3
1Goal of this Guide
This document describes how to evaluate the KLIPPEL Controlled Sound technology (KCS) by using the
KLIPPEL QC measurement framework. The following topics are covered:
•Measuring the frequency response
•Evaluation of the performance of active systems including KCS in the large signal domain
•Evaluation of the KCS speaker protection
•Evaluation of multi-tone distortion compensation
•How to treat Rub&Buzz problems
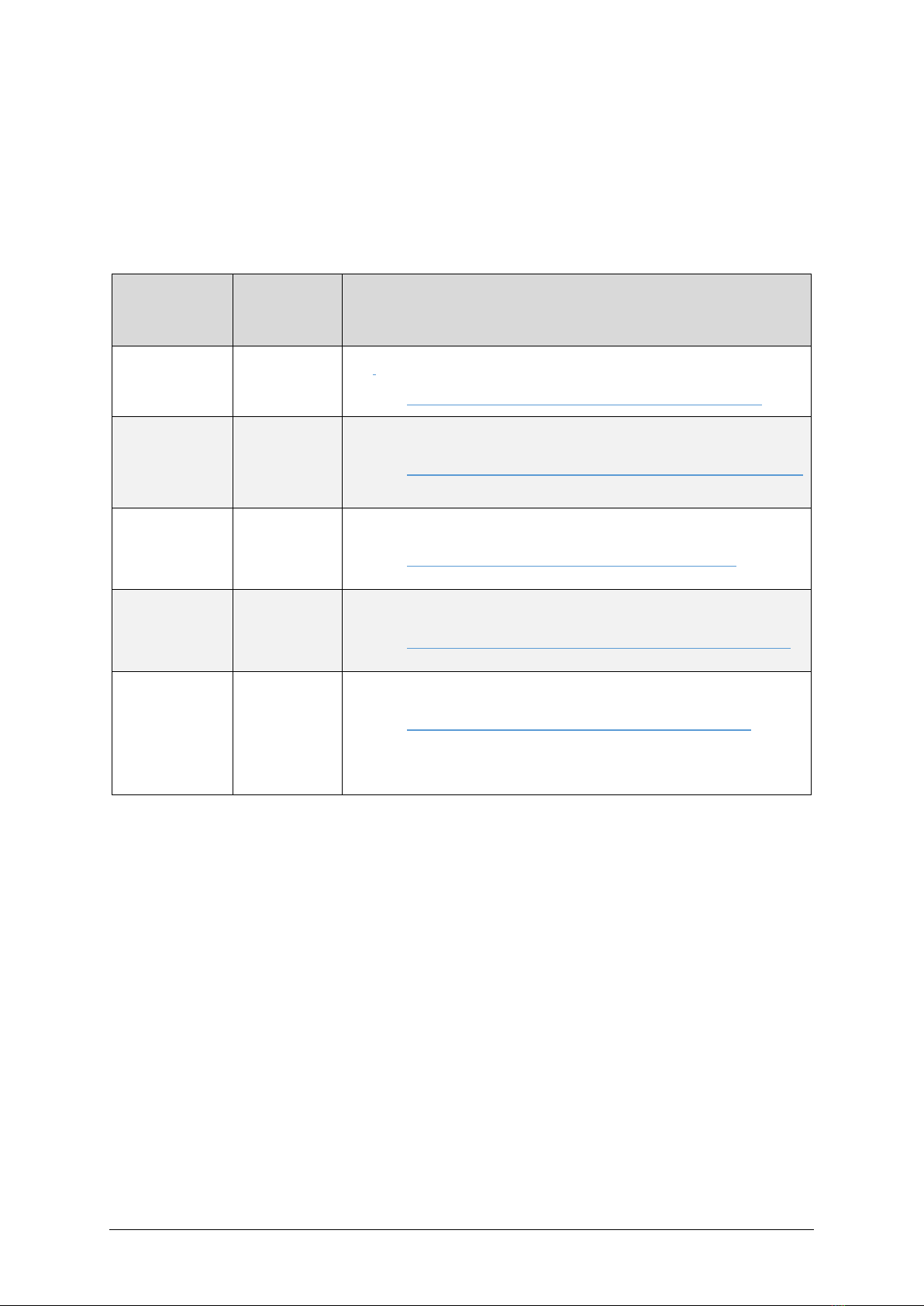
