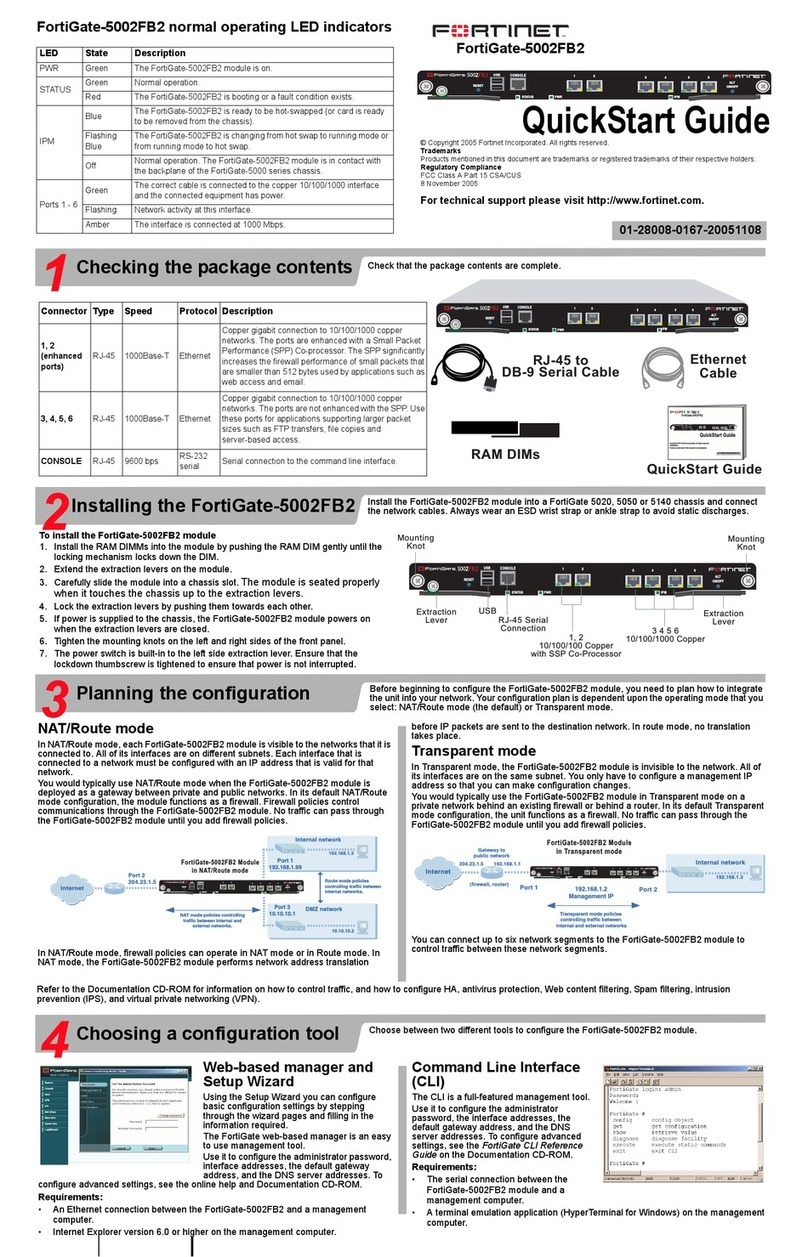
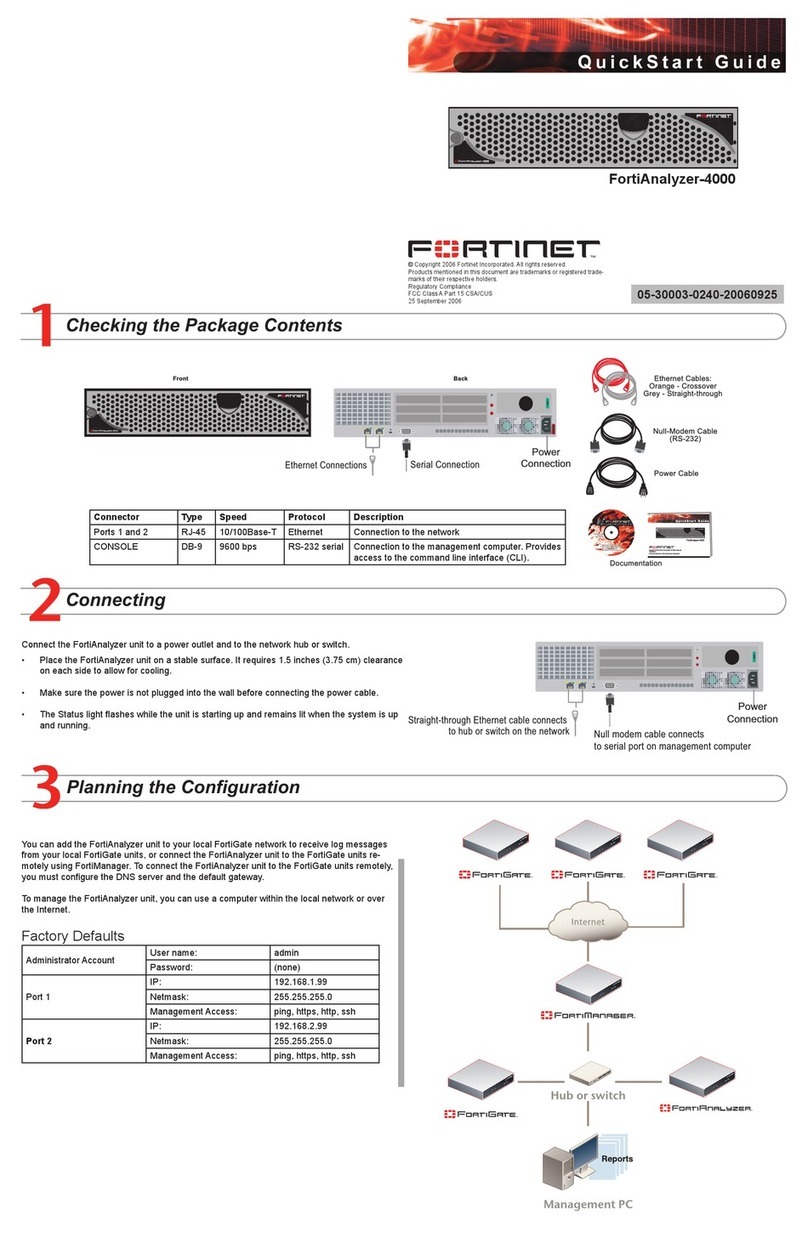
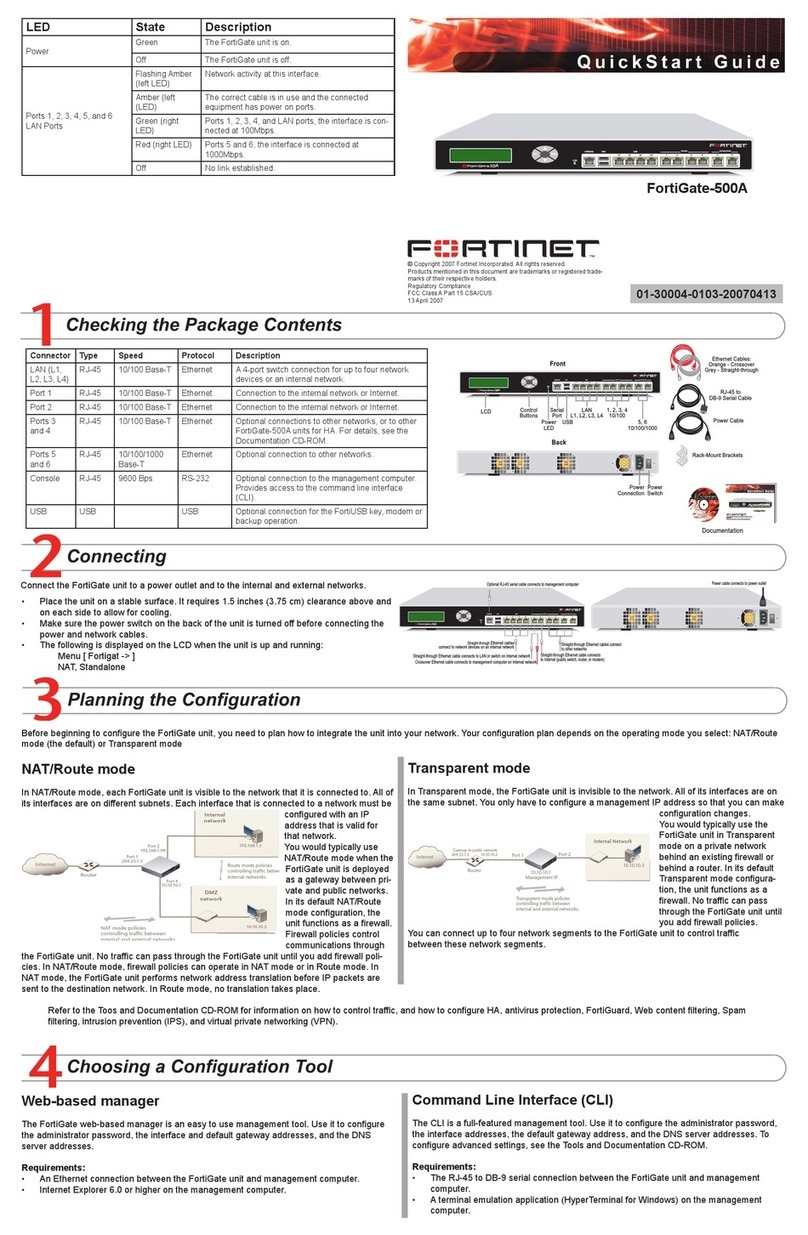
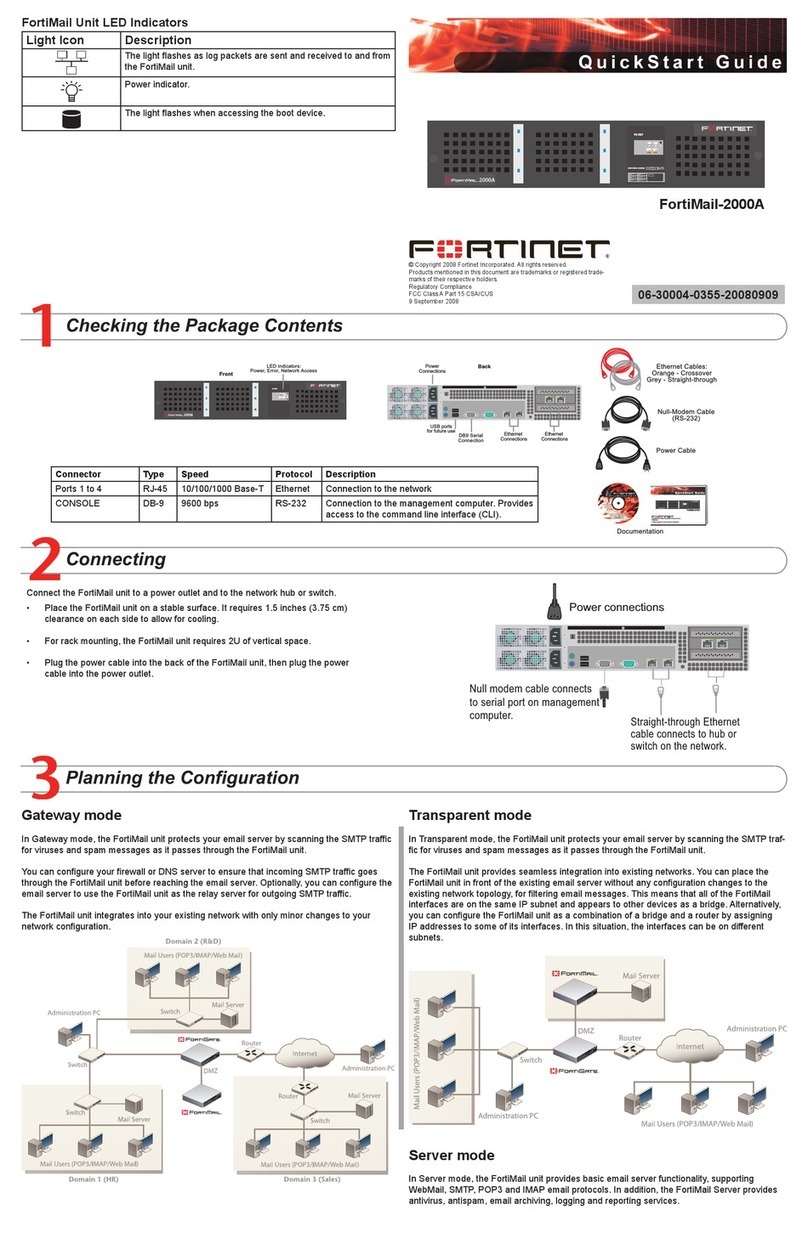
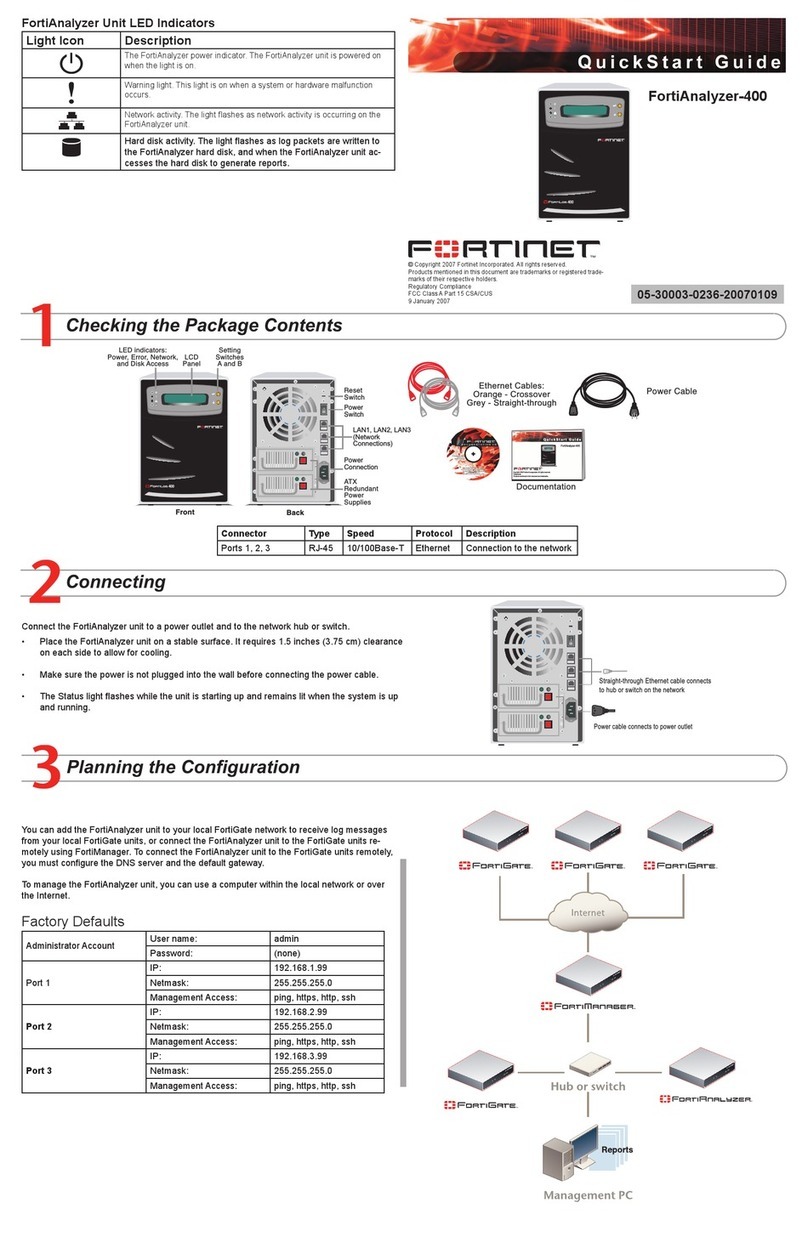
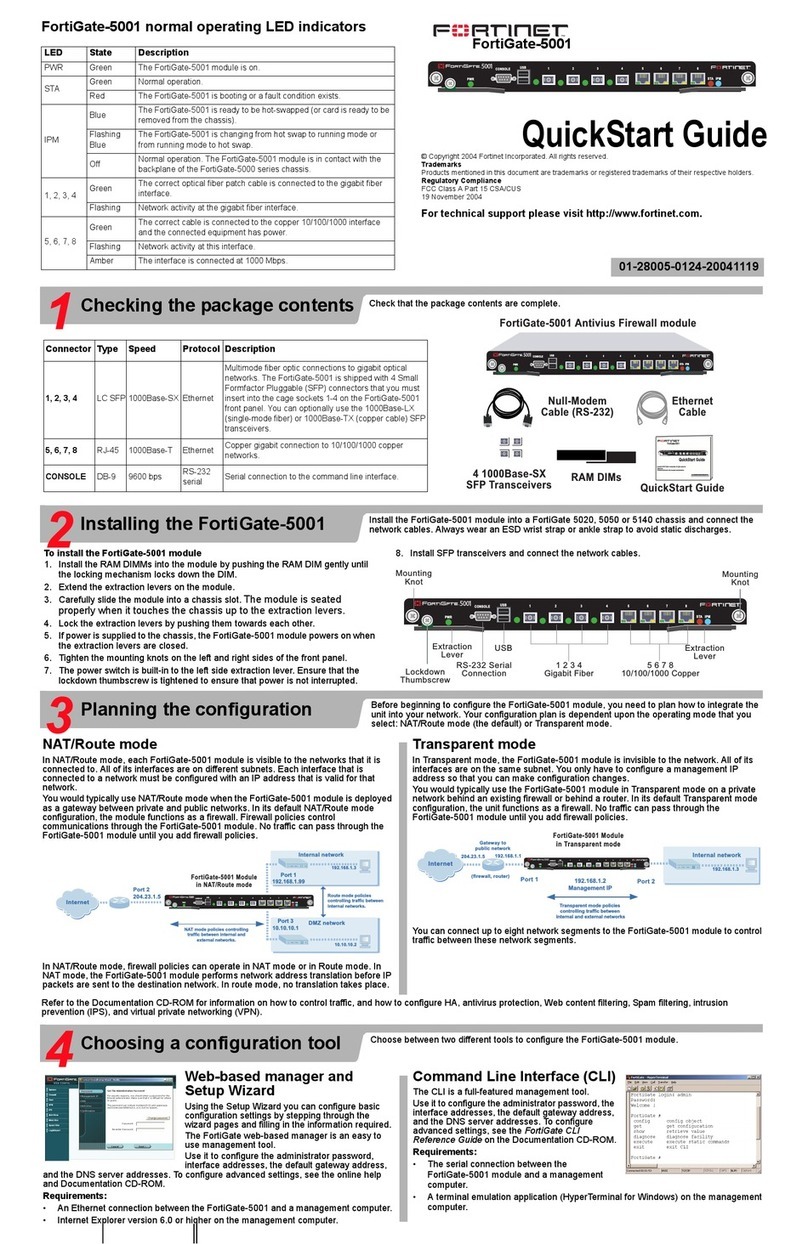
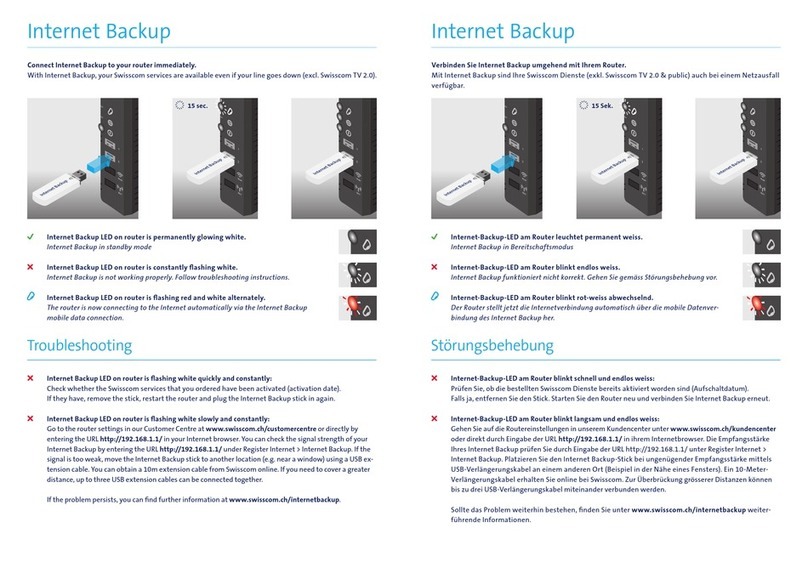
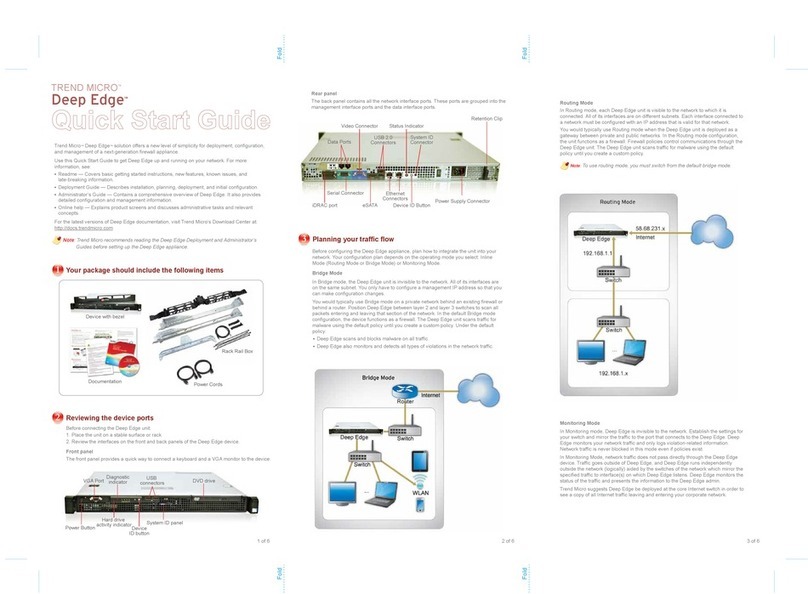
601-28007-0180-20050328 Fortinet Inc.
FortiGate to Cisco VPN 3000 Concentrator Interoperability
Infrastructure requirements
