Table of Contents
Preface .............................................................3
„
Safety precautions................................................4
Chapter 1 BEFORE USING THE INVERTER....1-1
1.1 Acceptance Inspection .............................. 1-1
1.2 External Views........................................... 1-2
Chapter 2 MOUNTING AND WIRING OF THE
INVERTER........................................2-1
2.1 Operating Environment ............................. 2-1
2.2 Installing the Inverter................................. 2-1
2.3 Wiring........................................................ 2-2
2.3.1 Removing and mounting the terminal
block covers...................................... 2-2
2.3.2 Terminal arrangement and screw
specifications .................................... 2-3
2.3.3 Recommended wire sizes................. 2-5
2.3.4 Wiring precautions............................2-7
2.3.5 Wiring for main circuit terminals and
grounding terminals ..........................2-8
2.3.6 Wiring for control circuit terminals... 2-11
2.3.7 Setting up the jumper switches.......2-18
Chapter 3 OPERATION USING THE KEYPAD . 3-1
3.1 Names and Functions of Keypad
Components.............................................. 3-1
3.2 Overview of Operation Modes...................3-2
Chapter 4 RUNNING THE MOTOR ...................4-1
4.1 Test Run.....................................................4-1
4.1.1 Checking prior to powering on...........4-1
4.1.2 Powering ON and checking...............4-1
4.1.3 Preparation before a test run
--Configuring function code data........4-2
4.1.4 Test run..............................................4-3
4.2 Operation...................................................4-3
Chapter 5 FUNCTION CODES............................5-1
5.1 Function Code Tables ................................5-1
Chapter 6 TROUBLESHOOTING ......................6-1
6.1If an Alarm Code Appears on the LED
Monitor......................................................6-1
6.2If anAbnormal Pattern Appears on the LED
Monitor while No Alarm Code is Displayed
....................................................6-3
Chapter 7 MAINTENANCE AND INSPECTION .7-1
7.1 Daily Inspection..........................................7-1
7.2 Periodic Inspection.....................................7-1
7.3 List of Periodical Replacement Parts.........7-3
7.4Inquiries about Product and Guarantee.....7-4
7.4.1 When making an inquiry....................7-4
7.4.2 Product warranty ...............................7-4
Chapter 8 SPECIFICATIONS.............................8-1
8.1 Standard Models........................................8-1
8.1.1 Three-phase 200 V class series........8-1
8.1.2 Three-phase 400 V class series........8-2
8.1.3 Single-phase 200 V class series .......8-3
8.2Terminal Specifications ..............................8-7
8.2.1 Terminal functions..............................8-7
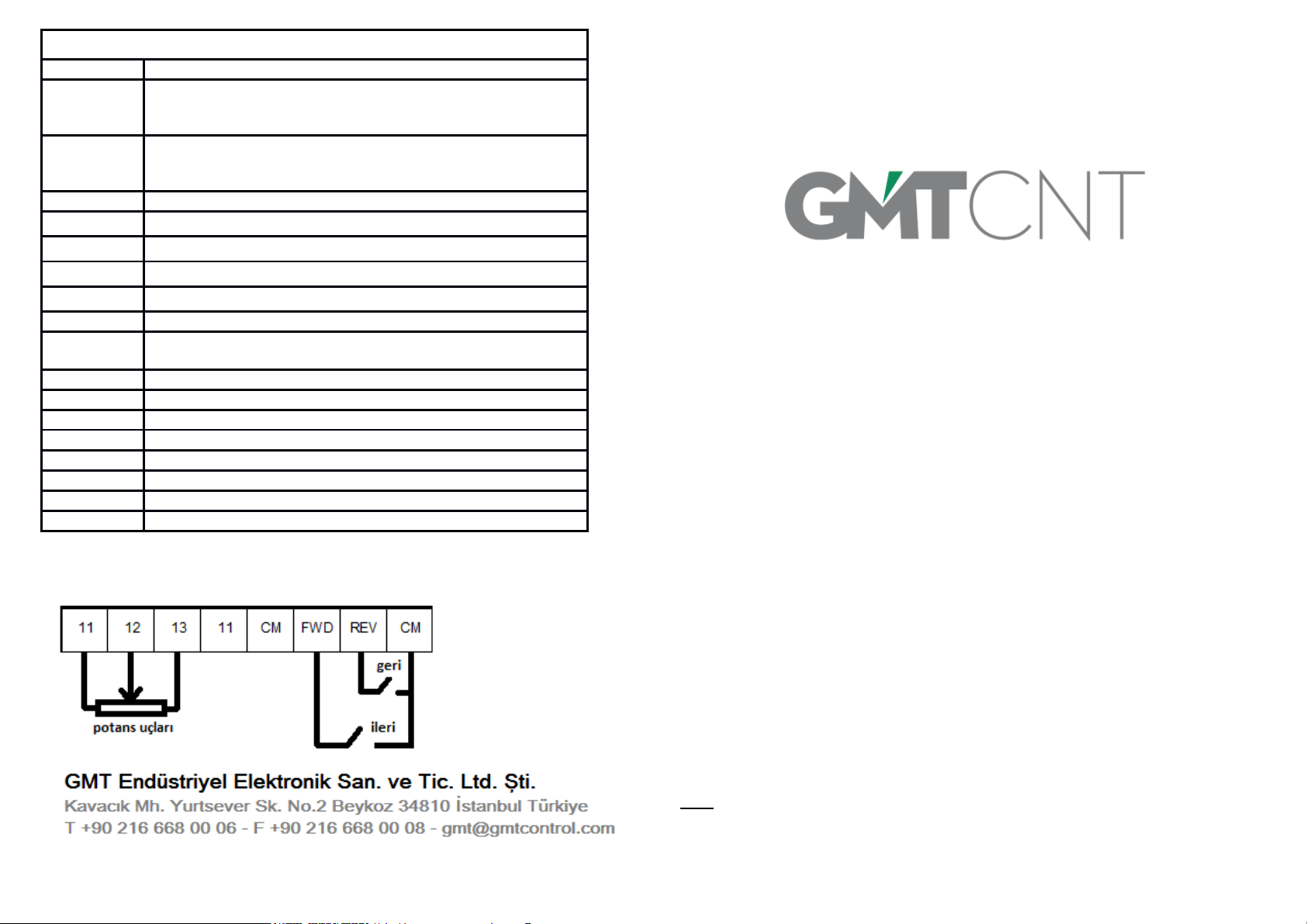
8.2.2 Connection diagram in operation
by external signal inputs....................8-7
8.3Protective Functions ................................8-11