Eleven Engineering HT-222 User manual

Table of Contents
1. Evaluation Kit Diagram
2. Evaluation Kit Setup
3. Evaluation Kit Features
4. Audio Test Method and Specications
5. RF Test Method and Specications
6. Sales and Support
1. Evaluation Kit Diagram
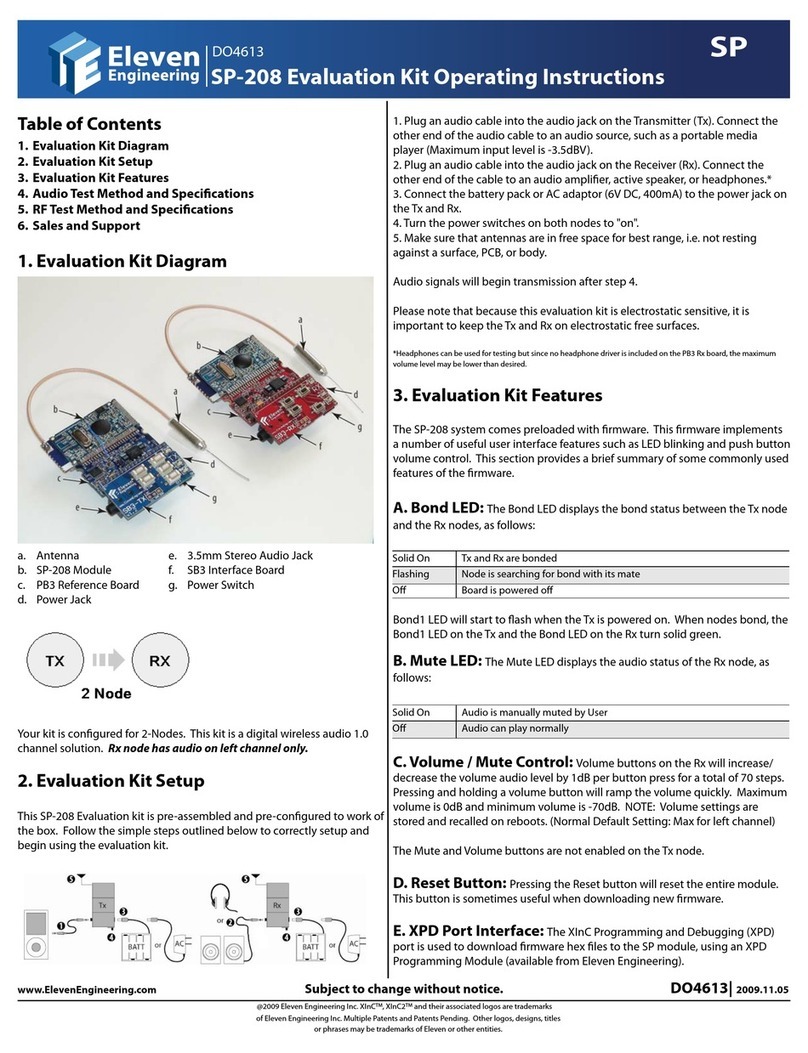
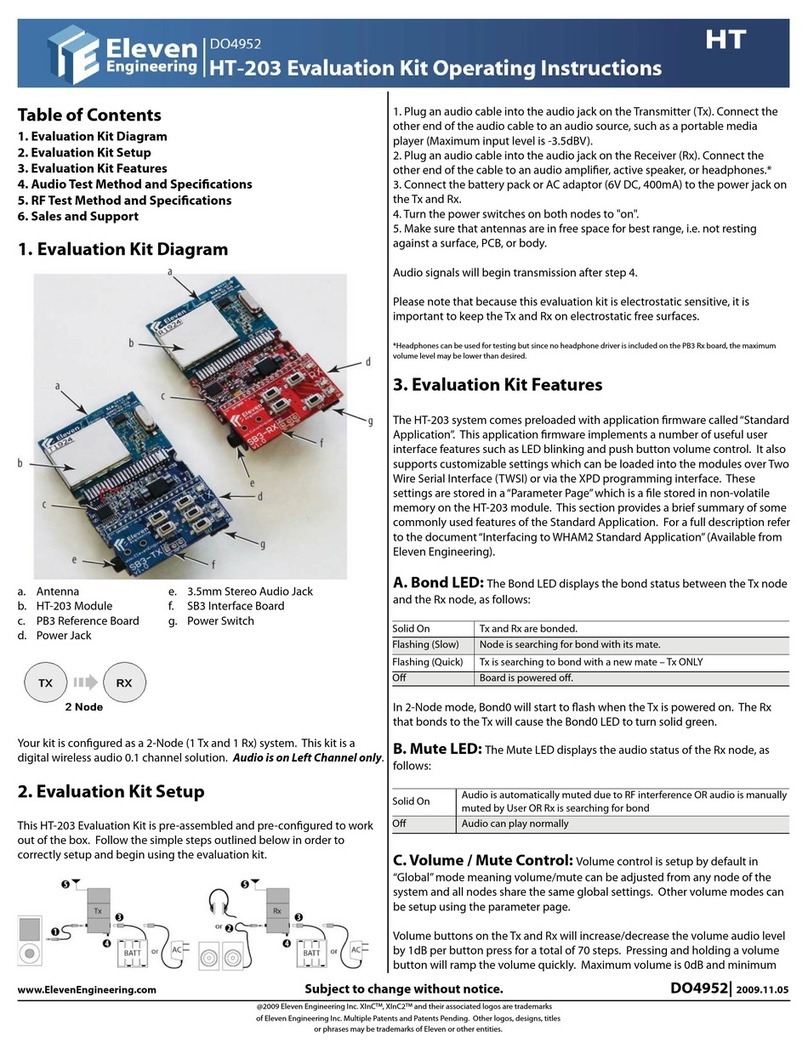
