Hifn 9155 User manual

Hifn Confidential
9150, 9155
Evaluation Card
User Guide

9150, 9155 Evaluation Card User Guide, UG-0210-00 Page 2
Hifn Confidential
UG-0210-00, 9150, 9155 Evaluation Card User Guide © April 15, 2010, Hi/fn®, Inc. All rights reserved.
04/10
No part of this publication may be reproduced, transmitted, transcribed, stored in a retrieval system, or
translated into any language in any form by any means without the written permission of Hi/fn, Inc. (“Hifn”)
Licensing and Government Use
Any Hifn software (“Licensed Programs”) described in this document is furnished under a license and may be
used and copied only in accordance with the terms of such license and with the inclusion of this copyright
notice. Distribution of this document or any copies thereof and the ability to transfer title or ownership of this
document’s contents are subject to the terms of such license.
Such Licensed Programs and their documentation have been developed at private expense and no part of such
Licensed Programs is in the public domain. Use, duplication, disclosure, and acquisition by the U.S.
Government of such Licensed Programs is subject to the terms and definitions of their applicable license.
Disclaimer
Hifn reserves the right to make changes to its products, including the contents of this document, or to
discontinue any product or service without notice. Hifn advises its customers to obtain the latest version of
relevant information to verify, before placing orders, that information being relied upon is current. Every
effort has been made to keep the information in this document current and accurate as of the date of this
document’s publication or revision.
Hifn warrants performance of its products to the specifications applicable at the time of sale in accordance
with Hifn's standard warranty or the warranty provisions specified in any applicable license. Testing and other
quality control techniques are utilized to the extent Hifn deems necessary to support such warranty. Specific
testing of all parameters, with the exception of those mandated by government requirements, of each product
is not necessarily performed.
Certain applications using Hifn products may involve potential risks of death, personal injury, or severe
property or environmental damage (“Critical Applications”). Hifn products are not designed, intended,
authorized, or warranted to be suitable for use in life saving, or life support applications, devices or systems
or other critical applications. Inclusion of Hifn products in such critical applications is understood to be fully at
the risk of the customer. Questions concerning potential risk applications should be directed to Hifn through a
local sales office.
In order to minimize risks associated with the customer's applications, adequate design and operating
safeguards should be provided by the customer to minimize inherent or procedural hazards. “Typical”
parameters can and do vary in different applications. All operating parameters, including “Typicals,” should be
validated for each customer application by the customer’s technical experts.
Hifn does not warrant that its products are free from infringement of any patents, copyrights or other
proprietary rights of third parties. In no event shall Hifn be liable for any special, incidental or consequential
damages arising from infringement or alleged infringement of any patents, copyright, or other third party
intellectual property rights.
The use of this product in stateful compression protocols (for example, PPP or multi-history applications) with
certain configurations may require a license from Motorola. In such cases, a license agreement for the right to
use Motorola patents may be obtained through Hifn or directly from Motorola.
Patents
May include one or more of the following United States patents: 4,701,745; 5,003,307; 5,016,009;
5,126,739; 5,146,221; 5,414,425; 5,463,390; 5,506,580; and 5,5532,694. Other patents pending.
Trademarks
Hi/fn®, MeterFlow®, MeterWorks®, and LZS®, are registered trademarks of Hi/fn, Inc. HifnTM,
FlowThroughTM, and the Hifn logo are trademarks of Hi/fn, Inc. All other trademarks and trade names are the
property of their respective holders.
IBM, IBM Logo, and IBM PowerPC are trademarks of International Business Machines Corporation in the
United States, or other countries.
Microsoft, Windows, Windows NT and the Windows logo are trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in the United
States, and/or other countries.
Exporting
This product may only be exported from the United States in accordance with applicable Export Administration
Regulations. Diversion contrary to United States laws is prohibited.
Hifn Confidential
If you have signed a Hifn Confidential Disclosure Agreement that includes this document as part of its subject
matter, please use this document in accordance with the terms of the agreement. If not, please destroy the
document.

9150, 9155 Evaluation Card User Guide, UG-0210-00 Page 3
Hifn Confidential
Contents
1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
1.1 Applications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9
2 Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
2.1 Card Layout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
2.2 Functional Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
2.2.1 Block Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
2.2.2 Hifn Security Processor Chip . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
2.2.3 Gigabit Ethernet Interfaces . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
2.2.4 Flash Memory Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
2.2.5 DDR2 SDRAM Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
2.2.6 RMII Fast Ethernet Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
2.2.7 JTAG Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
2.2.8 CPLD Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
2.2.9 GPIO Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
3 Connectors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
3.1 Power Connectors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .18
3.1.1 JP28: External Power Supply Connector. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
3.1.2 P4: PCI Connector . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
3.2 Ethernet Connectors. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
3.2.1 U54, U56: SFP Connectors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
3.2.2 U64, U65, U67: RJ45 Connectors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
3.3 P1: JTAG Connector . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20
3.4 Debug Connectors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
3.4.1 JP6: SFP Control/Status. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
3.4.2 Amp MICTOR Headers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
4 Jumpers, LEDs, and Switches . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
4.1 Jumpers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28

