Memec Virtex-4 User manual

Virtex-4™ MB Development Board
User’s Guide
Version 3.0
December 2005

December 20,2005
i
Table of Contents
1OVERVIEW .....................................................................................................................1
2THE VIRTEX-4 MB SYSTEM BOARD ..............................................................................1
3FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION .........................................................................................2
3.1 LVDS INTERFACE .......................................................................................................3
3.1.1 SPI-4.2 Interface.................................................................................................4
3.1.2 SPI-4.2 Pin Assignments.....................................................................................4
3.1.3 LVDS Connector.................................................................................................6
3.2 DDR SDRAM ............................................................................................................7
3.3 FLASH.......................................................................................................................8
3.4 CLOCK SOURCES ........................................................................................................9
3.4.1 Programmable LVDS Clock Source...................................................................11
3.4.2 ICS8442 Programmable LVDS Clock Synthesizer...............................................11
3.4.3 ICS8442 Clock Generation................................................................................13
3.4.4 ICS8442 Programming Modes...........................................................................14
3.4.5 ICS8442 M and N Settings ................................................................................14
3.5 10/100 ETHERNET PHY .............................................................................................18
3.6 LCD PANEL..............................................................................................................20
3.7 USB 2.0 TO RS232 PORT..........................................................................................20
3.8 RS232....................................................................................................................21
3.9 USER DIP AND PB SWITCHES.....................................................................................22
3.10 USER LEDS..........................................................................................................23
3.11 VBAT JUMPER......................................................................................................23
3.12 CONFIGURATION AND DEBUG PORTS.........................................................................23
3.12.1 JTAG Chain .....................................................................................................23
3.12.2 System ACE Module Connector.........................................................................24
3.12.3 Serial Data Flash..............................................................................................26
3.12.4 JTAG Port (PC4) ..............................................................................................31
3.12.5 Configuration Modes .........................................................................................31
3.13 VOLTAGE REGULATORS ..........................................................................................32
3.14 BANK I/O VOLTAGE................................................................................................33
3.15 P240 EXPANSION MODULE SIGNAL ASSIGNMENTS......................................................33
4REVISIONS...................................................................................................................36
APPENDIX A.......................................................................................................................37

December 20,2005 ii
Figures
FIGURE 1 -VIRTEX-4 MB DEVELOPMENT PLATFORM BLOCK DIAGRAM.............................................3
FIGURE 2-SPI-4.2 INTERFACE...................................................................................................4
FIGURE 3 –SAMTEC QSE TYPE CONNECTOR FOR THE SPI-4.2 INTERFACE....................................7
FIGURE 4 –DDRSDRAM INTERFACE.........................................................................................7
FIGURE 5 –FLASH INTERFACE....................................................................................................8
FIGURE 6 -CLOCK SOURCES ON THE VIRTEX-4 MB BOARD ..........................................................10
FIGURE 7 –ICS8442 CLOCK SYNTHESIZER ...............................................................................12
FIGURE 8 –ICS8442 CLOCK SYNTHESIZER INTERFACE TO THE FPGA...........................................15
FIGURE 9 –ICS8442 CLOCK SYNTHESIZER M AND N DIP SWITCHES ............................................16
FIGURE 10 –M AND N DIP SWITCHES FOR THE SYNTHESIZERS ....................................................16
FIGURE 11 –10/100 ETHERNET INTERFACE...............................................................................19
FIGURE 12 –USB 2.0 TO RS232 SERIAL INTERFACE..................................................................21
FIGURE 13 -RS232 INTERFACE ...............................................................................................22
FIGURE 14 –VITEX-4 MB DEVELOPMENT BOARD JTAG CHAIN.....................................................24
FIGURE 15 –SYSTEMACE MODULE..........................................................................................25
FIGURE 16 –VIRTEX-4 MB DEVELOPMENT BOARD CONFIGURATION INTERFACE..............................26
FIGURE 17 –VIRTEX-4 MB DEVELOPMENT BOARD JTAG CHAIN...................................................28
FIGURE 18 –SERIAL FLASH CONFIGURATION INTERFACE..............................................................29
FIGURE 19 –PC4 JTAG PORT CONNECTOR..............................................................................31
FIGURE 20 -VOLTAGE REGULATORS .........................................................................................32

December 20,2005
1
1Overview
The Memec Virtex-4™ MB Development Kit provides a complete development platform for
designing and verifying applications based on the Xilinx Virtex-4FPGA family. This kit enables
designers to implement DSP and embedded processor based applications with extreme flexibility
using IP cores and customized modules. The Virtex-4FPGA along with Xilinx MicroBlaze soft
processor core makes it possible to prototype processor based applications, enabling software
design teams early access to a hardware platform prior to working with the final product/target
board.
The Virtex-4 MB system board utilizes the Xilinx XC4VLX25/LX60/SX35-10FF668C FPGA. The
board includes 64MB of DDR SDRAM, 4MB of Flash, 16-bit LVDS Transmit and Receive ports,
programmable LVDS clock source, USB-RS232 Bridge, a 10/100 Ethernet PHY, 100 MHz clock
source, RS-232 port, and additional user support circuitry to develop a complete system. The
board also supports the Memec P240 expansion module standard, allowing application specific
expansion modules to be easily added.
