InHand EAP600 Series Operational manual

i
InHand Networks Enterprise AP
EAP600 Series Product User Manual
Version:V1.1-2023.10

ii
Declarations
Thank you for choosing our company's product! Before use, please carefully read
this user manual. By complying with the following statements, you will help maintain
intellectual property rights and legal compliance, ensuring that your user experience
aligns with the latest product information. If you have any questions or need written
permission, please feel free to contact our technical support team.
⚫Copyright Statement
This user manual contains copyrighted content, and the copyright belongs to
InHand Networks Technology and its licensors. Without written permission, no
organization or individual may excerpt, copy any part of the content of this manual, or
distribute it in any form.
⚫Disclaimer
Due to ongoing updates in product technology and specifications, the company
cannot guarantee that the information in the user manual is entirely consistent with the
actual product. Therefore, no disputes arising from any discrepancies between the
actual technical parameters and the user manual are accepted. Any changes to the
product will not be notified in advance, and the company reserves the right to make the
final changes and interpretations.
⚫Copyright Information
The content of this user manual is protected by copyright laws, and the copyright
belongs to InHand Networks and its licensors, reserving all rights. Without written
permission, the content of this manual may not be used, copied, or distributed without
authorization.

iii
Conventions
Symbol
Indication
[ ]
Referring to function modules or menus, such as in the [ Status ]
menu."
“ ”
Referring to a button name, such as Clicking the “Add” button.
〉
Multiple levels of menus are separated by "〉". For example, "File〉
New〉Folder" representsthe "Folder" menu item under the "New"
submenu, which is under the "File" menu.
Cautions
Please be mindful of the following points during the operation, as
improper actions may result in data loss or device damage.
Note
Supplement and provide necessary explanations for the
description of the operation.

iv
CONTENT
1. Overview............................................................................................................1
2. Hardware............................................................................................................2
2.1 LED Indicators.........................................................................................2
2.2 Perform a factory reset using the Reset button........................................3
3. Default Settings..................................................................................................4
4. Device Initialization Settings.............................................................................5
4.1 Environment Setup...................................................................................5
4.2 Internet Connection..................................................................................5
5. Function Configuration......................................................................................7
5.1 Dashboard................................................................................................7
5.1.1 Device Information.......................................................................7
5.1.2 Traffic Statistics............................................................................8
5.1.3 Wi-Fi Connections........................................................................8
5.2 Status........................................................................................................9
5.2.1 Link Monitoring............................................................................9
5.2.2 Clients...........................................................................................9
5.2.3 Events..........................................................................................10
5.2.4 Logs.............................................................................................11
5.3 Configuration.........................................................................................12
5.3.1 WAN...........................................................................................12
5.3.2 LAN ............................................................................................13
5.3.3 Radio...........................................................................................13
5.4 Wi-Fi......................................................................................................15
5.5 System....................................................................................................16
5.5.1 adm Management........................................................................16
5.5.2 Cloud Management.....................................................................16
5.5.3 Remote Access Control...............................................................17
5.5.4 Country & System Clock............................................................18
5.5.5 Device Option.............................................................................18
5.5.6 Configuration Management........................................................19

v
5.5.7 Device Alarms ............................................................................20
5.5.8 Tools ...........................................................................................21
5.5.9 Scheduled Reboot .......................................................................23
5.5.10 System Settings.........................................................................23
5.5.11 Log Server.................................................................................24
5.5.12 Other Settings............................................................................24
6. Security Precautions.........................................................................................26
7. Troubleshooting...............................................................................................27
7.1 Clients Cannot Connect to the Wireless Network .................................27
7.2 Wireless network is slow or experiencing instability............................27
7.3 AP Cannot Start Properly or Frequent Crashes .....................................28
7.4 Unable to Connect to a Specific Website or Service.............................28
7.5 Unable to access the Incloud Manager ..................................................28
8. Hardware Specification....................................................................................29

