiodetest.
4. Touch RED and BLACK test leads to-
gether to test continuity.
Check display – should reset to 0.00.
5. Disconnect one end of diode from cir-
cuit.
Diode must be totally isolated from circuit
in order to test its functionality.
6. Connect RED and BLACK test leads
across diode and view display.
Display will show one of three things:
• A typical voltage drop of around 0.7V.
• A voltage drop of 0 volts.
• A “1” will appear indicating the multim-
eter is overranged.
Fig. 11
Fig. 10
To measure Continuity (see Fig. 10):
1. Insert BLACK test lead into COM test
lead jack.
2. Insert RED test lead into test
lead jack.
3. Turn multimeter rotary switch to
200 function.
4. Touch RED and BLACK test leads to-
gether to test continuity.
Listen for tone to verify proper operation.
5. Connect RED and BLACK test leads
across component where you want to
check for continuity.
Listen for tone:
• If you hear tone – Circuit is closed or
shorted.
• If you don’t hear tone – Circuit is open.
Black
Red
Anode Cathode
BlackRed

250V MAX
15A MAX
FUSED
COM
DC
15A
20M
200
K
20K
2K 200 8CYL6CYL
TACH
X10
5CYL
4CYL
8CYL
OHMS
15
A
11
To measure Engine RPM (TACH) (see Fig.
12):
1. Insert BLACK test lead into COM test
lead jack.
2. Insert RED test lead into test
lead jack.
3. Connect RED test lead to TACH signal
wire.
• If vehicle is DIS (Distributorless Ignition
System), then connect RED test lead to
the TACH signal wire going from the DIS
module to the vehicle engine computer.
(refer to vehicle service manual for loca-
tion of this wire)
• Forallvehicleswithdistributors,connect
REDtestleadtonegativesideof primary
ignition coil. (refer to vehicle service
manual for location of ignition coil)
4. Connect BLACK test lead to a good
vehicle ground.
5. Turn multimeter rotary switch to cor-
rect CYLINDER selection.
6. Measure engine RPM (TACH) while en-
gine is cranking or running.
7. View reading on display.
• If using LO TACH, display reading is
actual RPM.
• Remembertomultiplydisplayreadingby
10 to get actual RPM.
If display reads 200, then actual engine
RPM is 10 times 200 or 2000 RPM.
7. Switch RED and BLACK test leads and
repeat Step 6.
8. Test Results
If the display showed:
• A voltage drop of 0 volts in both direc-
tions with the continuity beeper sound-
ing off, then the diode is shorted and
needs to be replaced.
• A“1”appearsinbothdirections,thenthe
diode is an open circuit and needs to be
replaced.
• The diode is good if the display reads
around0.5V–0.7V inone direction and a
“1”appearsintheotherdirectionindicat-
ing the multimeter is overranged.
Measuring Engine RPM
(TACH)
RPM refers to revolutions per minute. When
using TACH you must multiply the display
reading by 10 to get actual RPM. If display
reads 200 and the multimeter is set to 6
cylinder TACH, the actual engine RPM is 10
times 200 or 2000 RPM.
Typical
Ignition
Coil
Ground
Black
Red
Fig. 12