2The Virtex-4 MB System Board

December 20,2005 2
3Functional Description
A high-level block diagram of the Virtex-4™ MB development platform is shown below followed
by a brief description of each sub-section. A list of features for this board is shown below:
•Xilinx XC4VLX25/LX60/SX35-10FF668 FPGA
•64MB of DDR SDRAM
•4MB of Flash
•16-Bit LVDS Transmit and Receive Interfaces
•10/100 Ethernet PHY
•Programmable LVDS Clock Source (25-700 MHz)
•User LVDS Clock Outputs via Differential SMA Connectors
•On-board 100MHz LVTTL Oscillator
•On-board LVTTL Oscillator Socket (4/8-Pin Oscillators)
•P240 Connectors
•LCD Panel
•32Mb Serial Flash for FPGA configuration
•PC4 JTAG Programming/Configuration Port
•SystemACE™ Module Connector
•RS232 Port
•Four User LEDs
•Four User Push Button Switches
•An 8-position DIP Switch
•USB-RS232 Bridge

December 20,2005 3
P240 Module
RS232 Port
User LEDs
Virtex4 FPGA
XC4VLX25/LX60/
SX35
(FF668)
132-PinConnector
132-PinConnector
DDR SDRAM
(64MB)
LCD Panel
User Switches
XC9536XV
CPLD
Parallel Cable IV
JTAGPort
SAM Connector
Atmel Serial Flash
(AT45DB321B-TC)
Parallel Cable IV
Flash SPI Port
USB-RS232
Bridge
3.3V
Regulator
Voltage RegulatorsClock Sources
LVTTL OSC Socket
(4/8-Pin)
Programmable
LVDS Clock Source
LVTTL Clock
@100MHz
SMA Clock Output 2.5V
Regulator
1.2V
Regulator
Flash
(4MB)
16-Bit LVDS
Transmit &
Receive
10/100 PHY
Figure 1-Virtex-4 MB Development Platform Block Diagram
3.1 LVDS Interface
The Virtex-4 MB development board provides high-speed LVDS connectors supporting a SPI-4.2
interface. This interface consists of 36 LVDS signal pairs (72 FPGA signals) and 6 single-ended
signals. In addition to the SPI-4.2 interface, the LVDS interface is designed to support XSBI 16-bit
LVDS @644Mbps to support a 10GbE interface on the Virtex-4 MB development platform. The
following sections provide a brief description of the LVDS interface on this development board.

December 20,2005 4
3.1.1 SPI-4.2 Interface
The Virtex-4 MB development board provides a SPI-4.2 via a 16-bit parallel LVDS electrical
interface. The following figure shows the SPI-4.2 interface on the board. The transmit and receive
interface of the SPI-4.2 are implemented using LVDS signals while the status flow control signals
are implemented using single-ended LVTTL signals.
Virtex-4 FPGA
4VLX25-FF668
TDat[15:0]
TDClk
TCtl
TStat[1:0]
TSClk
TDat[15:0]
TDClk
TCtl
TStat[1:0]
TSClk
Transmit
Link Layer
Receive
Link Layer
LVDS
Connectors
RDat[15:0]
RDClk
RCtl
RStat[1:0]
RSClk
RDat[15:0]
RDClk
RCtl
RStat[1:0]
RSClk
SysClk_P LVDS Signals
LVTTL Signals
LVDS Signals
LVTTL Signals
SysClk_N
Figure 2-SPI-4.2 Interface
3.1.2 SPI-4.2 Pin Assignments
The following table shows the SPI-4.2 pin assignments for the 4VLX25/LX60/SX35 FPGA in the
FF668-pin package. These pin assignments must be used in the board design in order to meet
the SPI-4.2 interface core requirements.
Table 1– SPI-4.2 Transmit Pin Assignments
Virtex-4 Pin # LVDS Signal
Name J4 Connector Pin #
LVDS TX LVDS Signal
Name Virtex-4 Pin #
5.0V 125.0V
5.0V 345.0V
GND 56GND
3.3V 783.3V
3.3V 910 3.3V
GND 11 12 GND
