____________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________
4 TAU-4M.IP Subscriber gateway
TABLE OF CONTENTS
INTRODUCTION ............................................................................................................................................... 6
1 PRODUCT DESCRIPTION ............................................................................................................................. 7
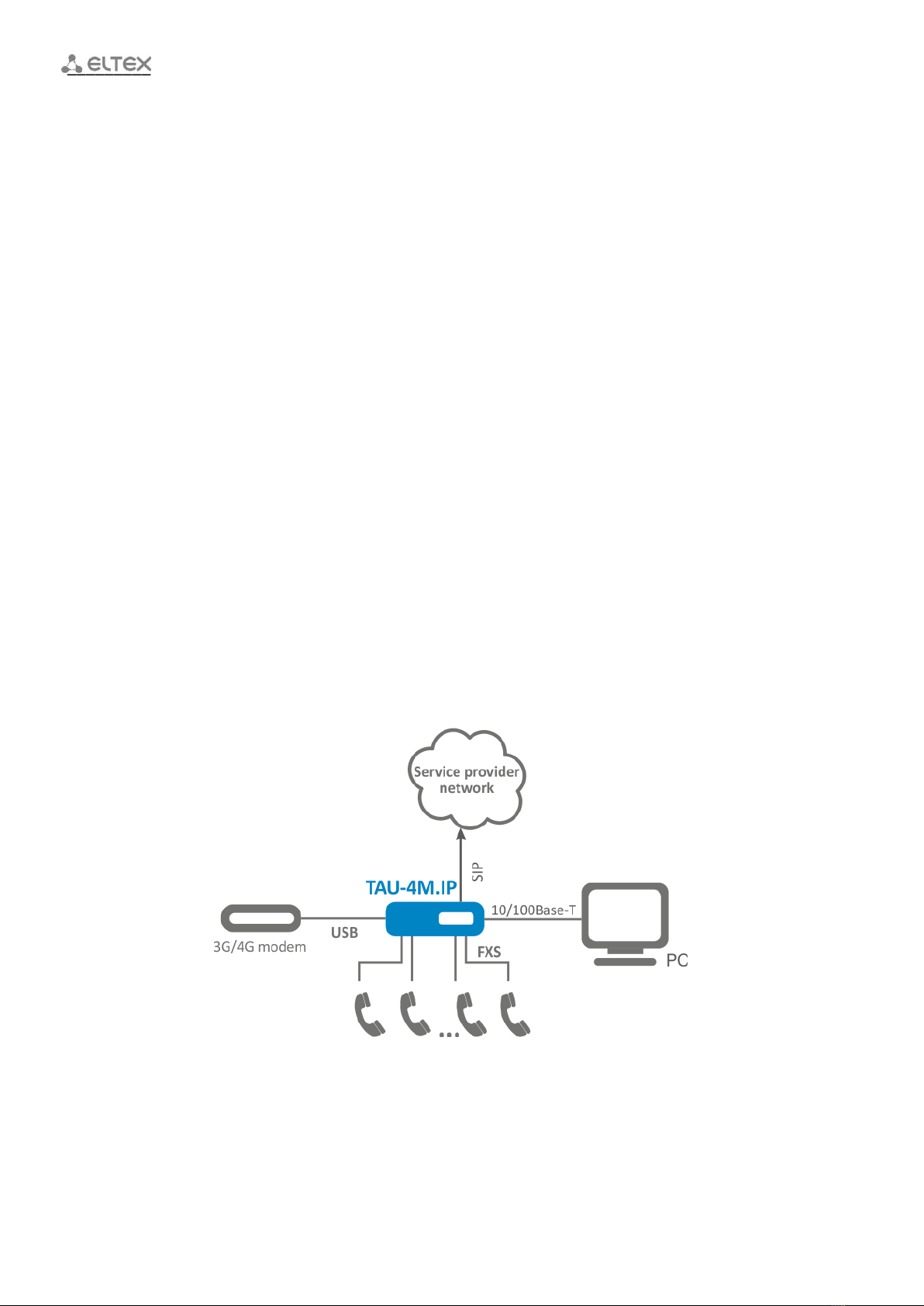
1.1 Purpose............................................................................................................................................... 7
1.2 Device specification............................................................................................................................ 7
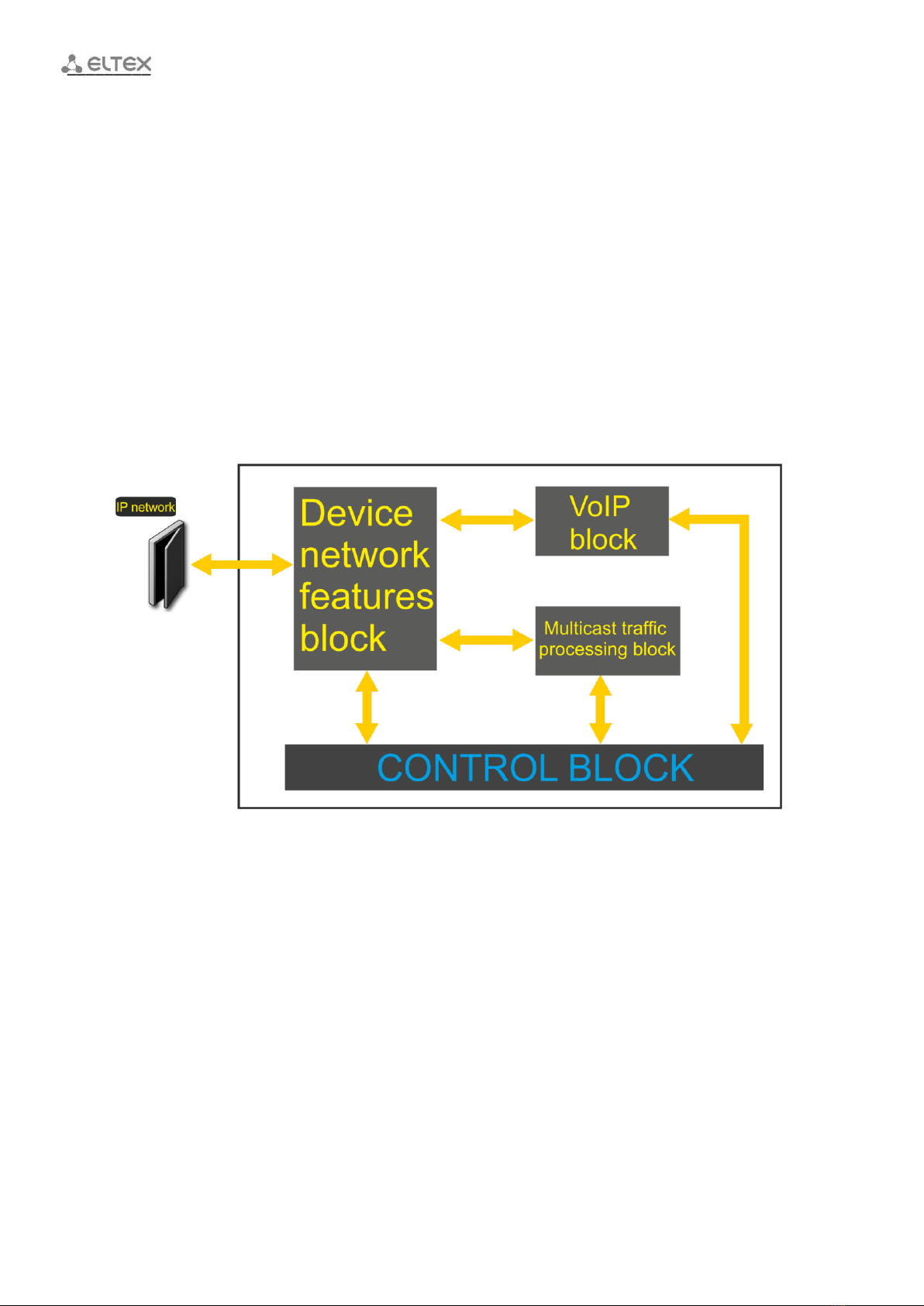
1.3 Device Design and Operating Principle .............................................................................................. 9
1.4 Main Specifications........................................................................................................................... 11
1.5 Design ............................................................................................................................................... 12
1.5.1 Top panel of the device .......................................................................................................... 12
1.5.2 Rear panel of the device ......................................................................................................... 13
1.6 Light indication ................................................................................................................................. 13
1.7 Reset to factory settings................................................................................................................... 14
1.8 Delivery Package............................................................................................................................... 14
2 DEVICE MANAGEMENT VIA WEB CONFIGURATOR..................................................................................15
2.1 Getting started.................................................................................................................................. 15
2.2 Changing users.................................................................................................................................. 15
2.3 WEB interface operation modes ...................................................................................................... 16
2.4 Applying and discarding changes made to configuration ................................................................ 17
2.4.1 Applying configuration............................................................................................................ 17
2.4.2 Discarding changes ................................................................................................................. 17
2.5 ‘Quick configuration’ menu.............................................................................................................. 18
2.5.1 Internet................................................................................................................................... 18
2.5.2 VoIP......................................................................................................................................... 21
2.5.3 IPTV......................................................................................................................................... 22
2.5.4 System..................................................................................................................................... 22
2.6 Advanced settings............................................................................................................................. 23
