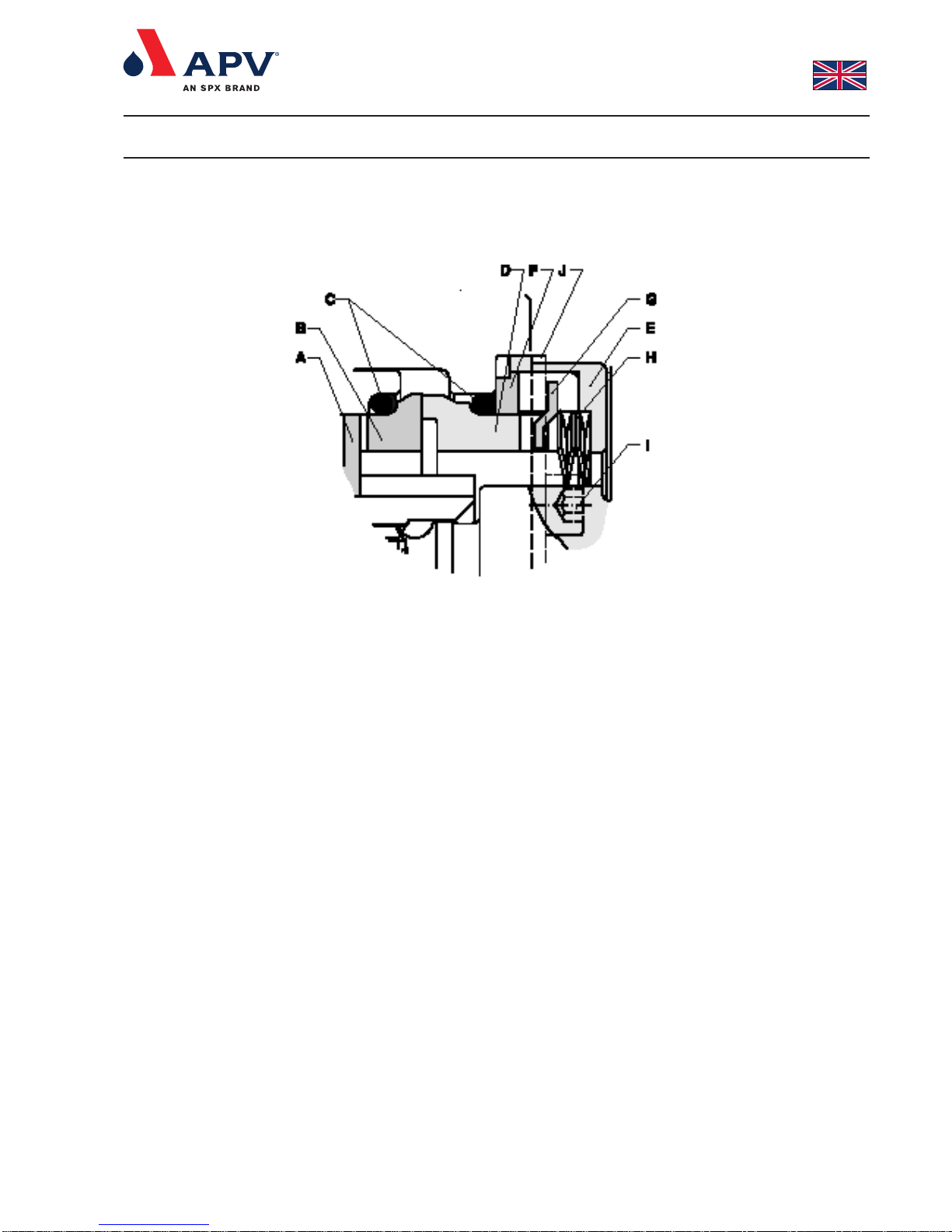
7
453272 ISS U 09.2004
1. Read the instructions before installing and starting the pump. Always follow
the guidelines for assembly in order to secure optimum operational reliability.
If in doubt, contact your local APV dealer.
Electrical Installation
2. Always check that the specifications of the motor and the motor control unit
are correct, particularly in operating environments where there may be a risk
of explosion.
3. Always ensure that all electrical installation is carried out by qualified staff.
4. Never hose down the electric motor directly with water or cleaning fluids.
5. Never dismantle the pump before the power supply to the motor has been
disconnected. The fuses should be removed and the cable disconnected
from the motor.
6. Pumps should only be installed, disassembled, repaired and assembled by
personnel trained in servicing of APV pumps, or by APV fitters.
For further information, please contact your local APV dealer.
Personal Injury
7. Never start the pump before the coupling guard between pump and motor
has been securely fitted.
8. There are rotating parts in the pump. Never put hands or fingers into a pump
while it is in operation..
9. Never touch the gearbox of the pump as it can become very hot.
10. Never touch the rotor case during operation. If the pump is being used for
hot fluids the rotor case may become very hot.
11. Always ensure that all pipe connections have been fitted and tightened
properly before the pump is started. If the pump is used for hot and/or
hazardous liquids, special care must be taken. In such cases, follow the local
regulations for personal safety when working with these products.
