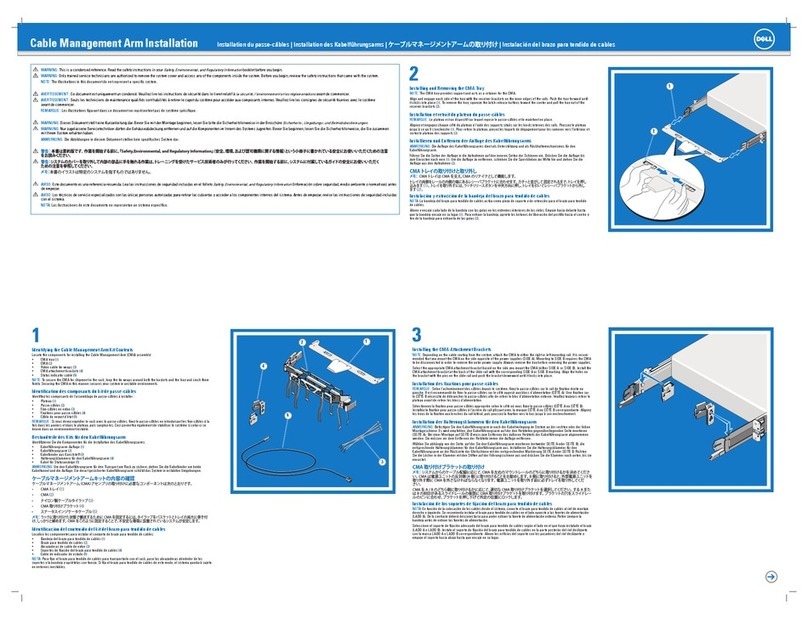
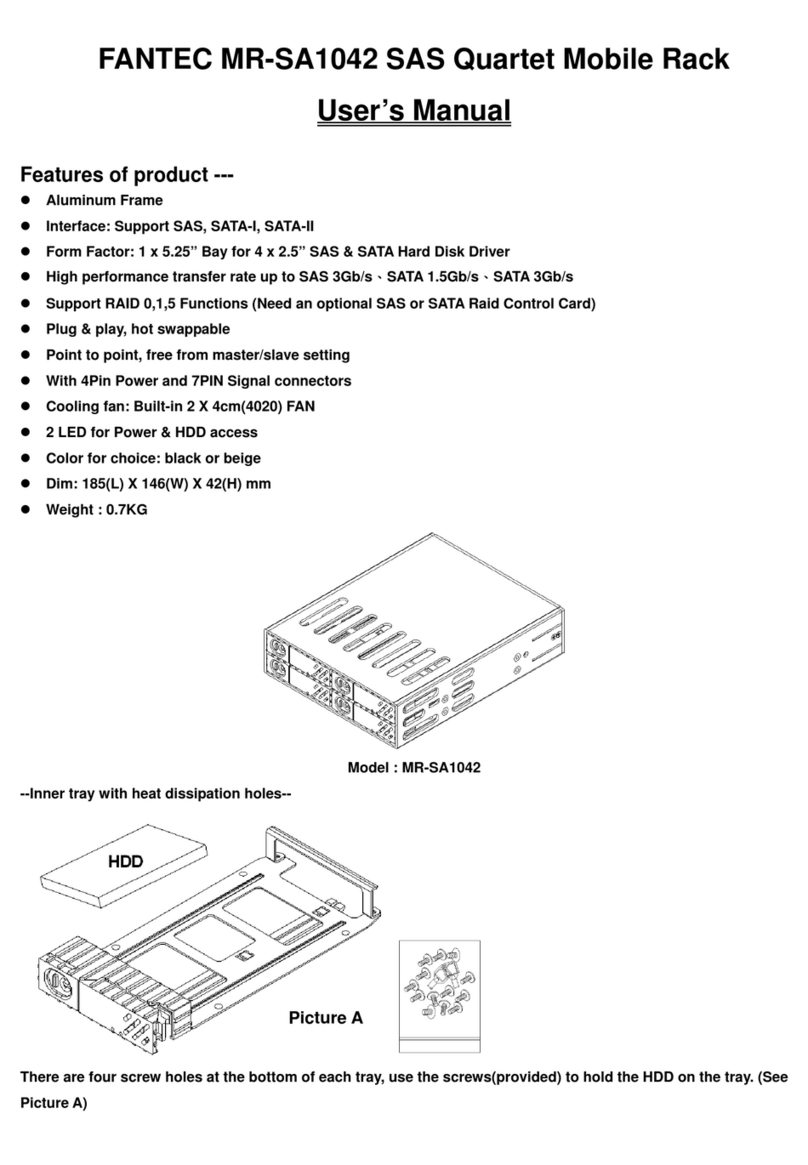
