AGA155 Product Manual Rev.1.3 Page 3
Contents
1Product Description _____________________________________________________ 4
1.1 General Description ______________________________________________________________ 4
1.2 Part Numbering _________________________________________________________________ 4
1.3 System Design___________________________________________________________________ 5
1.4 Technical Specifications ___________________________________________________________ 5
1.5 Environmental Specifications_______________________________________________________ 8
2Safety ________________________________________________________________ 9
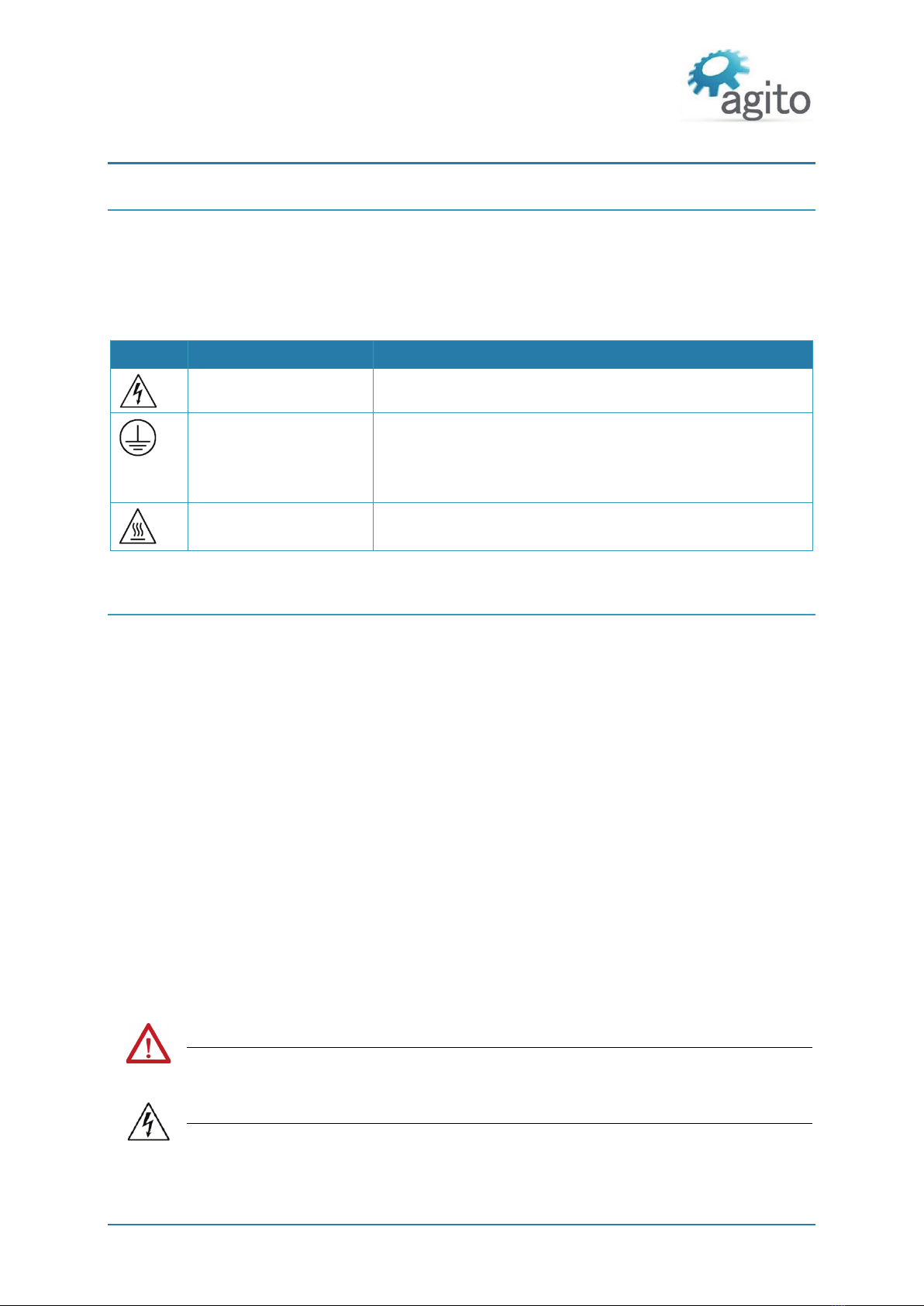
2.1 Safety Symbols __________________________________________________________________ 9
2.2 Safety Guidelines ________________________________________________________________ 9
2.3 Compliance ____________________________________________________________________ 10
3Installation ___________________________________________________________ 11
3.1 Unpacking and Packing___________________________________________________________ 11
3.2 Mounting _____________________________________________________________________ 11
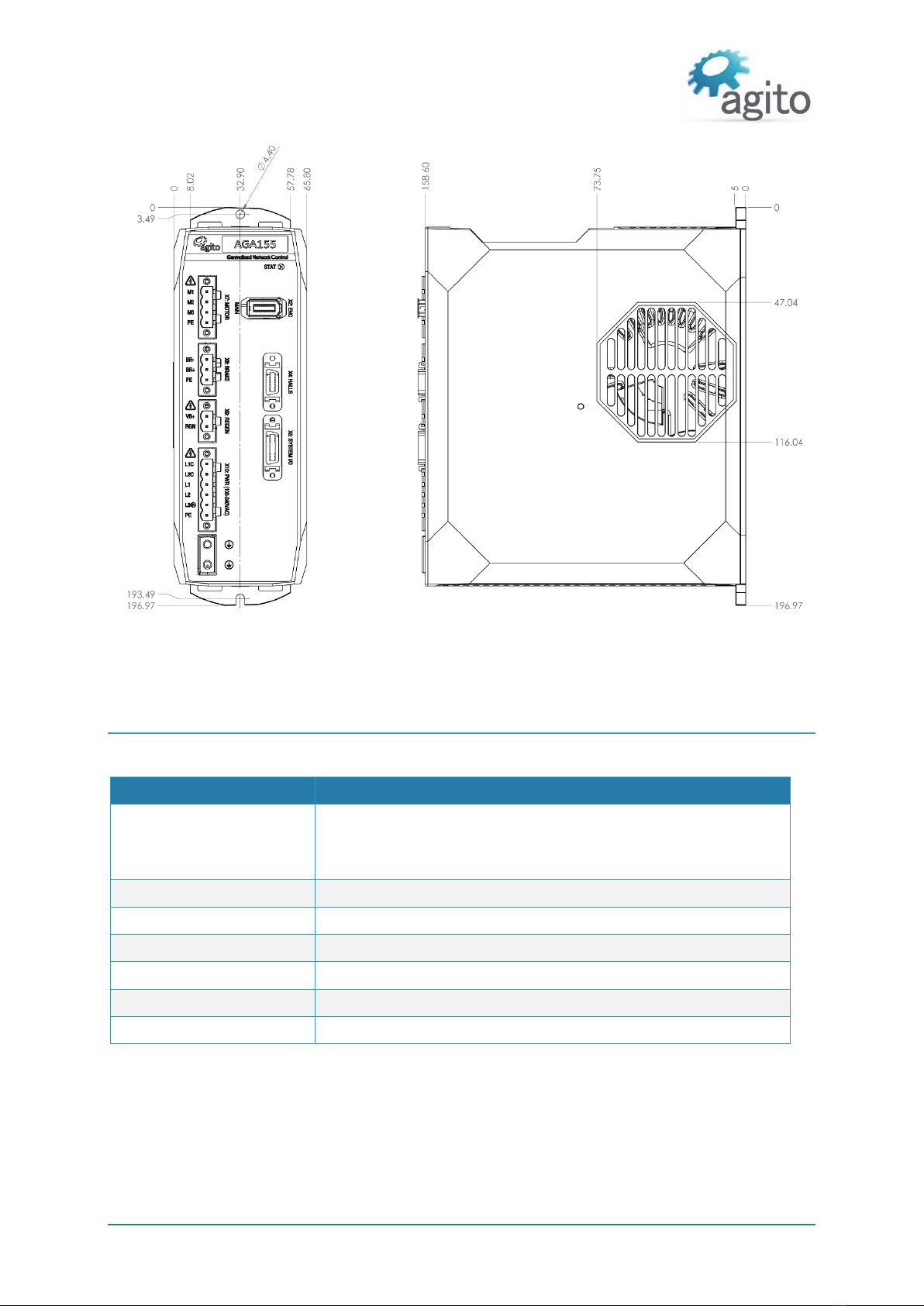
3.2.1 Mounting the AGA155 ____________________________________________________ 11
3.2.2 Mounting Multiple Power Amplifiers ________________________________________ 12
3.3 Electrical Installation ____________________________________________________________ 13
3.3.1 Power Wiring ___________________________________________________________ 13
3.3.2 Regeneration____________________________________________________________ 13
3.3.3 Circuit Breakers__________________________________________________________ 14
3.3.4 AC Line Filter ____________________________________________________________ 15
3.3.5 Safe Operating Area (SOA) _________________________________________________ 15
3.3.6 Grounding ______________________________________________________________ 16
Ground Domains_________________________________________________________ 17
Grounding Policy_________________________________________________________ 17
3.3.7 PT100/PT1000 Temperature Sensors ________________________________________ 17
