RouterBOARD 500 Series User's Manual
Table of Contents
Cop right.......................................................................................................................................1
Trademarks....................................................................................................................................1
Limited Warrant ............................................................................................................................1
Caution..........................................................................................................................................1
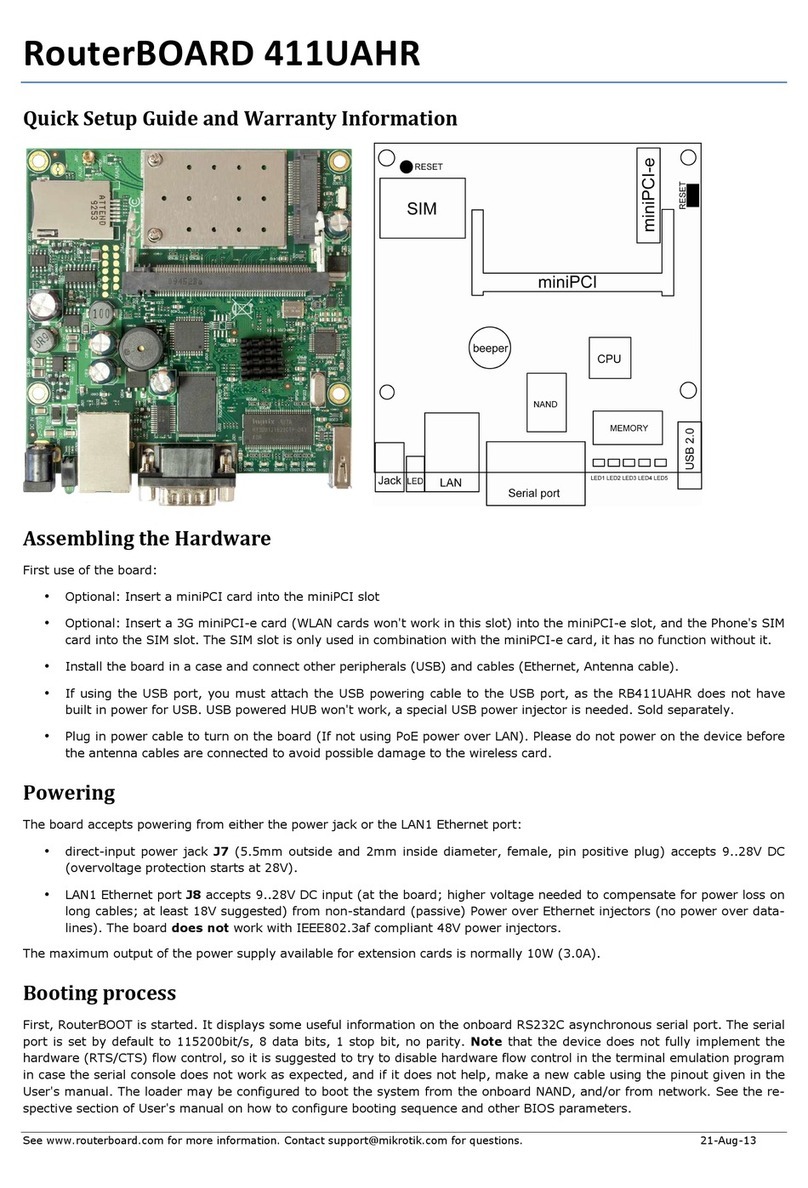
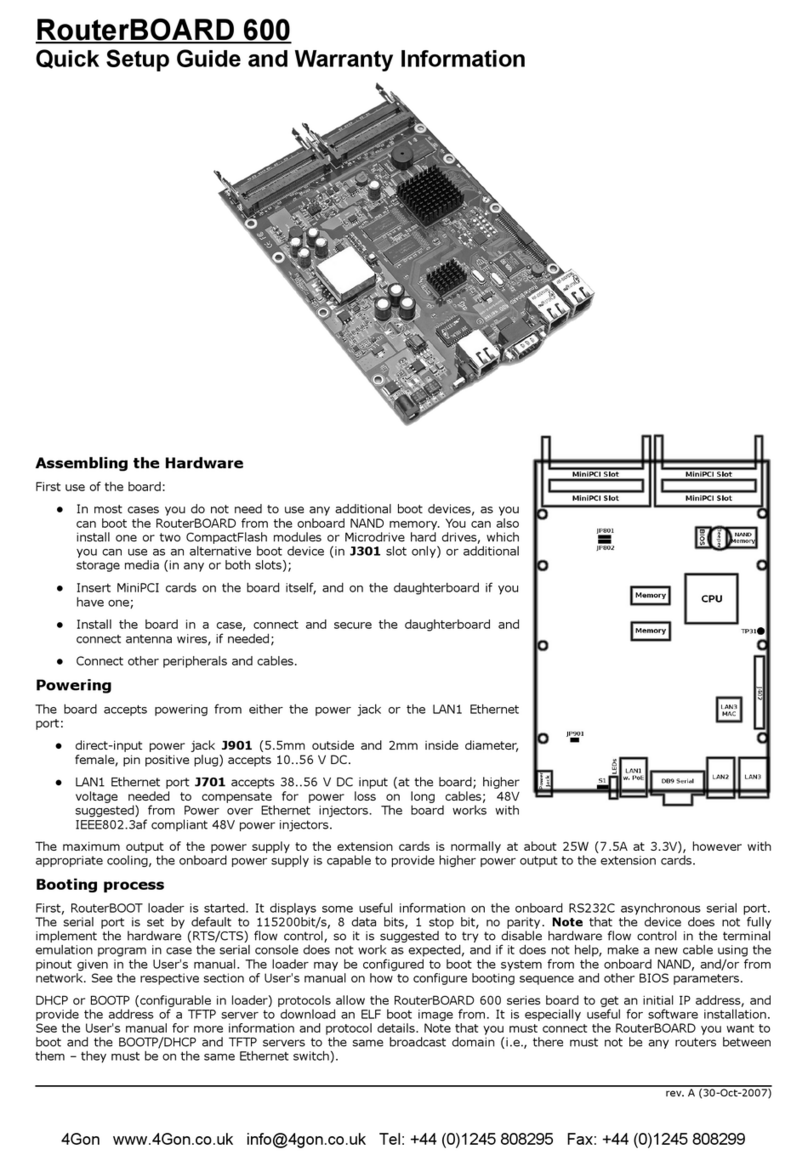
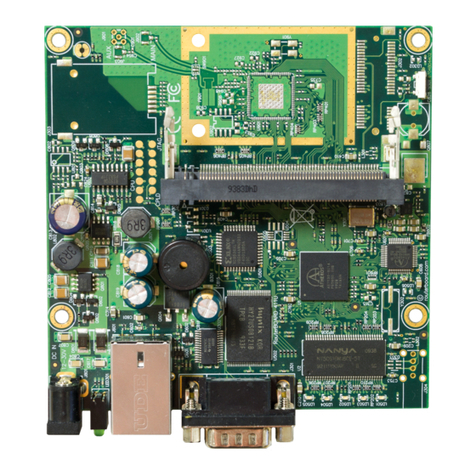
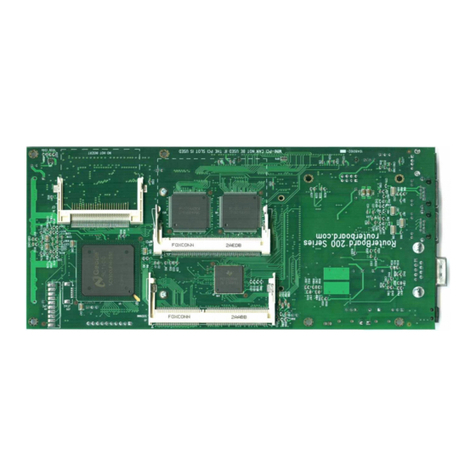
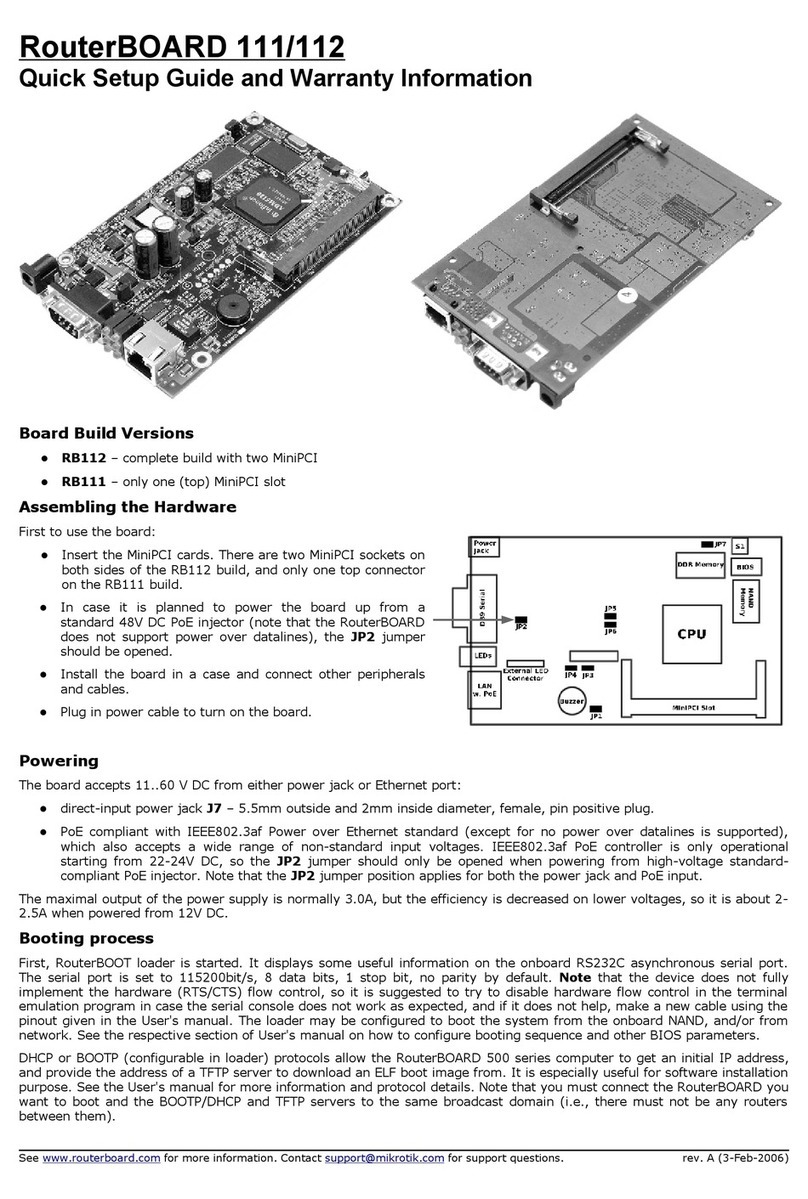
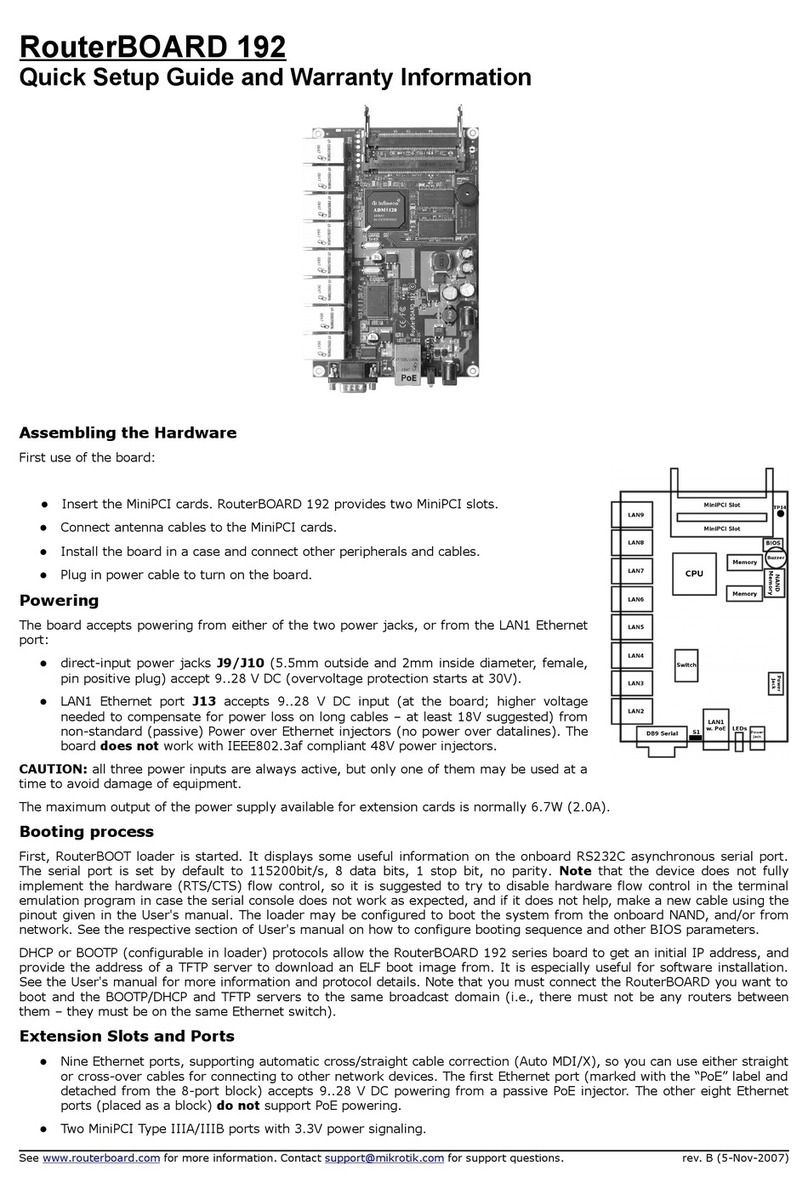
S stem Board View.........................................................................................................................3
S stem Board La out.......................................................................................................................4
Block Diagram................................................................................................................................4
Specifications.................................................................................................................................5
Daughterboard Options:..........................................................................................................5
Board Build Versions:..............................................................................................................5