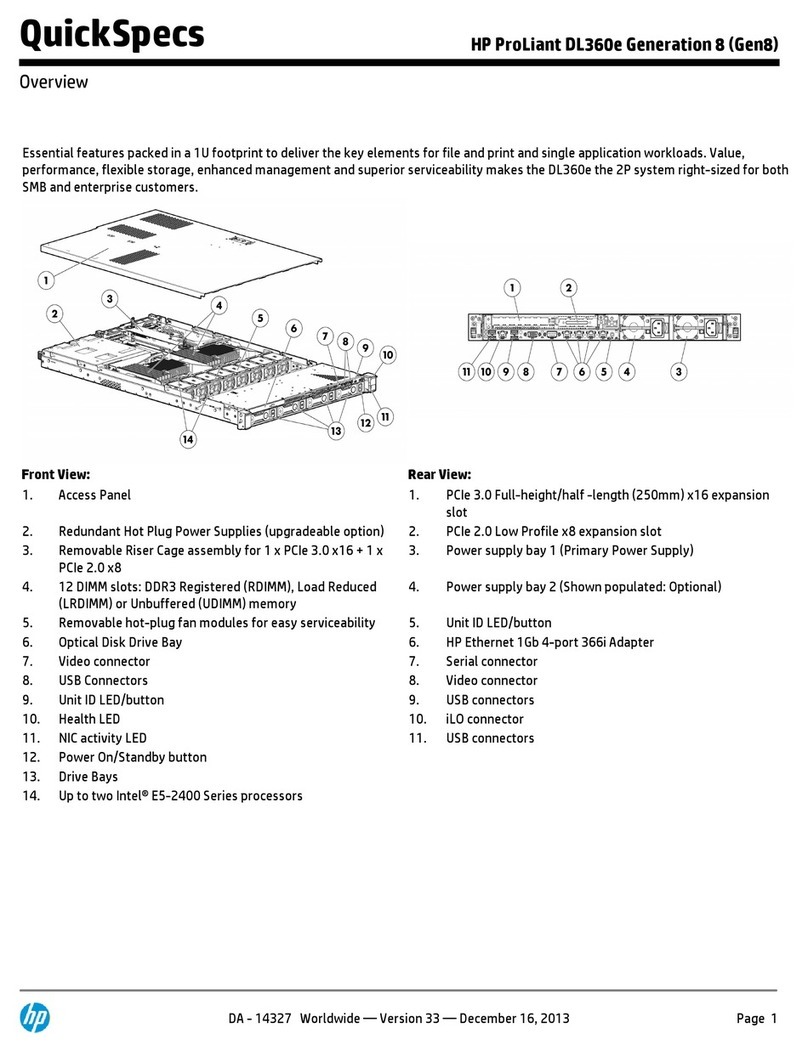
Bluegiga Technologies WRAP Instruction Manual