250V MAX
15A MAX
FUSED
COM
DC
15A
AUTO POWER OFF
CP7678
®
OFF
200
20
2
DC V
200
m
20M
200
K
20K
2K 200 8CYL6CYL TACH
X10
5CYL
4CYL
8CYL
6CYL
5CYL
4CYL
DWELL
DUTY
CYCLE
%
OHMS
°
15
A
250V MAX
15A MAX
FUSED
COM
DC
15A
AUTO POWER OFF
CP7678
®
OFF
200
20
2
DC V
200
m
20M
200
K
20K
2K 200 8CYL6CYL TACH
X10
5CYL
4CYL
8CYL
6CYL
5CYL
4CYL
DWELL
DUTY
CYCLE
%
OHMS
°
15
A
12
Measuring Dwell
Dwell measuring was extremely important on
breaker point ignition systems of the past. It
referred to the length of time, in degrees, that
thebreakerpointsremainedclosed,whilethe
camshaft was rotating. Today’s vehicles use
electronic ignition and dwell is no longer ad-
justable. Another application for dwell is in
testing the mixture control solenoid on GM
feedback carburetors.
5. Turn multimeter rotary switch to cor-
rect DWELL CYLINDER position.
6. View reading on display.
Measuring Duty Cycle
Duty Cycle refers to the percentage of time a
signal is “ON” verses “OFF”. A signal that is
“ON”halfthetimehasa50%DutyCycle.Duty
Cycleisusefulforcheckingsolenoids,relays,
switches, fuel injectors and any other compo-
nent that is switched “ON” and “OFF”.
To measure Dwell (see Fig. 13):
1. Insert BLACK test lead into COM test
lead jack.
2. Insert RED test lead into test
lead jack.
3. ConnectREDtestleadtoDWELLsignal
wire.
• If measuring DWELL on breaker point
ignition systems, connect RED test lead
to negative side of primary ignition coil.
(refer to vehicle service manual for loca-
tion of ignition coil)
• IfmeasuringDWELLonGMmixturecon-
trol solenoids, connect RED test lead to
ground side or computer driven side of
solenoid.(refertovehicleservicemanual
for solenoid location)
• If measuring DWELL on any arbitrary
ON/OFF device, connect RED test lead
to side of device that is being switched
ON/OFF.
4. Connect BLACK test lead to a good
vehicle ground.
Fig. 13
Fig. 14
To measure Duty Cycle (see Fig. 14):
1. Insert BLACK test lead into COM test
lead jack.
2. Insert RED test lead into test
lead jack.
3. Connect RED test lead to ON/OFF
switching side of device.
4. Connect BLACK test lead to a good
vehicle ground.
5. Turn multimeter rotary switch to DUTY
CYCLE position.
6. View reading on display.
Ground
Black
Red
Typical
Ignition
Coil
Black
Ground
Red
On/Off
Switching
Side
Power
Side
Solenoid

250V MAX
15A MAX
FUSED
COM
DC
15A
20M
200
K
20K
2K 200 8CYL6CYL TACH
X10
5CYL
4CYL
8CYL
OHMS
15
A
250V MAX
15A MAX
FUSED
DC
15A
20M
200
K
20K
2K 200 8CYL6CYL TACH
X10
5CYL
4CYL
8CYL
OHMS
15
A
COM
13
Section 2. AutomotiveTesting
The digital multimeter is a very useful tool for
trouble-shooting automotive electrical sys-
tems. This section describes how to use the
digitalmultimetertotestthestartingandcharg-
ing system, ignition system, fuel system, and
engine sensors. The digital multimeter can
also be used for general testing of fuses,
switches, solenoids, and relays.
General Testing
The digital multimeter can be used to test
fuses, switches, solenoids, and relays.
Testing Fuses
This test checks to see if a fuse is blown. You
can use this test to check the internal 15A
fuse inside the digital multimeter.
• If you hear tone - Fuse is good.
• If you don’t hear tone - Fuse is blown
and needs to be replaced.
NOTE: Always replace blown fuses with
same type and rating.
Testing Switches
Thistestcheckstoseeifaswitch“Opens”and
“Closes” properly.
Fig. 16
Red Black
Typical "Push"
Button Switch
To test Switches (see Fig. 16):
1. Insert BLACK test lead into COM test
lead jack.
2. Insert RED test lead into test
lead jack.
3. Turn multimeter rotary switch to
200 function.
4. Touch RED and BLACK test leads to-
gether to test continuity.
Listen for tone to verify proper operation.
5. Connect BLACK test lead to one side of
switch.
6. Connect RED test lead to other side of
switch.
Listen for tone:
• If you hear tone - The switch is closed.
• If you don’t hear tone - The switch is
open.
7. Operate switch.
Listen for tone:
To test Fuses (see Fig. 15):
1. Insert BLACK test lead into COM test
lead jack.
2. Insert RED test lead into test
lead jack.
3. Turn multimeter rotary switch to
200 function.
4. Touch RED and BLACK test leads to-
gether to test continuity.
Listen for tone to verify proper operation.
5. Connect RED and BLACK test leads to
opposite ends of fuse.
Listen for tone:
Fig. 15
Red Black
Fuse

