i
USER’S NOTICE.....................................................................................................................ii
MANUAL REVISION INFORMATION ..............................................................................ii
COOLING SOLUTIONS........................................................................................................ii
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION OF 845GVFD MOTHERBOARD
1-1 FEATURE OF MOTHERBOARD ...................................................................................... 1
1-2 SPECIFICATION.................................................................................................................. 2
1-3 PERFORMANCE LIST........................................................................................................ 3
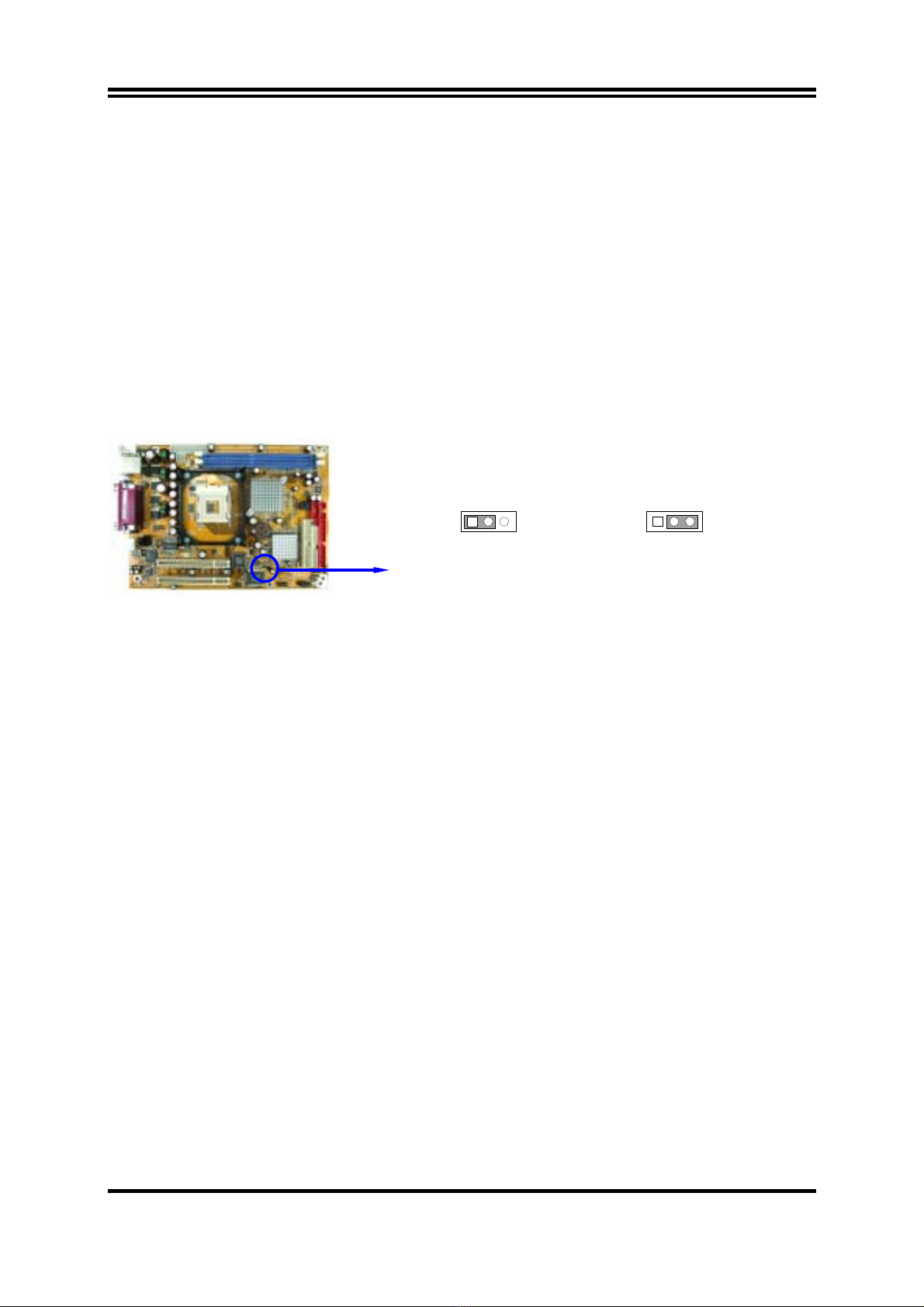
1-4 LAYOUT DIAGRAM & JUMPER SETTING ................................................................... 4
CHAPTER 2 HARDWARE INSTALLATION
2-1 HARDWARE INSTALLATION STEPS............................................................................. 6
2-2 CHECKING MOTHERBOARD'S JUMPER SETTING................................................... 6
2-3 INSTALL CPU....................................................................................................................... 7
2-3-1 GLOSSARY................................................................................................................ 7
2-3-2 ABOUT INTEL PENTIUM 4 478-PIN CPU ........................................................... 8
2-4 INSTALL MEMORY............................................................................................................ 9
2-5 EXPANSION CARD..............................................................................................................9
2-5-1 PROCEDURE FOR EXPANSION CARD INSTALLATION ............................... 10
2-5-2 ASSIGNING IRQ FOR EXPANSION CARD......................................................... 10
2-5-3 INTERRUPT REQUEST TABLE FOR THIS MOTHERBOARD....................... 10
2-6 CONNECTORS, HEADERS ................................................................................................ 11
2-6-1 CONNECTORS.......................................................................................................... 11
2-6-2 HEADERS .................................................................................................................. 13
2-7 STARTING UP YOUR COMPUTER.................................................................................. 17
CHAPTER 3 INTRODUCING BIOS
3-1 ENTERING SETUP............................................................................................................... 18
3-2 GETTING HELP ................................................................................................................... 18
3-3 THE MAIN MENU................................................................................................................ 19