Access Server
User’s and Developer’s Guide
Bluegiga Technologies

Access Server: User’s and Developer’s Guide
by Bluegiga Technologies
Published 2007-07-20 (3.2)
Copyright © 2001, 2002, 2003, 2004, 2005, 2006, 2007 Bluegiga Technologies
Bluegiga Technologies reserves the right to alter the hardware, software, and/or specifications detailed herein at any time without
notice, and does not make any commitment to update the information contained herein. Bluegiga Technologies assumes no
responsibility for any errors which may appear in this manual. Bluegiga Technologies’ products are not authorized for use as critical
components in life support devices or systems.
The WRAP is a registered trademark of Bluegiga Technologies. iWRAP, WRAP THOR and WRAP Access Server are trademarks of
Bluegiga Technologies.
The Bluetooth trademark is owned by the Bluetooth SIG Inc., USA, and is licensed to Bluegiga Technologies.
ARM and ARM9 are trademarks of ARM Ltd.
Linux is a trademark of Linus Torvalds.
All other trademarks listed herein belong to their respective owners.

Table of Contents
1. Introduction to Access Server............................................................................................................1
1.1. Licenses and Warranty ............................................................................................................2
1.2. Bluegiga Technologies Contact Information ........................................................................2
2. Getting Started with Access Server..................................................................................................3
2.1. Powering Up .............................................................................................................................3
2.2. WWW Interface ........................................................................................................................4
2.3. Shell Prompt Access.................................................................................................................6
2.3.1. Management Console .................................................................................................7
2.3.2. Accessing Remotely.....................................................................................................8
2.3.3. Transferring Files to/from Access Server ................................................................8
2.4. Introduction to Configuration................................................................................................9
2.5. Using the Setup WWW Interface...........................................................................................9
2.6. Using the setup Command Line Application ....................................................................17
2.7. Resetting a Configuration .....................................................................................................18
2.8. Exporting and Importing Configurations...........................................................................18
3. Using the System ...............................................................................................................................19
3.1. Network Interfaces.................................................................................................................19
3.2. Bluetooth .................................................................................................................................19
3.2.1. iWRAP Password Protection ...................................................................................19
3.2.2. LAN Access Profile....................................................................................................20
3.2.3. Serial Port Profile .......................................................................................................20
3.2.4. Object Push and File Transfer Profile......................................................................21
3.2.4.1. Incoming ObjP and FTP ...............................................................................21
3.2.4.2. Outgoing ObjP and FTP...............................................................................22
3.2.5. PAN Profiles ...............................................................................................................24
3.2.6. Changing the Bluetooth Range................................................................................24
3.2.7. btcli ..............................................................................................................................25
3.2.8. serialbluetooth............................................................................................................25
3.3. Compact Flash Cards.............................................................................................................25
3.3.1. Compact Flash GPRS Cards.....................................................................................25
3.3.2. Compact Flash GPS Card .........................................................................................26
3.3.3. Compact Flash Wi-Fi Cards......................................................................................26
3.4. USB Memory Dongles and Compact Flash Memory Cards ............................................26
3.5. Servers......................................................................................................................................27
3.5.1. Finder ..........................................................................................................................28
3.5.2. ObexSender ................................................................................................................29
3.5.3. SMS Gateway Server.................................................................................................29
3.5.4. User Level Watchdog ................................................................................................29
3.5.5. Remote Management ................................................................................................30
3.5.5.1. Overview........................................................................................................30
3.5.5.2. Management Packet Format........................................................................30
3.5.5.3. Management Packet Information File Format..........................................31
3.5.5.4. Management Operation Example: Hello World.......................................31
3.5.5.5. Management Operation Example: Software Update...............................32
3.5.5.6. Management Operation Example: IPQUERY ...........................................32
iii

3.5.5.7. Management Operation Example: Beep....................................................33
3.5.5.8. Management with USB Memory Dongle or Compact Flash Memory
Card ....................................................................................................................33
3.5.5.9. Listing and Uninstalling Software Component........................................33
3.5.6. FTP ...............................................................................................................................33
3.5.7. Web Server..................................................................................................................33
3.5.8. SNMP ..........................................................................................................................33
3.5.9. OpenVPN....................................................................................................................34
3.5.10. SSH.............................................................................................................................34
3.5.11. Telnet .........................................................................................................................34
3.5.12. NTP............................................................................................................................34
3.6. Utilities.....................................................................................................................................34
3.7. Real Time Clock......................................................................................................................39
3.8. Time Zone................................................................................................................................39
3.9. System Re-Install and Upgrade............................................................................................39
4. SPP-over-IP .........................................................................................................................................41
4.1. How SPP-over-IP Works .......................................................................................................41
4.1.1. Standard Operation...................................................................................................41
4.1.2. Repeater Operation ...................................................................................................42
4.1.3. SPP-over-IP over GPRS.............................................................................................42
4.1.4. Opening Connections from Access Server.............................................................43
4.1.5. SPP-over-IP and COM Ports ....................................................................................44
4.2. Configuring SPP-over-IP.......................................................................................................44
4.2.1. Forwarding Incoming Connections ........................................................................45
4.2.2. Maintaining and Forwarding Outgoing Connections..........................................45
4.2.3. Repeater Configuration ............................................................................................45
4.2.4. Wi-Fi Configuration ..................................................................................................46
4.2.5. GPRS Configuration..................................................................................................46
5. Obexsender .........................................................................................................................................47
5.1. Key Features............................................................................................................................47
5.2. Use Cases.................................................................................................................................47
5.2.1. Content Push ..............................................................................................................48
5.2.2. Content Pull................................................................................................................48
5.3. Configuration..........................................................................................................................49
5.3.1. Uploading Files..........................................................................................................49
5.3.2. Configuring Content Rules ......................................................................................50
5.3.3. How to Store Files Sent to Access Server ...............................................................50
5.4. Monitoring ObexSender........................................................................................................50
5.5. Bluetooth Device Database ...................................................................................................50
6. Software Development Kit ..............................................................................................................51
6.1. Introduction to SDK...............................................................................................................51
6.2. Installing SDK.........................................................................................................................51
6.2.1. Access Server Software Development Kit System Requirements ......................51
6.2.2. Questions Asked by the Install Script.....................................................................52
6.3. Creating Applications............................................................................................................52
6.3.1. Application Examples...............................................................................................52
6.3.1.1. Installing Examples.......................................................................................52
iv