250V MAX
15A MAX
FUSED
DC
15A
20M
200
K
20K
2K 200 8CYL6CYL TACH
X10
5CYL
4CYL
8CYL
OHMS
15
A
COM
•If you hear tone - The switch is closed.
• If you don’t hear tone - The switch is
open.
8. RepeatStep7toverifyswitchoperation.
Good Switch:
Tone turns ON and OFF as
you operate switch.
Bad Switch:
Tone always ON or tone al-
ways OFF as you operate switch.
14
4. Touch RED and BLACK test leads to-
gether and listen for tone.
5. ConnectBLACKtestleadtoonesideof
coil.
6. Connect RED test lead to other side of
coil.
7. View reading on display.
• Typical solenoid / relay coil resistances
are 200Ωor less.
• Refer to vehicle service manual for your
vehicles resistance range.
8. Test Results
Good Solenoid / Relay Coil:
Display in
Step 7 is within manufacturers specifica-
tion.
Bad Solenoid / Relay Coil:
• Display in Step 7 is not within manufac-
turers specifications.
• Displayreads overrangeon everyohms
range indicating an open circuit.
NOTE: Some relays and solenoids have
adiodeplacedacrossthecoil.Totestthis
diode see Testing Diodes on page 10.
To test Solenoids and Relays (see Fig. 17):
1. Insert BLACK test lead into COM test
lead jack.
2. Insert RED test lead into test
lead jack.
3. Turn multimeter rotary switch to
200 range.
Most solenoids and relay coil resistances
are less than 200Ω. If meter overranges,
turnmultimeterrotaryswitchtonexthigher
range. (see Setting the Range on page 6)
Testing Solenoids and Relays
This test checks to see if a solenoid or relay
have a broken coil. If the coil tests good, it is
still possible that the relay or solenoid are
defective. The relay can have contacts that
are welded or worn down, and the solenoid
maystickwhenthecoilisenergized.This test
does not check for those potential problems.
Fig. 17 Relay or
Solenoid
Red Black

