731B
a. RemoVethe to pCOve rfroiri the73iBa n d1oc ate
the input power selection switch on the inside of
the 73 IB.
b. Set the slide switch to the desired operating vol-
tage, 115(white dot) or 230 (red dot).
c. Install the proper fuse (i.e., AGC ViK for 115V ac
and AGC %A for 230V ac) in the rear panel fuse
holder.
2-8. The rear panel input power connector is athree
prong, U-ground connector which permits the in-
strument to be connected, via the power cord, to
the appropriate line power. The offset prong on
this connector is connected to the 73 IB chassis
and power supply, and should be connected, via
the power cord, to ahigh quality earth ground.
2-9. RACK INSTALLATION
2-10, The 73 1Bis designed for bench-top use or for in-
stallation in astandard 19-inch equipment rack, using one
of the optional accessory rack mounting kits. Information
regarding rack installation procedures is given in Section 6
of this manual.
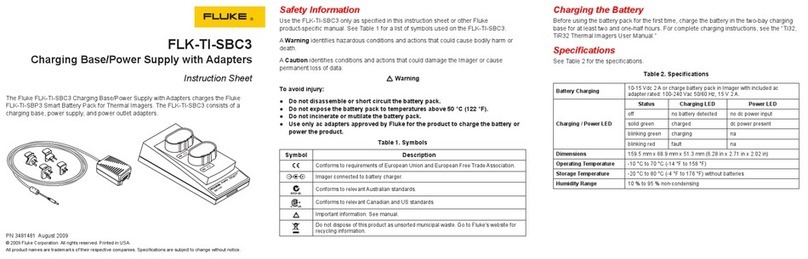
2-11. OPERATING FEATURES
2-12. The 731 Bcontrols, indicators and connectors
are shown in Figure 2-1, and described in Table 2-1.
2-13. OPERATING NOTES
2-14, The following paragraphs describe various condi-
tions which .should be considered before operating the 73 IB.
2-15. Guarded Operation
2-1 6, The 73 IB is equipped with aguard that isolates its
internal circuitry from the chassis and earth ground. A
GUARD terminal is provided on the Torntpanel, and when
used, greatly reduces errors caused by common mode vol-
tages. In general, guarded operation will be necessary under
the following conditions:
a. Wlren apotential exists between equipment power
line grounds.
b. Wlien long connecting leads are used to contact a
higli impedance load.
2-2
Figure 2-1. 731 BCONTROLS, INDICATORS AND CONNECTORS