6.3.1.2. Running Examples........................................................................................53
6.3.2. Creating a New Project .............................................................................................54
6.3.3. Building from the Command Line..........................................................................54
6.3.4. Transferring an Application to Access Server .......................................................55
6.3.4.1. Transferring an Application Using SCP or SFTP......................................55
6.3.4.2. Using SSHFS ..................................................................................................55
6.3.4.3. Transferring an Application Using Terminal Software ...........................55
6.3.4.4. Using NFS Mount .........................................................................................56
6.3.4.5. Using CIFS Mount ........................................................................................56
6.3.5. Running an Application Transferred to Access Server ........................................56
6.3.6. Using GNU Project Debugger (GDB) .....................................................................57
6.3.7. Native SDK .................................................................................................................57
7. iWRAP - The Bluetooth API............................................................................................................59
7.1. Terms........................................................................................................................................59
7.2. Starting iWRAP ......................................................................................................................59
7.3. Writing iWRAP Applications ...............................................................................................59
7.3.1. Forklistener.................................................................................................................60
7.3.2. iWRAP Client .............................................................................................................60
7.4. btcli - iWRAP Command Line Interface Utility.................................................................60
7.5. iWRAP Commands................................................................................................................61
INFO ......................................................................................................................................61
QUIT ......................................................................................................................................62
SET .........................................................................................................................................63
SAVE ......................................................................................................................................73
LOAD ....................................................................................................................................74
PING......................................................................................................................................75
PONG ....................................................................................................................................76
ECHO ....................................................................................................................................77
LOCK.....................................................................................................................................78
UNLOCK ..............................................................................................................................79
SHUTDOWN........................................................................................................................80
SLEEP ....................................................................................................................................81
LOG .......................................................................................................................................82
7.6. Finding Bluetooth Devices....................................................................................................84
INQUIRY...............................................................................................................................84
NAME ...................................................................................................................................85
7.7. Bluetooth Connections ..........................................................................................................86
CALL .....................................................................................................................................86
CONNECT............................................................................................................................88
NO CARRIER.......................................................................................................................90
RING......................................................................................................................................91
RINGING..............................................................................................................................92
CLOSE ...................................................................................................................................93
LIST........................................................................................................................................94
RSSI........................................................................................................................................96
TXPOWER ............................................................................................................................97
BER.........................................................................................................................................98
v

CLOCK..................................................................................................................................99
STATUS ...............................................................................................................................100
7.8. Service Discovery .................................................................................................................101
SDPSEARCH......................................................................................................................101
SDPATTR ............................................................................................................................103
SDPQUERY.........................................................................................................................105
SDP bdaddr ........................................................................................................................106
SDP ADD ............................................................................................................................107
SDP DEL..............................................................................................................................108
SDP LIST .............................................................................................................................109
7.9. Example Sessions .................................................................................................................110
7.10. Error Codes .........................................................................................................................110
8. I/O API ...............................................................................................................................................114
8.1. Led and Buzzer API.............................................................................................................114
8.2. GPIO API...............................................................................................................................114
9. Finder Protocol .................................................................................................................................115
9.1. Finder Search Message ........................................................................................................115
9.2. Finder Reply Message .........................................................................................................115
10. Advanced Use Cases for Access Server .....................................................................................116
10.1. Making Access Server Secure...........................................................................................116
10.2. Saving Bluetooth Pairing Information Permanently.....................................................116
10.3. Digital Pen...........................................................................................................................116
10.4. OpenVPN ............................................................................................................................117
10.4.1. Prerequisites ...........................................................................................................117
10.4.2. Installing OpenVPN..............................................................................................117
10.4.3. Creating Certificates and Keys ............................................................................118
10.4.4. Creating Configuration Files................................................................................120
10.4.4.1. Server Configuration File.........................................................................120
10.4.4.2. Client Configuration File .........................................................................122
10.4.5. Starting up VPN.....................................................................................................124
10.4.5.1. Starting up the Server...............................................................................124
10.4.5.2. Starting up the Client ...............................................................................125
11. Certification Information and WEEE Compliance ..................................................................126
A. Directory Structure.........................................................................................................................129
B. Setup Options ..................................................................................................................................131
B.1. Security settings ...................................................................................................................131
B.2. Generic settings....................................................................................................................133
B.3. Network settings..................................................................................................................135
B.3.1. Default interface settings .......................................................................................136
B.3.2. Ethernet cable settings............................................................................................137
B.3.3. Wi-Fi settings ...........................................................................................................137
B.3.4. GPRS settings...........................................................................................................138
B.4. Applications..........................................................................................................................139
B.4.1. FTP server settings..................................................................................................140
B.4.2. ObexSender settings ...............................................................................................141
B.4.2.1. Timeouts and delays ..................................................................................143
vi