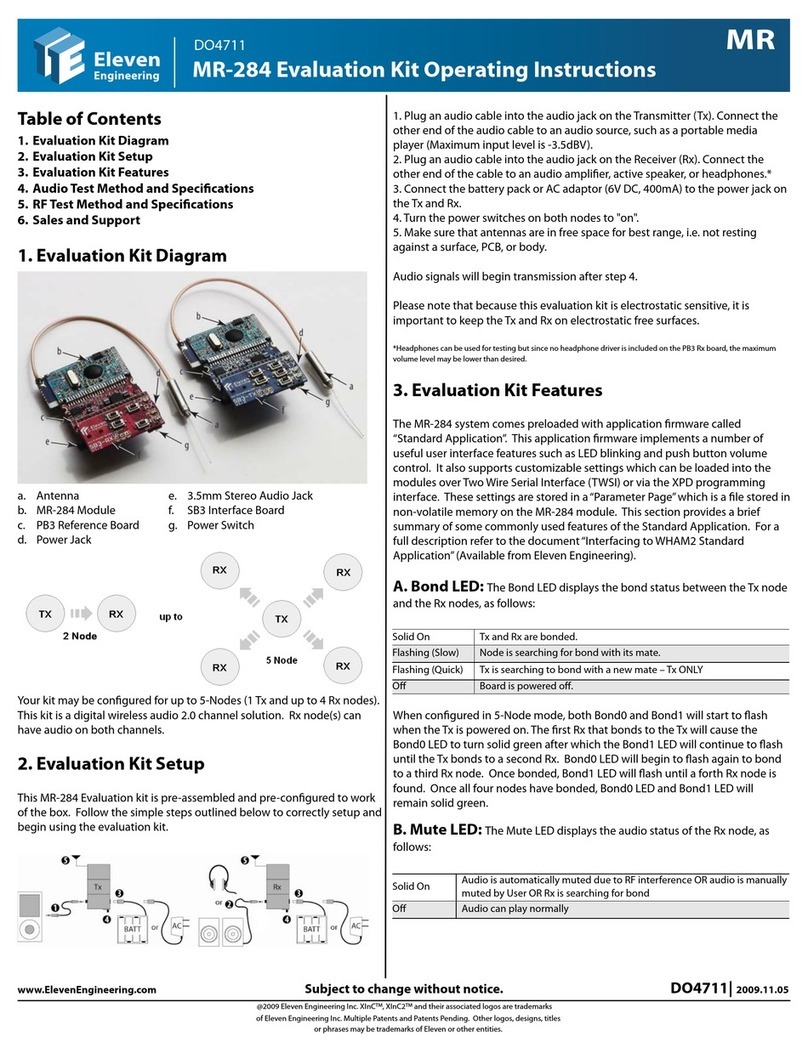
a. Antenna e. 3.5mm Stereo Audio Jack
b. HT-222 Module f. SB3 Interface Board
c. PB3 Reference Board g. Power Switch
d. Power Jack
Your kit may be congured as either 2-Node (1 Tx and 1 Rx) or 3-Node (1
Tx and 2 Rx). This kit is a digital wireless audio 2.0 channel solution. Rx
node(s) can have audio on both channels.