Hardware Guide..............................................................................................................................6
Memor and Storage Devices...................................................................................................6
Onboard Memor ...........................................................................................................6
Onboard NAND Storage Device........................................................................................6
CompactFlash Interface..................................................................................................6
Extension Slots......................................................................................................................6
MiniPCI Slot..................................................................................................................6
Input/Output Ports..................................................................................................................6
LAN1 Port with PoE.........................................................................................................6
LAN2 Port.....................................................................................................................6
LAN3 Port.....................................................................................................................6
DB9 Serial Port..............................................................................................................7
LEDs.....................................................................................................................................7
Power LED....................................................................................................................7
User LED......................................................................................................................7
MiniPCI LEDs.................................................................................................................7
User's Guide...................................................................................................................................7
Assembling the Hardware........................................................................................................7
Powering...............................................................................................................................7
Booting options......................................................................................................................8
Onboard NAND Storage Device........................................................................................8
Internal Storage Device..................................................................................................8
Booting from network.....................................................................................................8
Operating S stem Support.......................................................................................................8
S stem Architecture.......................................................................................................8
MikroTik RouterOS.........................................................................................................9
Linux............................................................................................................................9
RouterBOOT...................................................................................................................................9
Boot Loader Configuration........................................................................................................9
Configurable Options....................................................................................................10
Changing CPU Frequenc .......................................................................................................10
Boot Loader Upgrading..........................................................................................................10
Appendix......................................................................................................................................12
Connector Index...................................................................................................................12
Jumper Index.......................................................................................................................14
Button Index........................................................................................................................14
Ethernet Cables....................................................................................................................14
Full Serial Null-modem (Console) Cable....................................................................................14
2