B.4.2.2. Logging ........................................................................................................144
B.4.2.3. Delete log (confirm)....................................................................................145
B.4.3. Connector settings...................................................................................................146
B.4.4. wpkgd settings ........................................................................................................147
B.4.5. SMS gateway settings .............................................................................................148
B.5. iWRAP settings ....................................................................................................................149
B.5.1. Bluetooth profiles ....................................................................................................152
B.5.1.1. LAN access profile settings .......................................................................152
B.5.1.2. PAN user profile settings...........................................................................153
B.5.1.3. PAN generic networking profile settings................................................154
B.5.1.4. PAN network access point profile settings .............................................155
B.5.1.5. Connection forwarding..............................................................................155
B.5.1.6. Serial port profile settings .........................................................................155
B.5.1.7. Object push profile settings.......................................................................157
B.5.1.8. File transfer profile settings.......................................................................157
B.6. Advanced settings ...............................................................................................................158
B.6.1. Bluetooth commands..............................................................................................159
B.6.2. System information.................................................................................................159
B.6.3. Reboot system (confirm) ........................................................................................160
B.7. Summary of Setup Options................................................................................................160
C. Open Source Software Licenses...................................................................................................166
D. Supported Hardware .....................................................................................................................171
vii

List of Tables
2-1. The Management Console Port Settings ........................................................................................7
3-1. Access Server Network Interfaces.................................................................................................19
3-2. obexserver’s metas ..........................................................................................................................21
3-3. Parameters for obexsender-put .....................................................................................................22
3-4. Errorlevels from obexsender-put ..................................................................................................23
3-5. Parameters for obexsender-inquiry ..............................................................................................24
3-6. Errorlevels from obexsender-inquiry ...........................................................................................24
3-7. Access Server Servers......................................................................................................................27
3-8. Access Server Utilities.....................................................................................................................34
6-1. Examples, Their Usage and Purpose............................................................................................53
7-1. Supported Parameters for iWRAP SET Command....................................................................63
7-1. SAVE parameters.............................................................................................................................73
7-1. Log bitmask descriptions ...............................................................................................................82
7-2. Log target options............................................................................................................................82
7-5. Supported Keywords for Replacing SDP UUIDs or Attributes..............................................101
7-1. SDP Response Formatting Characters........................................................................................103
7-7. iWRAP Errors.................................................................................................................................110
7-8. Errors Masks...................................................................................................................................111
7-9. HCI Error Codes ............................................................................................................................111
7-10. L2CAP Error Codes.....................................................................................................................112
7-11. SDP Error Codes..........................................................................................................................113
7-12. RFCOMM Error Codes ...............................................................................................................113
9-1. Finder Tuple Format......................................................................................................................115
9-2. Finder Tuple IDs ............................................................................................................................115
11-1. Excerpt of Table 1B of 47 CFR 1.1310........................................................................................127
C-1. Open Source Licenses in Access Server Software Components ............................................166
C-2. Access Server Open Source Software Components and Their Licences...............................166
D-1. Supported Hardware by Access Server ....................................................................................171
viii

Chapter 1. Introduction to Access Server
Bluegiga’s WRAP™ product family offers for device manufacturers, integrators, companies and
developers a simple and fast way to set-up wireless communication systems between standard
or proprietary devices, networks, machines and instruments.
Access Server is a cutting edge wireless Bluetooth router. It supports multiple communication
standards including Ethernet, WiFi, and GSM/GPRS enabling full media-independent TCP/IP
connectivity. Access Server is easy to deploy and manage in existing wired and wireless net-
works without compromising speed or security. For rapid deployment, Access Server config-
urations can easily be copied from one device to another by using USB memory dongles. The
device can be fully managed and upgraded remotely over SSH secured links. Large numbers of
Access Servers can easily be controlled using Bluegiga Solution Manager (BSM), a web-based
remote management and monitoring platform.
Access Server usage scenarios and applications:
•Point-of-sales systems
•Logistics and transportation systems
•Telemetry and machine-to-machine systems
•Medical and healthcare systems
•Fitness and sport telemetry systems
•Cable replacement
•Content and application distribution to mobile phones and PDAs
Access Server key features:
•Enables Bluetooth networking between multiple devices and networks
•Serves up to 21 simultaneous Bluetooth connections
•Offers an open platform for adding local applications
•Acts as a transparent router or bridge
•Supports all key communication medias:
•Bluetooth
•Ethernet
•WiFi, GSM and GPRS with a Compact Flash card
•USB and RS232
•Incorporates a packet filtering firewall
•Is fast and easy to install
•Supports all relevant Bluetooth profiles and APIs
•100 meter range / Software configurable to support 10 meter range
•DHCP support for plug-and-play installation
•Uncompromised security: SSH, firewall, and 128 bit Bluetooth encryption
1