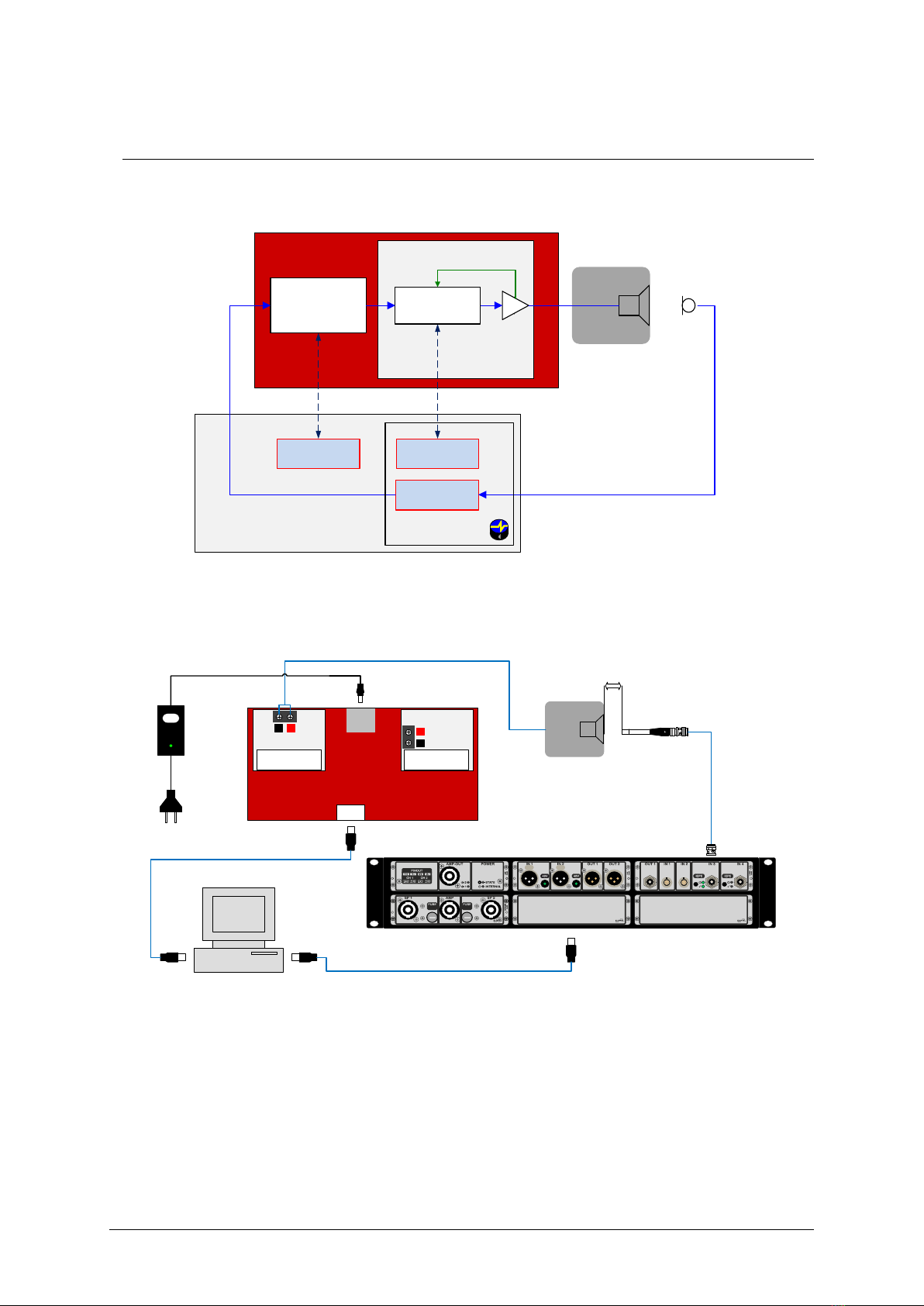
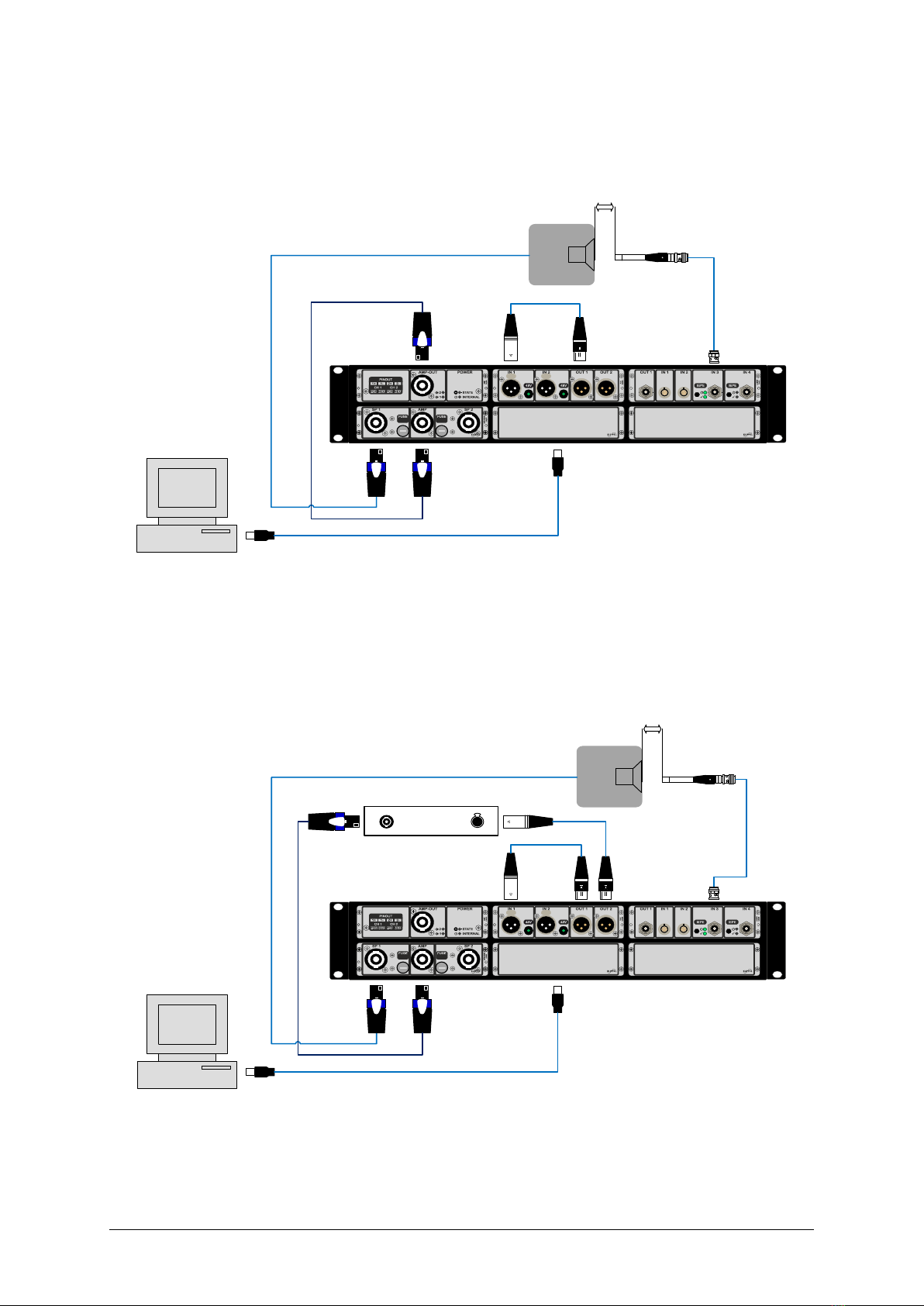
2Requirements
Its mandatory to read the document Manual KCS Monitor.pdf which teaches necessary KCS
basic knowledge before the KCS evaluation tutorials are executed!
Hardware:
•KCS hardware platform (e.g. Nuvoton Audio Development Board (NAD), Klippel Analyzer 3
(KA3), APE Evaluation Board etc.)
•Measurement Equipment. There are two options:
oKA3 measurement device:
▪Klippel Analyzer 3 (KA3)
▪Microphone
oNAD on-board microphone (DMIC):
▪Klippel Dongle
▪DMIC module mounted on NAD board
Software:
•Klippel dB-Lab of version >= 210.826
•Licenses for: QC Standard 6 for KCS, SPL task, Multi-tone distortion task, SYN, 3DL
•Additional License (only for QC measurement with NAD board DMIC): QC no PA hardware
required (== QC Standalone)
In addition, following Klippel dB-Lab operations are required:
•KCS Monitor operation comprising initial data for the particular DUT
•QC operation template KCS Evaluation Template.kdbx