Blade Network Technologies BLADEOS BMD00098 How to use

2350 Mission College Blvd.
Suite 600
Santa Clara, CA 95054
www.bladenetwork.net
BLADEOS™
Release Notes
1/10Gb Uplink Ethernet Switch Module for IBM BladeCenter®
Version 5.1
Part Number: BMD00098, December 2009

BLADE OS 5.1 Release Notes
2BMD00098, December 2009
Copyright © 2009 BLADE Network Technologies, Inc., 2350 Mission College Blvd. Suite 600, Santa
Clara, California, 95054, USA. All rights reserved. Reference number: BMD00098
This document is protected by copyright and distributed under licenses restricting its use, copying,
distribution, and decompilation. No part of this document may be reproduced in any form by any
means without prior written authorization of BLADE Network Technologies, Inc. Documentation is
provided “as is” without warranty of any kind, either express or implied, including any kind of
implied or express warrantyof non-infringement or the implied warranties of merchantability or
fitness for a particular purpose.
U.S. GovernmentEndUsers: Thisdocumentis provided with a“commercial item” asdefinedbyFAR
2.101 (Oct. 1995) and contains “commercial technical data” and “commercial software
documentation” as those terms are used in FAR 12.211-12.212 (Oct. 1995). Government End Users
are authorized to usethis documentation only in accordancewith those rights andrestrictionsset forth
herein, consistent with FAR 12.211- 12.212 (Oct. 1995), DFARS 227.7202 (JUN 1995) and DFARS
252.227-7015 (Nov. 1995).
BLADE Network Technologies, Inc. reserves the right to change any products described herein at any
time, and without notice. BLADE Network Technologies, Inc. assumes no responsibility or liability
arising from the use of products described herein, except as expressly agreed to in writing by BLADE
Network Technologies, Inc. The use and purchase of this product does not convey a license under any
patent rights, trademark rights, or any other intellectual property rights of BLADE Network
Technologies, Inc.
BLADE OS and BLADE are trademarks of BLADE Network Technologies, Inc. in the United States
and certain other countries. Any other trademarks appearing in this manual are owned by their
respective companies.
Originatedin theUSA.

BMD00098, December 2009 3
Release Notes
The 1/10Gb Uplink Ethernet Switch Module (GbESM) is one of up to four GbESMs that can be
installed in the IBM BladeCenter chassis.
These release notes provide the latest information regarding BLADEOS 5.1 for the 1/10Gb Uplink
Ethernet Switch Module. This supplement modifies information found in the complete
documentation:
BLADEOS 5.1 Application Guide for the 1/10Gb Uplink Ethernet Switch Module for IBM
BladeCenter
BLADEOS 5.1 Command Reference for the 1/10Gb Uplink Ethernet Switch Module for IBM
BladeCenter
BLADEOS 5.1 ISCLI Reference for the 1/10Gb Uplink Ethernet Switch Module for IBM
BladeCenter
BLADEOS 5.1 BBI Quick Guide for the 1/10Gb Uplink Ethernet Switch Module for IBM
BladeCenter
1/10Gb Uplink Ethernet Switch Module for IBM BladeCenter, Installation Guide
The publications listed above are available from the IBM support website:
http://www.ibm.com/systems/support
Please keep these release notes with your product manuals.

BLADE OS 5.1 Release Notes
4BMD00098, December 2009
Hardware Support
BLADEOS 5.1 software is supported only on the 1/10Gb Uplink Ethernet Switch Module
(Figure 1) for IBM BladeCenter. The GbESM is a high performance Layer 2-3 embedded network
switch that features tight integration with IBM BladeCenter management modules.
Figure 1 1/10Gb Uplink ESM Faceplate
The GbESM has the following port capacities:
Three external 10Gb SFP+ slots
Six external 1Gb Ethernet ports (RJ45)
One RS-232 serial console port
Two 100Mb internal management ports
Fourteen 1000Mb Ethernet internal ports
RS-232
console port
1
2
3
47
69
RJ45 ports
1Gb Ethernet
SFP+ slots
10Gb Ethernet

