Fortec Star Diamond Systems DS-MPE-CAN2L User manual

The information contained in this document has been carefully researched and is, to the best of our
knowledge, accurate. However, we assume no liability for any product failures or damages, immediate or
consequential, resulting from the use of the information provided herein. Our products are not intended for
use in systems in which failures of product could result in personal injury. All trademarks mentioned herein
are property of their respective owners. All specifications are subject to change without notice.
Manual
Diamond Systems
DS-MPE-CAN2L
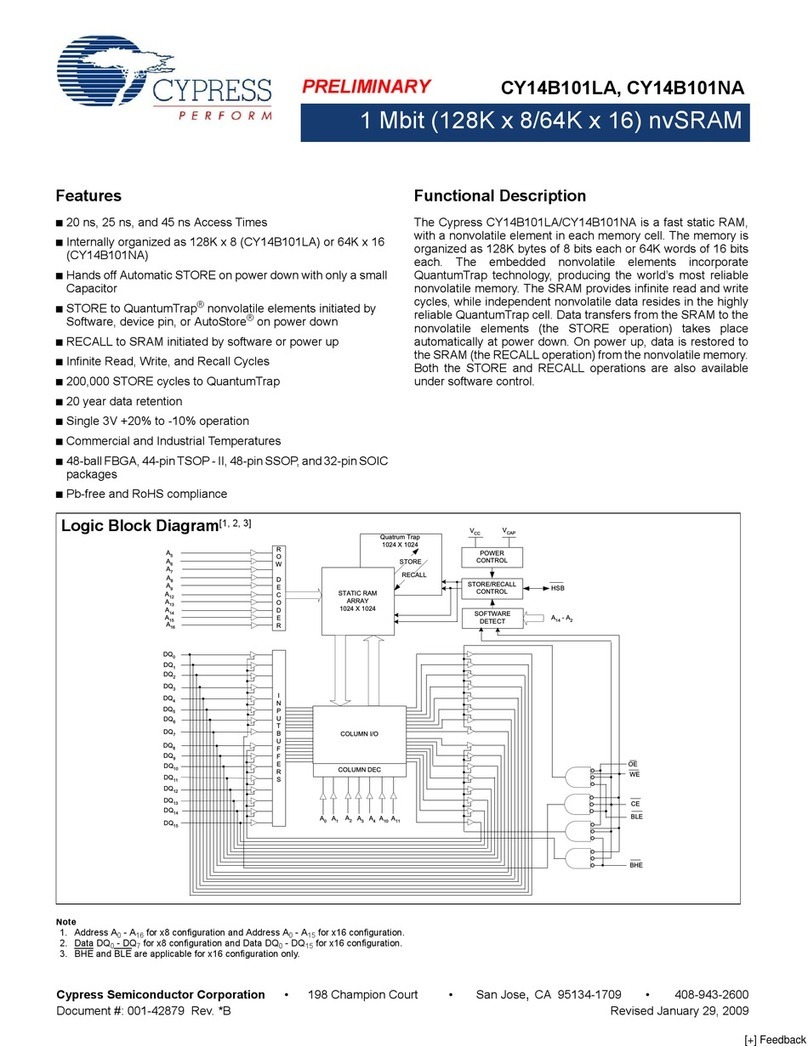
PCIe MiniCardI/O Expansion Module with Dual CANbus Ports

DS-MPE-CAN2L
PCIe MiniCard Dual CAN 2.0 Port Module
Rev A.1 April 2015
Revision
Date
Comment
A.0
4/25/2014
Initial release
A.1
4/09/2015
Updated Windows installation procedure
Copyright 2015
FOR TECHNICAL SUPPORT Diamond Systems Corporation
PLEASE CONTACT: 555 Ellis Street
Mountain View, CA 94043 USA
support@diamondsystems.com Tel 1-650-810-2500
Fax 1-650-810-2525
www.diamondsystems.com