3-4 STANDARD CMOS FEATURES ........................................................................................ 20
3-5 ADVANCED BIOS FEATURES .......................................................................................... 21
3-6 ADVANCED CHIPSET FEATURES .................................................................................. 23
3-6-1 DRAM TIMING SETTINGS.................................................................................... 24
3-7 INTEGRATED PERIPHERALS.......................................................................................... 25
3-7-1 ONBOARD IDE FUNCTION................................................................................... 25
3-7-2 ONBOARD DEVICE FUNCTION........................................................................... 26
3-7-3 ONBOARD SUPER IO FUNCTION ....................................................................... 27
3-8 POWER MANAGEMENT SETUP...................................................................................... 28
3-8-1 PM TIMER RELOAD EVENTS ............................................................................. 29
3-9 PNP/PCI CONFIGURATION SETUP ................................................................................ 29
3-9-1 IRQ RESOURCES .................................................................................................... 30
3-10 PC HEALTH STATUS ........................................................................................................ 31
3-11 MISCELLANEOUS CONTROL ........................................................................................ 32
3-12 LOAD STANDARD/OPTIMIZED DEFAULTS ............................................................... 33
3-13 SET SUPERVISOR/USER PASSWORD........................................................................... 33
CHAPTER 4 DRIVER & FREE PROGRAM INSTALLATION
MAGIC INSTALL SUPPORTS WINDOWS 98SE/ME/NT4.0/2000/XP.................................... 34
4-1 INF INSTALL INTEL 845 CHIPSET SYSTEM DRIVER.......................... 35
4-2 VGA INSTALL INTEL 845G VGA DRIVER................................................. 36
4-3 SOUND INSTALL ALC AUDIO CODEC DRIVER ........................................... 36
4-4 LAN INSTALL RTL810X LAN CONTROLLER DRIVER ......................... 37
4-5 PC-HEALTH WINBOND 83627THF HARDWARE DOCTOR ................................. 38
4-5-1 HOW TO UTILIZE PC-HEALTH.......................................................................... 39
4-6 MAGIC BIOS INSTALL BIOS LIVE UPDATE UTILITY .......................................... 39
4-7 IAA INSTALL INTEL APPLICATION ACCELERATOR SOFTWARE . 41
4-8 PC-CILLIN INSTALL PC-CILLIN2004 ANTI-VIRUS PROGRAM ...................... 41
4-9 HOW TO INSTALL USB 2.0 DRIVER............................................................................... 42
4-10 HOW TO DISABLE ON-BOARD SOUND......................................................................... 43
4-11 HOW TO UPDATE BIOS..................................................................................................... 43
TABLE OF CONTENT