Throughout this technical bulletin, the following example configuration is assumed:
• The network devices are assigned IP addresses as shown in Figure 1.
• The FortiGate-800 unit is operating in NAT mode.
• Both VPN gateways are assigned static public IP addresses.
Configuring the FortiGate-800
When a FortiGate unit receives a connection request from a remote VPN peer, it uses
IPSec phase 1 parameters to establish a secure connection and authenticate the VPN
peer. Then, if the firewall policy permits the connection, the FortiGate unit establishes
the tunnel using IPSec phase 2 parameters and applies the firewall encryption policy.
Key management, authentication, and security services are negotiated dynamically
through the IKE protocol.
To support these functions, the following general configuration steps must be
performed at the FortiGate unit:
• Define the phase 1 parameters that the FortiGate unit needs to authenticate the
remote peer and establish a secure connection. See “Define the phase 1
parameters” below.
• Define the phase 2 parameters that the FortiGate unit needs to create a VPN
tunnel with the remote peer. See “Define the phase 2 parameters” on page 7.
• Create a firewall encryption policy to control the permitted services and permitted
direction of traffic between the IP source and destination addresses. A single
encryption policy controls both inbound and outbound IP traffic through the VPN
tunnel. See “Define the firewall encryption policy” on page 8.
Define the phase 1 parameters
The phase 1 configuration defines the parameters that the FortiGate unit will use to
authenticate the VPN 3000 Concentrator and establish a secure connection. For the
purposes of this example, a preshared key will be used to authenticate the VPN 3000
Concentrator. The same preshared key must be specified at the FortiGate-800 and
the VPN 3000 Concentrator.
Before you define the phase 1 parameters, you need to:
• Reserve a name for the remote gateway.
• Obtain the IP address of the public interface to the remote gateway.
• Reserve a unique value for the preshared key.
Note: If the private network behind the FortiGate unit needs access to more than one private
network behind the VPN 3000 Concentrator, you must create a phase 2 configuration and a
firewall encryption policy for each private network behind the VPN 3000 Concentrator. You
cannot use FortiGate address groups to define destination addresses for a firewall encryption
policy.