250V MAX
15A MAX
FUSED
COM
DC
15A
AUTO POWER OFF
CP7678
®
OFF
200
20
2
DC V
200
m
20M
200
K
20K
2K 200 8CYL6CYL
TACH
X10
5CYL
4CYL
8CYL
6CYL
5CYL
4CYL
DWELL
DUTY
CYCLE
%
OHMS
°
15
A
15
Starting/Charging SystemTesting
The starting system “turns over” the engine. It consists of the battery, starter motor, starter
solenoid and/or relay, and associated wiring and connections. The charging system keeps the
battery charged when the engine is running. This system consists of the alternator, voltage
regulator, battery, and associated wiring and connections. The digital multimeter is a useful tool
for checking the operation of these systems.
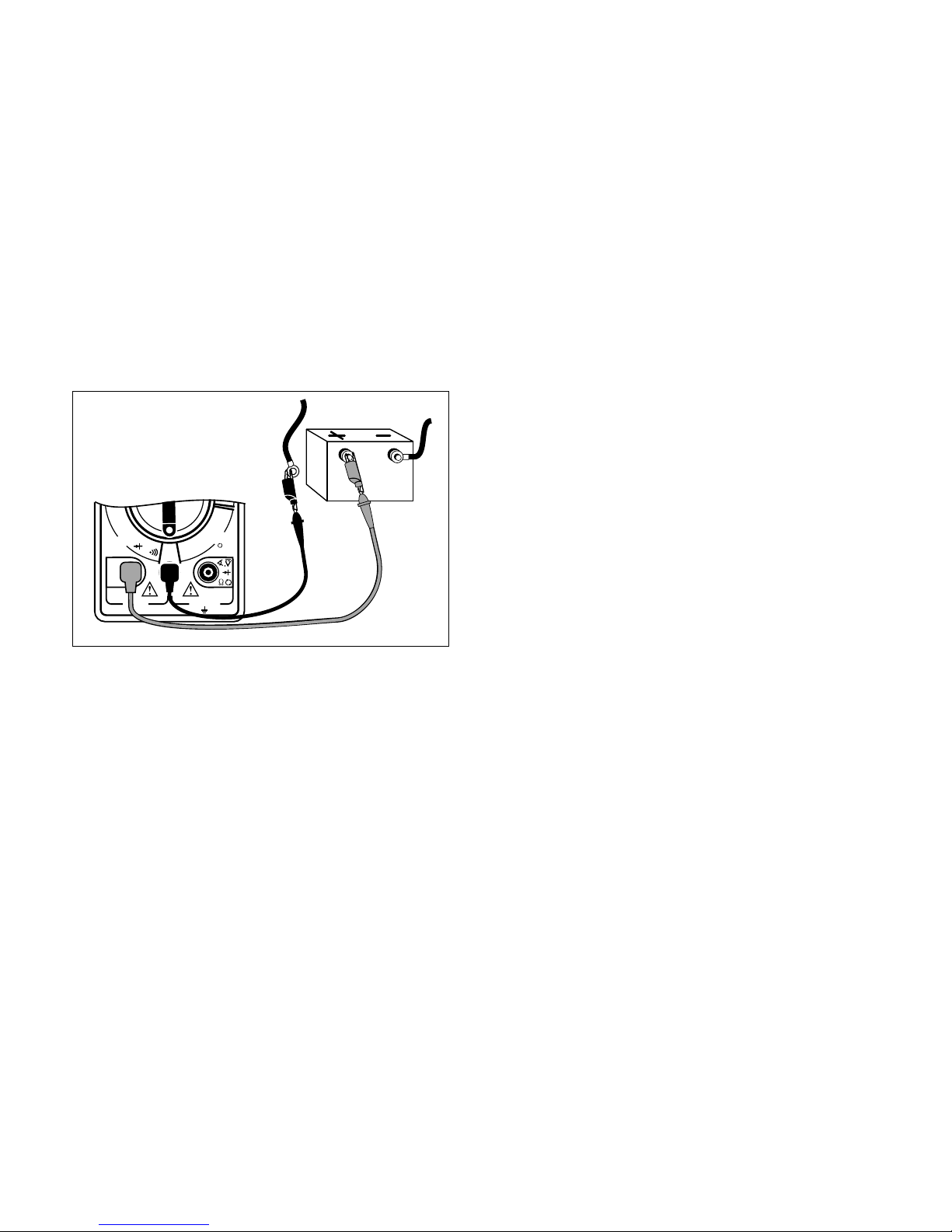
No Load Battery Test
Before you do any starting/charging system
checks,youmustfirsttestthebatterytomake
sure it is fully charged.
Fig. 18
BlackRed
Test Procedure (see Fig. 18):
1. Turn Ignition Key OFF.
2. Turn ON headlights for 10 seconds to
dissipate battery surface charge.
3. Insert BLACK test lead into COM test
lead jack.
4. Insert RED test lead into test
lead jack.
5. Disconnect positive (+) battery cable.
6. Connect RED test lead to positive (+)
terminal of battery.
7. Connect BLACK test lead to negative (-)
terminal of battery.
8. Turn multimeter rotary switch to 20V
DC range.
9. View reading on display.
10.Test Results.
Compare display reading in Step 9 with
chart below.
Voltage Percent Battery is Charged
12.60V
or greater 100%
12.45V 75%
12.30V 50%
12.15V 25%
If battery is not 100% charged, then charge it
before doing anymore starting/charging sys-
tem tests.
250V MAX
15A MAX
FUSED
COM
DC
15A
200
K
20K
2K 200 8CYL6CYL TACH
X10
5CYL
4CYL
OHMS
15
A
Engine Off Battery Current Draw
16
Fig. 19
Black Red
2. Insert BLACK test lead into COM test
lead jack.
3. InsertREDtestleadinto"15A"testlead
jack.
4. Disconnect positive (+) battery cable.
5. Connect RED test lead to positive (+)
battery terminal.
This test measures the amount of current
being drawn from the battery when the igni-
tion key and engine are both off. This test
helps to identify possible sources of exces-
sive battery current drain, which could even-
tually lead to a “dead” battery.
1. Turn Ignition Key and all accessories
OFF.
Make sure trunk, hood, and dome lights
are all OFF.
(See Fig. 19)
6. ConnectBLACKtestleadtopositive(+)
battery cable.
NOTE: Do not start vehicle during this test,
because multimeter damage may result.
7. Turn multimeter rotary switch to 15A
DC position.
8. View reading on display.
• Typical current draw is 100mA. (1mA =
0.001A)
• Refertovehicleservicemanualformanu-
facturersspecificEngineOffBatteryCur-
rent Draw.
NOTE: Radio station presets and clocks
are accounted for in the 100mA typical
current draw.
9. Test Results.
Normal Current Draw:
Display reading in
Step 8 is within manufacturers specifica-
tions.
Excessive Current Draw:
- Display reading in Step 8 is well outside
manufacturers specifications.
- Remove Fuses from fuse box one at a
time until source of excessive current
draw is located.
- Non-Fused circuits such as headlights,
relays, and solenoids should also be
checked as possible current drains on
battery.
- When source of excessive current drain
is found, service as necessary.