1
1. Overview
The EAP600, developed by InHand Networks, is a Wi-Fi 6 Access Point designed
for the commercial sector. This product delivers secure and high-speed network access,
catering to a wide range of industries. Harnessing the robust network access capabilities
of Wi-Fi 6, it provides a straightforward and efficient solution for small businesses,
enterprise branches, hotels, and any other settings requiring wireless coverage with
high-speed network access. With a comprehensive set of security features and
intelligent software services, it ensures an efficient and worry-free networking
experience, delivering a secure and dependable business data connection in wireless
environments.
Fig. 1 EAP600 application scenario

2
2. Hardware
2.1 LED Indicators
LED Indicator
Status and Description
PWR
OFF --- The device is Off.
Blink in green --- The system is starting.
Blink in green rapidly --- The system does not work properly.
Blink in green --- The system is upgrading.
WAN
OFF --- The network is disconnected.
Blink in green --- The router is connecting to the wired network.
Wi-Fi 2.4G
OFF --- AP mode disabled.
Always on --- Other anomalies.
Blink in rapidly green --- The device functions normally as an AP.
Wi-Fi 5G
OFF --- AP mode disabled.
Always on --- Other anomalies
Blink in green rapidly --- The device functions normally as an AP.
Note: The rapid blinking occurs every 200ms, and the steady blinking interval is 500ms.

3
2.2 Perform a factory reset using the Reset button.
Step 1: Power on the device, and within 10 seconds, long-press the Reset button
until the PWR indicator light rapidly blinks green with a 200ms interval.
Step 2: After the rapid blinking, release the Reset button and wait for the device
to complete the factory reset process. The PWR indicator light will stay constantly lit,
indicating that the factory reset is complete.

4
3. Default Settings
Function
Default Settings
Wi-Fi
1. The Wi-Fi 2.4 GHz access point (AP) is enabled, and its
SSID is EAP600–followed by the last six digits of the
wireless MAC address.
2. The Wi-Fi 5 GHz AP is enabled, and its SSID is EAP600-
5G–followed by the last six digits of the wireless MAC
address.
3. The authentication method is WPA2-PSK.
4. The two access points have the same password: The last
eight digits of the router's SN.
Network
access control
1. Local HTTPS service is enabled, using port 443.
2. The device management address is 192.168.10.1
Username
and password
The username is adm, and the password is 123456 by
default.

5
4. Device Initialization Settings
4.1 Environment Setup
Step 1: Connect the power cable and Ethernet cable. When using PoE (Power over
Ethernet) to power the EAP600, please ensure that the upstream device has PoE
functionality enabled.
Step 2: Set the PC and device management IP addresses in the same network
segment. The DHCP Server function is enabled by default, and the PC and device
must be in the same address segment. The PC needs to be connected to the device’s
Wi-Fi (SSID and password reference 3. Default Settings), and check whether the PC
has obtained an address, which should belong to the 192.168.10.0 network segment.
Fig. 4-1 EAP600 Web Login page
4.2 Internet Connection
The EAP600 supports single-port wired access, and users can configure it to use
DHCP or static IP address assignment based on their requirements. Click on
“Configuration > WAN” to select the network connection type.

6
Fig. 4-2-a Access the WAN editing interface
⚫DHCP: The device's WAN interface is set to enable DHCP service by default.
You can simply connect the WAN interface to the internet using an Ethernet cable to
establish the AP's network connection.
⚫Static IP: Users can manually configure the address assigned by the ISP or
upstream device. After the configuration is completed, the AP will connect to the
network using the specified static IP.
Fig. 4-2-b Configuring the AP to connect to the network via a static IP address

7
5. Function Configuration
5.1 Dashboard
Click on [ Dashboard ] in the left-hand menu to access the dashboard interface and
view the device's basic information, operating mode, traffic statistics, Wi-Fi connection
count, and other information.
Users can click the icon next to the "Name" field to customize the name of this
device.
Fig. 5-1 Dashboard interface
5.1.1 Device Information
Users can view basic device information in the "Dashboard > Device Info"
interface, including the device name, device model, device serial number, MAC address,
online duration, upstream interface address, and other details.
Fig. 5-1-1 Device Information interface