BLADE OS 5.1 Release Notes
BMD00098, December 2009 5
The GbESM contains three 10 Gigabit Small Form-factor, Pluggable (SFP+) slots. The 10Gb SFP+
slots can accept 1Gb copper transceivers, 10Gb optical transceivers, or Direct Attach Cables
(DAC).
Note – If a DAC is not programmed to meet MSA specifications (including length identifier), the
switch disables the port and generates a syslog message indicating that the DAC is not approved.
The GbESM does not disable the SFP+ ports when using MSA-compliant DAC cables. For best
results, the following cables have been qualified to work with the switch:
Table 1 Recommended SFP+ transceiver
Part number Description
BN-SP-CBL-1M SFP+ Copper Direct Attach Cable - 1 meter
BN-SP-CBL-3M SFP+ Copper Direct Attach Cable - 3 meters
BN-SP-CBL-7M SFP+ Copper Direct Attach Cable - 7 meters
BN-SP-CBL-10M SFP+ Copper Direct Attach Cable - 10 meters

BLADE OS 5.1 Release Notes
6BMD00098, December 2009
Updating the Switch Software Image
The switch software image is the executable code running on the GbESM. A version of the image
ships with the switch, and comes pre-installed on the device. As new versions of the image are
released, you can upgrade the software running on your switch. To get the latest version of software
available for your GbESM, go to:
http://www.ibm.com/systems/support
From the BLADEOS CLI, use the /boot/cur command to determine the current software version.
The typical upgrade process for the software image consists of the following steps:
Place the new image onto a FTP or TFTP server on your network, or on a local computer.
Transfer the new image to your switch.
Select the new software image to be loaded into switch memory the next time the switch is reset.
Loading New Software to Your Switch
The switch can store up to two different software images, called image1 and image2, as well as
boot software, called boot. When you load new software, you must specify where it should be
placed: either into image1, image2, or boot.
For example, if your active image is currently loaded into image1, you would probably load the
new image software into image2. This lets you test the new software and reload the original active
image (stored in image1), if needed.
To download a new software image to your switch, you will need the following:
The image and boot software loaded on a FTP or TFTP server on your network
Boot file: GbESM-1-10U-5.1.1.0_Boot.img
Image file: GbESM-1-10U-5.1.1.0_OS.img
Note – Be sure to download both the new boot file and the new image file.
The hostname or IP address of the FTP or TFTP server
The name of the new software image or boot file
Note – The DNS parameters must be configured if specifying hostnames.
When the above requirements are met, use one of the following procedures to download the new
software to your switch. You can use the BLADEOS CLI, the ISCLI, or the BBI to download and
activate new software.

BLADE OS 5.1 Release Notes
BMD00098, December 2009 7
Using the BLADEOS CLI
1. At the Boot Options# prompt, enter:
2. Enter the name of the switch software to be replaced:
3. Enter the hostname or IP address of the FTP or TFTP server.
4. Enter the name of the new software file on the server.
The exact form of the name will vary by server. However, the file location is normally relative to the
FTP or TFTP directory (usually /tftpboot).
5. Enter your username for the server, if applicable.
6. The system prompts you to confirm your request.
Once confirmed, the software will load into the switch.
7. When loading is complete, enter the following command at the Boot Options# prompt:
8. The system informs you of which software image (image1 or image2) is currently set to be
loaded at the next reset, and prompts you to enter a new choice:
Specify the image that contains the newly loaded software.
Boot Options# gtimg
Enter name of switch software image to be replaced
["image1"/"image2"/"boot"]: <image>
Enter hostname or IP address of FTP/TFTP server: <hostname or IP address>
Enter name of file on FTP/TFTP server: <filename>
Enter username for FTP server or hit return for
TFTP server: {<username>|<Enter>}
Boot Options# image
Currently set to use switch software "image1" on next reset.
Specify new image to use on next reset ["image1"/"image2"]:

