5
5000 SERIES AMPLIFIER
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
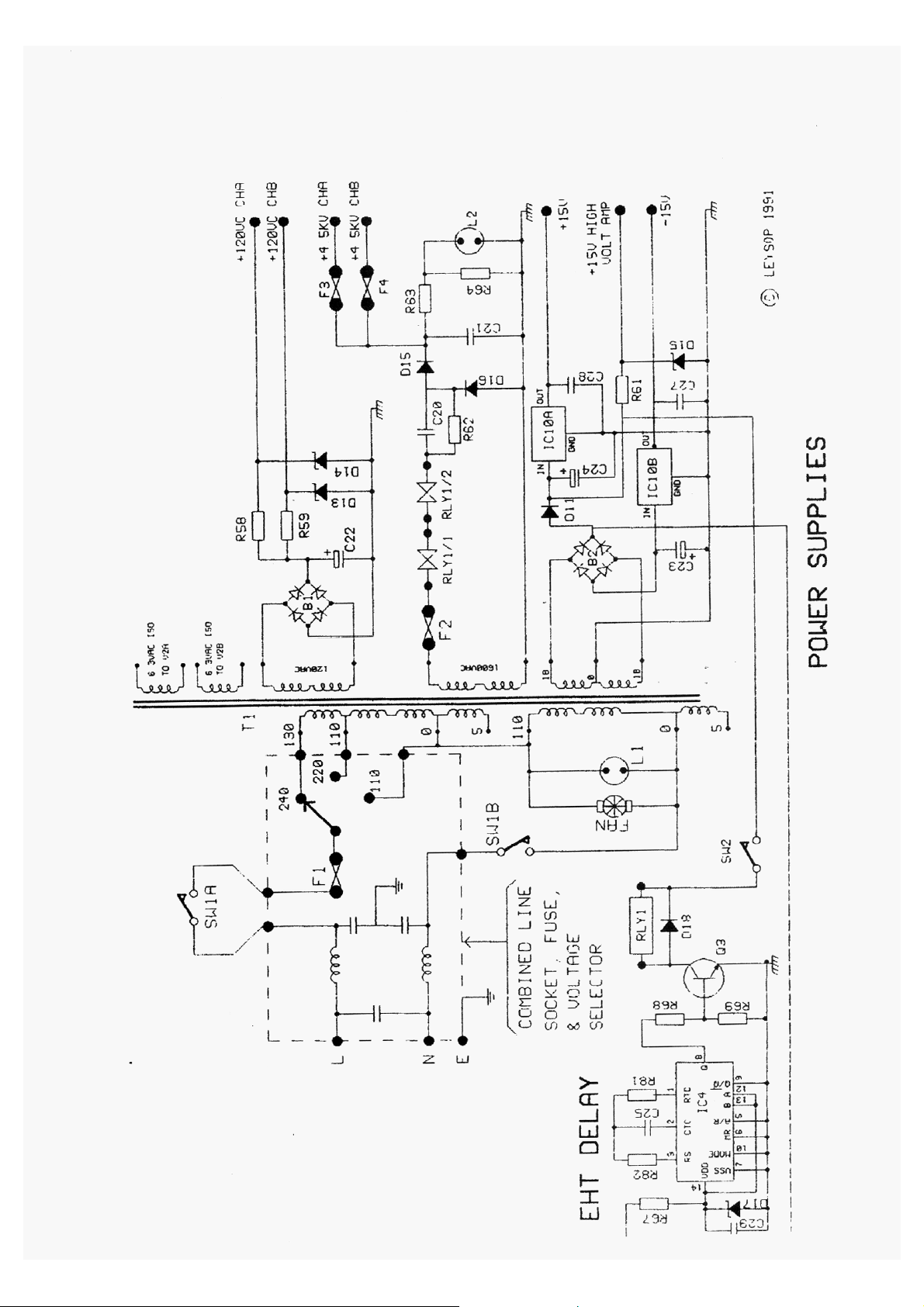
MAINS VOLTAGE SELECTOR AND FUSE
Before switching on the amplifier check the mains voltage selector, situated at the rear of the cabinet, is
set correctly and note that the mains fuse 2 Amp, 20mm type is mounted in the voltage selector. Fit the
output values by removing the amplifier from its case. Make certain that the amplifier is screwed back
into its case before switching on.
SWITCHING ON
Switch on the mains switch and note that the mains lamp comes on.
An internal delay circuit prevents the E.H.T. from switching on for a period of about 30 seconds. After
this time, the E.H.T. indicator will come on if the E.H.T. switch is in the ON position. The amplifier is
now ready for use, although it is recommended that full output swing at frequencies above 10 kHz should
not be demanded for a period of 5 minutes after switch on from cold.
NORMAL OPERATION
For normal operation the controls should be set as follows:-
DIFFERENTIAL zero
POSITIVE LIMIT 100%
NEGATIVE LIMIT 100%
SLEW RATE LIMIT off
The input to the amplifier may either be via the EXT input (linear range + 2.5 volts) or any of the wave
forms, square, sine or triangular from the internal oscillator as selected by the 'source selection' switch.
The frequency of the internal oscillator may be varied over the range 1Hz to 10 kHz. In addition, the
amplitude of the internal oscillator signal may varied over the range zero up to + 2.5 volts (100% setting)
by the amplitude control. The auxiliary outputs provide sine, square and triangular wave forms of
approximately constant amplitudes of + 2.5V pk-pk, irrespective of the wave form selected by the 'Source
selector' switch and also independent of the amplitude control.
DIFFERENTIAL BIAS CONTROLS (INPUT BIAS CONTROL)
The 'Differential bias controls' adjust the mean levels of the A and B output channels.
With the bias control set to zero both A and B channel outputs will be biased to 1.7 kV. When the
'Differential bias' controls are set to positive maximum (10%) the A output bias will be 1.95 kV, and the
B output bias will be 1.45 kV. Thus VA- VB= 0.5 kV which is 10% of the maximum differential output.
When the 'differential bias' controls are set to negative maximum, A output bias is 1.45 kV and B output
bias is 1.95 kV. The Differential bias control/input bias control allows the output levels to be precisely
adjusted across the pockels cells for 'zero voltage input conditions', thereby achieving the best extinction
ratio or lowest residual phase modulation.