2. Evaluation Kit Setup
This HT-222 Evaluation Kit is pre-assembled and pre-congured to work
out of the box. Follow the simple steps outlined below in order to
correctly setup and begin using the evaluation kit.
1. Plug an audio cable into the audio jack on the Transmitter (Tx). Connect the
other end of the audio cable to an audio source, such as a portable media
player (Maximum input level is -3.5dBV).
2. Plug an audio cable into the audio jack on the Receiver (Rx). Connect the
other end of the cable to an audio amplier, active speaker, or headphones.*
3. Connect the battery pack or AC adaptor (6V DC, 400mA) to the power jack on
the Tx and Rx.
4. Turn the power switches on both nodes to "on".
5. Make sure that antennas are in free space for best range, i.e. not resting
against a surface, PCB, or body.
Audio signals will begin transmission after step 4.
Please note that because this evaluation kit is electrostatic sensitive, it is
important to keep the Tx and Rx on electrostatic free surfaces.
*Headphones can be used for testing but since no headphone driver is included on the PB3 Rx board, the maximum
volume level may be lower than desired.
3. Evaluation Kit Features
The HT-222 system comes preloaded with application rmware called “Standard
Application”. This application rmware implements a number of useful user
interface features such as LED blinking and push button volume control. It also
supports customizable settings which can be loaded into the modules over Two
Wire Serial Interface (TWSI) or via the XPD programming interface. These
settings are stored in a“Parameter Page” which is a le stored in non-volatile
memory on the HT-222 module. This section provides a brief summary of some
commonly used features of the Standard Application. For a full description refer
to the document “Interfacing to WHAM2 Standard Application”(Available from
Eleven Engineering).
A. Bond LED: The Bond LED displays the bond status between the Tx node
and the Rx node, as follows:
Solid On Tx and Rx are bonded.
Flashing (Slow) Node is searching for bond with its mate.
Flashing (Quick) Tx is searching to bond with a new mate – Tx ONLY
O Board is powered o.
When congured in 3 Node mode, both Bond0 and Bond1 will start to ash
when the Tx is powered on. The rst Rx that bonds to the Tx will cause the
Bond0 LED to turn solid green after which the Bond1 LED will continue to ash
until the Tx bonds to a second Rx. When congured in 2-Node mode only
Bond0 is functional.
B. Mute LED: The Mute LED displays the audio status of the Rx node, as
follows:
Solid On Audio is automatically muted due to RF interference OR audio is manually
muted by User OR Rx is searching for bond
O Audio can play normally
C. Volume / Mute Control: Volume control is setup by default in
“Global” mode meaning volume/mute can be adjusted from any node of the
system and all nodes share the same global settings. Other volume modes can
be setup using the parameter page.
www.ElevenEngineering.com Subject to change without notice. DO4927| 2009.11.05
@2009 Eleven Engineering Inc. XInCTM, XInC2TM and their associated logos are trademarks
of Eleven Engineering Inc. Multiple Patents and Patents Pending. Other logos, designs, titles
or phrases may be trademarks of Eleven or other entities.