8
5.1.2 Traffic Statistics
Users can check the usage of traffic on various upstream interfaces since EAP600
was powered on through the "Dashboard > Traffic Statistics" feature. The data for
traffic statistics will reset after the device is restarted. If you need to view historical
traffic records, you can do so on the corresponding device's details page in the InHand
Cloud Manager.
Fig. 5-1-2 Traffic statistics
5.1.3 Wi-Fi Connections
Users can view the number of active SSIDs and the client count for each SSID that
is connected to the EAP600 through the "Dashboard > Wi-Fi Connections" feature.
Fig. 5-1-3 view the Wi-Fi connection status

9
5.2 Status
Click on the [ Status ] option in the left menu to enter the status page, where you
can check the device's link status, clients, events, logs, and other information.
5.2.1 Link Monitoring
Link monitoring is used to track and evaluate the real-time performance,
availability, and stability of network connections. Users can use the "Status > Link
Monitoring" function to view the health status of upstream links and information such
as throughput, latency, and packet loss for each interface.
Fig. 5-2-1 Link Monitor Data
5.2.2 Clients
Clients typically refer to wireless devices connected to an access point (AP), such
as laptops, smartphones, tablets, and other similar devices.
Users can access detailed client information connected to the EAP600 via the
"Status > Clients" feature. This information includes client names, IP addresses, MAC
addresses, VLAN, connected SSID, RSSI, operating channels, Wi-Fi standards, traffic
usage, online duration, and more.

10
Fig. 5-2-2 Wireless Client Connection Information
5.2.3 Events
[ Event ] is used to record information related to the device's status, performance,
and user-triggered operations. This helps IT personnel understand the network's
operational status, detect problems promptly, and take necessary measures. It is a
valuable tool for network monitoring and troubleshooting.
Users can access event information generated during the device's operation via the
"Status > Events" function. This helps users understand the device's operational status
and can be useful for troubleshooting issues. New events will be updated at the
beginning of the table.
Fig. 5-2-3 Check the recorded events
At the top of the event list, you can filter the displayed content by setting the time
and selecting the event level. You can also export or clear recorded events using the
"Clear Events" and "Export Events" buttons. In addition, you can set the number of
events displayed per page and use the fast page navigation at the bottom right of the
page. The currently supported event types that can be recorded include:

11
⚫Successful User Login
⚫Failed User Login
⚫Configuration Changes
⚫High CPU Utilization
⚫High Memory Utilization
⚫Device Reboot
⚫Firmware Upgrade
⚫Client Status Changes
⚫Connection Status Changes
⚫These events are recorded to help you monitor and manage the device's operation
and network activity.
5.2.4 Logs
The log function is used to record the raw return information of the device's
operation under various circumstances. It is typically employed by IT or research and
development personnel for the analysis and troubleshooting of issues.
Users can access the device's system logs by navigating to the "Status > Logs"
section. System logs provide detailed information about the device's operation, and they
are invaluable for troubleshooting when issues arise. Users have the option to download
and clear logs as needed.
You can filter the displayed log entries based on log level or by entering keywords.
New log entries are added to the end of the log, keeping the most recent events at
the bottom of the log.

12
Fig. 5-2-4 Check the recorded logs
5.3 Configuration
Click on the "Config" button in the left-side navigation menu to access the
configuration page. On this page, you can set up the device's WAN/LAN interface
settings and RF parameters.
5.3.1 WAN
The EAP600 supports single-port wired access, and users can configure it to use
DHCP or static IP address assignment based on their requirements. Click on
“Configuration > WAN” to select the network connection type.
Fig. 5-3-1 Access the WAN editing interface
⚫DHCP: The EAP600 can dynamically obtain an internet IP address by using
the DHCP server of the upstream router.
⚫Static IP: Users can manually configure the address assigned by the ISP or
upstream device. After the configuration is complete, the AP will connect to
the network using the specified static IP.
⚫The default MTU value is 1500, and the valid input range is from 128 to 1500.