9150, 9155 Evaluation Card User Guide, UG-0210-00 Page 4
Hifn Confidential
4.1.1 JP34: Device ID Header (DEV-ID). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
4.1.2 JP45: Secure Features Header (SEC) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
4.1.3 JP49: System Configuration Header 1 (MISC-1) . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
4.1.4 JP42: System Configuration Header 2 (MISC-2) . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
4.1.5 JP43: SMI/I2C Interface Select Header . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
4.1.6 JP41: Flash/RTC Interface Select Header . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
4.2 LEDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
4.2.1 Communications Status LEDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
4.2.2 Card Status LED . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
4.2.3 915x Status LEDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
4.3 Switches. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
5 Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
5.1 PHY Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
5.1.1 SFP Ports (Host-0 and Net-0) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
5.1.2 MDI Ports (Host-1 and Net-1) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
5.1.3 MII Port. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
6 Specifications. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
6.1 General . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
6.2 Environmental . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Addendum I Document Changes/Revisions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38

9150, 9155 Evaluation Card User Guide, UG-0210-00 Page 5
Hifn Confidential
List of Figures
Figure 1-1. Evaluation Card Typical Application . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10
Figure 2-1. Evaluation Card Layout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Figure 2-2. Evaluation Card Block Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
Figure 3-1. 915x Evaluation Card Connectors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .18
Figure 3-2. SFP Connector Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21
Figure 3-3. Debug Connector Usage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Figure 4-1. Jumpers, LEDs, and Switch Locations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .28
Figure 4-2. JP34 Device ID Jumper Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .29
Figure 4-3. JP45 Secure Features Jumpers Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .29
Figure 4-4. JP49 System Configuration Header 1 Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .29
Figure 4-5. JP42 System Configuration Header 2 Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .30
Figure 4-6. JP43 SMI/I2C Select Header Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .31
Figure 4-7. JP41 Flash/RTC Select Header Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .32

9150, 9155 Evaluation Card User Guide, UG-0210-00 Page 6
Hifn Confidential
List of Tables
Table 2-1. PHY Device Operating Modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
Table 2-2. JTAG Chip and Revision IDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Table 2-3. General Purpose I/O Pins. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16
Table 3-1. External Power Supply Connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .19
Table 3-2. PCI Power Pin Assignment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .19
Table 3-3. SFP Transceiver Modules . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Table 3-4. JTAG Connector Pinout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Table 3-5. SFP Control/Status Connector . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Table 3-6. J6: Net-0/Net-1Gigabit Port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .23
Table 3-7. J5: Host-1 Gigabit Port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .24
Table 3-8. J7: Host-0 Gigabit Port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .24
Table 3-9. J1: System Interfaces . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Table 3-10. J2: DDR2 Addr/Ctl . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Table 3-11. J3: DDR2 Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .26
Table 3-12. JP48: 915x Serial Port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Table 4-1. Device ID Configuration Jumpers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .29
Table 4-2. JP49 System Configuration Header 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Table 4-3. JP42 System Configuration Header 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Table 4-4. JP43 SMI/I2C Select Header . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Table 4-5. JP41 Flash/RTC Select Header . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .32
Table 4-6. PHY-Driven Communications LEDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Table 4-7. 915x-Driven Communications LEDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Table 4-8. LEDs for RMII AC Access Port. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .33
Table 4-9. Card Status LED . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .33
Table 4-10. 915x Status LED. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .34
Table 4-11. Switches . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Table 6-1. Evaluation Card Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Table 6-2. Environmental Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .37

9150, 9155 Evaluation Card User Guide, UG-0210-00 Page 7
Hifn Confidential
Preface
About this Document
Welcome to the User Guide for the Hifn 9150/9155 Evaluation Card. This document
provides details on configuration, connection and operation of the 9150/9155 Evaluation
Card.
The term “915x” will be used to denote either of the 9150 or 9155 devices. A single
evaluation card supports both the 9150 and 9155 devices and has the following part
number:
915xREF
Audience
This document assumes you are already familiar with the Hifn 9150 or 9155 security
processor devices. The intended audience is integrators and application developers
responsible for and familiar with software and hardware architecture of a target system.
Prerequisite
Before proceeding, you should generally understand:
• Software and hardware of the target system
• General networking concepts
Related Documents
• UG-0202, 9150, 9155 FlowThrough Application Programming Interface
Programming Guide
• UG-0204, 9150, 9155 Security Manager Application Programming Interface
Programming Guide
Document Organization
This document is organized as follows:
Chapter 1, “Introduction", describes the system application and basic connectivity.
Chapter 2, “Overview", provides brief description of each of the major components and
interfaces.

9150, 9155 Evaluation Card User Guide, UG-0210-00 Page 8
Hifn Confidential
Chapter 3, “Connectors", provides connectivity details for the power and signal interfaces.
Chapter 4, “Jumpers, LEDs, and Switches", defines the jumpers, LEDs and switch settings.
Chapter 5, “Operation", describes the high level evaluation card operation and PHY
configuration.
Chapter 6, “Specifications", lists the A/C, D/C and environmental specification for the
evaluation card.
Customer Support
For technical support about this product, please contact your local Hifn sales office,
representative, or distributor.
Web Site
For general information about Hifn and Hifn products refer to:
www.hifn.com

