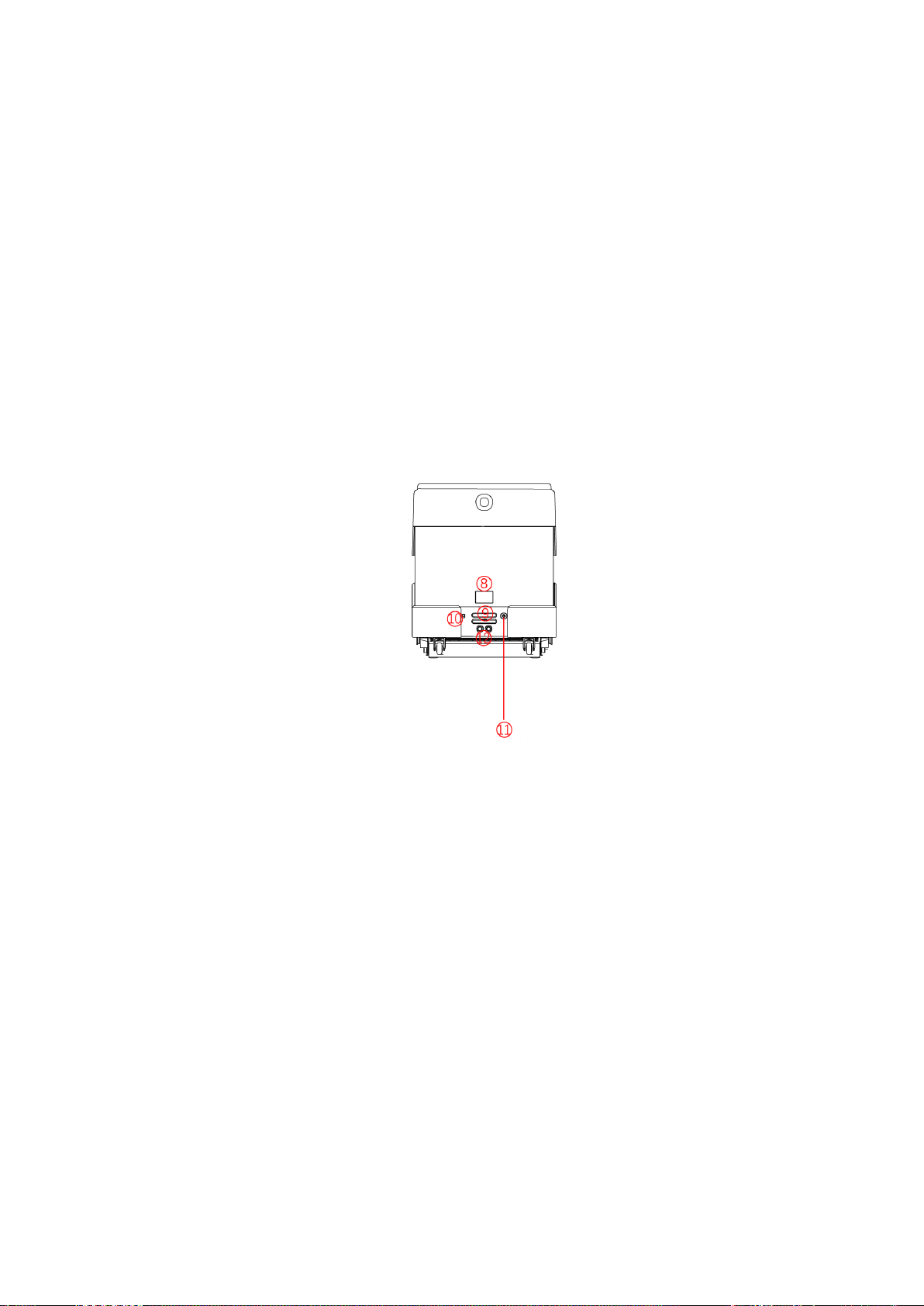
Introduction to Robots
Use environment requirements
Please use this product in accordance with the instructions of the manual.
Any loss caused by improper use shall be borne by the user.
Do not use in places with stairs or drops
There should not be a lot of black marble and black reflective cabinets at
the height of 27 cm
Do not travel on the ground with high friction: thicker and softer carpets
Do not use in a large amount of stagnant water and similar environments
There should be no densely placed thin-legged chairs in the travel area
Do not use in an environment above 50°C and below 0°C
Do not use on uneven and sloped roads
There are a lot of transparent glass and thin-legged tables and chairs,
which can be used depending on the construction of the map and the test
situation