2.5V 13 14 2.5V
December 20,2005 5
2.5V 15 16 2.5V
GND 17 18 GND
R8 TSCLK 19 20 NC
NC 21 22 NC
GND 23 24 GND
T8 TSTAT0 25 26 NC
T7 TSTAT1 27 28 NC
GND 29 30 GND
A7 TDat_N(15) 31 32 TDat_N(14) D7
A8 TDat_P(15) 33 34 TDat_P(14) D8
GND 35 36 GND
E10 TDat_N(13) 37 38 TDat_N(12) A5
F10 TDat_P(13) 39 40 TDat_P(12) A6
G8 TDat_N(11) 41 42 TDat_N(10) C7
F8 TDat_P(11)43 44 TDat_P(10) B7
GND 45 46 GND
D5 TDat_N(9) 47 48 TDat_N(8) B9
C5 TDat_P(9) 49 50 TDat_P(8) A9
GND 51 52 GND
B3 TDat_N(7) 53 54 TDat_N(6) D4
A3 TDat_P(7) 55 56 TDat_P(6) C4
GND 57 58 GND
D6 TDat_N(5) 59 60 TDat_N(4) E5
E7 TDat_P(5) 61 62 TDat_P(4) E6
GND 63 64 GND
G7 TDat_N(3) 65 66 TDat_N(2) C1
F7 TDat_P(3) 67 68 TDat_P(2) C2
GND 69 70 GND
H7 TDat_N(1) 71 72 TDat_N(0) E4
H8 TDat_P(1) 73 74 TDat_P(0) D3
GND 75 76 GND
C8 TCtl_N 77 78 TDCLK_N F9
D9 TCtl_P 79 80 TDCLK_P E9
GND 81 82 GND
GND 83 84 GND
GND 85 86 GND
GND 87 88 GND
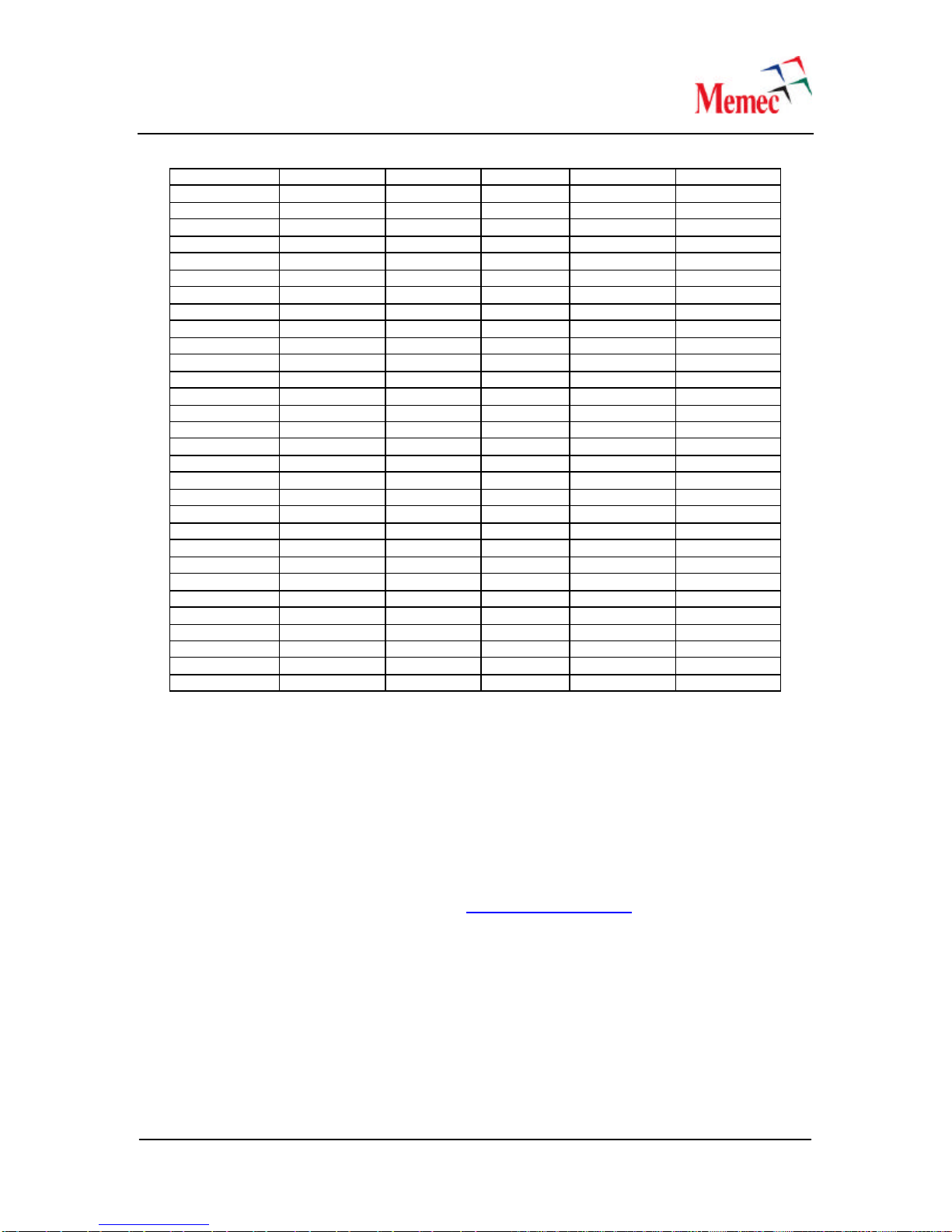
Table 2–SPI-4.2 Receive Pin Assignments
Virtex-4 Pin # LVDS Signal
Name J5 Connector Pin #
LVDS RX LVDS Signal
Name Virtex-4 Pin #
5.0V 125.0V
5.0V 345.0V
GND 56GND
3.3V 783.3V
3.3V 910 3.3V
GND 11 12 GND
2.5V 13 14 2.5V
2.5V 15 16 2.5V
GND 17 18 GND
U5 RSCLK 19 20 NC
NC 21 22 NC
GND 23 24 GND
J1 RSTAT0 25 26 NC
December 20,2005 6
J2 RSTAT1 27 28 NC
GND 29 30 GND
AB4 RDat_N(15) 31 32 RDat_N(14) AB2
AC4 RDat_P(15) 33 34 RDat_P(14) AB3
GND 35 36 GND
AB5 RDat_N(13) 37 38 RDat_N(12) AC1
AC5 RDat_P(13) 39 40 RDat_P(12) AC2
AE3 RDat_N(11) 41 42 RDat_N(10) AD1
AF3 TDat_P(11) 43 44 RDat_P(10) AD2
GND 45 46 GND
AE4 RDat_N(9) 47 48 RDat_N(8) AC3
AF4 RDat_P(9) 49 50 RDat_P(8) AD3
GND 51 52 GND
AF5 RDat_N(7) 53 54 RDat_N(6) Y7
AF6 RDat_P(7) 55 56 RDat_P(6) AA7
GND 57 58 GND
Y9 RDat_N(5) 59 60 RDat_N(4) AD4
AA9 RDat_P(5) 61 62 RDat_P(4) AD5
GND 63 64 GND
Y1 RDat_N(3) 65 66 RDat_N(2) V7
Y2 RDat_P(3) 67 68 RDat_P(2) W7
GND 69 70 GND
Y8 RDat_N(1) 71 72 RDat_N(0) AA10
AA8 RDat_P(1) 73 74 RDat_P(0) Y10
GND 75 76 GND
AA1 RCtl_N 77 78 RDCLK_N AF10
AB1 RCtl_P 79 80 RDCLK_P AF11
GND 81 82 GND
GND 83 84 GND
GND 85 86 GND
GND 87 88 GND
3.1.3 LVDS Connector
The design of the SPI-4.2 interface requires use of a high-speed and high quality connector. The
V4MB development board uses the SAMTEC QSE type connector for this interface. The QSE-
040-01-L-Dx-Aconnector from SAMTEC provides up to 28 LVDS signal connections in addition
to an adequate number of ground connections for improving the signal quality. Two of these
connectors are used on the V4MB development board to implement the SPI-4.2 interface. In
addition, a mating LVDS extension cable is available from Samtec (part number #EQCD-040-
06.00-TTR-TBL-1). The following figure shows the QSE type connector from SAMTEC (the
picture is obtained from the SAMTEC web site (http://www.samtec.com/).
December 20,2005 7
Figure 3–SAMTEC QSE Type Connector for the SPI-4.2 Interface
3.2 DDR SDRAM
The Virtex-4™ MB development board provides 64MB of DDR SDRAM memory (x16). A high-
level block diagram of the DDR SDRAM interface is shown below followed by a table describing
the SDRAM memory interface signals.