9150, 9155 Evaluation Card User Guide, UG-0210-00 Page 9
Hifn Confidential
1 Introduction
The Hifn 9150/9155 (915x) Evaluation Card is a standard PCI form-factor card that
connects as a “bump-in-the-wire” in Gigabit Ethernet links. It plugs into a standard 32-bit
PCI slot, however it only uses the PCI connector for power. An optional power connection
layout is provided to allow using the evaluation card on a bench top, rather than installed
in a PCI slot.
All communications with the card is done through its rear-panel Gigabit Ethernet
connections, or optionally via the 100 Mbps Fast Ethernet control port at the opposite edge
of the card. The primary ports are capable of operating at 10/100/1000 Mbps speeds (in
copper mode).
The Hifn 915x FlowThrough™ security processor chip is the heart of this card. Its two host
ports and two network ports interface through four separate single-port Gigabit PHY devices
to the rear panel Ethernet connectors. These four interfaces make up two distinct channels
through the 915x where each channel is composed of one host port and one network port.
The channel 0 ports utilize “SFP” pluggable modules, allowing either copper or fiber-optic
connections. The channel 1 ports are supported with RJ-45 copper-only connectors.
All of the bus interfaces to the 915x devices are instrumented with MICTOR test connectors
for interfacing with a Logic Analyzer or digital oscilloscope. A JTAG test connector is also
populated to allow boundary scan testing as well as for access to the on-chip processors.
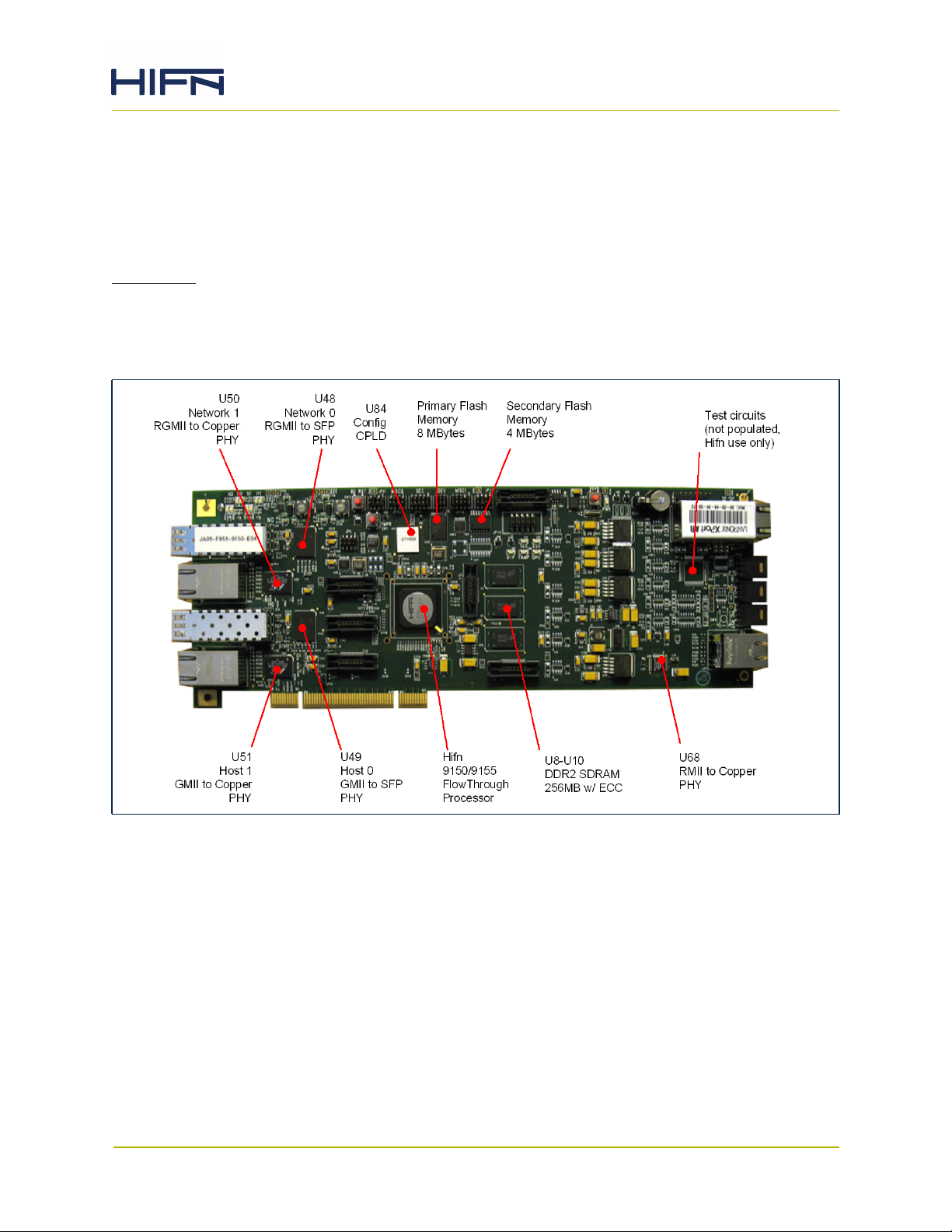
1.1 Applications
The 915x Evaluation Card is a useful tool to allow design, development and debug of
software running on a target host system. The host port(s) of the 915x Evaluation Card are
connected to GigE ports on the host platform (i.e. HBA, TBA, NIC, Switch) and the network
port(s) are connected into a test network.
Refer to the sample system diagram in Figure 1-1.