BLADE OS 5.1 Release Notes
8BMD00098, December 2009
Using the ISCLI
1. In Privileged EXEC mode, enter the following command:
2. Enter the hostname or IP address of the FTP or TFTP server.
3. Enter the name of the new software file on the server.
The exact form of the name will vary by server. However, the file location is normally relative to the
FTP or TFTP directory (usually tftpboot).
4. Enter your username and password for the server, if applicable.
5. The system prompts you to confirm your request.
Once confirmed, the software will load into the switch.
6. When loading is complete, use the following command in Global Configuration mode to select
which software image (image1 or image2) you want to run in switch memory for the next
reboot:
The system will then verify which image is set to be loaded at the next reset:
Router# copy {tftp|ftp}{image1|image2|boot-image}
Address or name of remote host: <name or IP address>
Source file name: <filename>
User name: {<username>|<Enter>}
Router(config)# boot image {image1|image2}
Next boot will use switch software image1 instead of image2.

BLADE OS 5.1 Release Notes
BMD00098, December 2009 9
Using the BBI
You can use the Browser-Based Interface to load software onto the GbESM. The software image to
load can reside in one of the following locations:
FTP server
TFTP server
Local computer
After you log onto the BBI, perform the following steps to load a software image:
1. Click the Configure context tab in the toolbar.
2. In the Navigation Window, select System > Config/Image Control.
The Switch Image and Configuration Management page appears.
3. If you are loading software from your computer (HTTP client), skip this step and go to the next.
Otherwise, if you are loading software from a FTP/TFTP server, enter the server’s information in
the FTP/TFTP Settings section.
4. In the Image Settings section, select the image version you want to replace (Image for Transfer).
If you are loading software from a FTP/TFTP server, enter the file name and click Get Image.
If you are loading software from your computer, click Browse.
In the File Upload Dialog, select the file and click OK. Then click Download via Browser.
Once the image has loaded, the page refreshes to show the new software.

BLADE OS 5.1 Release Notes
10 BMD00098, December 2009
New and Updated Features
BLADEOS 5.1 for 1/10Gb Uplink Ethernet Switch Module (GbESM) has been updated to include
new and enhanced features in support of server and peer switch discovery, as well as failure
detection at the link layer. In addition, there are enhancements to existing implementations in the
areas of dynamic routing protocols, configuration and reporting.
The list of features below summarizes the updated features. For more detailed information about
configuring GbESM features and capabilities, refer to the complete BLADEOS 5.1 documentation
as listed on page 3.
Remote Monitoring
BLADEOS 5.1 now supports Remote Monitoring (RMON).
RMON allows network devices to exchange network monitoring data, gather cumulative and
history statistics for Ethernet interfaces, and create and trigger alarms for user-defined events.
An RMON management application can be used to access RMON MIB information on the GbESM,
as described in RFC 1757. The switch supports RMON Group 1 (Statistics), Group 2 (History),
Group 3 (Alarms), and Group 9 (Events).
RMON properties are configured globally in the RMON menu, and enabled on a per-port basis in
the Port menu:
Link Layer Detection Protocol
BLADEOS 5.1 now supports 802.1AB Link Layer Detection Protocol (LLDP). Using LLDP, the
GbESM advertises port and link information to other LLDP-capable devices and accepts their
LLDP advertisements for the purpose of discovering pertinent information about remote ports.
Switch port information and any remote device information is stored in a Managed Information
Base (MIB). Higher-layer management tools may access the MIB to accumulate and report such
information, and even to and discover configuration inconsistencies between systems on the same
IEEE 802 LAN.
The LLDP configuration menu is accessed using the following CLI command:
#/cfg/rmon (global RMON menu)
-and-
#/cfg/port <x>/rmon (per-port RMON menu)
#/cfg/l2/lldp