DS-MPE-CAN2L User Manual Rev A.1 www.diamondsystems.com Page 2
CONTENTS
1. Important Safe Handling Information .............................................................................................................3
2. Introduction .......................................................................................................................................................4
2.1 Description.....................................................................................................................................................4
2.2 Features.........................................................................................................................................................4
2.3 Operating System Support ............................................................................................................................4
2.4 Mechanical, Electrical, Environmental...........................................................................................................4
3. Packing List.......................................................................................................................................................4
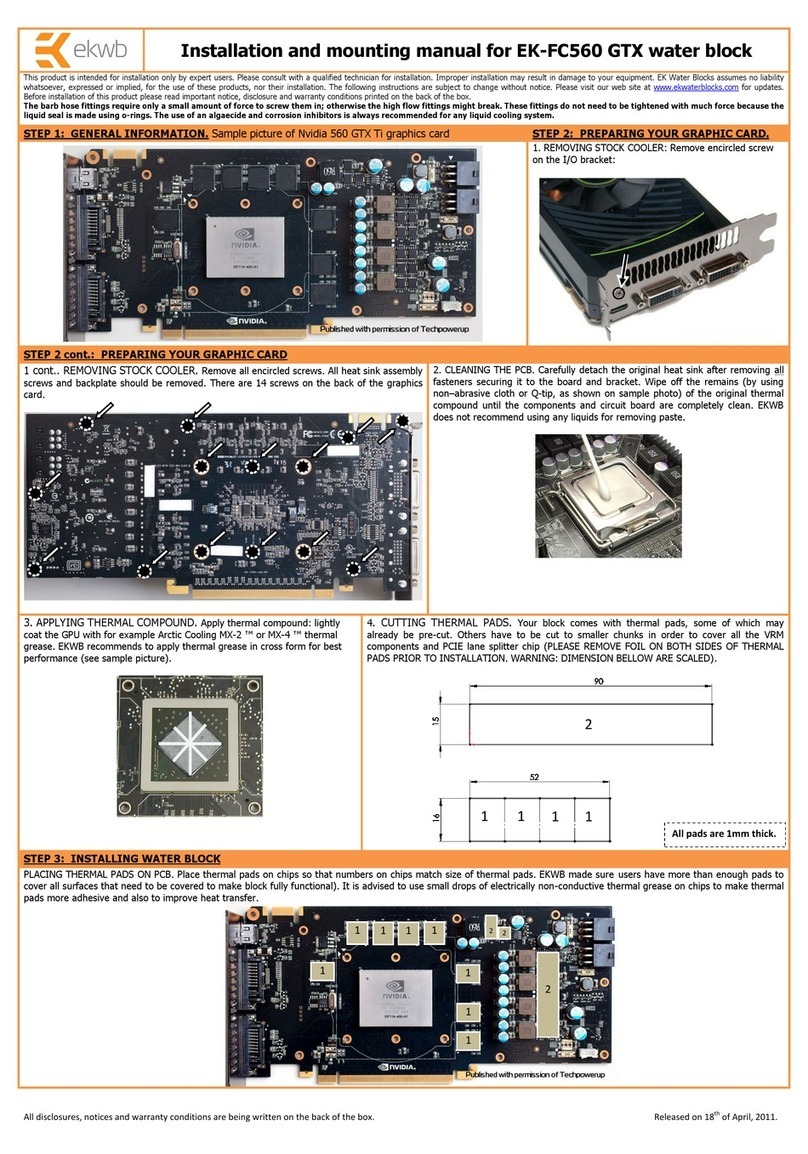
4. Functional Overview.........................................................................................................................................5
4.1 Functional Block Diagram..............................................................................................................................5
4.2 Mechanical Board Drawing............................................................................................................................6
4.3 CAN Controllers.............................................................................................................................................6
4.4 Transceivers ..................................................................................................................................................7
4.5 Isolation .........................................................................................................................................................7
4.6 Power Supply.................................................................................................................................................7
5. Installation .........................................................................................................................................................7
6. Connector Pinout and Pin Description...........................................................................................................8
6.1 PCIe MiniCard Edge Connector (J1).............................................................................................................8
6.2 CAN Ports (J4, J7).........................................................................................................................................8
7. Jumper Configuration ......................................................................................................................................9
8. Linux Driver installation................................................................................................................................ 10
8.1 Installing the Software ................................................................................................................................ 10
8.2 Setting the Baud Rate ................................................................................................................................ 11
8.3 Setting the CAN ID and Message Length .................................................................................................. 12
8.4 Writing a Message...................................................................................................................................... 13
8.5 Viewing Messages...................................................................................................................................... 14
9. Configure and Manage the Ports in Linux .................................................................................................. 16
9.1 API to Configure and Manage CAN Ports .................................................................................................. 16
9.2 Compiling User Application using CANLib Library ..................................................................................... 19
10. Driver installation and Demo Application for Windows............................................................................. 20
10.1 Installing the PCI-CAN Driver ..................................................................................................................... 20
10.2 Run the Windows Application..................................................................................................................... 24
10.3 Setting the Baud Rate ................................................................................................................................ 25
10.4 Setting the CAN ID and Message Length .................................................................................................. 26
10.5 Writing a Message...................................................................................................................................... 27
10.6 Viewing Messages...................................................................................................................................... 28
11. API to Configure and Manage CAN Ports on Windows ............................................................................. 29
12. Specifications................................................................................................................................................. 33