Chapter 1. Introduction to Access Server
•Simple and secure mounting accessory available
•Bluetooth, CE, and FCC certified
•Compliant with Bluetooth 1.1, 1.2 and 2.0 Specification
1.1. Licenses and Warranty
Warning
Bluegiga Technologies is hereby willing to license the enclosed WRAP product and
its documentation under the condition that the terms and conditions described in
the License Agreement are understood and accepted. The License Agreement is
supplied within every WRAP product both in hard copy. It is also available on-line
at http://bluegiga.com/as/current/doc/eula.pdf. The use of the WRAP product
will indicate your assent to the terms. If you do not agree to these terms, Bluegiga
Technologies will not license the software and documentation to you, in which
event you should return this complete package with all original materials, equip-
ment, and media.
Some software components are licensed under the terms and conditions of an open source li-
cense. Details can be found in Appendix C. Upon request, Bluegiga will distribute a complete
machine-readable copy of the source of the aforementioned open source software components
during a period of three (3) years from the release date of the software. Delivery costs of the
source code will be charged from the party requesting the source code.
The Bluegiga WRAP Product Limited Warranty Statement is available on-line at
http://bluegiga.com/as/current/doc/warranty.pdf.
1.2. Bluegiga Technologies Contact Information
Please see http://www.bluegiga.com/ for news and latest product offers. For more information,
contact <[email protected]>.
Please check http://bluegiga.com/as/ for software and documentation updates.
processing of your support request, please include as detailed information on your product and
your problem situation as possible.
Please begin your email with the following details:
•Access Server product type
•Access Server product serial number
•Access Server software version
•End customer name
•Date of purchase
2

Chapter 2. Getting Started with Access Server
Access Server can be controlled in three ways:
•by using the WWW interface
•by entering commands and using applications at the Access Server shell prompt
•by sending and/or retrieving files to/from Access Server.
Note: The default username is root and the default password is buffy.
2.1. Powering Up
To get started with Access Server, connect it to your local area network (LAN) by using an
Ethernet cable, and connect the power adapter. Access Server will power up and retrieve the
network settings from your network’s DHCP server.
Access Server will also use Zeroconf (also known as Zero Configuration Networking or Au-
tomatic Private IP Addressing) to get an unique IP address in the 169.254.x.x network. Most
operating systems also support this. In other words, you can connect your controlling laptop
with a cross-over Ethernet cable to Access Server, then power up Access Server, and the devices
will automatically have unique IP addresses in the 169.254.x.x network.
Note: If you need to configure the network settings manually and cannot connect first by using Zero-
conf, you can do it by using the management console. For more information, see Section 2.3.1.
The physical interface locations of Access Server are described in Figure 2-1 and Figure 2-2.
Figure 2-1. Access Server Connectors
Note: There is no power switch in Access Server. The adapter is the disconnection device; the socket-
outlet shall be installed near the equipment and shall be easily accessible. Unplug and plug the power
adapter to switch the power on and off. The power led in Figure 2-2 is on when the power adapter is
connected.
3

Chapter 2. Getting Started with Access Server
Figure 2-2. Access Server LEDs
All the blue status LEDs are turned off when the boot procedure is finished and Access Server
is ready to be connected.
2.2. WWW Interface
Most Access Server functionality can be controlled through the WWW interface by using any
standard WWW browser.
The wrapfinder application (see Figure 2-3), available for the Windows operating system from
Bluegiga Techforum (http://www.bluegiga.com/techforum/) provides an easy-to-use interface
for finding Access Servers (with SW version 2.1.0 or later) in the local area network.
Figure 2-3. Access Server Finder Application
When wrapfinder is launched, it automatically identifies the broadcast address of the network
it runs in and sends a special query packet (UDP broadcast) to Access Servers. Most important
information in their answers is then shown in table format.
You can change the broadcast address used for finding Access Servers. A new scan can be done
by clicking Rescan.
Select an Access Server by clicking its serial number, and click Details to see more information
(such as all Bluetooth addresses and friendly names) on Access Server. See Figure 2-4 for details.
4

