Contents
1 Revision History ....................................................................................... 6
1.1 Revision 1.0....................................................................................... 6
2 Getting Started........................................................................................ 7
2.1 Box Contents ..................................................................................... 7
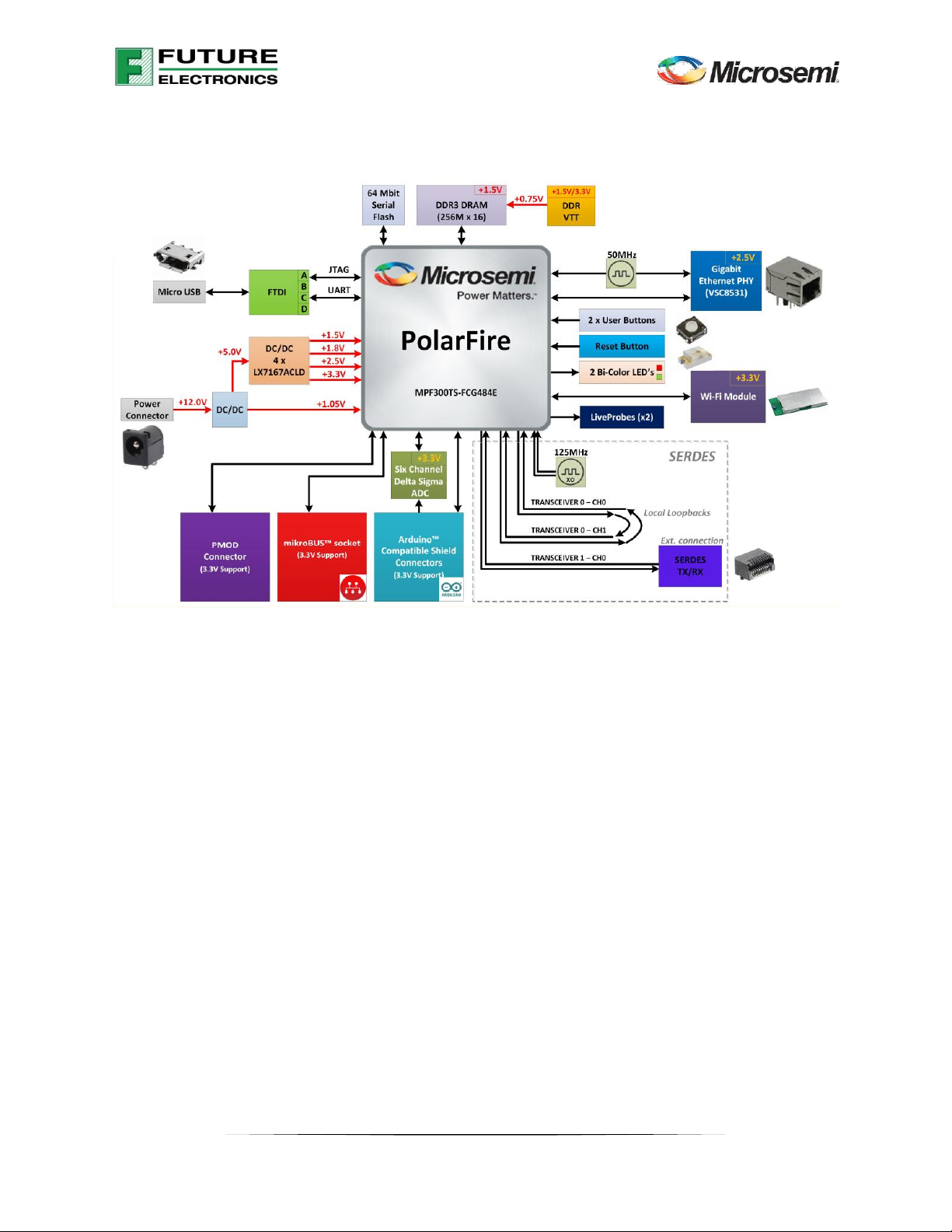
2.2 Block Diagram .................................................................................... 8
2.3 Board Overview .................................................................................. 8
2.4 Powering Up the Board ........................................................................ 11
3 Installation and Setting ............................................................................. 12
3.1 Software Settings ............................................................................... 12
3.2 Hardware Settings .............................................................................. 12
3.2.1 Power Supply LEDs ........................................................................ 12
3.2.2 Test Points ................................................................................. 12
3.2.3 Power Sources ............................................................................. 12
4 Board Components and Operations................................................................ 14
4.1 DDR3 Memory Interface........................................................................ 14
4.2 SPI Serial Flash .................................................................................. 14
4.3 Transceivers ..................................................................................... 15
4.3.1 XCVR0 Interface ........................................................................... 15
4.3.2 XCVR1 Interface ........................................................................... 16
4.3.3 125-MHz Transceiver Reference Clock ................................................. 16
4.4 Microsemi PHY (VSC8531) ..................................................................... 17
4.5 Panasonic Wi-Fi (PAN9320) .................................................................... 18
4.6 Microchip ADC (MCP3903) ..................................................................... 19
4.7 Programming .................................................................................... 19
4.7.1 FTDI ......................................................................................... 19
4.8 System Reset .................................................................................... 20
4.9 50-MHz Oscillator ............................................................................... 20
4.10 User Interface................................................................................... 21
4.10.1 User LEDs ................................................................................... 21
4.10.2 Push-Button Switches..................................................................... 21
4.10.3 Live Probes Header ....................................................................... 22
4.10.4 SFP+ Connector ............................................................................ 22