DS-MPE-CAN2L User Manual Rev A.1 www.diamondsystems.com Page 3
1. IMPORTANT SAFE HANDLING INFORMATION
WARNING!
ESD-Sensitive Electronic Equipment
Observe ESD-safe handling procedures when working with this product.
Always use this product in a properly grounded work area and wear appropriate
ESD-preventive clothing and/or accessories.
Always store this product in ESD-protective packaging when not in use.
Safe Handling Precautions
This board contains a high density connector with many connections to sensitive electronic components. This
creates many opportunities for accidental damage during handling, installation and connection to other
equipment. The list here describes common causes of failure found on boards returned to Diamond Systems for
repair. This information is provided as a source of advice to help you prevent damaging your Diamond (or any
vendor’s) embedded computer boards.
ESD damage –This type of damage is usually almost impossible to detect, because there is no visual sign of
failure or damage. The symptom is that the board eventually simply stops working, because some component
becomes defective. Usually the failure can be identified and the chip can be replaced. To prevent ESD damage,
always follow proper ESD-prevention practices when handling computer boards.
Damage during handling or storage –On some boards we have noticed physical damage from mishandling. A
common observation is that a screwdriver slipped while installing the board, causing a gouge in the PCB surface
and cutting signal traces or damaging components.
Another common observation is damaged board corners, indicating the board was dropped. This may or may not
cause damage to the circuitry, depending on what is near the corner. Most of our boards are designed with at
least 25 mils clearance between the board edge and any component pad, and ground / power planes are at least
20 mils from the edge to avoid possible shorting from this type of damage. However these design rules are not
sufficient to prevent damage in all situations.
A third cause of failure is when a metal screwdriver tip slips, or a screw drops onto the board while it is powered
on, causing a short between a power pin and a signal pin on a component. This can cause overvoltage / power
supply problems described below. To avoid this type of failure, only perform assembly operations when the
system is powered off.
Sometimes boards are stored in racks with slots that grip the edge of the board. This is a common practice for
board manufacturers. However our boards are generally very dense, and if the board has components very close
to the board edge, they can be damaged or even knocked off the board when the board tilts back in the rack.
Diamond recommends that all our boards be stored only in individual ESD-safe packaging. If multiple boards are
stored together, they should be contained in bins with dividers between boards. Do not pile boards on top of each
other or cram too many boards into a small location. This can cause damage to connector pins or fragile
components.
Power supply wired backwards –Our power supplies and boards are not designed to withstand a reverse
power supply connection. This will destroy each IC that is connected to the power supply (i.e. almost all ICs). In
this case the board will most likely will be unrepairable and must be replaced. A chip destroyed by reverse power
or by excessive power will often have a visible hole on the top or show some deformation on the top surface due
to vaporization inside the package. Check twice before applying power!
Overvoltage on digital I/O line –If a digital I/O signal is connected to a voltage above the maximum specified
voltage, the digital circuitry can be damaged. On most of our boards the acceptable range of voltages connected
to digital I/O signals is 0-5V, and they can withstand about 0.5V beyond that (-0.5 to 5.5V) before being damaged.
However logic signals at 12V and even 24V are common, and if one of these is connected to a 5V logic chip, the
chip will be damaged, and the damage could even extend past that chip to others in the circuit