3.4 Electrical Interfaces _____________________________________________________________ 18
3.4.1 Interface X14: I/O and Brake Power _________________________________________ 18
3.4.2 Interface X15: Safety _____________________________________________________ 19
3.4.3 Interface X7: Motor ______________________________________________________ 21
For Brushless Motor ______________________________________________________ 21
For Brushed (or Voice Coil) Motor ___________________________________________ 21
3.4.4 Interface X8: Static Brake __________________________________________________ 22
3.4.5 Interface X9: Regeneration_________________________________________________ 23
3.4.6 Interface X10: Power _____________________________________________________ 24
3.4.7 Interface X13: Central-i____________________________________________________ 25
3.4.8 Interface X2: Main Encoder ________________________________________________ 26
3.4.9 Interface X4: Halls ________________________________________________________ 27
3.4.10 Interface X5: System I/Os __________________________________________________ 29
I/Os Circuit Diagrams _____________________________________________________ 30
4Operation____________________________________________________________ 33
4.1 Motor Configuration_____________________________________________________________ 33
4.2 Drive/Motor Overload Protection __________________________________________________ 35
4.2.1 I2T Over Load protection __________________________________________________ 35
4.2.2 Motor Stuck ____________________________________________________________ 37
4.2.3 Motor Temperature Protection _____________________________________________ 37
4.3 Tuning ________________________________________________________________________ 38
4.3.1 Commissioning __________________________________________________________ 38
4.3.2 Current Loop Tuning______________________________________________________ 39
4.3.3 Auto Velocity and Position Loop Tuning ______________________________________ 40
4.3.4 Manual Velocity and Position Loop Tuning ____________________________________ 43
5Maintenance and Servicing ______________________________________________ 45