2.6.1 WEB interface basic elements ................................................................................................ 23
2.6.2 'Network' menu ...................................................................................................................... 23
2.6.3 'VoIP' menu............................................................................................................................. 45
2.6.4 'IPTV' menu............................................................................................................................. 74
2.6.5 'System' menu......................................................................................................................... 75
2.7 System Monitoring ........................................................................................................................... 94
2.7.1 'Internet' submenu ................................................................................................................. 94
2.7.2 'VoIP' submenu ....................................................................................................................... 95
2.7.3 'Ethernet Ports' submenu....................................................................................................... 98
2.7.4 'DHCP' submenu ..................................................................................................................... 99
2.7.5 'ARP' submenu........................................................................................................................ 99
2.7.6 'Device' submenu.................................................................................................................. 100
2.7.7 'CPU' submenu...................................................................................................................... 100
2.7.8 'Conntrack' submenu............................................................................................................ 101
2.7.9 'Routes' submenu ................................................................................................................. 102
2.7.10 'Call History' submenu ....................................................................................................... 103
2.7.11 ‘Diagnostics’ submenu....................................................................................................... 104
2.8 Configuration example ................................................................................................................... 105
3 VALUE ADDED SERVICES USAGE ............................................................................................................108
3.1 Call Transfer.................................................................................................................................... 108
3.2 Call Waiting..................................................................................................................................... 111
3.3 Three-way conference.................................................................................................................... 111
3.3.1 Local conference................................................................................................................... 111
3.3.2 Remote conference .............................................................................................................. 113
4 CONNECTION ESTABLISHMENT ALGORITHMS....................................................................................... 114
4.1 Algorithm of a Successful Call via SIP Protocol............................................................................... 114
4.2 Call Algorithm Involving SIP Proxy Server....................................................................................... 115