1Overview......................................................................................................................................................................4
2Laird Connectivity Lyra P Part Numbers........................................................................................................................4
3Kit Contents.................................................................................................................................................................5
4Main Board –Features.................................................................................................................................................5
4.1 Key Features.......................................................................................................................................................5
5Understanding the Development Board.........................................................................................................................6
6Software Development Selection Switch SW1...............................................................................................................7
7Specifications...............................................................................................................................................................7
7.1 Recommended Operating Conditions...................................................................................................................7
7.2 Current Consumption...........................................................................................................................................7
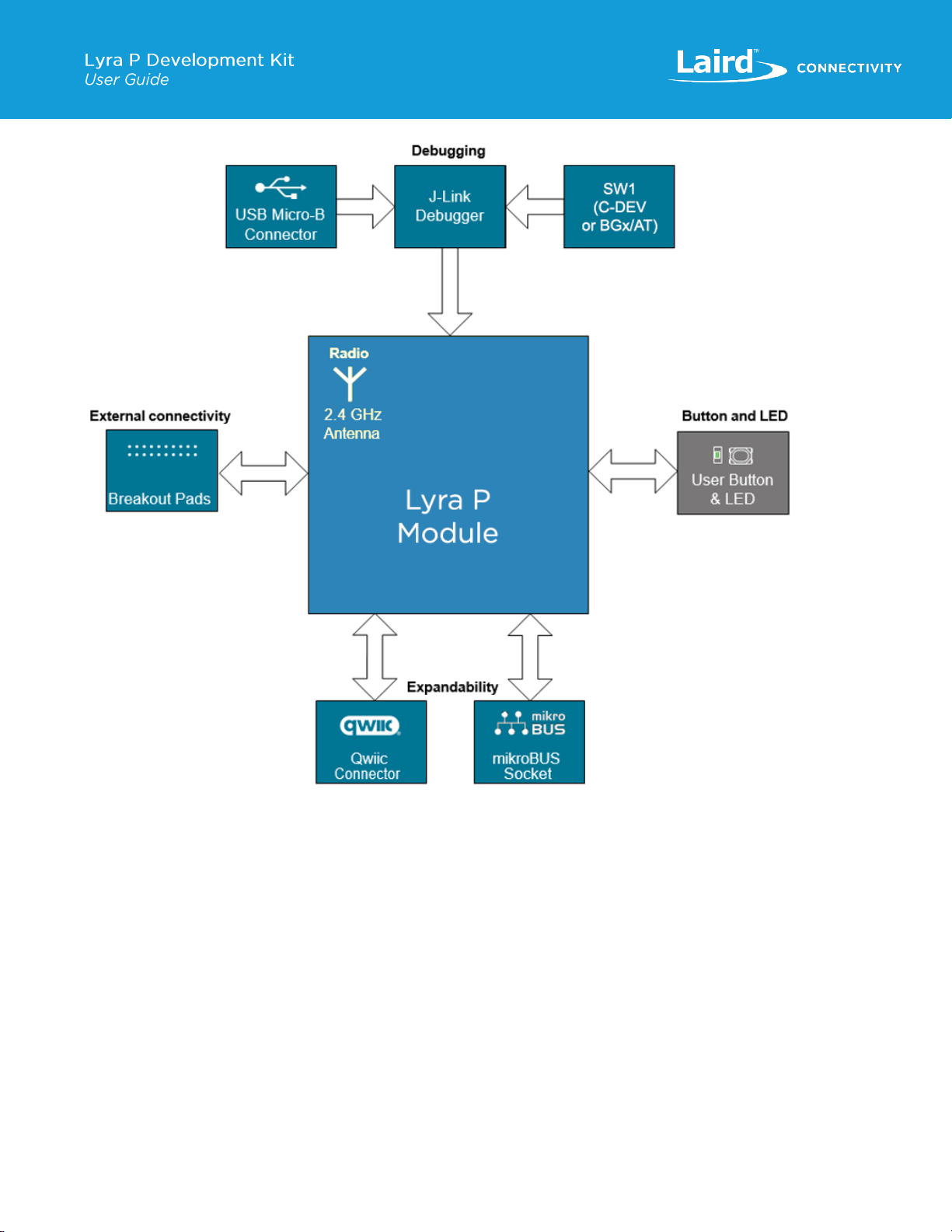
8Functional Blocks.........................................................................................................................................................8
8.1 Hardware Block Diagram.....................................................................................................................................8
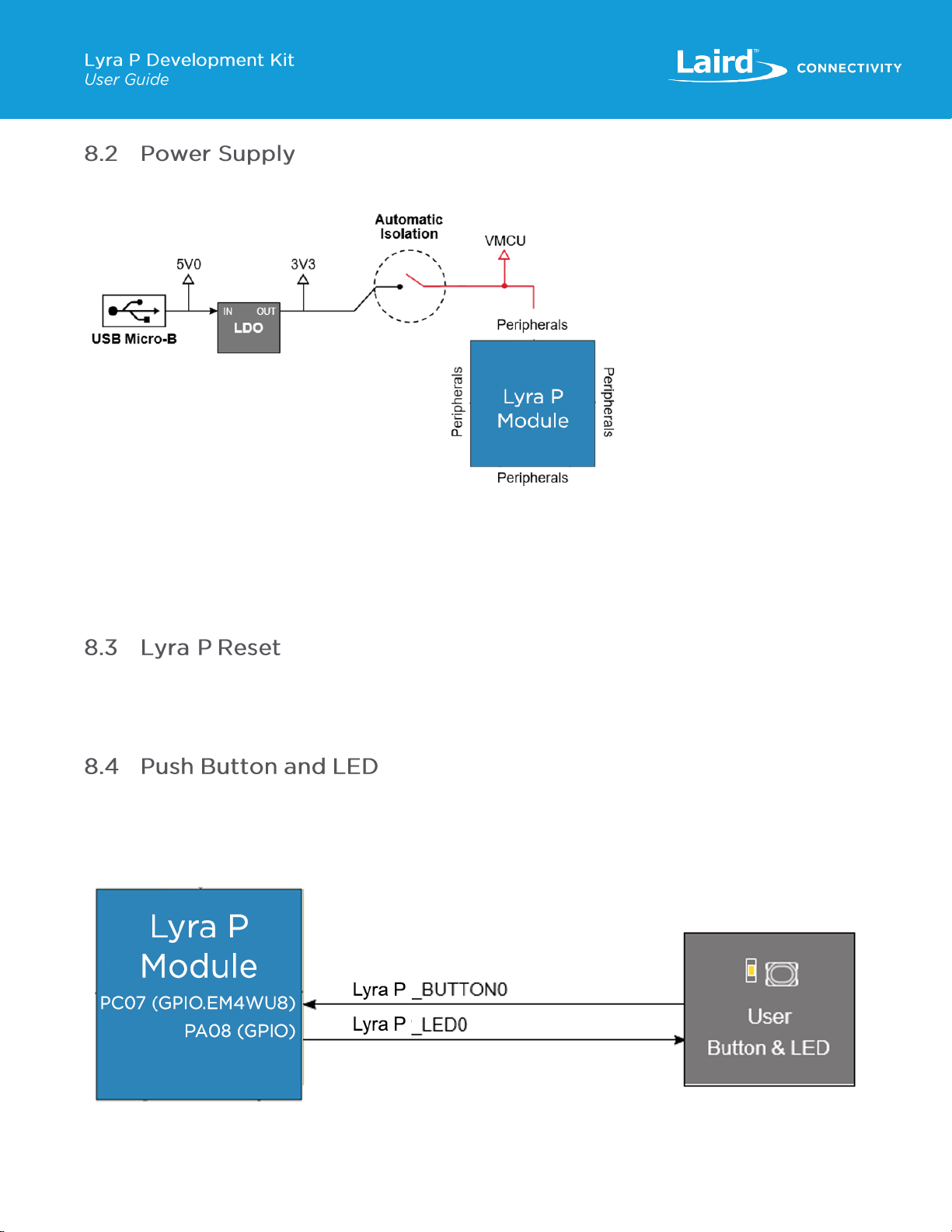
8.2 Power Supply....................................................................................................................................................10
8.3 Lyra P Reset .....................................................................................................................................................10
8.4 Push Button and LED........................................................................................................................................10
8.4.1 BOOT pin (PC07) and BUTTON 0 (silkscreen BTN0)....................................................................................11
8.5 On-board Debugger...........................................................................................................................................11
8.6 Hardware Connectors........................................................................................................................................12
8.6.1 Breakout Pads Pinout...................................................................................................................................13
8.6.2 MikroBUS Socket.........................................................................................................................................14
8.6.3 Qwiic Connector...........................................................................................................................................15
8.6.4 Debug USB Micro-B Connector ....................................................................................................................15
9Debugging.................................................................................................................................................................16
9.1 On-board Debugger...........................................................................................................................................16
9.2 Virtual COM Port...............................................................................................................................................16
10 Schematic, Assembly Drawing, 3DModel....................................................................................................................16