Volume buttons on the Tx and Rx will increase/decrease the volume audio
level by 1dB per button press for a total of 70 steps. Pressing and holding
a volume button will ramp the volume quickly. Maximum volume is 0dB
and minimum volume is -70dB. NOTE: Volume settings are stored and
recalled on reboots. (Normal Default Setting: Max for both channels)
D. RF Mating: A Tx node and an Rx node will not connect to each
other unless they have the same 16 bit Mating ID stored in their
respective parameter pages. Out of the box, the HT evaluation kit is
already pre-mated. RF Mating is the procedure of matching (or re-
matching) the 16 bit Mating ID of 2 or more nodes.
RF Mating is usually initiated by pressing and holding the RF Mating
button on the Tx for more than 3 seconds until the Tx bond LED ashes
quickly. The Tx will then generate a 16 bit random number to use for the
new Mating ID. The Tx then attempts to mate with Rx nodes. The Rx
nodes briey enter RF mating mode every time they are powered on, so
power must be cycled on each Rx node that you want mated to the Tx. RF
Mating has a default timeout of 1 minute. If the Tx does not nd any Rx
nodes before the timeout it will terminate RF Mating mode and revert
back to the previous Mating ID. If successful mating occurs before timing
out, the number of Rx nodes that mate to the Tx will dene the new
topology after RF Mating has timed out or completed (i.e., 2-Node or 3-
Node).
E. Audio Level Standby: The Audio Level Standby Feature is
implemented on the TX node. This feature is implemented in order to
reduce power consumption when the audio level drops below a
particular threshold. When the audio level drops below this threshold for
a predetermined amount of time, the Tx sends a sleep command to the
Rx. The Rx will then enter a low power sleep mode and will wait for the
audio level to rise above the threshold. (Normal Default Setting: 78
seconds)
F. Reset Button: Pressing the Reset button will reset the entire
module. This button is sometimes useful when downloading new
rmware.
G. XPD Port Interface: The XInC Programming and Debugging
(XPD) port is used to download rmware hex les to the HT-222 module,
using an XPD Programming Module (available from Eleven Engineering).
For more information regarding the XPD Port, XPD Module, and the
procedure for programming modules refer to the document
“Downloading Firmware to XInC Processors” (Available from Eleven
Engineering).
H. Two Wire Serial Interface (TWSI): The HT system
incorporates an I2C compatible two wire control interface, used to
congure the system’s optional settings. The TWSI also provides
developers with a method to transfer data over the wireless link.
i) TWSI controls: HT settings (buer size, audio mode, mating ID,
etc.) may be programmed via TWSI; however, when these settings
are adjusted most will trigger a system reset. Some settings meant
for real time controls (volume and mute control, etc.) can be set live
without triggering a reset.
ii) Pass-through TWSI data channel: User data sent into the
audio Tx is directly output “as-is”from the audio Rx and similarly for
the reverse direction (Rx to Tx).
NOTE: When using a custom external audio chip, fundamental rmware
modications may be required to congure the chip registers. These changes
can not be done with the TWSI.
I. Parameter Pages: The HT system comes pre-loaded with a parameter
page that congures the default functionality of the system. Some of the
commonly changed registers are listed below.
Addr 00/01 Mating ID number
Addr 02 RF Conguration (RF mating, Static ID, Dynamic Mating)
Addr 03 Buer Size (Latency)
Addr 06 General Conguration (TWSI Mode, TWSI Interrupt Enabled, Sleep, Noise
Gate)
Addr 0E Audio Conguration (Stereo, Right Channel, Left Channel, Local/Global
Volume mode, l2S/Left-Justied mode)
www.ElevenEngineering.com HT-222 Evaluation Kit Instructions DO4927| 2009.11.05
Page 2/4

4. Audio Test Method and Specications
A. Test Method
Power Required 6V DC 400mA (one for Tx, one for Rx)
Rx Resistive Load 10 KΩ
Audio Analyzer Filters AES17 LPF “IN” unless otherwise specied
T
x Input Conditions 997Hz @ -3.5 dBV = Full Scale Input
Rx Output Level Maximum * (Set by Volume Control)
Distance Apart No closer than ~1 m **
Notes • Nodes should be tested on ESD safe surfaces and ideally elevated above surface on ESD safe mounts.