Chapter 2. Getting Started with Access Server
Figure 2-4. Details Dialog of Access Server Finder
Click Connect or double-click a serial number to connect to the selected Access Server by using
a WWW browser.
Click Exit to close the program.
Note: To find Access Server’s IP address without wrapfinder, see Section 2.3.2.
To access the WWW interface, enter the IP address of Access Server to the browser’s address
field and press Enter (see Figure 2-5).
Figure 2-5. Access Server WWW Interface
From the top-level page, click Setup to log in to the configuration interface. The default user-
name is root and the default password is buffy (see Figure 2-6).
5

Chapter 2. Getting Started with Access Server
Figure 2-6. WWW Login Prompt for Access Server Setup
After logging in, you can configure several Access Server settings (see Figure 2-7). These are
discussed in detail in Section 2.4.
Figure 2-7. The WWW Configuration Interface of Access Server
2.3. Shell Prompt Access
Shell prompt access may be needed for advanced controlling operations that cannot be per-
formed by using the WWW interface.
You can get to the shell prompt by using either SSH or the management console. The manage-
ment console is only needed to change the network configuration settings if you cannot config-
6

Chapter 2. Getting Started with Access Server
ure the network by using DHCP or Zeroconf. The management console is connected to Access
Server with a serial cable. All further controlling activities can be performed remotely using SSH
sessions over Ethernet or Bluetooth LAN/PAN connection.
If you can establish an SSH connection from a device that has Bluetooth LAN Access or PAN pro-
file support, you do not need the management console. Just connect to Access Server by using
LAN Access or PAN profile. Access Server can be seen in Bluetooth inquiries as "Wserialno_n",
where "serialno" is the serial number of the device and "n" is the number of the Bluetooth base-
band in question (model 2293 has three Bluetooth basebands, any of which can be connected).
After you have connected to the server (no PIN code, username or password needed), establish
an SSH connection to the device at the other end of the connection, typically 192.168.160.1. You
can also use the wrapfinder application to find the IP address (see Section 2.2 for details).
Note: Bluetooth LAN Access and PAN profiles are disabled by default. Use the WWW interface to
enable them, if needed. The PAN profile can also be enabled by sending the enable-pan.wpk file
(available on-line at http://bluegiga.com/as/current/enable-pan.wpk) to Access Server by using
Bluetooth Object Push profile or by inserting a USB memory dongle with the file in its root direc-
tory to Access Server’s USB port.
Note: The default username is root and the default password is buffy.
2.3.1. Management Console
If you do not have a Bluetooth LAN/PAN client and if Access Server is not connected to your
LAN, or if you do not know the IP address given to Access Server, you can get the first shell
prompt access by using the management console.
To setup the management console, proceed as follows:
1. Have a PC with a free COM port.
2. Power off Access Server.
3. Configure your terminal application, such as HyperTerminal in Windows, to use the settings
below for your computer’s free COM port
Setting Value
Speed 115200bps
Data Bits 8
Parity None
Stop Bits 1
Flow Control None
Table 2-1. The Management Console Port Settings
4. Connect the serial cable shipped with Access Server to your PC’s free COM port.
5. Connect the serial cable to the management (user) port in Access Server (see Figure 2-1).
6. Power on Access Server.
7. Enter letter bin the terminal application during the first five seconds, while the blue LEDs
in Access Server turn on one by one.
8. The management console is now activated and you can see the boot log in your terminal
window.
7

Chapter 2. Getting Started with Access Server
Note: The boot process may stop at the following U-Boot prompt:
Hit any key to stop autoboot: 0
U-Boot>
If this happens, enter command boot to continue to boot Linux.
9. Wait for the device to boot up and end with the following prompt:
Please press Enter to activate this console.
10. Press Enter to activate the console. You will be logged in as root in directory /root:
[root@wrap root]
11. You can now control Access Server from the management console.
2.3.2. Accessing Remotely
When Access Server is connected to a LAN, it tries to get the IP address by using DHCP and
Zeroconf by default. You can then use the wrapfinder application to find the IP address (see
Section 2.2).
If you cannot get the IP address by using the wrapfinder, another way to see the IP address of
Access Server is to connect with a management console (see previous section), power on the
unit and, after the system is up and running, give the ifconfig nap command. The inet addr
field for the nap interface contains the IP address of Access Server. For example, in the following
capture from the management console, the IP address is 192.168.42.3.
[root@wrap /]$ ifconfig nap
nap Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 00:07:80:00:BF:01
inet addr:192.168.42.3 Bcast:192.168.42.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
inet6 addr: fe80::207:80ff:fe00:bf01/64 Scope:Link
UP BROADCAST MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
RX packets:12635 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:8 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:100
RX bytes:1686246 (1.6 MiB) TX bytes:1640 (1.6 KiB)
Interrupt:24 Base address:0xc000
You can use this address to connect to Access Server remotely over SSH, SCP or SFTP.
Note: The default username is root and the default password is buffy.
2.3.3. Transferring Files to/from Access Server
You can transfer files to and from Access Server by using, for example:
•SCP (secure copy over SSH)
•SFTP (secure FTP connection over SSH)
•FTP (plain FTP connection)
Note: FTP is disabled by default for security reasons. Use SFTP instead.
8