BLADE OS 5.1 Release Notes
BMD00098, December 2009 11
Uni-Directional Link Discovery Protocol
BLADEOS 5.1 now supports the Uni-Directional Link Discovery (UDLD) protocol, compliant
with RFC 5171. UDLD operates at Layer 2 in conjunction with existing IEEE 802.3 Layer 1 fault
detection mechanisms. It is used between peer devices to detect and disable unidirectional Ethernet
links caused, for instance, by mis-wired cable strands, interface malfunctions, or media converter
faults.
UDLD is configured on a per-port basis. It is disabled by default. The UDLD configuration menu is
available using the following CLI command:
Operation/Administration/Maintenance Protocol
BLADEOS 5.1 now supports IEEE 802.3ah Operation, Administration, and Maintenance (OAM)
protocol. OAM allows the switch to detect faults on physical port links. Using OAM, if the Local
Information that a port sends does not match the Remote Information received, the link is
determined to be in an anomalous condition and is automatically disabled.
OAM is configured on a per-port basis. It is disabled by default. The OAM configuration menu is
available using the following CLI command:
sFlow Monitoring
BLADEOS 5.1 now supports sFlow technology for monitoring traffic in data networks. The switch
software includes an embedded sFlow agent which can be configured on a per-port basis to sample
network traffic and provide continuous statistical report information to a central sFlow analyzer.
sFlow features are disabled by default, but may be configured using the following menu:
#/cfg/port <x>/udld
#/cfg/port <x>/oam
#/cfg/sys/sflow

BLADE OS 5.1 Release Notes
12 BMD00098, December 2009
Internal Loopback Interface
BLADEOS 5.1 now supports up to five loopback interfaces.
A loopback interface is an interface which is assigned an IP address, but is not associated with any
particular physical port. The loopback interface is thus always available for higher layer protocols
to use and advertise to the general network, regardless of which specific ports are in operation.
Loopback interfaces can be of benefit in a number of protocols, improving access to a switch, as
well as increasing its reliability, security, and scalability. In addition, loopback interfaces can add
flexibility and simplify management, information gathering, and filtering.
One example of this increased reliability is for OSPF to use a loopback interface in combination
with host routes to advertise an interface route which will be available regardless of the status of
individual physical links. This provides a higher probability that the routing traffic will be received
and subsequently forwarded.
Further reliability and performance could be provided by configuring parallel BGP paths to a
loopback interface on a peer device, which would result in improved load sharing.
Access and security can be improved through filtering. Incoming traffic can be filtered by rules that
specify loopback interfaces as the only acceptable destination addresses.
Information gathering and filtering as wellas management can potentially be simplified if protocols
such as SNMP use loopback interfaces for receiving and sending trap and log type information.
The Loopback Interface configuration menu is accessed using the following CLI command:
Rate Limiting
BLADEOS 5.1 now supports traffic rate limits for packets broadcast, multicast, and unknown
unicast packets. For each port, the maximum number of packets permitted per second for each
packet type can be specified. The following commands have been added to the Port menu
(/cfg/port <x>) to support rate limiting:
brate <value>|dis Broadcast limit, 0 to 262143 packets per second, or no limit.
mrate <value>|dis Multicast limit, 0 to 262143 packets per second, or no limit.
drate <value>|dis Unknown unicast limit, 0 to 262143 packets per second, or no limit.
#/cfg/l3/loopif <loopback interface number (1-5)>