DS-MPE-CAN2L User Manual Rev A.1 www.diamondsystems.com Page 4
2. INTRODUCTION
2.1 Description
DS-MPE-CAN2L implements a CAN protocol bus controller that performs serial communications according to the
CAN 2.0A and CAN 2.0B specifications. The protocol uses a multi-master bus configuration for the transfer of
frames between nodes of the network and manages error handling with no burden on the host processor.
2.2 Features
2 CAN 2.0B ports with a 1Mbps data rate and programmable interrupts
31 receive buffers for improved performance
1 high priority transmit buffer and 16 standard priority transmit buffers
16 programmable acceptance filters
11-bit and 29-bit identifiers
500V port-to-port and input-to-output isolation
Driver supports dual-independent and dual-redundant modes
Latching connectors for increased ruggedness
2.3 Operating System Support
Linux 2.6.16, 2.6.27, 2.6.31 and 2.6.32
Windows 7
2.4 Mechanical, Electrical, Environmental
PCIe MiniCard full size format
Dimensions: 50.95mm x 30mm (2” x 1.18”)
-40°C to +85°C ambient operating temperature
Power input requirements: +3.3VDC +/- 5%
3. PACKING LIST
The DS-MPE-CAN2L product comes with the PCIe MiniCard hardware assembly,
a cable kit with two dual serial cables, and a hardware kit containing jumpers
and mounting screws.
Quantity
Part Number
Description
1
9150500
DS-MPE-CAN2L hardware assembly
1
6800500
Hardware Kit with jumpers and screws
1
CK-CAN2L
Cable Kit with two CAN cables

DS-MPE-CAN2L User Manual Rev A.1 www.diamondsystems.com Page 5
4. FUNCTIONAL OVERVIEW
4.1 Functional Block Diagram
The DS-MPE-CAN2L block diagram is shown below.

DS-MPE-CAN2L User Manual Rev A.1 www.diamondsystems.com Page 6
4.2 Mechanical Board Drawing
The DS-MPE-CAN2L conforms to the PCIe MiniCard electromechanical specification revision 1.2, full size format.
Overall dimensions are 50.95mm L x 30.00mm W.
The two mounting holes are isolated from the CPU ground and not connected to any ground lines.
4.3 CAN Controllers
The module offers two CAN controllers implemented as FPGA cores inside a Xilinx Spartan 6 FPGA. The core
provides the following key features:
Conforms to the ISO 11898 -1, CAN 2.0A, and CAN 2.0B standards
Supports both standard (11-bit identifier) and extended (29-bit identifier) frames
Supports bit rates up to 1Mbps
Transmit message FIFO with a user-configurable depth of up to 64 messages
Transmit prioritization through one High-Priority Transmit buffer
Automatic re-transmission on errors or arbitration loss
Receive message FIFO with a user-configurable depth of up to 64 messages
Acceptance filtering with a user-configurable number of up to 16 acceptance filters
Sleep Mode with automatic wake-up
Loop Back Mode for diagnostic applications
Maskable Error and Status Interrupts
Readable Error Counters