• Cables should be as far away as possible from equipment that can introduce noise into nodes. (i.e. CRT monitors, AC Transformers,
etc )
• Batteries can be used to eliminate 50/60Hz noise.
• The antenna orientation shown is for audio testing. A dierent antenna orientation may be better suited for maximum RF range
performance.
* Evaluation Kits are shipped with output level set to MAX.
** To avoid RF swamping.
www.ElevenEngineering.com HT-222 Evaluation Kit Instructions DO4927| 2009.11.05
Page 3/4

B. Operating Conditions and Audio Characteristics
Parameter Symbol Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
Audio Input Line Level FSI VCC=3.3V 0.668 Vrms
T
x In -3.5 dBV
Audio Output Line Level FSO = FS VCC=3.3V
0.741 Vrms
(Left/Right) Rx Out -2.59 dBV
System Gain FSI to FSO @ 997 Hz 0.91 dB
SNR A-weighted SNR Both CH RE: >92 dB FS
SNR un-weighted 997 Hz @ FS >90 dB FS
T
HD+N Left Channels THD+N 997 Hz @ -1 dB FS <0.007 %
Crosstalk 20-20kHz RE: 997 Hz @ FS <62 dB
Audio Bandwidth BW ±0.5 dB RE: 997 Hz @ FS 20 20k Hz
Pass Band Ripple
<±0.5 dB
Channel Level Di. 0.2 dB
Bonded Current Draw Tx 217 224 235 mA
Rx 115 125 130 mA
Latency * tL20 ms
Sleep Mode Rx Average Power ** PAVE 71.6 mW
All measurements conducted with AES17 LPF “IN” unless other wise specied.
* Can be customer specied and adjusted via the parameter page.
** Sleep Mode Power may be further reduced at the expense of increased wake-up time by modifying rmware.
5. RF Test Method and Specications
A. Test Method
Antenna Orientation See above diagram for orientation for maximum RF range
performance
Indoor Range* ~25 m line of sight
T
x Setup ~1.3 m high, stationary, powered with 6V DC 400mA power
adaptor
Rx Setup ~1.2 m high, mobile, powered with 4 AA batteries
Oce Space Open design with some cubicles
Oce footprint 26 m x 19 m
Notes • Antenna orientation is important to overall RF range
performance.
• Layout of the testing space aects RF performance.
Reections of the RF can cause interference.
• Obstacles such as the tester’s body, walls, and cubicles can
aect the range, wherever possible keep node antennas in
line of sight.
• Other RF devices operating in the 2.4GHz spectrum can
aect the RF performance such as microwaves, wireless
routers, and other equipment sharing the 2.4GHz band.
*Range stated is as measured in Eleven Oce Space at 20ms latency.
B. RF Characteristics & Behavior
The following RF characteristics include pertinent information for FCC, ETSI, and
ARIB STD T-66 regulations for RF devices.
Parameter Symbol Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
Raw Data Rate Rdr 1.536 Mbps
T
otal Channels CH 38 Ch
Hopping Channels CHh 20 Ch
T
X Output Power Pout 14 16 18 dBm
Antenna
Impedance ZAnt 50 Ω
Frequency Range 2.403 2.479 GHz
Indoor Range* Ri 25 m
*Range stated is as measured in Eleven Oce space at 20ms latency, customer range may vary (see Notes in Section 5A).
6. Sales and Support
Sales. Visit www.ElevenEngineering.com/Sales & Support/ to nd an Eleven
Technical Support. For all product questions and inquiries visit Eleven's online
support page at www.ElevenEngineering.com/Sales & Support/ or contact FAE
www.ElevenEngineering.com HT-222 Evaluation Kit Instructions DO4927| 2009.11.05
Page 4/4
Other Eleven Engineering Motherboard manuals
Popular Motherboard manuals by other brands
Fujitsu Siemens Computers
Fujitsu Siemens Computers D1961 Technical manual

Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments TPS62350EVM-201 user guide

Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments K2G quick start guide

Avalue Technology
Avalue Technology EBM-SKLU user manual

Renesas
Renesas RA6 Series quick start guide
ASROCK Rack
ASROCK Rack EP2C612D8HM user manual