BLADE OS 5.1 Release Notes
BMD00098, December 2009 13
Hot Links
BLADEOS 5.1 now supports Hot Links. Hot Links provides basic link redundancy with fast
recovery for network topologies that require Spanning Tree to be turned off.
Hot Links allows up to five triggers, each of which consists of a pair of layer 2 interfaces that may
contain either an individual port or trunk. One interface is the Master, and the other is a Backup.
While the Master interface is active and forwarding traffic, the Backup interface is placed in a
standby state and blocks traffic. If the Master interface fails, the Backup interface becomes active
and forwards traffic. Once the Master interface is restored, it transitions to the standby state and
blocks traffic unless the Backup interface fails.
OSPF Enhancements
BLADEOS 5.1 includes multiple enhancements to the GbESM Open Shortest Path First (OSPF)
implementation:
Passive Interfaces
OSPF interfaces may be configured as passive. Passive interfaces send LSAs to active
interfaces, but do not receive LSAs, hello packets, or any other OSPF protocol information
from active interfaces. Passive interfaces behave as stub networks, allowing OSPF routing
devices to be aware of devices that do otherwise participate in OSPF (either because they do
not support it, or because the administrator chooses to restrict OSPF traffic exchange or
transit). The following command has been added:
Point-to-Point Networks
For LANs that have only two OSPF routing agents (the GbESM and one other device),
specifying the interfaces as part of a point-to-point network allows the switch to significantly
reduce the amount of routing information it must carry and manage, enhancing OSPF
efficiency. The following command has been added:
Sub-second timers
To increase OSPF convergence speed, hello and dead timers for OSPF interfaces and virtual
interfaces can now specified in milliseconds by adding “ms” to the number. For example:
Loopback Interface Address
OSPF can now be configured to use the GbESM internal loopback address in advertising its
Router ID.
#/cfg/l3/ospf/if <x>/passive {enable|disable}
#/cfg/l3/ospf/if <x>/ptop {enable|disable}
#/cfg/l3/ospf/if <x>/hello 200ms (200 milliseconds)

BLADE OS 5.1 Release Notes
14 BMD00098, December 2009
LACP Trunk Enhancements
BLADEOS 5.1 now supports up to eight links in each LACP Link Aggregation Group (LAG).
Layer 2 Failover Enhancements
BLADEOS 5.1 includes multiple enhancements to the Layer 2 Failover feature to support advanced
NIC teaming:
In addition to the automatic monitoring triggers for trunk links, the switch software now
supports new manual monitoring triggers. This allows you to define a list of ports and/or static
or dynamic trunks to disable when a link failure thresdhold is reached on set of trigger ports
and/or static or dynamic trunks.
Up to twoLACP keys can be used for each failover trigger. Previously, only one per trigger was
supported.
ACL Precedence Enhancement
With BLADEOS 5.1, the implementation of Access Control Lists (ACLs) has been standardized to
use ascending order of precedence.
ACLs that are assigned to a port are now processed in numeric sequence, based on ACL number.
Lower-numbered ACLs take precedence over higher-numbered ACLs within each precedence
group. For example, ACL 1 (if assigned to the port) is evaluated first and has top priority within
precedence group 1.
When upgrading from an earlier version of BLADEOS, the ACLs are automatically renumbered to
maintain prior function within the new order of precedence.
Forwarding Database Enhancements
Configuration of the Forwarding Database (FDB) aging feature has been simplified. Because FDB
aging required the same value configured in all Spanning Tree Groups (STGs), the per-STG aging
parameters have been replaced with a single, global configuration command:
#/cfg/l2/stg <STG number>/brg/aging <value> (old per-STG command)
-replaced by-
#/cfg/l2/fdb/aging <value> (new global command)

BLADE OS 5.1 Release Notes
BMD00098, December 2009 15
ISL Layer 2 Protocol Enhancements
BLADEOS 5.1 now supports additional Layer 2 protocols on Inter-Switch Link (ISL) ports:
VRRP
STP
RSTP/MSTP
802.1Q VLAN Tagging
802.1p QoS/CoS
802.1X Port-Based Access Control
ACLs
STP Fast Uplink Bridge Priority
With BLADEOS 5.1, the Fast Uplink Convergence bridge priority has been set to 65535.
CLI List and Range Inputs
For CLI commands that allow an individual item to be selected from within a numeric range, lists
and ranges of items can now be specified. For example, the /info/vlan command permits the
following options:
The numbers in a range must be separated by a dash: <start of range>-<end of range>
Multiple ranges or list items are permitted using a comma: <range or item 1>,<range or item 2>
Do not use spaces within list and range specifications.
Ranges can also be used to apply the same command option to multiple items. For example, to
enable multiple ports with one command:
Note – Port ranges accept only port numbers, not aliases such as INT1 or EXT1
#/info/vlan (show all VLANs)
#/info/vlan 1 (show only VLAN 1)
#/info/vlan 1,3,4095 (show listed VLANs)
#/info/vlan 1-20 (show range 1 through 20)
#/info/vlan 1-5,90-99,4090-4095 (show multiple ranges)
#/info/vlan 1-5,19,20,4090-4095 (show a mix of lists and ranges)
#/cfg/port 1-4/ena (Enable ports 1 though 4)