DS-MPE-CAN2L User Manual Rev A.1 www.diamondsystems.com Page 7
4.4 Transceivers
The transceivers are Analog Devices ADM3053 combination isolation and transceiver. It provides isolated +5V to
power the isolated side of the transceiver. This isolated +5V is available on the I/O connector.
4.5 Isolation
The module supports 500V isolation between each CAN port and the host, and between each CAN port and the
other, via the ADM3053 isolated transceiver. An optional high-voltage resistor can be installed across each
isolation barrier to enable leakage current flow between the isolated transceiver grounds and the host ground.
4.6 Power Supply
The module is powered by +3.3V from the PCIe MiniCard socket. It provides all other required voltages on board,
including +5V for the CAN transceivers and the FPGA core voltages.
5. INSTALLATION
The DS-MPE-CAN2L plugs in to any socket meeting the PCIe MiniCard specifications. It has two connectors,
one for each pair of serial ports, a protocol configuration jumper block, and a pair of mounting holes. To install the
DS-MPE-CAN2L, fully insert the board into a PCIe MiniCard connector and secure in place by inserting one screw
from the hardware kit into each of the mounting holes, see the diagram below.
J1 PCIe MiniCard edge finger connector
Mounting holes
J3 termination jumper block
J7 CAN connector
J6 termination jumper block
J4 CAN connector

DS-MPE-CAN2L User Manual Rev A.1 www.diamondsystems.com Page 8
6. CONNECTOR PINOUT AND PIN DESCRIPTION
6.1 PCIe MiniCard Edge Connector (J1)
The DS-MPE-CAN2L module is compatible with the standard Mini PCIe socket pinout as shown below.
WAKE#
1
2
+3.3VAUX_3
COEX1
3
4
GND9
COEX2
5
6
+1.5V_1
CLKREQ#
7
8
UIM_PWR
GND1
9
10
UIM_DATA
REFCLK-
11
12
UIM_CLK
REFCLK+
13
14
UIM_RESET
GND2
15
16
UIM_VPP
KEY
RSVD(UIM_C8)
17
18
GND10
RSVD(UIM_C4)
19
20
W_DISABLE#
GND3
21
22
PERST#
PERN0
23
24
+3.3VAUX_4
PERP0
25
26
GND11
GND4
27
28
+1.5V_2
GND5
29
30
SMB_CLK
PETN0
31
32
SMB_DATA
PETP0
33
34
GND12
GND6
35
36
USB_D-
GND7
37
38
USB_D+
+3.3VAUX_1
39
40
GND13
+3.3VAUX_2
41
42
LED_WWAN#
GND8
43
44
LED_WLAN#
RSVD1
45
46
LED_WPAN#
RSVD2
47
48
+1.5V_3
RSVD3
49
50
GND14
RSVD4
51
52
+3.3VAUX_5
6.2 CAN Ports (J4, J7)
Each of the two CAN ports has its own 4-pin latching connector with the following pin out.
1
Ground Iso
2
CAN L
3
CAN H
4
Ground Iso
Connector Part Number / Description
BM04B-GHS-TBT 4 pos, 1.25mm, vertical, latching, SMD

DS-MPE-CAN2L User Manual Rev A.1 www.diamondsystems.com Page 9
7. JUMPER CONFIGURATION
The DS-MPE-CAN2L module has two line termination jumper blocks, one for each port. Jumper block J3 is for
port J4, and jumper block J6 is for port J7. Jumper blocks J3 and J6 are identical. The default is no jumpers
installed. To add termination for a port’s bias line (jumper position B), CAN-H line (jumper position H), or CAN-L
line (jumper position L), add a jumper at B, H or L location respectively.
B
H
L
O
O
O
O
O
O