9150, 9155 Evaluation Card User Guide, UG-0210-00 Page 10
Hifn Confidential
The intent of the evaluation card is to simulate the actual software environment of the end
system to the greatest extent possible. This is easily achieved due to the FlowThrough
nature of the Hifn 915x devices. From the host perspective, software commands sent out
the Ethernet port will be intercepted and acted upon just as if the chip were installed on the
same PCB as the host GMAC/TOE/Network Processor. Given this, the evaluation card can be
used to test virtually all of the customer-developed software at both the driver and the
application layers. This includes: boot-load, initialization, port control & monitoring,
fragment reassembly, and security management.
Figure 1-1. Evaluation Card Typical Application
9150, 9155 Evaluation Card User Guide, UG-0210-00 Page 11
Hifn Confidential
2 Overview
2.1 Card Layout
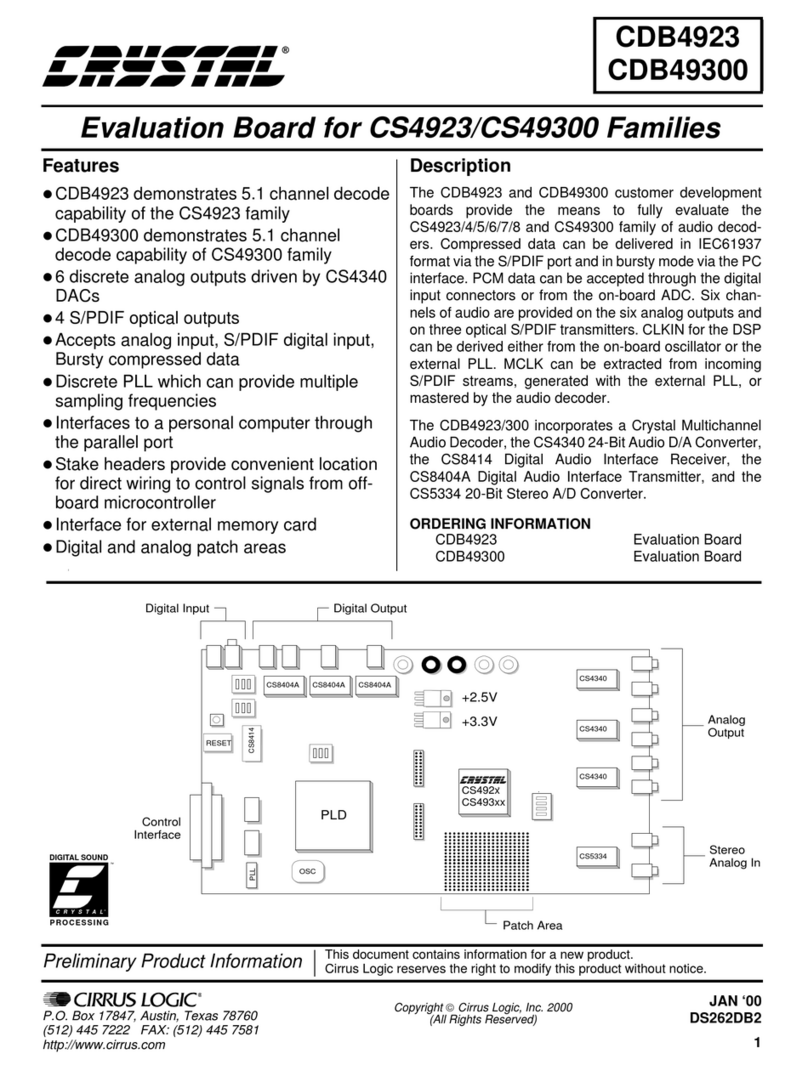
Figure 2-1 below identifies the significant functional components on the evaluation card
with the exception of the LEDs, jumpers, connectors, and switches, which are described
fully in a later chapter. The Hifn security processor chip is in the center of the card and
clearly labeled.
Figure 2-1. Evaluation Card Layout