BLADE OS 5.1 Release Notes
16 BMD00098, December 2009
Chassis Internal Network
BLADEOS 5.1 now supports BladeCenter Chassis Internal Network (CIN). CIN provides internal
connectivity between blade server ports and the internal Advanced Management Module (AMM)
port. This allows blade server users to access the AMM via CLI, web-browser, or SNMP session,
and allows the AMM to use services on the blades, such as LDAP, SMTP, DNS, and NTP.
BC-S Chassis Support
BLADEOS 5.1 supports the BladeCenter BC-S chassis. When the GbESM is installed in the BC-S
chassis, the following information displays reflect the BC-S port mapping:
Port link information (/info/link) for switches installed in bay 1 and bay 2:
Alias Port Speed Duplex Flow Ctrl Link
---- ----- ----- -------- --TX-----RX-- ------
INT1A 1 1000 full yes yes up
INT1B 2 1000 full yes yes up
INT2A 3 1000 full yes yes up
INT2B 4 1000 full yes yes up
INT3A 5 1000 full yes yes down
INT3B 6 1000 full yes yes up
INT4A 7 1000 full yes yes up
INT4B 8 1000 full yes yes up
INT5A 9 1000 full yes yes up
INT5B 10 1000 full yes yes up
INT6A 11 1000 full yes yes up
INT6B 12 1000 full yes yes up
SMGT1 13 1000 full yes yes up
SMGT2 14 1000 full yes yes up
MGT1 15 100 full yes yes up
EXT1 17 10000 any yes yes up
EXT2 18 10000 any yes yes up
EXT3 19 10000 any yes yes up
EXT4 20 1000 any yes yes up
EXT5 21 1000 any yes yes up
EXT6 22 1000 any yes yes up
EXT7 23 1000 any yes yes up
EXT8 24 1000 any yes yes up
EXT9 25 1000 any yes yes up

BLADE OS 5.1 Release Notes
BMD00098, December 2009 17
Port link information (/info/link) for switches installed in bay 3 and bay 4:
Port information (/info/port) for switches installed in bay 1 and bay 2:
Alias Port Speed Duplex Flow Ctrl Link
---- ----- ----- -------- --TX-----RX-- ------
INT1 1 1000 full yes yes up
INT2 2 1000 full yes yes up
INT3 3 1000 full yes yes down
INT4 4 1000 full yes yes up
INT5 5 1000 full yes yes up
INT6 6 1000 full yes yes up
MGT1 15 100 full yes yes up
EXT1 17 10000 any yes yes up
EXT2 18 10000 any yes yes up
...
Alias Port Tag Fast Lrn Fld PVID NAME VLAN(s)
----- ---- --- ---- --- --- ---- -------------- --------------------
INT1A1yn ee 1INT1A 1 4095
INT1B2yn ee 1INT1B 1 4095
INT2A3yn ee 1INT2A 1 4095
INT2B4yn ee 1INT2B 1 4095
INT3A5yn ee 1INT3A 1 4095
INT3B6yn ee 1INT3B 1 4095
INT4A7yn ee 1INT4A 1 4095
INT4B8yn ee 1INT4B 1 4095
INT5A9yn ee 1INT5A 1 4095
INT5B 10 y n e e 1 INT5B 1 4095
INT6A 11 y n e e 1 INT6A 1 4095
INT6B 12 y n e e 1 INT6B 1 4095
SMGT1 13 y n e e 1 SMGT1 1 4095
SMGT2 14 y n e e 1 SMGT2 1 4095
MGT1 15 y n e e 4095*MGT1 4095
EXT1 17 n n e e 1 EXT1 1
EXT2 18 n n e e 1 EXT2 1
EXT3 19 n n e e 1 EXT3 1
EXT4 20 n n e e 1 EXT4 1
EXT5 21 n n e e 1 EXT5 1
EXT6 22 n n e e 1 EXT6 1
EXT7 23 n n e e 1 EXT7 1
EXT8 24 n n e e 1 EXT8 1
EXT9 25 n n e e 1 EXT9 1