250V MAX
15A MAX
FUSED
COM
DC
15A
AUTO POWER OFF
CP7678
®
OFF
200
20
2
DC V
200
m
20M
200
K
20K
2K 200 8CYL6CYL TACH
X10
5CYL
4CYL
8CYL
6CYL
5CYL
4CYL
DWELL
DUTY
CYCLE
%
OHMS
°
15
A
17
Cranking Voltage - Battery Load Test
This test checks the battery to see if it is
deliveringenoughvoltagetothestartermotor
under cranking conditions.
5. Connect BLACK test lead to negative (-)
terminal of battery.
6. Turn multimeter rotary switch to 20V
DC range.
7. Crank engine for 15 seconds continu-
ously while observing display.
8. Test Results.
Compare display reading in Step 7 with
chart below.
Fig. 20
Red Black
Test Procedure (see Fig. 20):
1. Disableignitionsystemsovehiclewon’t
start.
Disconnect the primary of the ignition coil
or the distributor pick-up coil or the cam/
crank sensor to disable the ignition sys-
tem. Refer to vehicle service manual for
disabling procedure.
2. Insert BLACK test lead into COM test
lead jack.
3. Insert RED test lead into test
lead jack.
4. Connect RED test lead to positive (+)
terminal of battery.
Voltage Temperature
9.6V or greater 70 °F and Above
9.5V 60 °F
9.4V 50 °F
9.3V 40 °F
9.1V 30 °F
8.9V 20 °F
8.7V 10 °F
8.5V 0 °F
If voltage on display corresponds to above
voltage vs. temperature chart, then cranking
system is normal.
If voltage on display does not correspond to
chart, then it is possible that the battery,
batterycables,startingsystemcables,starter
solenoid, or starter motor are defective.
1
10
2
4
5
6 8
7
7
9
8
96
2
4
5
3
3
18
Voltage Drops 5. Turnmultimeterrotaryswitchto200mV
DC range.
If multimeter overranges, turn multimeter
rotary switch to the 2V DC range. (See
Setting the Range on page 6)