Virtex-4 FPGA
LX25/LX60-FF668 DDRSDRAM
(64MB)
Control
Data[0:15]
Address[0:12]
Figure 4–DDR SDRAM Interface
Table 3–DDR SDRAM Interface Pin Assignments
Signal Name Description FPGA Pin #
ddr_addr[0] Address 0 N23
ddr_addr[1] Address 1 K23
ddr_addr[2] Address 2 N24
ddr_addr[3] Address 3 J23
ddr_addr[4] Address 4 V23
ddr_addr[5] Address 5 P23
ddr_addr[6] Address 6 U23
ddr_addr[7] Address 7 P24
ddr_addr[8] Address 8 T24
ddr_addr[9] Address 9 R23
ddr_addr[10] Address 10 K24
ddr_addr[11] Address 11 T23
ddr_addr[12] Address 12 R24
ddr_dq[0]Data 0 K20
ddr_dq[1] Data 1 J20
ddr_dq[2] Data 2 L20

December 20,2005 8
ddr_dq[3] Data 3 J21
ddr_dq[4] Data 4 M20
ddr_dq[5] Data 5 K22
ddr_dq[6] Data 6 N20
ddr_dq[7] Data 7 J22
ddr_dq[8] Data 8 T21
ddr_dq[9] Data 9 P20
ddr_dq[10] Data 10 T20
ddr_dq[11] Data 11 T19
ddr_dq[12] Data 12 U22
ddr_dq[13] Data 13 P22
ddr_dq[14] Data 14 U21
ddr_dq[15] Data 15 U20
ddr_ba[0] Bank Select 0 L23
ddr_ba[1] Bank Select 1 M24
ddr_dm[0] Write Mask0 M22
ddr_dm[1] Write Mask1 N22
ddr_dqs[0] Data Strobe0 M19
ddr_dqs[1] Data Strobe1 N19
ddr_csn Chip Select L24
ddr_rasn Row Address Strobe M21
ddr_casn Column Address Strobe M23
ddr_wen Write Enable L21
ddr_clk Clock R20
ddr_clkn Clock R19
ddr_clke Clock Enable K21
3.3 Flash
The Virtex-4™ MB development board provides 4MB of flash memory (x16). A high-level block
diagram of the flash interface is shown below followed by a table describing the flash memory
interface signals.
Virtex-4 FPGA
LX25-FF668 Flash
(4MB)
Control
Data[0:15]
Address[0:20]
Figure 5–Flash Interface
Table 4–Flash Interface Pin Assignments
Signal Name Description FPGA Pin #
flash_addr[0] Address 0 M2
flash_addr[1] Address 1 T6
flash_addr[2] Address 2 R5

December 20,2005 9
flash_addr[3] Address 3 P5
flash_addr[4] Address 4 P6
flash_addr[5] Address 5 P7
flash_addr[6] Address 6 P8
flash_addr[7] Address 7 N8
flash_addr[8] Address 8 K6
flash_addr[9] Address 9 J7
flash_addr[10] Address 10 M7
flash_addr[11] Address 11 M8
flash_addr[12] Address 12 L8
flash_addr[13] Address 13 K7
flash_addr[14] Address 14 J4
flash_addr[15] Address 15 J6
flash_addr[16] Address 16 R3
flash_addr[17] Address 17 N7
flash_addr[18] Address 18 N5
flash_addr[19] Address 19 L7
flash_addr[20] Address 20 M6
flash_d[0] Data 0 P2
flash_d[1] Data 1 R2
flash_d[2] Data 2 U1
flash_d[3] Data 3 K3
flash_d[4] Data 4 L3
flash_d[5] Data 5 M4
flash_d[6] Data 6 N4
flash_d[7] Data 7 P3
flash_d[8] Data 8 R1
flash_d[9] Data 9 T1
flash_d[10] Data 10 K4
flash_d[11] Data 11 L4
flash_d[12] Data 12 M3
flash_d[13] Data 13 N3
flash_d[14] Data 14 P4
flash_d[15] Data 15 R4
flash_cen Chip Select M1
flash_oen Output Enable N2
flash_wen Write Enable J5
flash_rdy Ready M5
flash_reset Reset K5
3.4 Clock Sources
The Clock Generation section of the Virtex-4 MB board provides all the necessary clocks for a
MicroBlaze processor, the I/O devices located on the board, as well as the DDR SDRAM
memory. In general, the clock sources on the board are grouped into two categories; differential
and single-ended clock sources. The differential clock sources are primarily used by the LVDS
interface, while the single-ended clock sources are used by the processor section.
An on-board 100MHz oscillator provides the system clock input to the processor section. This
100Mhz clock will be used by the Virtex-4 Digital Clock Managers (DCMs) to generate various
processor clocks. In addition to the above clock inputs, a socket is provided on the board that can
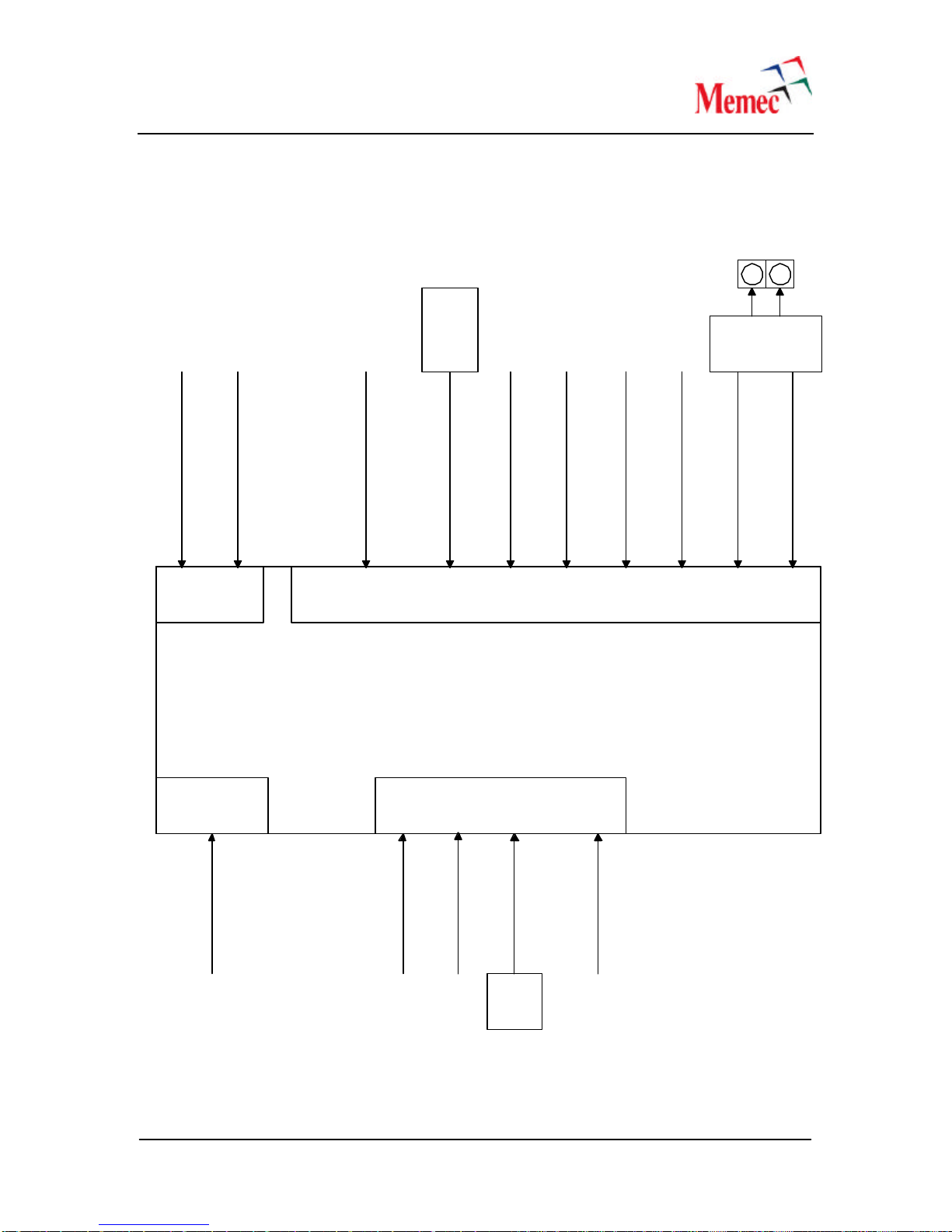
December 20,2005 10
be used to provide single ended LVTTL clock input to the FPGA via an 8 or 4-pin oscillator. The
following figure shows the clock resources on the Virtex-4 MB development board.
