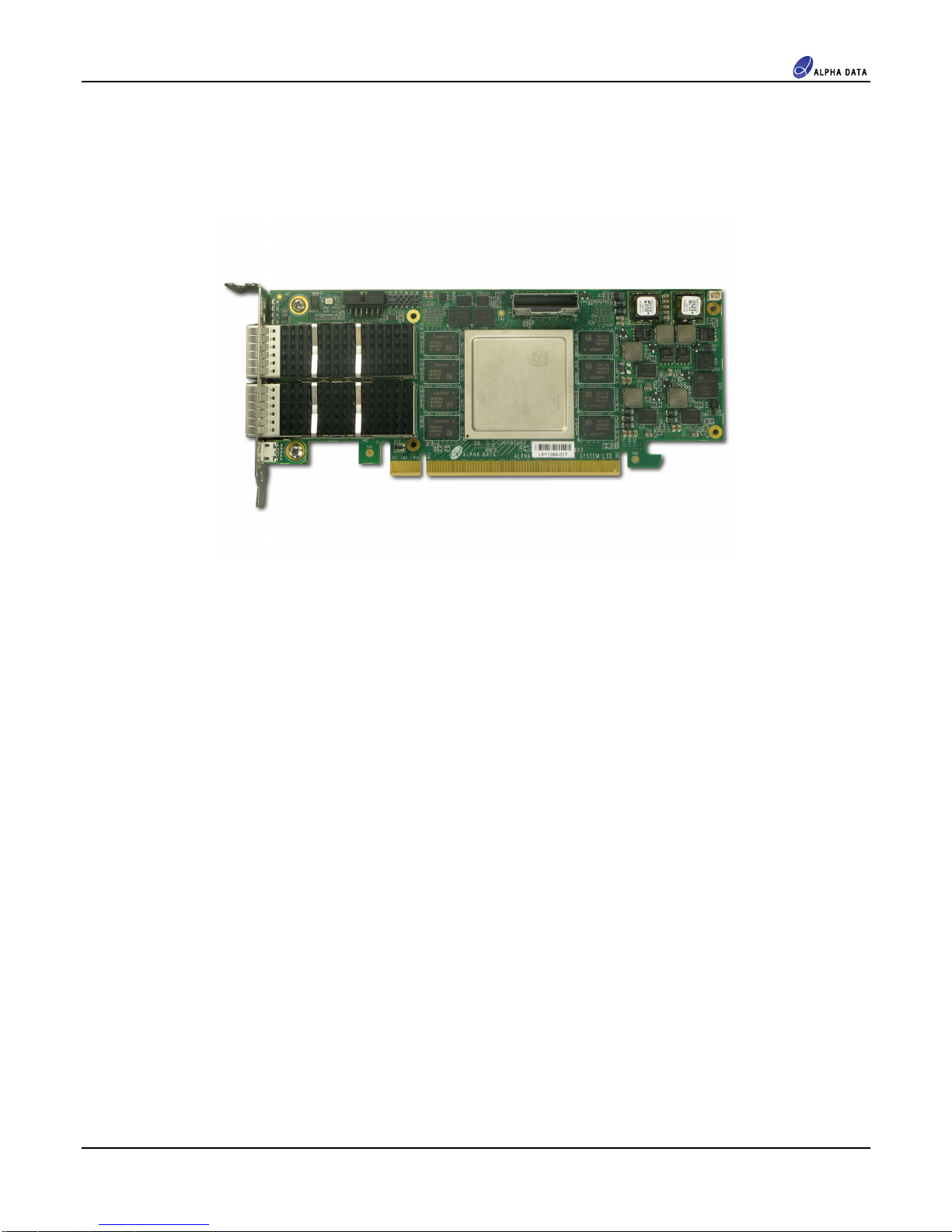
ADM-PCIE-9V3 User Manual
Table Of Contents
Introduction ......................................................................................................................................