6. Crank engine until steady reading is on
display.
• Recordresultsateachpointasdisplayed
on multimeter.
• Repeat Step 4 & 5 until all points are
checked.
7. Test Results –
Estimated Voltage Drop of Starter Cir-
cuit Components
Component Voltage
Switches 300mV
Wire or Cable 200mV
Ground 100mV
Battery Cable Connectors 50mV
Connections 0.0V
• Comparevoltagereadingsin Step 6with
above chart.
• If any voltages read high, inspect com-
ponent and connection for defects.
• Ifdefectsarefound,serviceasnecessary.
This test measures the voltage drop across
wires, switches, cables, solenoids, and con-
nections. With this test you can find excessive
resistance in the starter system. This resis-
tancerestrictstheamountofcurrentthatreaches
the starter motor resulting in low battery load
voltage and a slow cranking engine at starting.
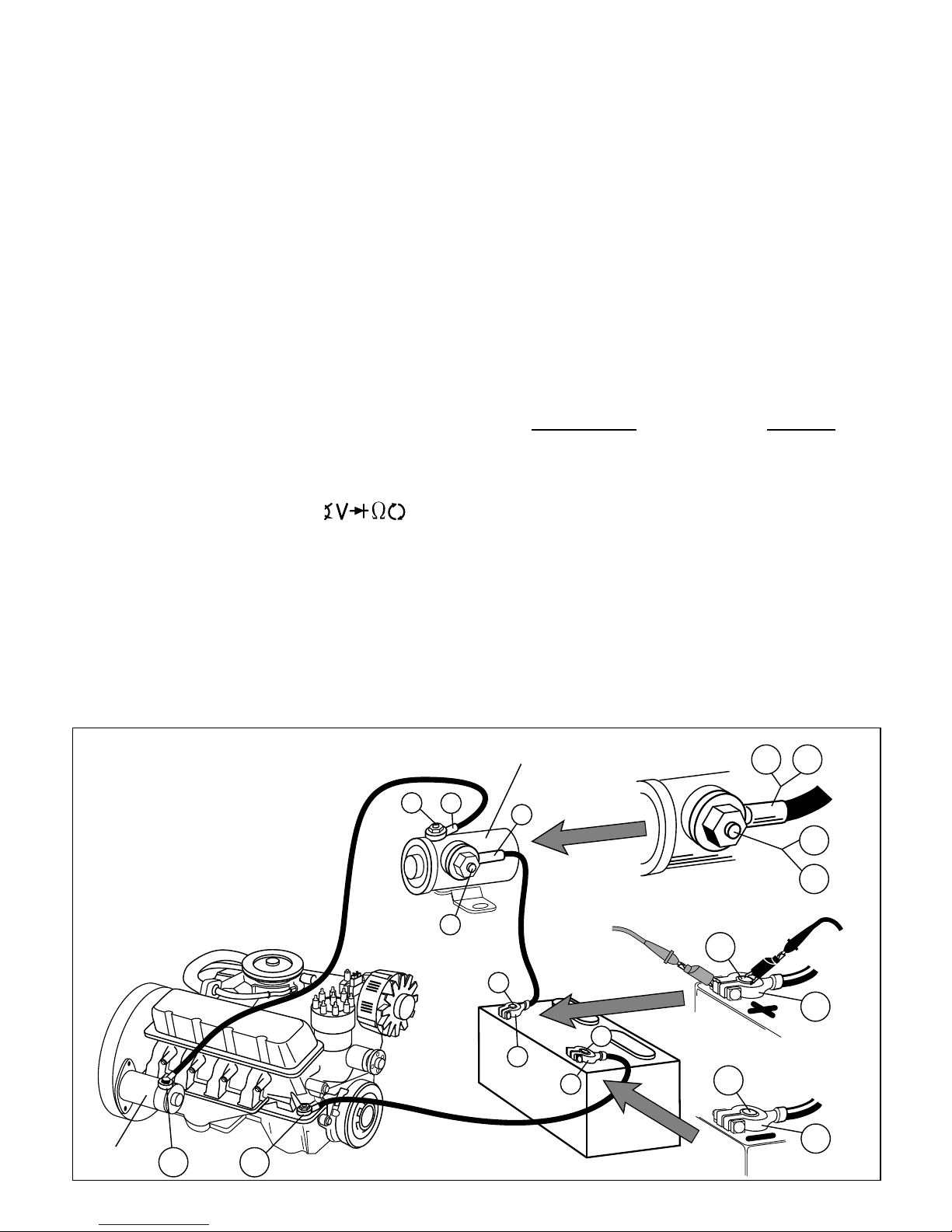
Test Procedure (see Fig. 21):
1. Disableignitionsystemsovehiclewon’t
start.
Disconnect the primary of the ignition coil
or the distributor pick-up coil or the cam/
crank sensor to disable the ignition sys-
tem. Refer to vehicle service manual for
disabling procedure.
2. Insert BLACK test lead into COM test
lead jack.
3. Insert RED test lead into test
lead jack.
4. Connect test leads.
Refer to Typical Cranking Voltage Loss
Circuit (Fig. 21).
• Connect RED and BLACK test leads al-
ternately between 1 & 2, 2 & 3, 4 & 5, 5
& 6, 6 & 7, 7 & 8, 8 & 9, and 8 & 10.
Red Black
Fig. 21 Typical Cranking Voltage
Loss Circuit Solenoid
This is a representative sample of one
type of cranking circuit. Your vehicle
may use a different circuit with
different components or locations.
Consult your vehicle service manual.
Starter