DS-MPE-CAN2L User Manual Rev A.1 www.diamondsystems.com Page 10
8. LINUX DRIVER INSTALLATION
8.1 Installing the Software
The following steps are used to install the CAN interface utility software under the Linux operating system.
Step-1:
Download the DSC_CAN2L_PCI_LINUX_V1.7.zip file from the DS-MPE-CAN2L webpage
(http://www.diamondsystems.com/products/dsmpecan2l). Click on Linux driver package v1.0.7 in the Downloads
section of the webpage. Use the following command to unzip the files:
Unzip DSC_CAN2L_PCI_LINUX_V1.7.zip
A DSC_CAN2L_PCI_LINUX_V1.7 directory will be created where the zip file is extracted. The
DSC_CAN2L_PCI_LINUX_V1.7 directory contains the following files.
ls –l
1. CAN_Monitor : CAN Monitor demo application directory
2. CANLib : CAN Linux shared library.
3. dsc_can2_pci_driver: Linux CAN driver.
4. qt-opensource-linux-x86-5.2.1.run : Qt Installer which is required by the PCI CAN Interface utility.
Step-2:
Install the Qt shared libraries using the Qt Installer. Execute the command below and follow the Qt Installer
instructions. Use the command below to install the Qt shared libraries. Install Qt at the default locations.
cd DSC_CAN2L_PCI_LINUX_V1.7
./qt-opensource-linux-x86-5.2.1.run
Note: The Qt shared libraries should be installed only once.
Step-3:
PCI CAN Utility is based on the CANLib library. Copy the shared library to “/lib” directory.
cd CANLib
cp libCAN.so /lib
Please note : Step-3 should be done only once.
Step-4:
Load the PCI CAN interface driver using the command below from the dsc_can2_pci_driver directory where the
zip file is extracted.
cd dsc_can2_pci_driver
insmod dsc_can2_pci.ko
Step-5:
Start the PCI CAN Utility using the command below from the CAN_Monitor directory where the zip file is
extracted.
cd CAN_monitor
./CAN

DS-MPE-CAN2L User Manual Rev A.1 www.diamondsystems.com Page 11
This command will open the CAN interface utility. To start the CAN utility in the future, follow Steps 4 and 5 only.
8.2 Setting the Baud Rate
Using the CAN interface utility software, the baud rate for each port can be selected. On the desired CAN port,
select the baud rate from the Baud Rate drop-down menu. After selecting the desired baud rate, press “Connect”
to connect with specified baud rate as shown in below figure.
To change the baud rate, click on “Disconnect” and select a new baud rate.

DS-MPE-CAN2L User Manual Rev A.1 www.diamondsystems.com Page 12
8.3 Setting the CAN ID and Message Length
Set the CAN ID and CAN message length for each CAN port by entering the desired numbers into the ID and Len
fields respectively for that port.

DS-MPE-CAN2L User Manual Rev A.1 www.diamondsystems.com Page 13
8.4 Writing a Message
To write a message on a CAN port, define the CAN message by entering the desired data into the Data (Hex)
fields. Then click on “Write Message” as shown in the below figure.
To transmit to a different CAN ID, change the data in the CAN ID field, enter the desired data into the Data (Hex)
fields, and click on “Write Message”.
To change the message length, change the CAN message length to the new length, enter the desired data into
the Data (Hex) fields, and click on “Write Message”.
To transmit a different CAN message to the same CAN ID, change the CAN message to the desired data, and
click on “Write Message”.

DS-MPE-CAN2L User Manual Rev A.1 www.diamondsystems.com Page 14
8.5 Viewing Messages
Transmitted messages are listed in the CAN message box for the sending CAN port as shown in below figure.

DS-MPE-CAN2L User Manual Rev A.1 www.diamondsystems.com Page 15
Received CAN messages are listed in the CAN message box for the CAN port receiving the message as shown
in below figure.

DS-MPE-CAN2L User Manual Rev A.1 www.diamondsystems.com Page 16
9. CONFIGURE AND MANAGE THE PORTS IN LINUX
The CANLib library provides the set of APIs to configure and manage the CAN ports. The CANLib library can be
used to build the CAN user application. It is a shared library built on top of Linux platform and using the driver
provided functionality. To compile the CANLib shared library, use the below command
cd CANLib
make
All the CAN APIs prototypes are defined in the can.h file. This file is located in the CANLib directory. Include the
can.h file in the user application to use all these APIs.
9.1 API to Configure and Manage CAN Ports
init_can0() & init_can1() : These function will initialize the CAN#0 & CAN#1 ports respectively.
Both these functions return the CAN file descriptor (fd). The return value of these functions should be retained
for all subsequent APIs. Its prototypes are defined in the can.h file. Declare two CAN file descriptors and
retains its return values.
#include “can.h”
…
int can0_fd;
int can1_fd;
…
can0_fd = init_can0() ;
if ( can0_fd < 0 )
{
printf("Error while initializing the CAN#0\n") ;
exit(0) ;
}
…
can1_fd = init_can1() ;
if ( can1_fd < 0 )
{
printf("Error while initializing the CAN#1\n") ;
exit(0) ;
}