1.1 Key Features ................................................................................................................................. 1
1.2 Order Code .................................................................................................................................... 1
2 PCB Information .............................................................................................................................. 2
2.1 Physical Specifications .................................................................................................................. 2
2.2 Chassis Requirements ................................................................................................................... 2
2.2.1 PCI E press ............................................................................................................................... 2
2.2.2 Mechanical Requirements ......................................................................................................... 2
2.2.3 Power Requirements ................................................................................................................. 2
2.3 Thermal Performance .................................................................................................................... 3
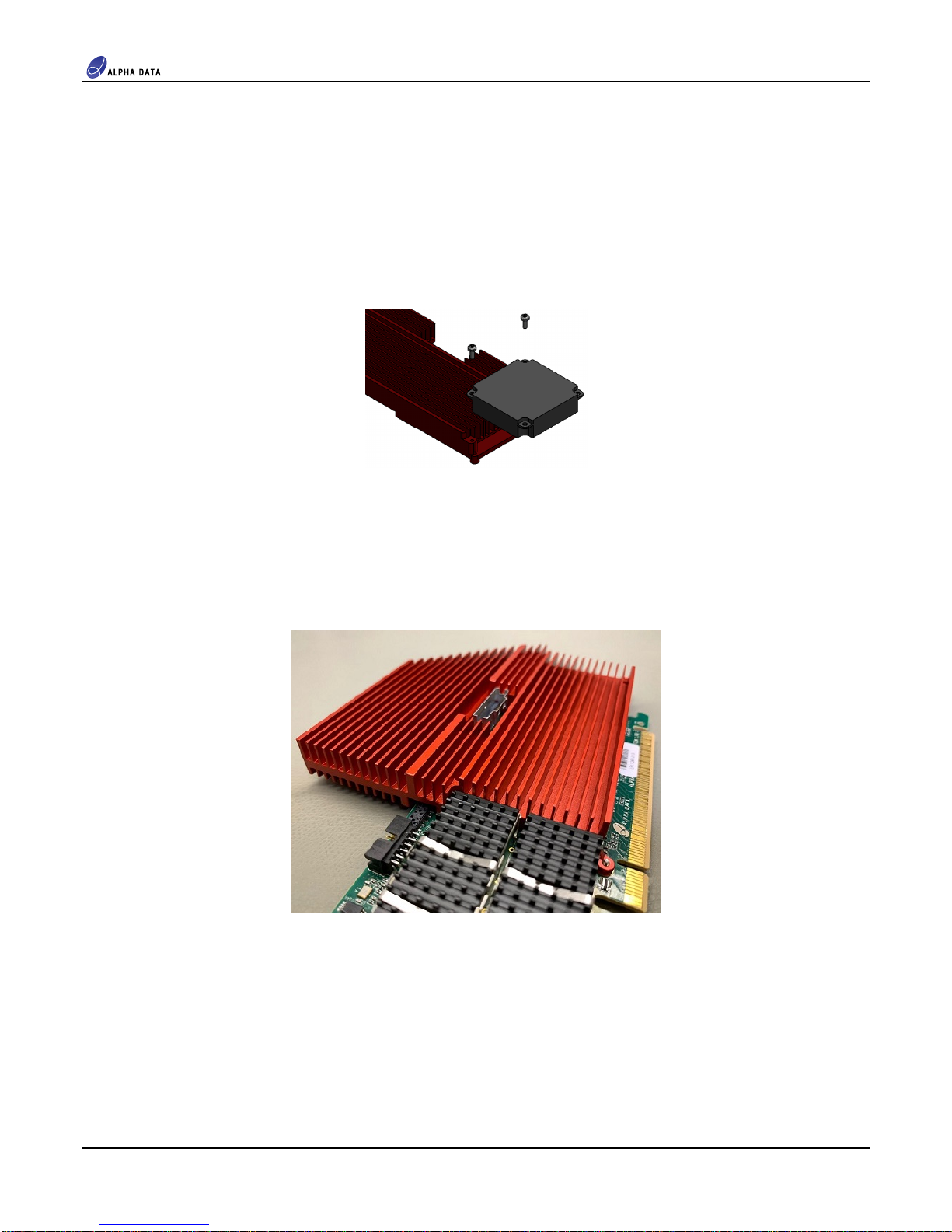
2.4 Optional Blower ............................................................................................................................. 4
2.5 Full Height Heat Sink ..................................................................................................................... 4
3 Functional Description .................................................................................................................... 5
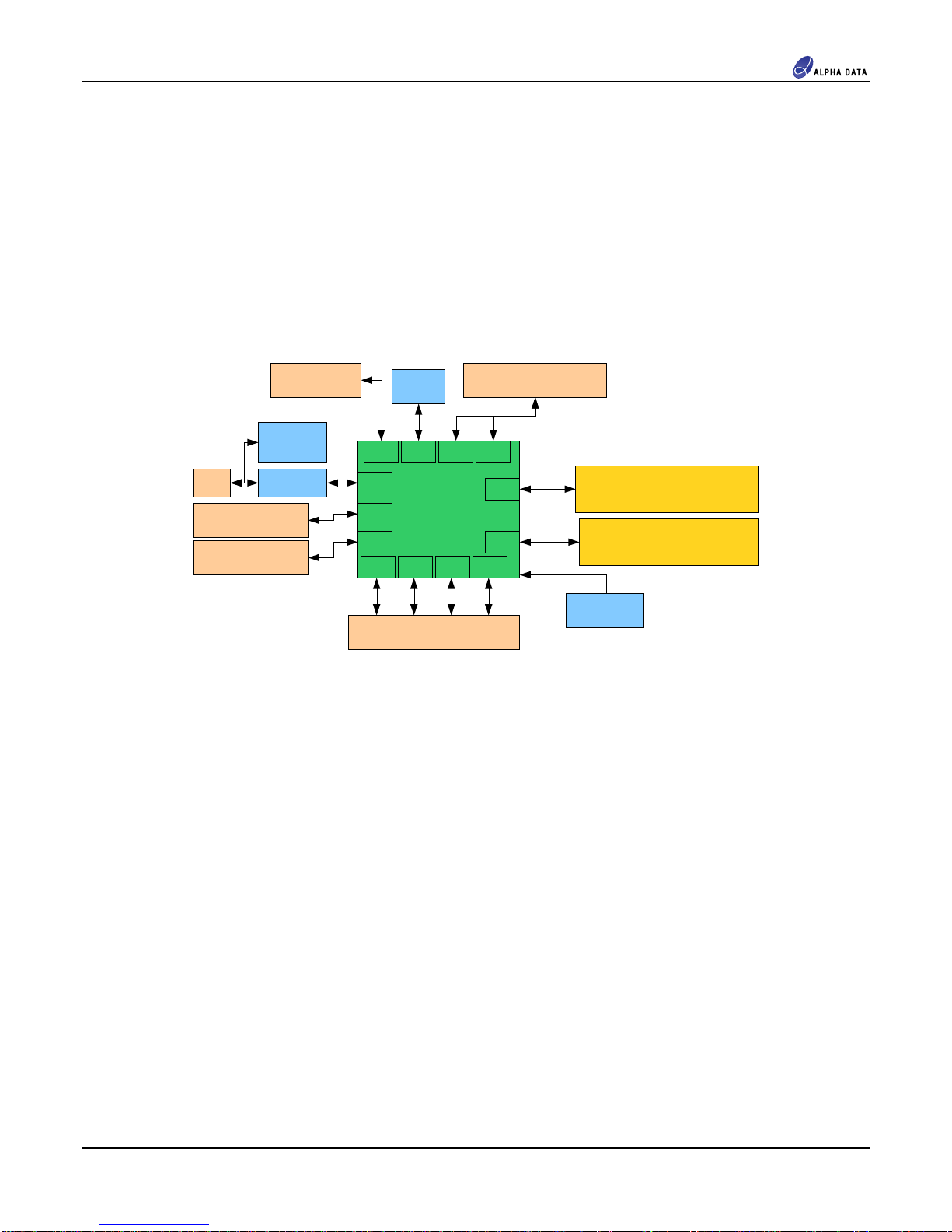
3.1 Overview ........................................................................................................................................ 5
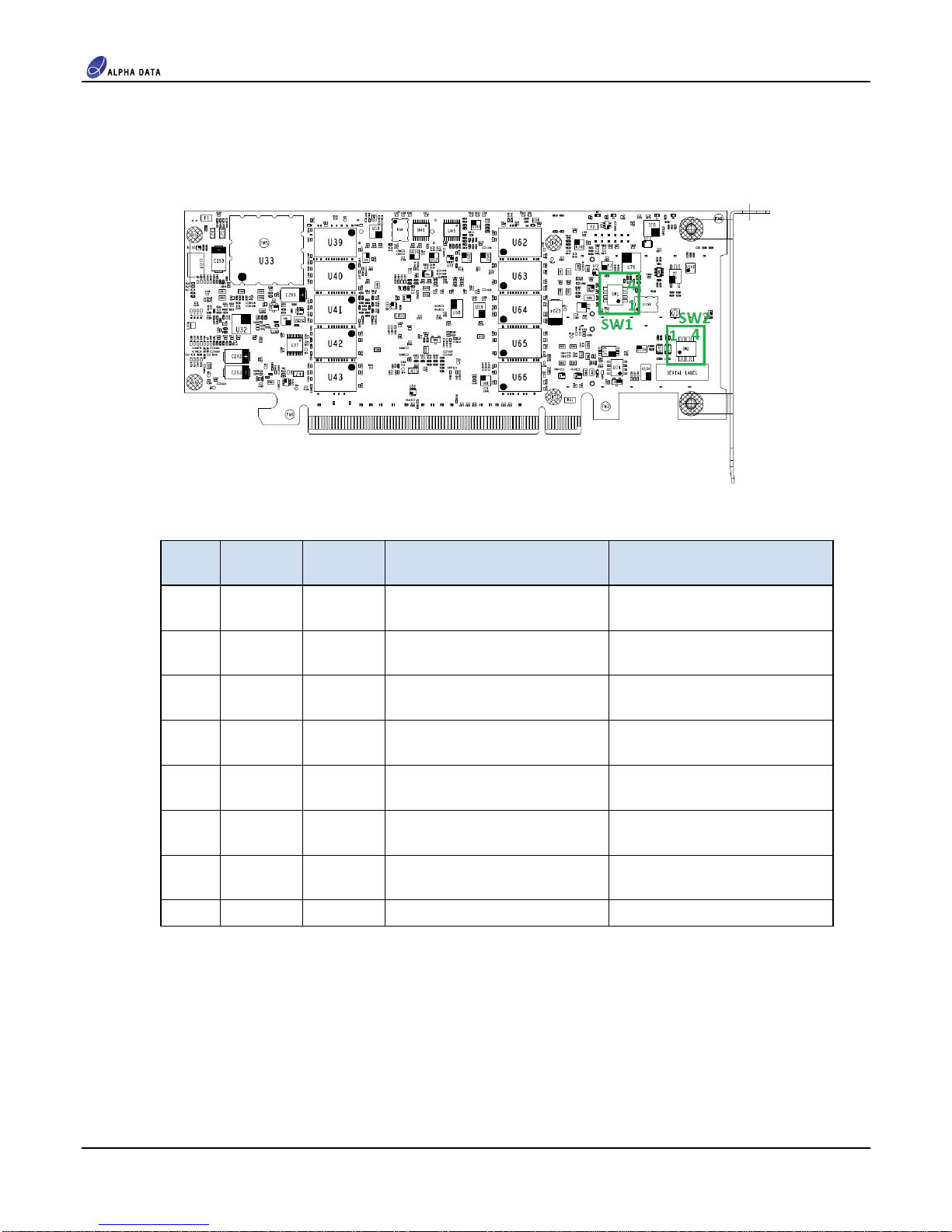
3.1.1 Switches .................................................................................................................................... 6