Virtex-4™
XC4VL25/LX60-FF668
Programmable
LVDS Clock
Source
Bank 1 Bank 3
Bank 4
C15 B13 A16 B15
AE14 AE10
D12 E13
AF11AF10
SAM
CLock
OSC
Socket
ETH_TXC
ETH_RXC
CLK_SOCKET
CLK_PROG_N
CLK_PROG_P
SPI_RDCLK_N
SPI_RDCLK_P
LVTTL
OSC
@100
MHz
SMA
Connectors
LIO_CLKIN_N
LIO_CLKIN_P
P240
Differential
CLock
SPI_TSCLK
LIO_CLKIN_0
LIO_CLKIN_1
P240
Single-ended
CLock
SPI
Status
Clock
CLK_100
DDR_CLK
DDR
Feedback
Clock
B17 A17 A10 B10
SAM_CLK
Bank 10
R8
Figure 6-Clock Sources on the Virtex-4 MB Board
December 20,2005 11
The following table provides a brief description of each clock input to the Virtex-4 FPGA.
Table 5-Clock Inputs
Signal Name FPGA Pin # Description
CLK_PROG_P,
CLK_PROG_N A10,
B10 Positive and Negative Differential System Clock Inputs –
These clock inputs are connected to the output of an LVDS clock
synthesizer. This programmable clock source can generate a
clock frequency of 25 to 700MHz. Refer to the Programmable
LVDS Clock Source section for more information.
LIO_CLKIN_P,
LIO_CLKIN_N B17,
A17 P240 Module Differential Clock Input –This clock input is
connected to the P240 connector located on the Virtex-4 board.
LIO_CLKIN_0,
LIO_CLKIN_1 D12,
E13 P240 Module Single-ended Clock Input s–These clock inputs
are connected to the P240 connector located on the Virtex-4
board.
SPI_RDCLK_P,
SPI_RDCLK _N AF11,
AF10 Positive and Negative Differential SPI-4.2 Receive Clock
Inputs –These clock inputs are connected to the LVDS receive
connector on theVirtex-4 MB board. For the SPI-4.2
applications, these clock inputs are the SPI-4.2 receive clock
outputs.
DDR_CLK C15 DDR Feedback Clock Input –This clock input is connected to
the DDR clock.
CLK_100 B13 System Clock –This clock input is connected to a 100MHz
LVTTL oscillator.
CLK_SOCKET AE14 LVTTL Clock Input –LVTTL socket on the Virtex-4 board.
SPI_TSCLK R8 SPI-4.2 Transmit Status Clock Input –This clock input is
connected to the SPI-4.2 transmit status clock output.
ETH_RXC A16 Ethernet Receive Clock Input –This clock input is connected
to the Ethernet receive clock.
ETH_TXC B15 Ethernet Transmit Clock Input –This clock input is connected
to the Ethernet transmit clock.
SAM_CLK AE10 SystemACE Module Clock Input –This clock input is
connected to the SystemACE Module connector.
3.4.1 Programmable LVDS Clock Source
A programmable LVDS clock synthesizer is used on the Virtex-4 MB development board to
generate a reference clock input to the LVDS interface. The use of this variable clock source,
allows designers to prototype various interconnect technologies with different clock source
requirements. The differential output port is also well suited for DSP applications when driving
external DACs or ADCs.
3.4.2 ICS8442 Programmable LVDS Clock Synthesizer
The Virtex-4 MB development board design uses the ICS8442 LVDS clock synthesizer for
generating various clock frequencies. A list of features included in the ICS8442 device is shown
below.
•Output frequency range: 25MHz to 700MHz
•RMS period jitter: 2.7ps (typical)
•Cycle-to-cycle jitter: 27ps (typical)
•Output rise and fall time: 650ps (maximum)
•Output duty cycle: 48/52
December 20,2005 12
The following figure shows a high-level block diagram of the ICS8442 programmable LVDS clock
synthesizer.