9150, 9155 Evaluation Card User Guide, UG-0210-00 Page 12
Hifn Confidential
2.2 Functional Overview
2.2.1 Block Diagram
Figure 2-2. Evaluation Card Block Diagram
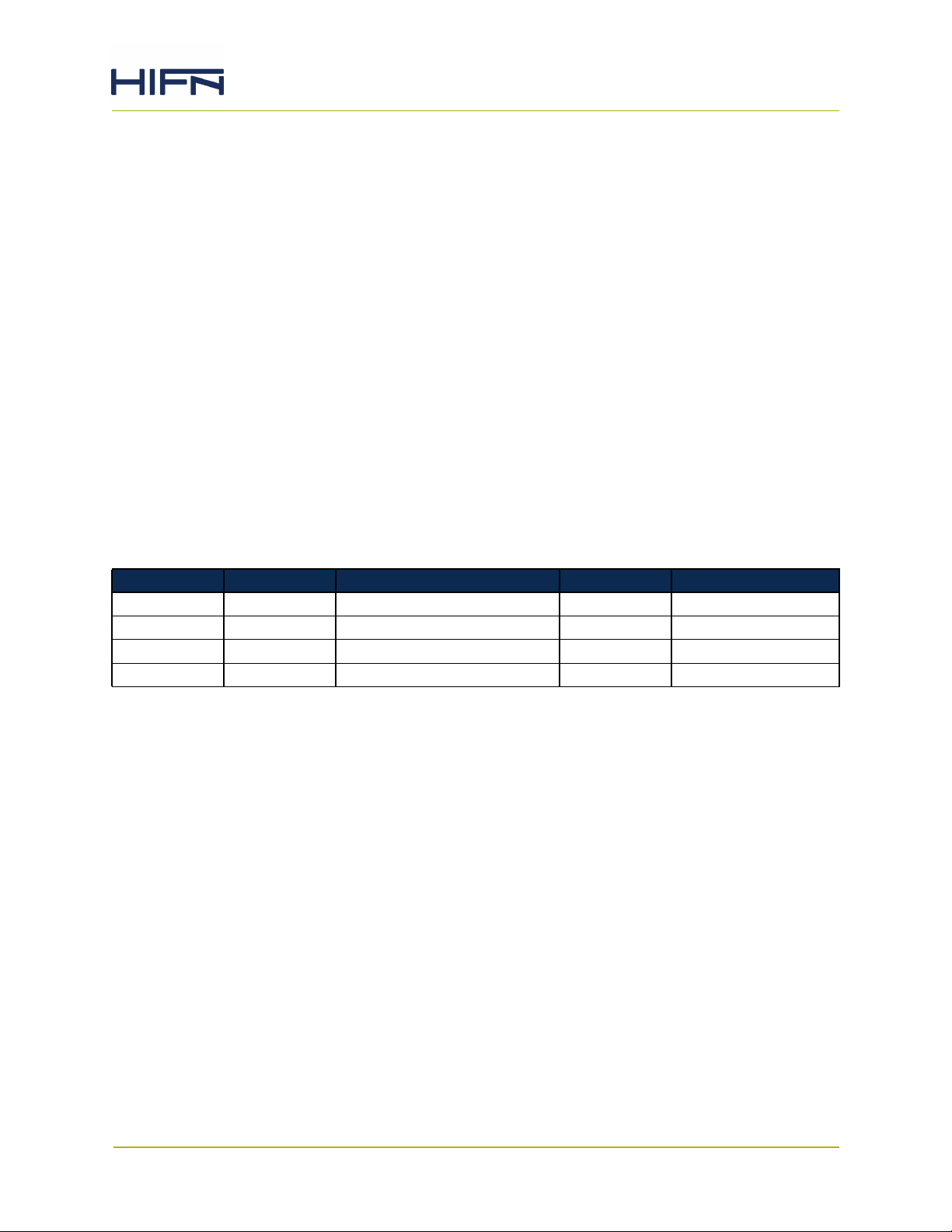
9150, 9155 Evaluation Card User Guide, UG-0210-00 Page 13
Hifn Confidential
2.2.2 Hifn Security Processor Chip
At the heart of the evaluation card is the Hifn 915x applied services processor. The 915x
device combines high performance throughput, full Internet Key Exchange (IKE) support,
Internet Protocol Security (IPsec) support, and Internet Protocol Payload Compression
(IPComp) support with the intelligent packet processing functionality of Hifn's product
family.
Consult the 9150, 9155 Applied Services Processor Data Sheet and 9150, 9155 User Guide
for complete details on each device.
2.2.3 Gigabit Ethernet Interfaces
On this evaluation card, the Hifn applied services processor’s Gigabit Ethernet interfaces are
connected to either copper or fiber cabling environments through physical layer devices
(PHY) and connectors. For MAC-PHY connections to copper cabling and RJ45 connectors, the
Marvell 88E1111 PHY is used. For MAC-PHY connections to SFP connectors, the Vitesse
VSC8211 PHY is used. Refer to the table below for the combinations of PHY devices and
operating modes.
The evaluation card also supports other interface modes including TBI and SERDES. Please
note, however, that support for other interfaces requires card modifications that should not
be attempted by the user.
Each of the four gigabit Ethernet interfaces is accessible for debug or monitoring through a
high-density test connector (Amp MICTOR series) that easily interfaces to a logic analyzer.
Use of these connectors is discussed in a later section.
2.2.4 Flash Memory Interface
The eSC (sometimes referred to as the AP) is an embedded RISC core in the 915x chip that
is used to perform functions such as error and exception handling, and IKE processing. This
processor core on the evaluation card has access to the external flash memory devices
described in this section.
Flash memory can be used to store processor boot images, configuration data for other on-
card devices such as network physical layer devices, and code development/storage. A flash
write utility is provided with the 915x SDK to allow code images and configuration data to
be written to flash.
Table 2-1. PHY Device Operating Modes
Port Mode Connectivity Vendor Part Number
Network-0 RGMII SFP (Copper or Fiber) Vitesse VSC8211
Network-1 RGMII Copper (RJ45) Marvell 88E1111
Host-0 GMII SFP (Copper or Fiber) Vitesse VSC8211
Host-1 GMII Copper (RJ45) Marvell 88E1111

9150, 9155 Evaluation Card User Guide, UG-0210-00 Page 14
Hifn Confidential
The flash memory devices on the evaluation card are designed to be compatible with the 4-
wire SPI serial interface which is composed of the following signals: chip select, clock, serial
data in, and serial data out. These signals are shared with other chip functions on the eSC
processor's GPIO pins. The eSC flash memory interface signals are also available for debug
on one of the MICTOR debug connectors as shown in Section 3.4.
Flash Memory Devices
Two styles of flash memory devices are provided on the 915x Evaluation Card.
The two different flash memory devices are configured on the evaluation card as primary
flash and secondary flash. The terms ‘primary’ and ‘secondary’ are used to distinguish
which flash is connected to FLASH_CS0 (ESC_GPIO[0]) and FLASH_CS1 (ESC_GPIO[4]).
Selection of the primary and secondary flash can be configured through the MISC-2 header
as described in Section 4.1.4. The default configuration has the primary flash assigned to
an 8-MByte Atmel device (AT45DB642D) and secondary flash assigned to a 4-MBytes Atmel
device (AT25DF321).
Please note that the 915x security processor requires a minimum of 8MB when the flash
interface is utilized. Due to this requirement, the AT25DF321 is no longer recommended.
2.2.5 DDR2 SDRAM Interface
Each of the embedded 915x processor cores (DPU, eSC, PCP) has access to external DDR2
SDRAM memory. The 915x chip supports up to 512 Mbytes of DDR2 SDRAM memory,
excluding the optional ECC.
The 915x Evaluation Card is shipped with 256 MBytes of DDR2 SDRAM memory. The DDR2
SDRAM interface is available for debug and monitoring on Amp MICTOR-style connectors
(one for address/control, one for data). Note that the DDR2 SDRAM interface signals are
high speed SSTL-18 signals, and appropriate adapters and test equipment must be used
when probing these signals.
2.2.6 RMII Fast Ethernet Interface
The 915x Evaluation Card includes a general purpose RMII (100 Mbps) Ethernet MAC
interface. This interface may be used for out-of-band boot load, chip initialization and
management, as well as for inter-chip communications when multiple chips are used to
scale the performance or port count. All of the management features that can be
accomplished “in-band” over the host side GMAC ports can also be accomplished via the
RMII port.
Note
The RMII port is intended only for local communications between 915x devices or to a
control processor. It is NOT intended to be connected to a network interface since it does
not support the requisite networking features that would be required such as unique MAC
addressing, ARP, etc.
The MII interface consists of the seven RMII signals, a Fast Ethernet PHY transceiver, and
an integrated magnetics-RJ45 connector module.