13
5.3.2 LAN
This page is only visible when the device is operating in FAT-Router mode. For
more details, please refer to 5.5.10 System Settings.
When the device operates in FAT-Routing mode, users can create subnets and
VLANs for different network segments in "Config > LAN" and configure subnet
properties.
Fig. 5-3-2 Add a local network
The "Network Type" field provides two available modes:
⚫Standard: Clients connected to the standard mode network can access the
Internet and the device's web interface.
⚫Guest: Clients connected to the guest mode network can only access the
Internet and cannot log in to the device's web interface.
Edit Local Network: You can adjust the parameters of an existing local network,
and the configuration fields are the same as when creating a new network.
5.3.3 Radio
Radio Frequency (RF) refers to the wireless communication technology used by
access points (APs) in a wireless local area network. It primarily involves the
configuration and adjustment of AP RF parameters to ensure optimal wireless coverage
and performance.

14
Users can configure the device's Wi-Fi radio settings, such as the operating
channels, radio power, and wireless mesh features, under "Config > Radio" in the
device settings.
Fig. 5-3-3-a Edit the radio’s parameters
You can configure the frequency width and transmit power for 2.4GHz and 5GHz
radio frequencies under "Configuration > Radio > Radio Settings." When you set the
“Transmit Power” to "Custom," you must manually enter the power value. The valid
input range for power is between 1 and 20, with the default value being 20.
Fig.5-3-3-b Set the Transmit Power manually
The wireless Mesh network feature is disabled by default. When enabled in
"config > radio > mesh," devices of the same model can quickly form a network through
Mesh.
Fig.5-3-3-c Enable the Wireless Mesh

15
5.4 Wi-Fi
Wi-Fi functionality provides wireless local area network (LAN) connectivity for
devices such as computers, smartphones, tablets, and more. It allows these devices to
connect to a network wirelessly, providing internet access and communication
capabilities.
EAP600 offers the ability to provide multiple SSIDs for wireless network access.
Users can customize and configure different SSIDs for various purposes in the
[ Wi-Fi] interface.
Fig. 5-4-a SSID List
By clicking on the "Wi-Fi > SSIDs" section and then the "Add/Edit" button, you
can add a new SSID or edit an existing one. You can choose to hide the SSID. In this
case, users will need to manually enter the SSID name and password on their client
devices, and the SSID won't be visible in the list of available Wi-Fi networks.
Fig. 5-4-b Add a new SSID
Cautions:
⚫The device comes with two default main SSIDs for the 2.4GHz and 5GHz bands,
and these main SSIDs cannot be modified or deleted.
Table of contents
Popular Wireless Access Point manuals by other brands

MikroTik
MikroTik RouterBOARD SXT G-5HnD Quick setup guide and warranty information