250V MAX
15A MAX
FUSED
COM
DC
15A
AUTO POWER OFF
CP7678
®
OFF
200
20
2
DC V
200
m
20M
200
K
20K
2K 200 8CYL6CYL TACH
X10
5CYL
4CYL
8CYL
6CYL
5CYL
4CYL
DWELL
DUTY
CYCLE
%
OHMS
°
15
A
19
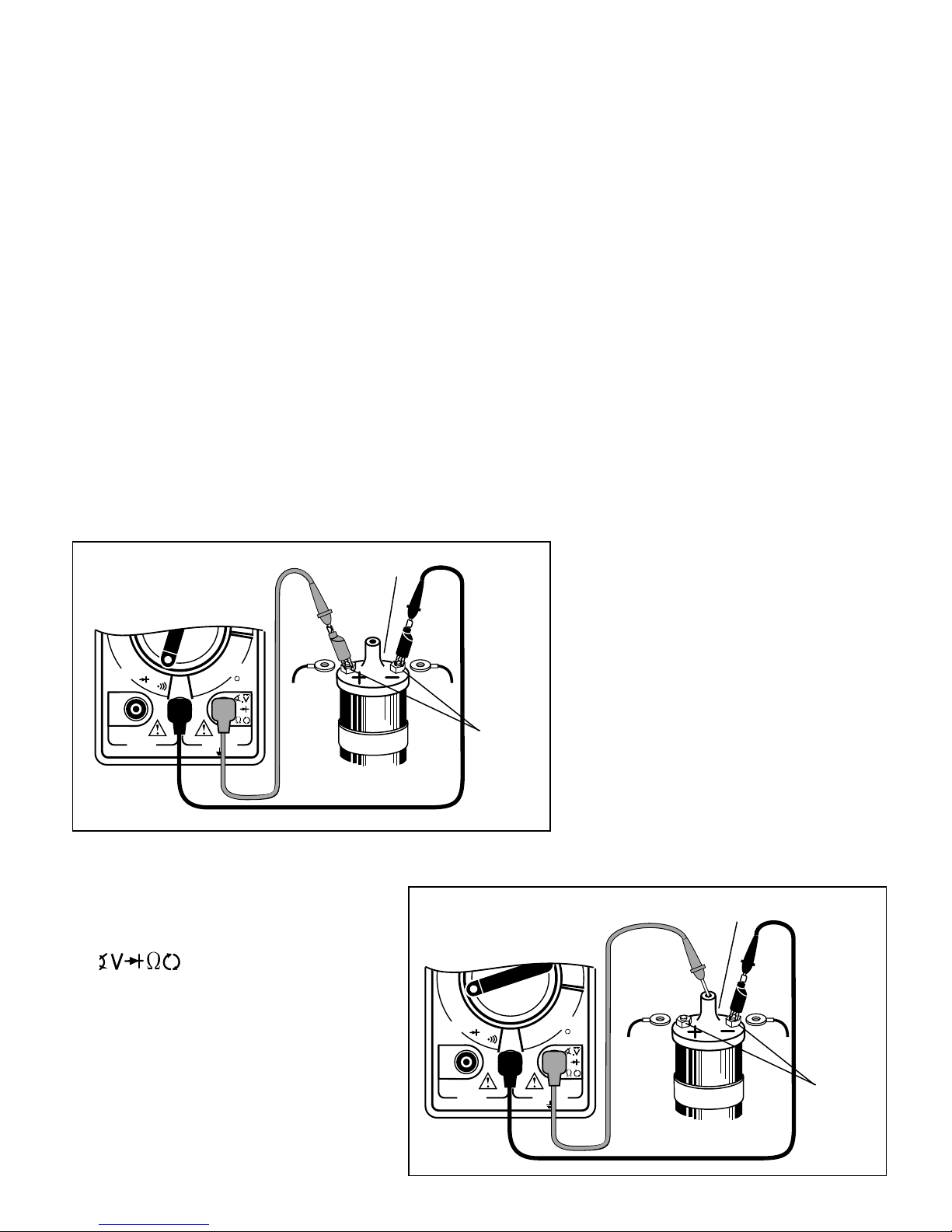
Charging System Voltage Test
Thistest checksthe charging system to see if
it charges the battery and provides power to
the rest of the vehicles electrical systems
(lights, fan, radio etc).
Fig. 22
Red Black
Test Procedure (see Fig. 22):
1. Insert BLACK test lead into COM test
lead jack.
2. Insert RED test lead into test
lead jack.
3. Connect RED test lead to positive (+)
terminal of battery.
4. Connect BLACK test lead to negative (-)
terminal of battery.
5. Turn multimeter rotary switch to 20V
DC range.
6. Start engine - Let idle.
7. Turn off all accessories and view read-
ing on display.
• Chargingsystemisnormalifdisplayreads
13.2 to 15.2 volts.
• If display voltage is not between 13.2 to
15.2 volts, then proceed to Step 13.
8. Open throttle and Hold engine speed
(RPM) between 1800 and 2800 RPM.
Holdthis speed through Step 11 - Have an
assistance help hold speed.
9. View reading on display.
Voltage reading should not change from
Step 7 by more than 0.5V.
10.Load the electrical system by turning
on the lights, windshield wipers, and
setting the blower fan on high.
11.View reading on display.
Voltageshouldnotdropdownbelowabout
13.0V.
12.Shut off all accessories, return engine
to curb idle and shut off.
13.Test Results.
• If voltage readings in Steps 7, 9, and 11
were as expected, then charging system
is normal.
• Ifany voltage readings in Steps 7, 9, and
11 were different then shown here or in
vehicle service manual, then check for a
loose alternator belt, defective regulator
or alternator, poor connections, or open
alternator field current.
• Refer to vehicle service manual for fur-
ther diagnosis.
250V MAX
15A MAX
FUSED
COM
DC
15A
20M
200
K
20K
2K 200 8CYL6CYL
TACH
X10
5CYL
4CYL
8CYL
OHMS
15
A
250V MAX
15A MAX
FUSED
COM
DC
15A
20M
200
K
20K
2K 200 8CYL6CYL TACH
X10
5CYL
4CYL
8CYL
OHMS
15
A
20
Ignition SystemTesting