9150, 9155 Evaluation Card User Guide, UG-0210-00 Page 15
Hifn Confidential
2.2.7 JTAG Interface
The JTAG (Joint Test Action Group) interface provides access to the boundary-scan logic
within the 915x devices. The boundary-scan logic is used for testing the interconnections
between the 915x and other integrated circuits on the printed circuit card at manufacturing
time. The boundary-scan logic is compliant with the IEEE 1149.1 standard for boundary-
scan testing. In addition, the JTAG interface is used for chip manufacturing tests and is also
used by Hifn for developing and debugging the firmware for the embedded processors. The
JTAG connector and pin descriptions are shown in a later chapter.
The JTAG circuit in the 915x device has a Chip ID and a Revision ID that is used by the test
equipment to identify the device and revision level in order to run the appropriate test
patterns. The following table shows the JTAG Chip and Revision IDs for the 915x devices.
2.2.8 CPLD Interface
In order to easily configure the evaluation card for a variety of interface options and test
configurations, a CPLD (complex programmable logic device) is used to provide the majority
of connectivity for pins used for chip configuration including GPIO. Although there is no
customer access to the CPLD internal logic elements, a brief summary of the CPLD functions
is included here for Hifn professionals:
• Host/Network Link and Activity LED Mux
• 3-Way Mux for all GPIO pins (Reset Capture, Primary Usage, and Disconnect for PC
Mode
• Control of all 915x config pins (PLL_MODE, DDR2_CONFIG, GMAC_CONFIG, etc)
• Interface for Lantronix XPORT-AR module
• Interface to SFP modules
• Interface to Flash Memory, Ds3641, and RTC chips
2.2.9 GPIO Interface
The eSC and DPU embedded processor cores both contain 16-bit external GPIO (General
Purpose Input/Output) buses that can be used for functions such as boot mode
configuration, Flash memory connectivity, or customer-specific functions. All GPIO pins
default to inputs and are sampled following reset for various configuration purposes.
Internal registers accessed by the eSC and DPU processors control the I/O direction of each
pin. Other internal registers are used to read the GPIO pin states when they are inputs or
set their state when they are an output.
Table 2-2. JTAG Chip and Revision IDs
Model JTAG Chip ID JTAG Revision ID
915x 0x0002526D 0x02
9150, 9155 Evaluation Card User Guide, UG-0210-00 Page 16
Hifn Confidential
Most of the GPIO pins have pre-defined functions as shown in the table below. These
functions are subject to change, so the user should consult the latest data sheet revision
applicable to the Hifn device selected for detailed and accurate GPIO descriptions.
Table 2-3. General Purpose I/O Pins
Signal Name Primary Use Reset Capture Reset Capture Function Card Connection
dpu_gpio[15] Host1_Link Unused Unused CPLD (LED Mux)
dpu_gpio[14] Host0_Link Unused Unused CPLD (LED Mux)
dpu_gpio[13] Host1_Act Unused Unused CPLD (LED Mux)
dpu_gpio[12] Host0_Act Unused Unused CPLD (LED Mux)
dpu_gpio[11] Net1_Link Unused Unused CPLD (LED Mux)
dpu_gpio[10] Net0_Link Unused Unused CPLD (LED Mux)
dpu_gpio[9] Net1_Act Unused Unused CPLD (LED Mux)
dpu_gpio[8] Net0_Act Unused Unused CPLD (LED Mux)
dpu_gpio[7] DPU Status
LED
1=LED on
0= LED off
Unused Unused CPLD (LED Driver)
dpu_gpio[6] MDIO/SDA Unused Unused GPIO Mux
dpu_gpio[5] MDC/SCL serdes_hidrv 0=tx_lvl[4:0] should
be set to 5'b 01000
(1.0v transmit level)
1=tx_lvl[4:0] should
be set to 5'b 11000
(1.16v transmit level)
GPIO Mux
dpu_gpio[4] Net0
TX_DISABLE
ddr_config_1 ddr_config_1:
ddr_config[1:0]
determines the size of
the installed DDR2
SDRAM memory
00=64MB
01=128MB
10=256MB
11=512MB
CPLD (GPIO Mux)
dpu_gpio[3] Net1
TX_DISABLE
ddr_config_0 ddr_config_0 CPLD (GPIO Mux)
dpu_gpio[2] Net0
RX_LOSS
RGMII Voltage
Level
1=1.5V HSTL, 0=2.5V
LVCMOS
CPLD (GPIO Mux)
dpu_gpio[1] Net1
RX_LOSS
boot_config_1 1=Flash, 0=No Flash CPLD (GPIO Mux)
dpu_gpio[0] Secure Mode
LED
boot_config_0 0=All PPCI commands
received over Host0 /
Host1 will be
discarded.
1=Accept PPCI
commands over Host0
/ Host1
CPLD (GPIO Mux)