BLADE OS 5.1 Release Notes
18 BMD00098, December 2009
Port information (/info/port) for switches installed in bay 3 and bay 4:
Other Features
BLADEOS 5.1 now also supports
PVRST
Alias Port Tag Fast Lrn Fld PVID NAME VLAN(s)
----- ---- --- ---- --- --- ---- -------------- --------------------
INT1 1 y n e e 1 INT1 1 4095
INT2 2 y n e e 1 INT2 1 4095
INT3 3 y n e e 1 INT3 1 4095
INT4 4 y n e e 1 INT4 1 4095
INT5 5 y n e e 1 INT5 1 4095
INT6 6 y n e e 1 INT6 1 4095
MGT1 15 y n e e 4095*MGT1 4095
EXT1 17 n n e e 1 EXT1 1
EXT2 18 n n e e 1 EXT2 1
...

BLADE OS 5.1 Release Notes
BMD00098, December 2009 19
Supplemental Information
This section provides additional information about configuring and operating the GbESM and
BLADEOS.
Management Module
The “Fast POST=Disabled/Enabled” inside the IBM management module Web interface “I/O
Module Admin Power/Restart” does not apply to the GbESM.
Solution: To boot with Fast or Extended POST, go to the “I/O Module Admin/Power/Restart”
window. Select the GbESM, and then choose “Restart Module and Run Standard Diagnostics”
or “Restart Module and Run Extended Diagnostics.”
The following table correlates theFirmware Type listed in the IBM management module’s Web
interface “Firmware VPD” window to the GbESM software version:
Within the IBM management module Web interface, the Java applets of “Start Telnet Session”
and “Start Web Session” do not support changing of default known ports 23 and 80
respectively.
Solution: If the Telnet or HTTP port on the GbESM is changed to something other than the
default port number, the user must use a separate Telnet client or Web browser that supports
specifying a non-default port to start a session to the GbESM user interface.
Table 2 Firmware Type list
Firmware Type Description
Boot ROM GbESM Boot code version
Main Application 1 Currently running image
Main Application 2 Backup image

BLADE OS 5.1 Release Notes
20 BMD00098, December 2009
Management Module/GbESM Connectivity
Currently, the IBM management module is designed to provide one-way control of the GbESM. As
a result, the GbESM may lose connectivity to the management module via the management port
under the following conditions:
If new IP attributes are pushed from the management module to the GbESM while the IP
Routing table is full, the new attributes will not be applied.
Solution: Enable “External Management over all ports,” connect to the switch using other
interface and then clear the routing table. Then push the IP address from the management
module. If this does not work, use Solution 2 below.
If you execute the /boot/reset CLI command on the GbESM or the GbESM resets itself, the
management module might not push the IP attributes to the switch, and connectivity may be
lost.
Solution 1: If you should experience any connectivity issues between the switch module and the
management module, go to the “I/O Module Configuration” window on the management module’s
Web interface. Under the “New Static IP Configuration” section, click Save to trigger the
management module to push the stored IP attributes to the switch module.
Solution 2: If Solution 1 does not resolve your connectivity issue, then go to the “I/O Module
Admin/Power/Restart” window on the management module’s Web interface. Restart the switch
module in question.
Solution 3: If this still does not resolve the issue, enable Preserve new IP configuration on all resets
setting on the management module and restart the switch module via the “I/O Module
Admin/Power/Restart” window on the management module’s Web interface.
Note – As a rule, always use the management module Web interface to change the GbESM
management IP attributes (IP address, mask and gateway), and then click Save to push the IP
attributes to the switch module. Use of the command-line interface to change the switch module
management IP attributes may result in duplicated entries for the management IP Interface in the
switch route table and/or loss of connectivity via the management module.
This manual suits for next models
1
Table of contents
Other Blade Network Technologies Software manuals
Popular Software manuals by other brands