The ignition system is responsible for providing the spark that ignites the fuel in the cylinder.
Ignition system components that the digital multimeter can test are the primary and secondary
ignitioncoilresistance,sparkplugwireresistance,halleffectswitches/sensors, reluctancepick-
up coil sensors, and the switching action of the primary ignition coil.
Ignition Coil Testing
This test measures the resistance of the pri-
mary and secondary of an ignition coil. This
test can be used for distributorless ignition
systems (DIS) provided the primary and sec-
ondary ignition coil terminals are easily ac-
cessible.
Test Procedure:
1. If engine is HOT let it COOL down be-
fore proceeding.
2. Disconnect ignition coil from ignition
system.
6. Connect test leads.
• Connect RED test lead to primary igni-
tion coil positive (+) terminal.
• Connect BLACK test lead to primary ig-
nition coil negative (-) terminal.
• Refer to vehicle service manual for loca-
tion of primary ignition coil terminals.
7. View reading on display.
SubtracttestleadresistancefoundinStep
5 from above reading.
Fig. 23
Typical Cylindrical
Ignition Coil
BlackRed
Primary
Coil
Secondary
Coil
Fig. 24
Typical Cylindrical
Ignition Coil
Black
Secondary
Coil
Primary
Coil
Red
3. Insert BLACK test lead into
COM test lead jack (see Fig.
23).
4. Insert RED test lead into
test lead jack.
5. Turn multimeter rotary switch
to 200Ωrange.
8. If vehicle is DIS, repeat Steps 6
and 7 for remaining ignition
coils.
9. Test Results - Primary Coil
• Typical resistance range of pri-
mary ignition coils is 0.3 - 2.0Ω.
• Refer to vehicle service manual
for your vehicles resistance
range.
Other manuals for SunPro CP7678
1
Table of contents
Other Actron Multimeter manuals

Actron
Actron Digital Multimeter CP7676 User manual

Actron
Actron CP7847 User manual

Actron
Actron Digital Multimeter CP7676 User manual

Actron
Actron CP7849 User manual

Actron
Actron CP7677 User manual

Actron
Actron SunPro CP7678 User manual

Actron
Actron Digital Multitester CP7674 User manual

Actron
Actron Sunpro CP7605 User manual

Actron
Actron CP7849 User manual

