DS-MPE-CAN2L User Manual Rev A.1 www.diamondsystems.com Page 17
Baud Rate Configuration
set_baudrate() : This function configures the baud rate for the specified CAN port. By default it will not
configure any baud rate. Below code snippet describes the usage of setting baud rate to 500kbps.
// Set 500k Baud rate for CAN#0
ret_val = set_baudrate(can0_fd, CAN_SPEED_500K ) ;
if ( ret_val < 0 )
{
printf("Error while setting the baud rate \n") ;
exit(0) ;
}
// Set 500k Baud rate for CAN#1
ret_val = set_baudrate(can1_fd, CAN_SPEED_500K ) ;
if ( ret_val < 0 )
{
printf("Error while setting the baud rate \n") ;
exit(0) ;
}
In the above code, can0_fd and can1_fd should contain the values returned by
init_can0 and init_can1 function.
Use below macros for setting the different baud rates. These macros can also be
found in can.h file.
CAN_SPEED_1M
CAN_SPEED_800K
CAN_SPEED_500K
CAN_SPEED_250K
CAN_SPEED_125K
CAN_SPEED_100K
CAN_SPEED_50K
CAN_SPEED_20K
CAN_SPEED_10K
CAN Transmit & Receive
can_tx() & can_rx() : These functions are be used to Transmit and Receive the CAN messages respectively.

DS-MPE-CAN2L User Manual Rev A.1 www.diamondsystems.com Page 18
CAN Transmit Prototype
int can_tx( int can_fd, unsigned char msgType, unsigned int can_id, int
len,unsigned char *data) ;
Assign the appropriate values, before calling the can_tx function.
can0_fd: CAN descriptor, return value from init_can0() function
msgType = MSG_STANDARD ; // or MSG_EXTENDED.
can_id = 0x12;
//if the msgType is MSG_STANDARD then can_id value should be in the range of 0x0 to
0x7FF (11 bit value)
//Else if the msgType is MSG_EXTENDED then can_id value should be in the range 0x0
to 0x1FFFFFFF (29 bit value)
len = 4 //This field can be of 0 to 8 ; // CAN Transmit Data Length (DLC)
data: This field depends on the above CAN Data length len field.
In this case, len is 4 then the CAN message data will be of 4 bytes long and each
byte can have values from 0x0 to 0xFF (8-bits )
data[0] = 0x1A ;
data[1] = 0xAB ;
data[2] = 0x22 ;
data[3] = 0x4D ;
ret_val = can_tx(can0_fd, msgType, can_id, dlc, data) ;
if ( ret_val < 0 )
{
printf("Error while transmitting the CAN message.\n") ;
close(can1_fd) ;
exit(0) ;
}
The above sample code will transmit the CAN standard message with CAN ID=0x12 of data length=4 and
message data = {0x1A, 0xAB, 0x22, 0x4D};
Table of contents
Other Fortec Star Computer Hardware manuals
Popular Computer Hardware manuals by other brands

Intel
Intel BX80605X3440 - Quad Core Xeon X3440 Reference

National Instruments
National Instruments NI 9263 Getting started

Lantronix
Lantronix XPort user guide
NXP Semiconductors
NXP Semiconductors MSC8113 Reference manual

Sun Microsystems
Sun Microsystems Sun Fire Cabinet Installation and reference manual

Intel
Intel NUC 11 Pro Kit NUC11TNKv7 user guide

CalDigit
CalDigit RAID Card Getting started

Advantech
Advantech ROM-5722 user manual

National Instruments
National Instruments Compact FieldPoint Mounting Accessories... quick start guide

Koolance
Koolance EX2-755 user manual

Help Tech
Help Tech Handy Tech Active Star user manual
Sierra Wireless
Sierra Wireless AirCard 59 Series quick start guide