Cisco
Cisco 4700M Configuration guide

ACRONIS
ACRONIS BACKUP RECOVERY 10 ADVANCED SERVER - installation guide

Fujitsu
Fujitsu Solaris 10 Hardware platform guide

Juniper
Juniper PHYSICAL LAYER - CONFIGURATION GUIDE V11.1.X Configuration guide
ActionTec
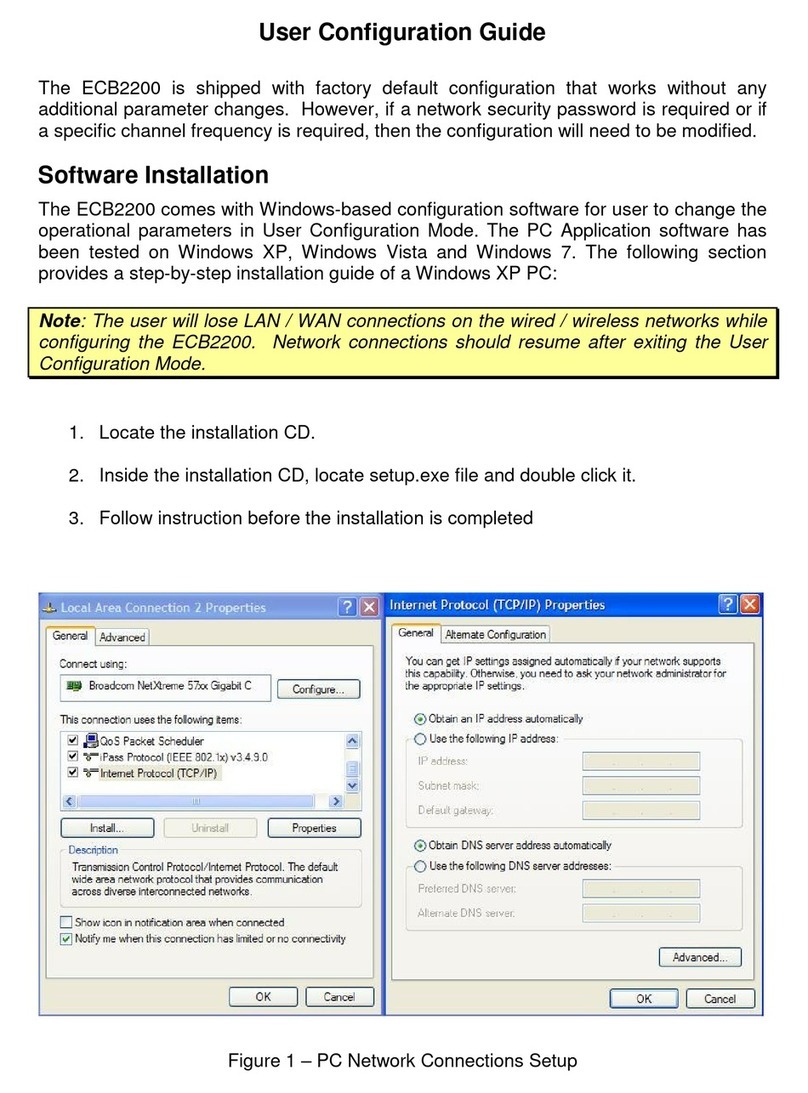
ActionTec ECB2200 User configuration guide

Adaptec
Adaptec 2110S - SCSI RAID Controller user guide