9150, 9155 Evaluation Card User Guide, UG-0210-00 Page 17
Hifn Confidential
esc_gpio[15] eSC_gpio
[15]
MemClr 0=Some parts of
SRAM left uncleared
during soft reset
1=Clear SRAM
memory during reset
CPLD (GPIO Mux)
esc_gpio[14] OTP_VPP_EN
_N
Unused Active low signal to
control the OTP_VPP
voltage
CPLD
esc_gpio[13] CAPTURE_
COMPLETE
Unused 0=reset capture not
complete
1=reset capture
complete
CPLD
esc_gpio[12] eSC_gpio
[12]
Secure_Feature
[4]
Reserved CPLD (GPIO Mux)
esc_gpio[11] eSC_gpio
[11]
Secure_Feature
[3]
Reserved CPLD (GPIO Mux)
esc_gpio[10] eSC_gpio
[10]
Secure_Feature
[2]
Reserved CPLD (GPIO Mux)
esc_gpio[9] eSC_gpio[9] Secure_Feature
[1]
Suite B Only CPLD (GPIO Mux)
esc_gpio[8] eSC_gpio[8] Secure_Feature
[0]
Bypass Disable CPLD (GPIO Mux)
esc_gpio[7] eSC Status Unused Unused CPLD (LED Driver)
esc_gpio[6] PHY
Interrupt
Device_ID[2] Device_ID[2] CPLD (GPIO Mux)
esc_gpio[5] Flash_CS2 Device_ID[1] Device_ID[1] CPLD (GPIO Mux)
esc_gpio[4] eSC_Flash_C
S1/I2C Data
Device_ID[0} Device_ID[0} GPIO Mux
esc_gpio[3] eSC_Flash_
SO
RMII MAC/PHY 1=PHY, 0=MAC CPLD (GPIO Mux)
esc_gpio[2] eSC_Flash_
SI
100M/1G Boot 1= 100M boot, 0= 1G
boot
CPLD (GPIO Mux)
esc_gpio[1] eSC_Flash_
CLK
Unused Unused GPIO Mux
esc_gpio[0] eSC_Flash_
CS0
Unused Unused CPLD (GPIO Mux)
Table 2-3. General Purpose I/O Pins
Signal Name Primary Use Reset Capture Reset Capture Function Card Connection
9150, 9155 Evaluation Card User Guide, UG-0210-00 Page 18
Hifn Confidential
3 Connectors
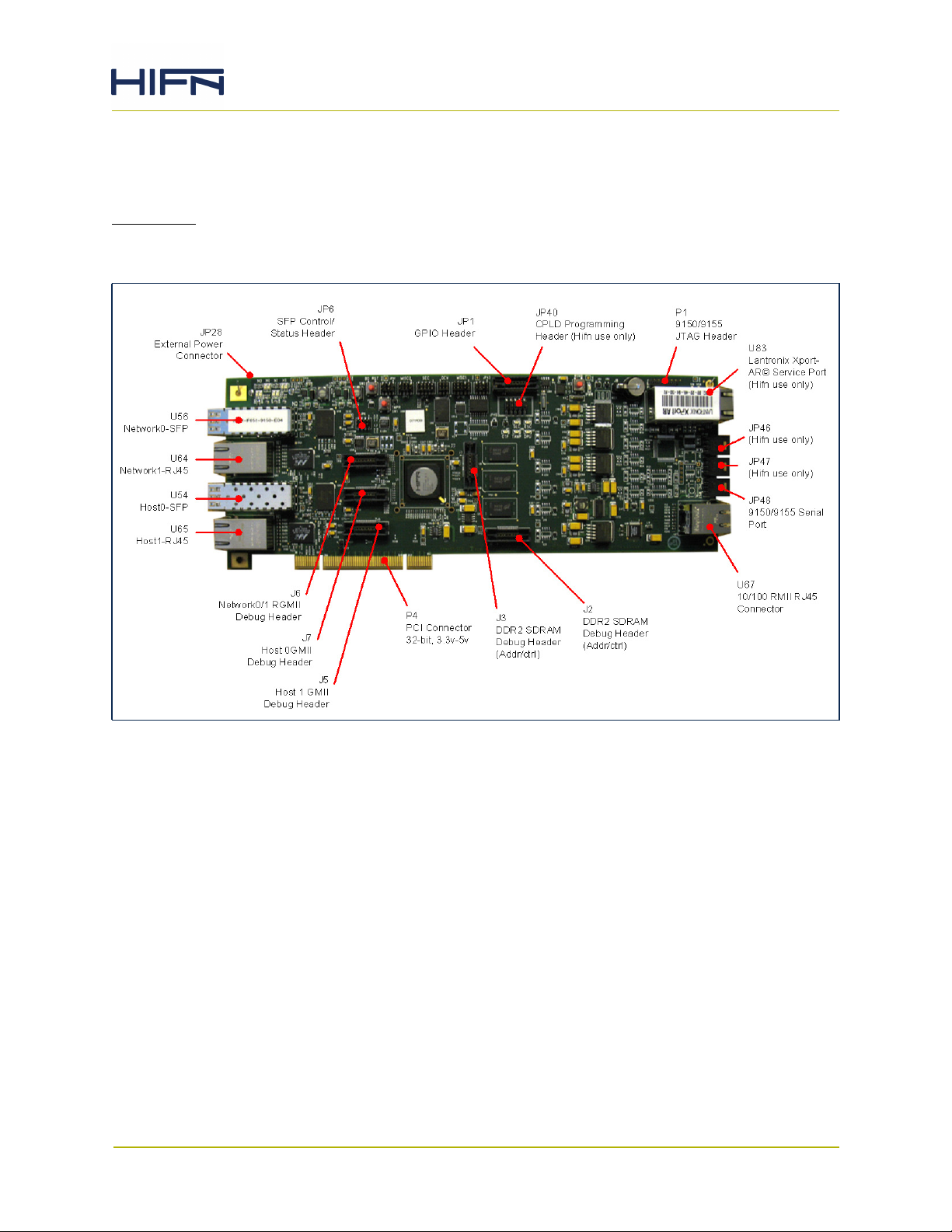
Figure 3-1 illustrates the location of the power and signal connectors on the 915x
Evaluation Card:
3.1 Power Connectors
The 915x Hifn Evaluation Card can be powered from either an external power supply or
through the PCI connector. Two voltages are required for proper operation: +5V and
+3.3V.
3.1.1 JP28: External Power Supply Connector
A four-pin plastic power connector is provided in the upper left-hand corner on the back
side of the card. The connector style is right-angle disk-drive style power connector and
uses a Molex connector PN 53109-0410. A suitable mating receptacle is the
AMP 1-480424-0. The pins are numbered from 1 to 4 on the PCB, from left to right, with
Figure 3-1. 915x Evaluation Card Connectors

