2
Content
Thanks for using the product.........................................................................................................1
Chapter 1 Human-Machine Interface...........................................................................................4
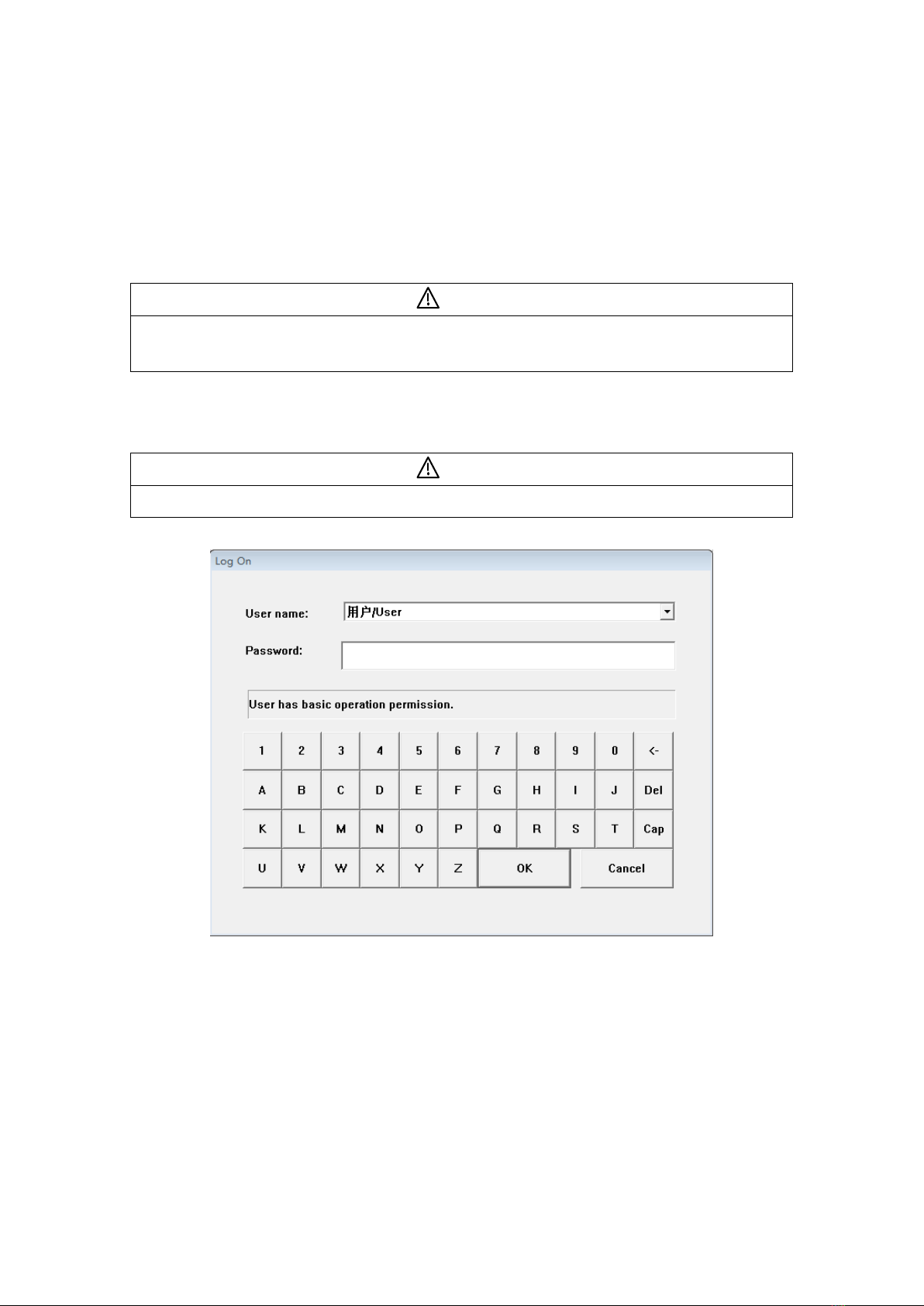
1.1 Log-In.....................................................................................................................................4
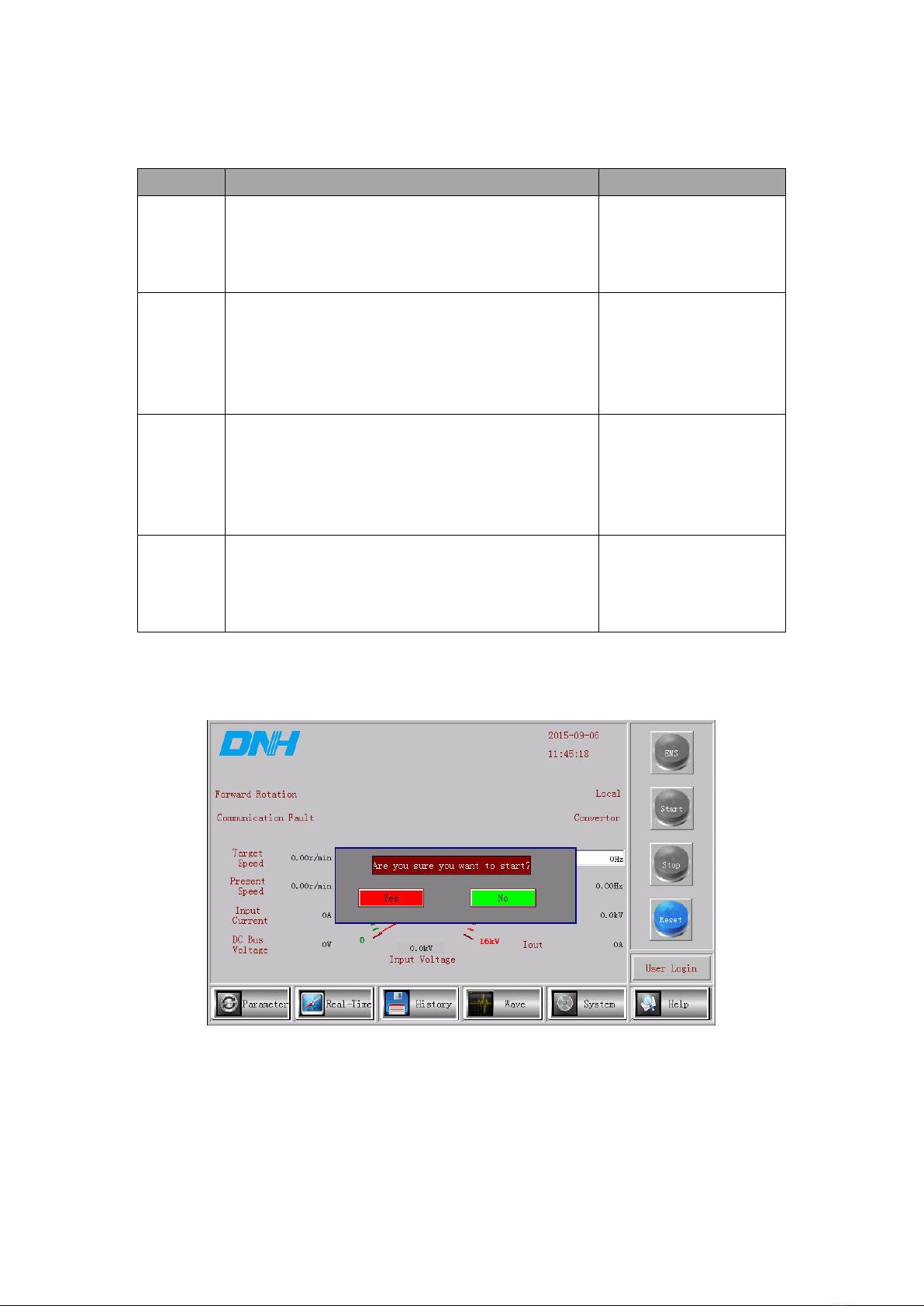
1.2 Main Screen...........................................................................................................................5
1.2.1 Control Button Area .........................................................................................................5
1.2.2 Function Button Area .......................................................................................................7
1.2.3 State Display Area............................................................................................................7
1.3 Parameter Setup Screen .......................................................................................................9
1.3.1 Speed Regulation Parameters...........................................................................................9
1.3.2 Control Parameters.........................................................................................................12
1.3.3 vector Parameters...........................................................................................................13
1.3.4 Motor Parameters...........................................................................................................15
1.3.5 Communication Parameters ...........................................................................................15
1.3.6 Sensor/Measurement Range...........................................................................................16
1.4 Real Time Data Screen .......................................................................................................16
1.4.1 System State...................................................................................................................17
1.4.2 Inverter Unit State..........................................................................................................18
1.4.3 Digital Port State............................................................................................................19
1.4.4 Analog Port State............................................................................................................20
1.4.5 Data State .......................................................................................................................21
1.4.6 Synchronoscope .............................................................................................................21
1.5 Historical Data Screen ........................................................................................................22
1.5.1 Fault History ..................................................................................................................22
1.5.2 Alarm History.................................................................................................................23
1.5.3 Operating Record ...........................................................................................................24
1.5.4 Runtime Log ..................................................................................................................24
1.6 Waveform Display Screen ..................................................................................................25
1.6.1 Instantaneous Curve.......................................................................................................25
1.6.2 Running Curve ...............................................................................................................26
1.6.3 Fault Record...................................................................................................................27
1.7 Help Screen..........................................................................................................................28
Chapter 2 Trial Run......................................................................................................................31
2.1 Trial Run Steps ....................................................................................................................31