Aerohive
Aerohive access point Deployment guide

D-Link
D-Link DWL-3600AP Administrator's guide

4IPNET
4IPNET OWL400 Quick installation guide

Huawei
Huawei R230D Product description
Abocom
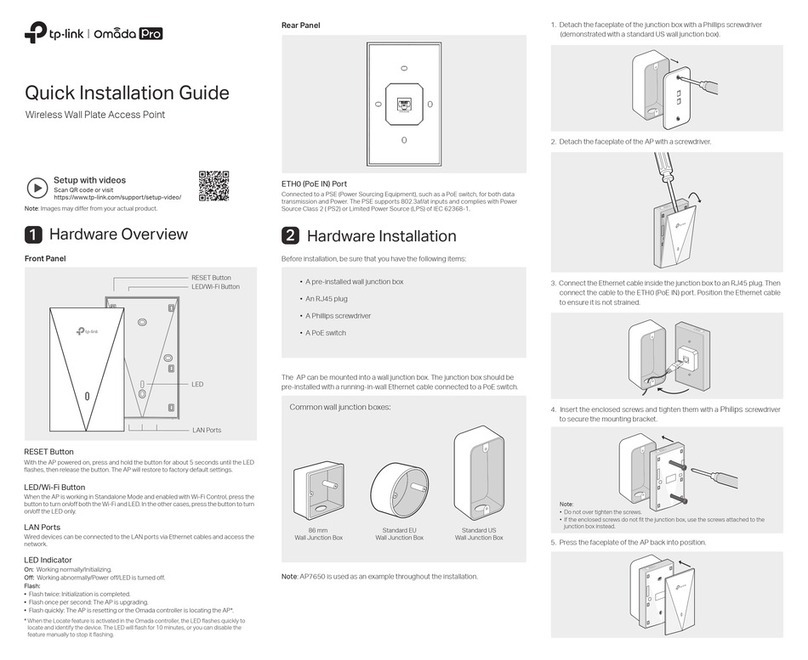
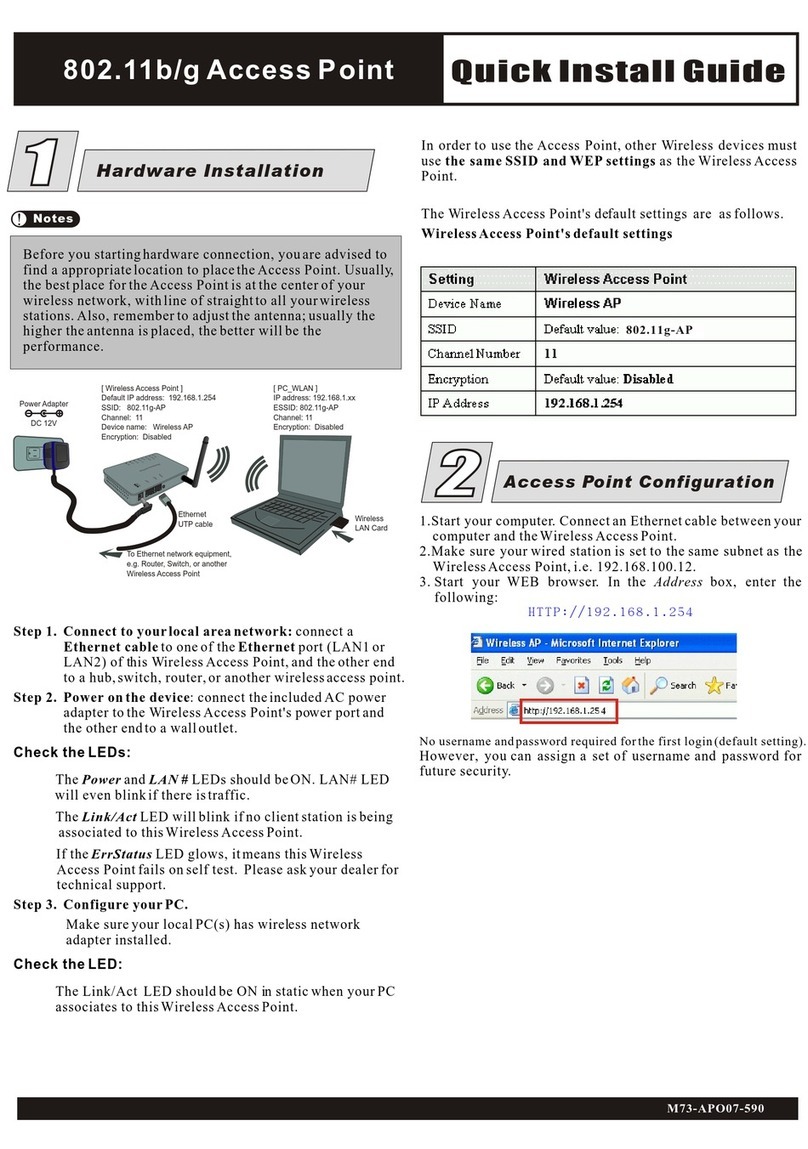
Abocom 802.11g Wireless Access Point WAP253 Quick install guide

NETGEAR
NETGEAR ME102 - Wireless Access Point reference guide

SonicWALL
SonicWALL sonicpoint ACI Getting started guide

ZyXEL Communications
ZyXEL Communications ZyAIR G-5100 user guide

NETGEAR
NETGEAR WAX204 installation guide

Cisco
Cisco Meraki Go GR62 installation guide

Arista
Arista OEM-AP-O105E Getting started guide