3.1.2 LEDs .......................................................................................................................................... 7
3.2 Clocking ......................................................................................................................................... 8
3.2.1 PCIe Reference Clocks ............................................................................................................. 8
3.2.2 Fabric Clock ............................................................................................................................... 8
3.2.3 Programming Clock (EMCCLK) ................................................................................................. 9
3.2.4 QSFP28 ..................................................................................................................................... 9
3.2.5 Ultraport SlimSAS .................................................................................................................... 10
3.2.6 DDR4 SDRAM Reference Clocks ............................................................................................ 10
3.3 PCI E press ................................................................................................................................. 11
3.4 DDR4 SDRAM ............................................................................................................................. 11
3.5 QSFP28 ....................................................................................................................................... 12
3.6 OpenCAPI Ultraport SlimSAS ...................................................................................................... 13
3.7 System Monitor ............................................................................................................................ 14
3.7.1 System Monitor Status LEDs ................................................................................................... 15
3.8 USB Interface .............................................................................................................................. 16
3.9 Configuration ............................................................................................................................... 16
3.9.1 Configuration From Flash Memory .......................................................................................... 16
3.9.1.1 Building and Programming Configuration Images ............................................................... 17
3.9.2 Configuration via JTAG ............................................................................................................ 17
3.10 GPIO Connector .......................................................................................................................... 18
3.10.1 Direct Connect FPGA Signals .................................................................................................. 18
3.10.2 Timing Input ............................................................................................................................. 18
3.11 User EEPROM ............................................................................................................................. 19
Appendix A Complete Pinout Table .................................................................................................................. 2
List of Tables
Table 1 Mechanical imensions ..................................................................................................................... 2
Table 2 Available Power By Rail ..................................................................................................................... 2
Table 3 Switch Functions ................................................................................................................................ 6
Table 4 LE etails ........................................................................................................................................ 7
Table 5 PCIe Reference Clocks ..................................................................................................................... 8
Table 6 Fabric Clock ....................................................................................................................................... 9
Table 7 EMCCLK ............................................................................................................................................ 9