ICS8442
M[0:8]
N[0:1]
Parallel LoadSerial Load
S_DATA
S_CLOCK
S_LOAD
nP_LOAD
CLKOUT0CLKOUT1
Control Inputs
VCO_SEL
XTAL_SEL
TEST_CLK
MR
TEST
FOUT0
nFOUT0
FOUT1
nFOUT1
XTAL1
XTAL2
Clock Input
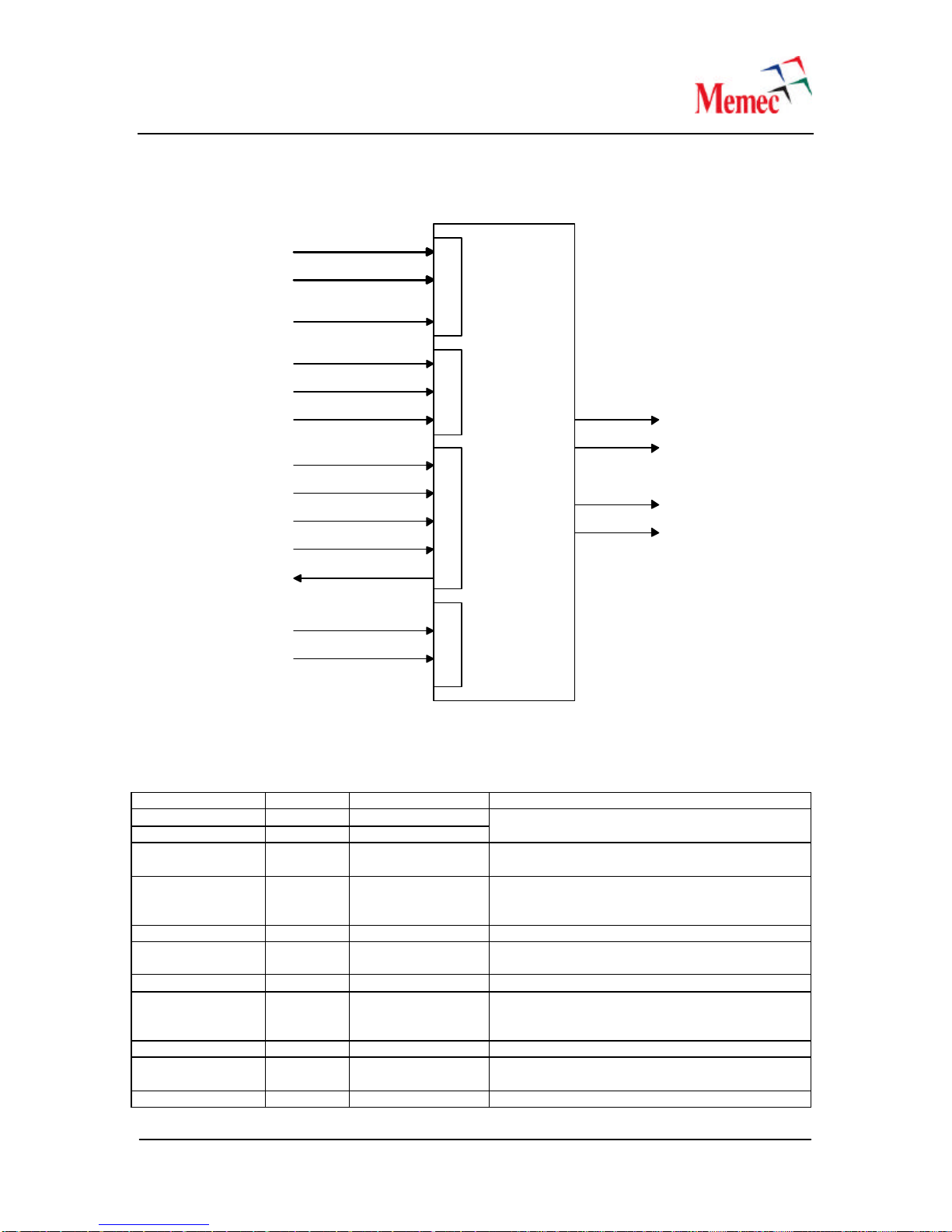
Figure 7–ICS8442 Clock Synthesizer
Table 6–ICS8442 Clock Synthesizer Pin Description
Signal Name Direction Pull up/Pull down Description
M[0:4], M[6:8] Input Pull down
M[5] Input Pull up The M divider inputs, latched on the rising edge
of the nP_LOAD signal.
N[0:1] Input Pull down The N divider inputs, latched on the rising edge
of the nP_LOAD signal.
TEST Output The TEST output is active during the serial mode
of operations. Please refer to the datasheet for
more information.
MR Input Pull down Active high reset signal.
S_CLOCK Input Pull down Serial interface clock input. Data is shifted into
the device on the rising edge of this clock.
S_DATA Input Pull down Serial interface data input.
S_LOAD Input Pull down Serial interface load signal. The contents of the
serial data shift register is loaded into the internal
dividers on the rising edge of this signal.
TEST_CLK Input Pull down Test clock input.
nP_LOAD Input Pull down The rising edge of this signal is used to load the
M and N divider inputs into the device.
XTAL1, XTAL2 Input Crystal clock input/output

December 20,2005 13
XTAL_SEL Input Pull up This signal is used to select between the crystal
and the TEST_CLK input to the device. When
this high, crystal is selected.
VCO_SEL Input Pull up This signal is used to place the internal PLL in
the bypass mode. When this signal is setto low,
the PLL is placed in the bypass mode. For
normal operations, this signal must be set to
high.
FOUT0, FOUT1 Output Positive LVDS clock outputs
nFOUT0, nFOUT1 Output Negative LVDS clock outputs
The Input Clock Select signals of the ICS8442 can be used to provide a reference clock input to
the device other than the 25MHz crystal oscillator (for test purposes). The following table shows
how these Input Clock Select signals are used to generate the output clock or to test the ICS8442
device. Please refer to the ICS8442 datasheet for more information on using the TEST_CLK
clock input.
Table 7–Input Clock Select Signal Description
VCO_SEL XTAL_SEL Reference Clock Input FOUT[0:1]
00TEST_CLK TEST_CLK/N (the TEST_CLK mustbe between
10 and 25MHz). This mode can be used to test
the ICS8442 device by routing the input clock to
the outputs.
0125MHz crystal 25MHz crystal/N (This mode can be used to test
the ICS8442 device by routing the 25MHz
crystal clock to the outputs).
10TEST_CLK ICS8442 PLL Output/N (Normal Operation)
1125MHz crystal ICS8442 PLL Output/N (Normal Operation)
3.4.3 ICS8442 Clock Generation
The ICS8442 output clocks are generated based on the following formula (assuming the crystal
clock input is set to 25MHz):
FOUT[0:1] = 25 x M/N
Where 8 < M < 28 and N can take a value of 1, 2, 4, or 8. The variable M is determined by setting
the binary number M[0:8] while N is set according to the following table:
Table 8–ICS8442 N Settings
Output Clock Frequency Range (MHz)N[1:0] NMinimum Maximum
00 1200 700
01 2100 350
10 450 175
11 825 87.5
For example, to generate a 62.5MHz clock, N[1:0] will be set to “10” (it can also be set to “11”
since either one will be the correct frequency range for the 62.5MHz clock) and M will be set to
“000001010” (decimal 10). So, from the above formula:
FOUT[0:1] = 25 x 10/4 = 62.5Mhz

December 20,2005 14
The following table shows how the M and N values can be set to generate a clock source for a
few common applications. All the values for M and N are based on the 25MHz crystal clock input
to the ICS8442 device. A complete list of frequencies generated by the ICS8442 (based on a
25MHz input clock) is provided in the following sections.