9150, 9155 Evaluation Card User Guide, UG-0210-00 Page 19
Hifn Confidential
pin 1 of the connector associated with the only square pad on the PCB footprint. A standard
PC power supply can be modified to include the mating connector and must include the
connections listed in the table below.
!
Caution
Do not use un-modified disk-drive power cable as this will result
in catastrophic damage to the card.
3.1.2 P4: PCI Connector
A PCI connector is available solely for the purposes of providing an alternative power
source. There are no other PCI connections provided, so slot assignment is not an issue as
long as +3.3V and +5.5V are provided as per the following table.
Note
PRSNT1* and PRSNT2* are grounded through 0-ohm resistors on the evaluation card.
!
Caution
Do not reverse polarity on power connections. Possible damage
to the card may result
3.2 Ethernet Connectors
Four Gigabit Ethernet interfaces and one RMII 100Mbps Ethernet interface exist on this
card.
Table 3-1. External Power Supply Connections
Pin Number Description
1 +3.3V
2 GND
3 GND
4 +5V
Table 3-2. PCI Power Pin Assignment
Pin Number Description
A21, B25, A27, B31, A33, B36, A39, B41, B43, A45, A53,
B54
+3.3V
B3, A12, B12, A13, B13, B15, B17, A18, B22, A24, B28,
A30, B34, A35, A37, B38, A42, B46, A48, A56, B57
GND
A5, B5, B6, A8, A61, B61, A62, B62 +5V

9150, 9155 Evaluation Card User Guide, UG-0210-00 Page 20
Hifn Confidential
3.2.1 U54, U56: SFP Connectors
The Host-0 and Network-0 network ports are configured as SFP ports (Small FormFactor
Pluggable). On-card Gigabit Ethernet PHY devices provide the necessary GMII/TBI/RGMII/
RTBI and embedded SERDES interfaces to receive and transmit data on these ports to and
from the Hifn security processor. SFP ports are physically composed of a 20-pin surface-
mount connector that is encased in a metal cage that provides some amount of heat
transfer and EMI protection. Note that this evaluation card is not designed to comply with
any EMI susceptibility or interference standards. Though SFP ports were originally designed
for use in optical networking, SFP transceivers are now available which support copper
cabling (RJ45-style connectors).
There are many suppliers for SFP transceivers, and the minimum requirements for their use
with this evaluation card are: 3.3V, 1.250 Gbps. The following transceivers have been used
successfully at Hifn and may be ordered through Hifn along with the evaluation card.
Each of the SFP modules' internal EEPROMs and registers are accessible through a two-wire
serial interface (I2C via GPIO) that is connected through the on-card CPLD device. Since all
SFP modules are hard-wired for the same I2C address, the evaluation card also includes an
I2C mux that can be accessed via I2C commands. Please contact Hifn for further details on
GPIO-driven SFP communication.
3.2.2 U64, U65, U67: RJ45 Connectors
The Host-1 and Network-1 network ports and the RMII port are configured with RJ45
connectors that provide copper Ethernet connectivity with the vast majority of network
infrastructures.
Please note that the RMII port is not intended to be connected to a generic LAN since it
does not support the requisite networking features that would be required such as unique
MAC addressing, ARP, etc. Rather, it is intended to connect to the customer's host control
processor running specialized code for managing the 915x chip. Refer to the 9150, 9155
User Guide, UG-0195 for further information.
3.3 P1: JTAG Connector
Access to the Hifn security processor’s JTAG interface is accomplished through an on-card
seven-pin single-in-line header at location P1. To support the more common two-row by 5-
pin JTAG connector, a simple transition header can be assembled (contact Hifn for further
information). The JTAG connector's pins are numbered 1 through 7 from top to bottom, and
the JTAG signals are assigned to those pins as shown in the following table.
Table 3-3. SFP Transceiver Modules
Hifn SKU Number Part Number Description
SFP FTRJ-8619 Finisar Short Wavelength (850nm) SFP Transceiver
SFP FCMJ-8521 Finisar 1000Base-T Copper SFP Transceiver
This manual suits for next models
1
Table of contents