12. Never dismantle the pump until the isolating valves on the suction and
discharge side have been closed and the immediate pipe system has been
drained. If the pump is used for hot and/or hazardous fluids, special
precautions must be taken. In such cases follow the local regulations for
personal safety when working with these products.
Pump damage
13. Always remove assembly tools from the pump before starting it up.
14. Always ensure that no debris of any kind is present in the pump.
15. Always ensure that the pump is filled with liquid before it is started.
16. Always ensure that the pump and the motor shafts are properly aligned .
17. Always ensure that the suction and discharge valves isolating the pump are
fully open before starting the pump.
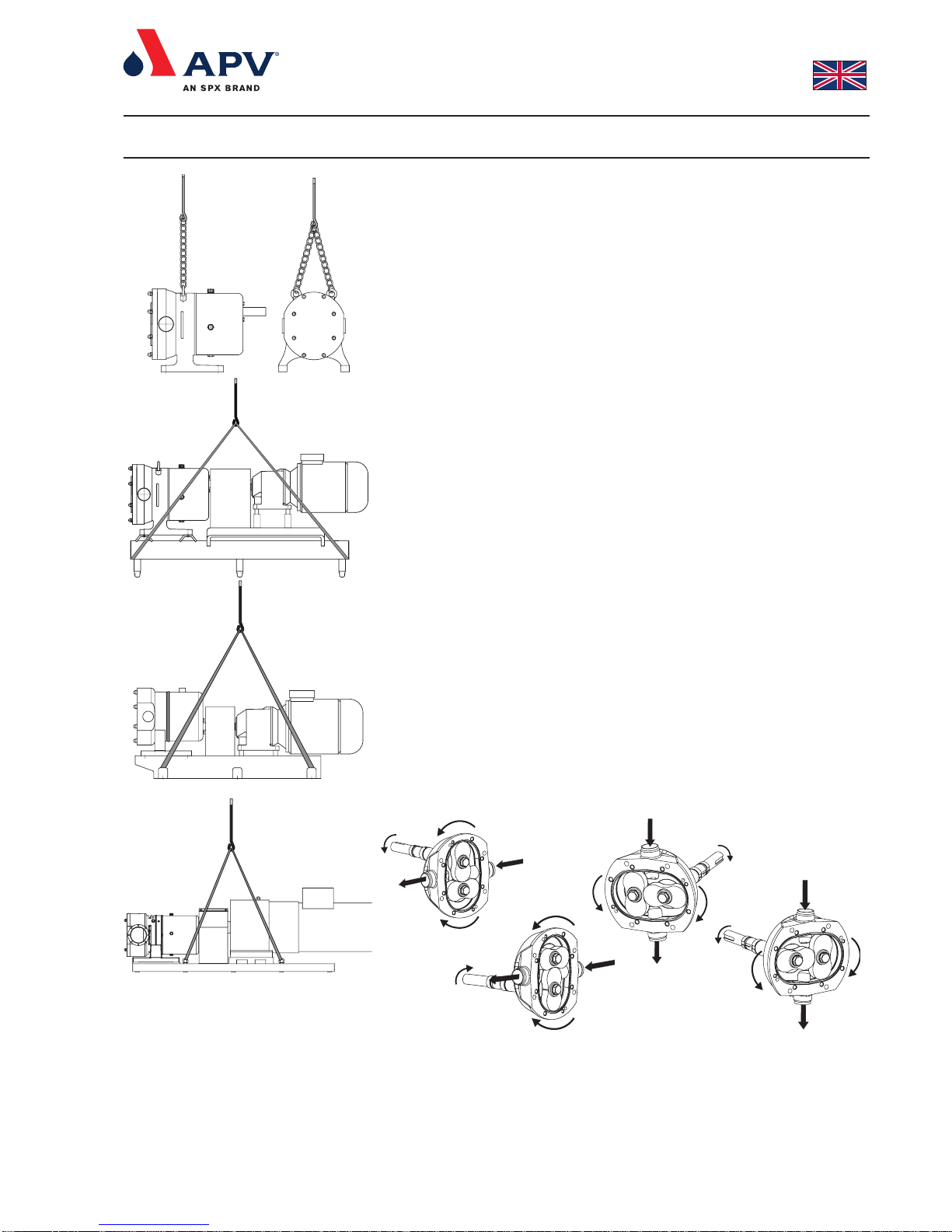
18. Always use securely fitted lifting straps when lifting the pump with a hoist or
similar lifting gear. Check whether there are any special lifting instructions.
19. Always ensure that the gearbox case is filled with an APV recommended
gear oil to the appropriate level.
20. Never close or obstruct the outlet of the pump as the pressure in the system
will increase above the specified maximum pressure of the pump and cause
damage to the pump.
21. Never drop parts - especially rotors and front covers - on the floor.
22. Never exceed the maximum temperature specified on the pump nameplate.
23. Never exceed the maximum allowable pressure specified below:
Max. 33 bar: DW6 and DW7
Max. 28 bar: DW5
Max. 23 bar: DW2; DW3 and DW4
Max. 18 bar: DW1
These pressures apply for water at 20°C.
The differential pressure must not exceed the pressure stated on the nameplate.
0. Warnings