Table 9–Examples of the ICS8442 M and N Settings
ICS8442 M and N SettingsInterconnect
Technology FOUT0 and
FOUT1 (MHz) M8 M7 M6 M5 M4 M3 M2 M1 M0 N1 N0
Gigabit Ethernet 62.5 00000101010
53.125 00001000111Fiber Channel 106.25 00001000110
Infiniband 125 00001010010
XAUI 156.25 00001100110
3.4.4 ICS8442 Programming Modes
The ICS8442 provides two different methods of programming the M and N values into the device;
a Parallel Mode and a Serial Mode. In parallel mode, M and N values are programmed into the
device when the nP_LOAD signal pulses low. In the serial mode, the I2C pins (S_DATA and
S_CLOCK) along with the S_LOAD signal are used to shift the M and N values into the device.
Please refer to the ICS8442 datasheet for more information on programming modes of loading
the M and N values into the device.
3.4.5 ICS8442 M and N Settings
The following figure shows how the ICS8442 programmable LVDS clock synthesizer is used on
the Virtex-4 MB board. DIP Switches are provided on the board for manual setting of the M and N
values.

December 20,2005 15
Virtex-4
FPGA ICS8442
M[0:8]
N[0:1]
Parallel LoadSerial Load
25Mhz
S_DATA
S_CLOCK
S_LOAD
nP_LOAD
DIP Switch
CLKOUT0
CLKOUT1
SMA
Connectors
Control Inputs
VCO_SEL
XTAL_SEL
TEST_CLK
MR
TEST
FOUT0
nFOUT0
FOUT1
nFOUT1
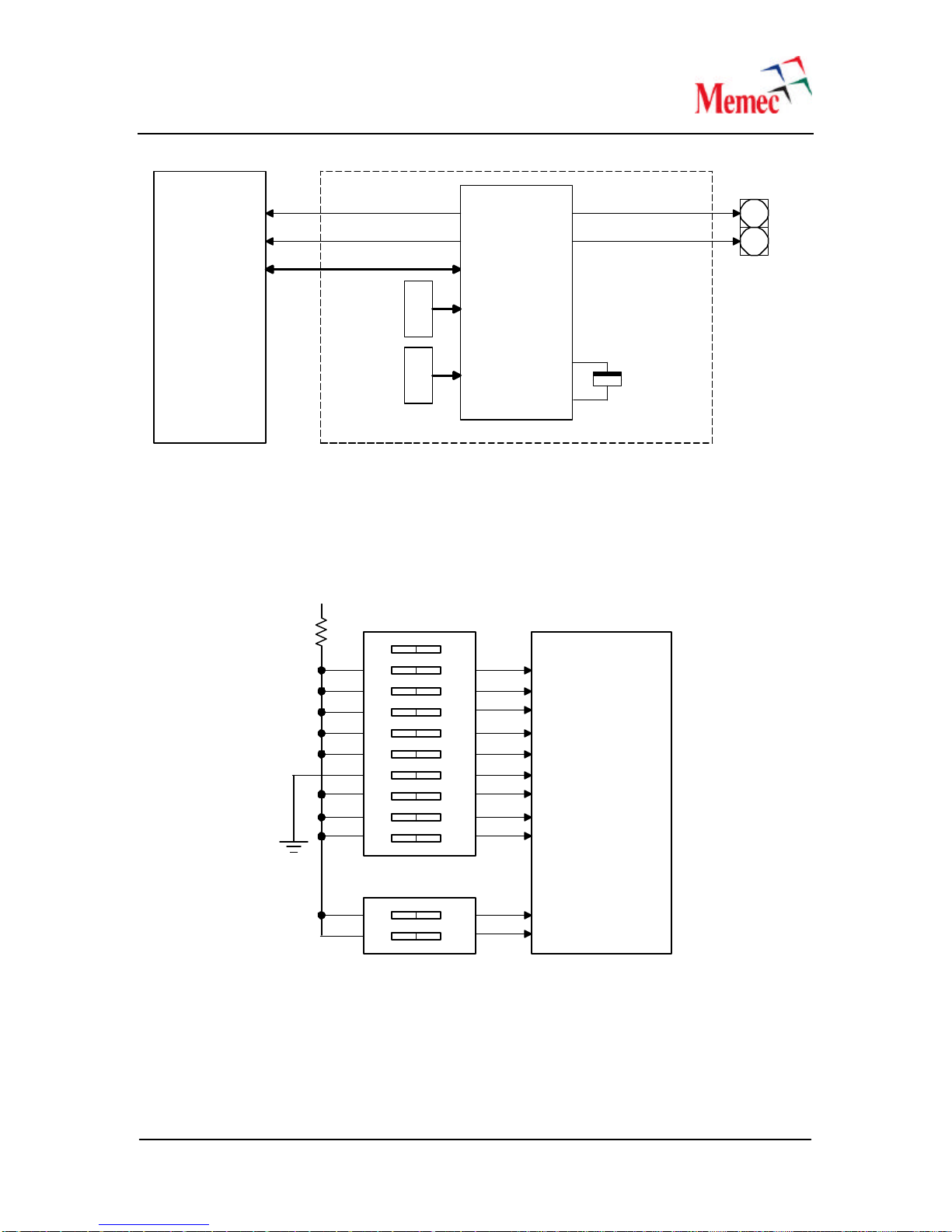
Figure 8–ICS8442 Clock Synthesizer Interface to the FPGA
As shown in the above figure, the ICS8442 device outputs two identical LVDS clock sources. One
of these clock sources can be used to provide the reference clock input to the LVDS interface on
the Virtex-4 MB development board, while the other clock output can be used to trigger a scope
during testing. The second output could also be used to provide a low jitter, LVDS clock source
to a user board, such as the P240 module.