Chapter 2. Getting Started with Access Server
Tip: If enabled, use the integrated FTP client on the Internet Explorer (type ftp://root:buffy@wrap-
ip-address/ in the address bar)
•Bluetooth OBEX (Object Push and File Transfer Profiles) to/from directory /tmp/obex in Ac-
cess Server
•NFS (mount an NFS share from a remote computer as a part of Access Server’s file system)
•SSHFS (mount an Access Server directory over SSH as a part of any other Linux host file
system)
To download and install SSHFS, visit http://fuse.sourceforge.net/sshfs.html.
•CIFS (mount a Common Internet File System share from a remote computer as a part of Access
Server’s file system). A CIFS client, available in a separate installation packet, is required.
•USB memory dongle (see Section 3.4 for more information).
•Xmodem/Ymodem/Zmodem (use rz/rx/rb/sz/sx/sb commands from the management con-
sole)
For examples of transferring files, see Section 6.3.4.
2.4. Introduction to Configuration
When Access Server is installed and powered up for the first time, the default configuration
settings are being used. With these settings, Access Server automatically configures its network
settings assuming that it is connected to a LAN network with a DHCP server running. Addition-
ally, Access Server also uses Zero Configuration Networking (also known as Automatic Private
IP Addressing) to connect to the 169.254.x.x network, which can be used if the network has no
DHCP server.
After booting up, the only Bluetooth profiles enabled are the Object Push and File Transfer Pro-
files, used to send files to/from Access Server.
More Bluetooth profiles can be enabled, and most of Access Server settings can be configured
by using the setup application. It has a WWW interface at http://wrap-ip/setup but it can also
be run at the command line.
All configurable settings in the setup application are listed in Appendix B with short help texts.
Note: The default username is root and the default password is buffy.
2.5. Using the Setup WWW Interface
The easiest way to change Access Server settings is to use the WWW interface. Accessing the
WWW interface is instructed in Section 2.2.
A typical WWW configuration page is shown in Figure 2-8 (This page can be found at Setup
−→ Security settings)
9

Chapter 2. Getting Started with Access Server
Figure 2-8. Example WWW Setup Page
The different parts of the WWW Setup page are discussed in the following list:
•Status area
The status area serves two purposes:
•It indicates that the changes are permanently saved when the user clicks the Save button
(or when the user clicks a toggling Yes/No link).
•If invalid values were entered in one or more fields, an error message is shown in this area
(see Figure 2-9).
10

Chapter 2. Getting Started with Access Server
Figure 2-9. Trying to Save an Invalid Input
Note: It is typically necessary to reboot Access Server for the changes to take effect. This can be
done through the WWW interface (Advanced settings menu).
•Number or text entry fields
Most of the configurable settings are text (or number) entry fields. For some fields, such as
the IP address or netmask, there are restrictions on the input format. Setup validates the input
at save time and accepts valid data only. The fields with errors are shown to the user so that
mistakes can be fixed (see Figure 2-9).
•Help -link
Click the Help link to retrieve the setup page again with requested help information displayed.
For an example, see Figure 2-10.
11

Chapter 2. Getting Started with Access Server
Figure 2-10. Help Links in WWW Setup
Warning
If you have made changes to the settings on the page before clicking Help and
not saved them yet, they are lost.
•Yes and No radio buttons
These buttons are typically used to configure a setting that can be either enabled or disabled,
and this setting has no effect on the visibility of other settings.
•Reset button
Reset button resets the fields to the values currently in use at Access Server. In other words,
the Reset button discards unsaved changes.
Note: The Reset button does not make a "factory reset".
•Save button
Save button sends the WWW page to the setup application for validation. If the values in the
fields are valid, they are permanently saved and the page is refreshed with the Changes have
been saved. message at the top. The accepted values are shown in the page fields.
12
Other manuals for WRAP
1
Table of contents
Other Bluegiga Technologies Server manuals
Popular Server manuals by other brands

Sun Microsystems
Sun Microsystems Netra X4200 M2 Service manual

Sun Microsystems
Sun Microsystems Blade X6450 Service manual

HP
HP t5745 - Thin Client Quickspecs

HP
HP Integrity Superdome SX1000 Recovery guide
Oracle
Oracle X8-2L Service manual

Sun Microsystems
Sun Microsystems Sun Fire V60 Series Release notes