December 20,2005 16
Virtex-4
FPGA ICS8442
CLKOUT0
CLKOUT1
SMA
Connectors
CONTROL
CLK_PROG_P
CLK_PROG_N
SW3SW9
M[8:0]N1:0]
25Mhz
Figure 9–ICS8442 Clock Synthesizer M and N DIP Switches
The following tables show the DIP Switch settings for M and N selections. Please refer to Table 6
for the information on pull-up and pull-down resistors provided internal to the ICS8442 device for
the M and N input signals.
Synthesizer
5
4
3
2
1
6
7
8
M8
10
9
ON
2
1
ON
M7
M6
M5
M4
M3
M2
M1
M0
N1
N0
3.3V
OFF
OFF
SW9
SW3
Figure 10 –M and N DIP Switches for the Synthesizers
December 20,2005 17
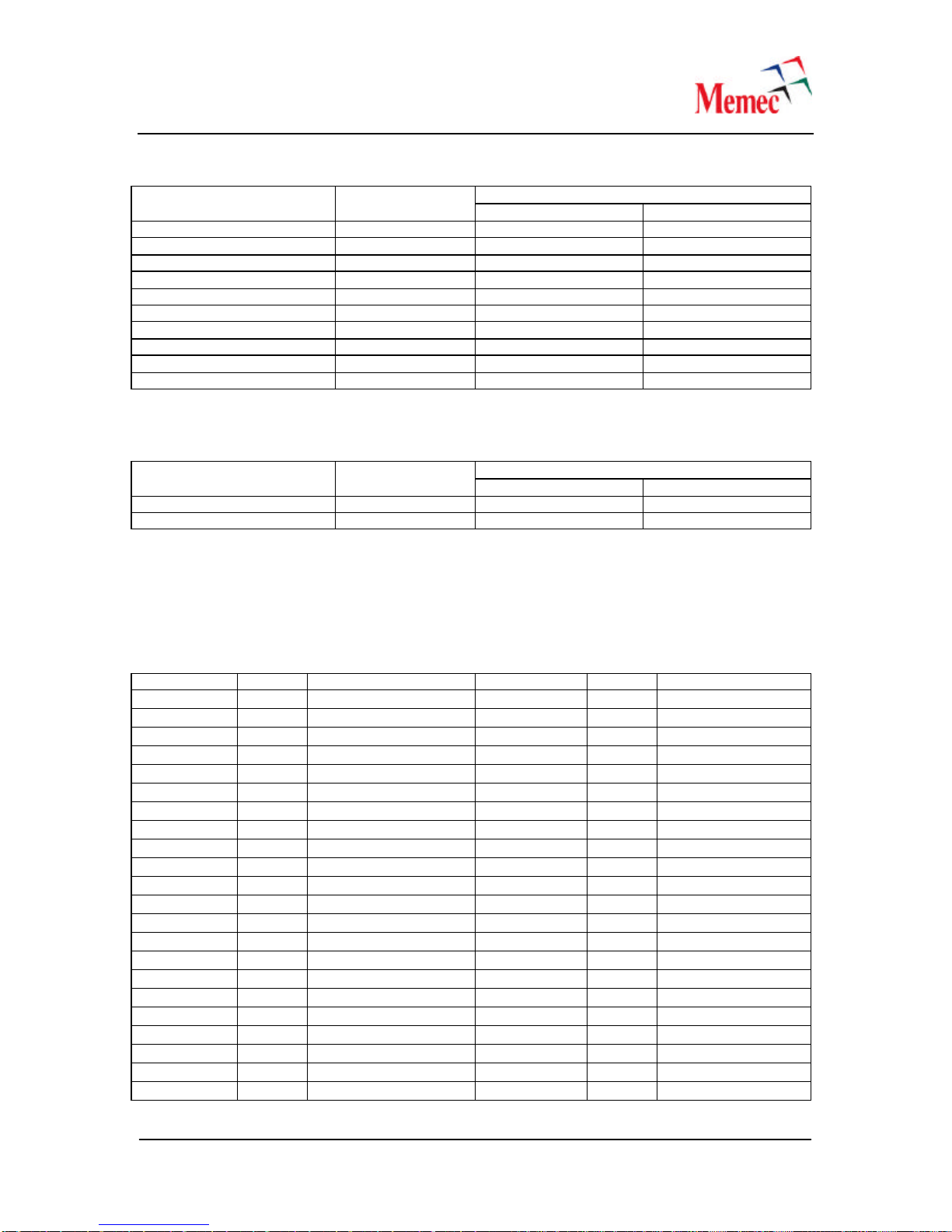
Table 10 –DIP Switch Setting for M[8:0]
Switch Position
SW1, SW10, and SW2
M[8:0] OFF ON
DIP1 M8 01
DIP2 M7 01
DIP3 M6 01
DIP4 M5 10 Note (1)
DIP5 M4 01
DIP6 M3 01
DIP7 M2 01
DIP8 M1 01
DIP9 M0 01
DIP10 Unused NA NA
Note(1) –The polarity of M5 (DIP4) is the opposite of all other DIP switch positions.
Table 11 –DIP Switch Setting for N[1:0]
Switch Position
SW9, SW11, and SW13
N[1:0] OFF ON
DIP1 N1 01
DIP2 N0 01
The following table shows a complete list of frequencies generated by the ICS8442 device based
on a 25MHz crystal reference clock input.
Table 12 –Synthesizer Clock Outputs for M and N Values
M[8:0] N[1:0] FOUT[1:0] (MHz) M[8:0] N[1:0] FOUT[1:0] (MHz)
000001000 11 25 (Min) 000011000 10 150
000001001 11 28.125 000011001 10 156.25
000001010 11 31.25 000001101 01 162.5
000001011 11 34.375 000011010 10 162.5
000001100 11 37.5 000011011 10 168.75
000001101 11 40.625 000001110 01 175
000001110 11 43.75 000011100 10 175
000001111 11 46.875 000001111 01 187.5
000001000 10 50 000001000 00 200
000010000 11 50 000010000 01 200
000010001 11 53.125 000010001 01 212.5
000001001 10 56.25 000001001 00 225
000010010 11 56.25 000010010 01 225
000010011 11 59.375 000010011 01 237.5
000001010 10 62.5 000001010 00 250
000010100 11 62.5 000010100 01 250
000010101 11 65.625 000010101 01 262.5
000001011 10 68.75 000001011 00 275
000010110 11 68.75 000010110 01 275
000010111 11 71.875 000010111 01 287.5
000001100 10 75 000001100 00 300
000011000 11 75 000011000 01 300
Table of contents