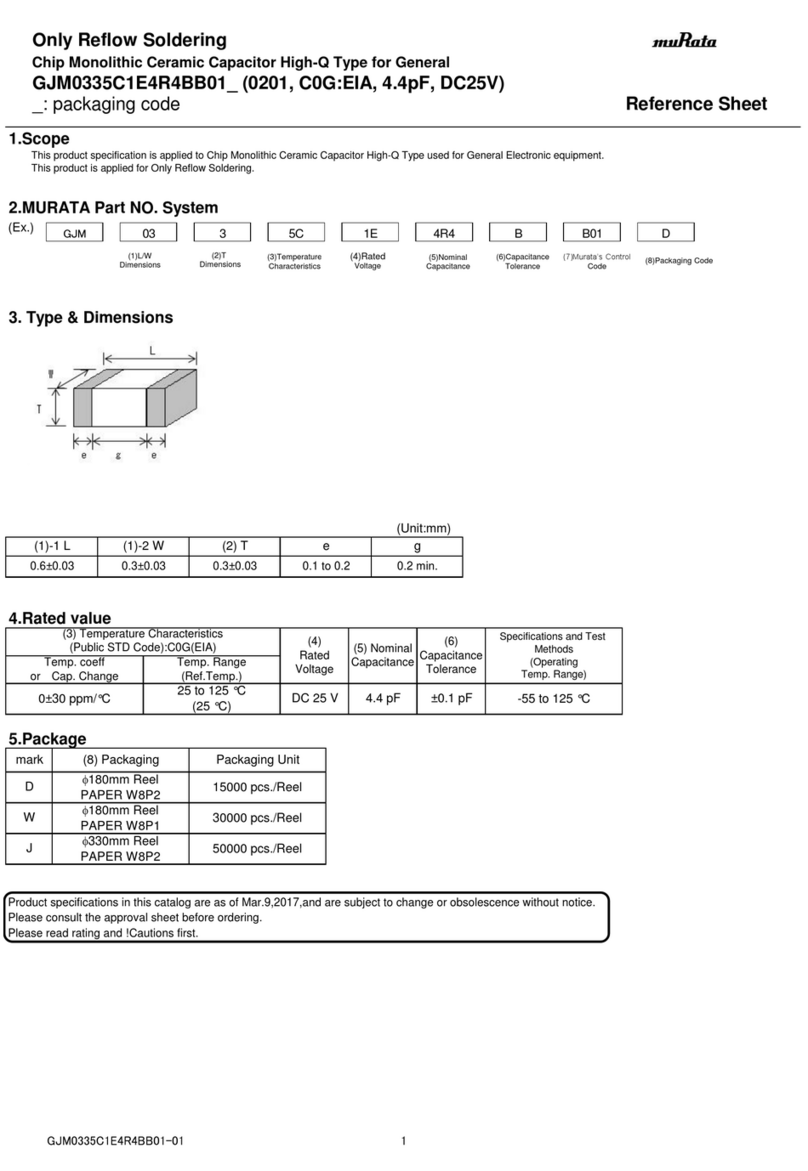
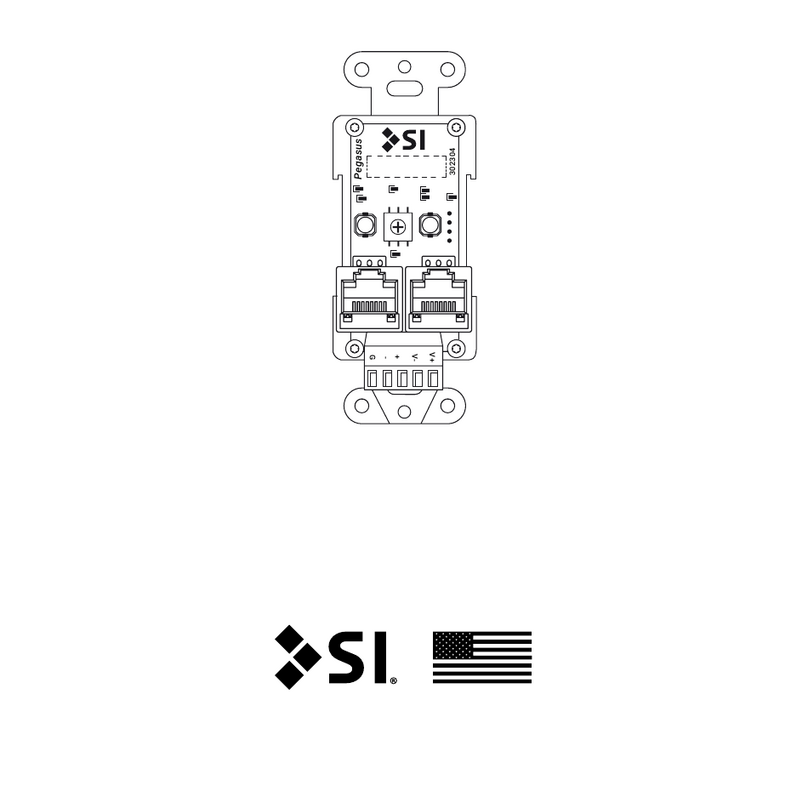
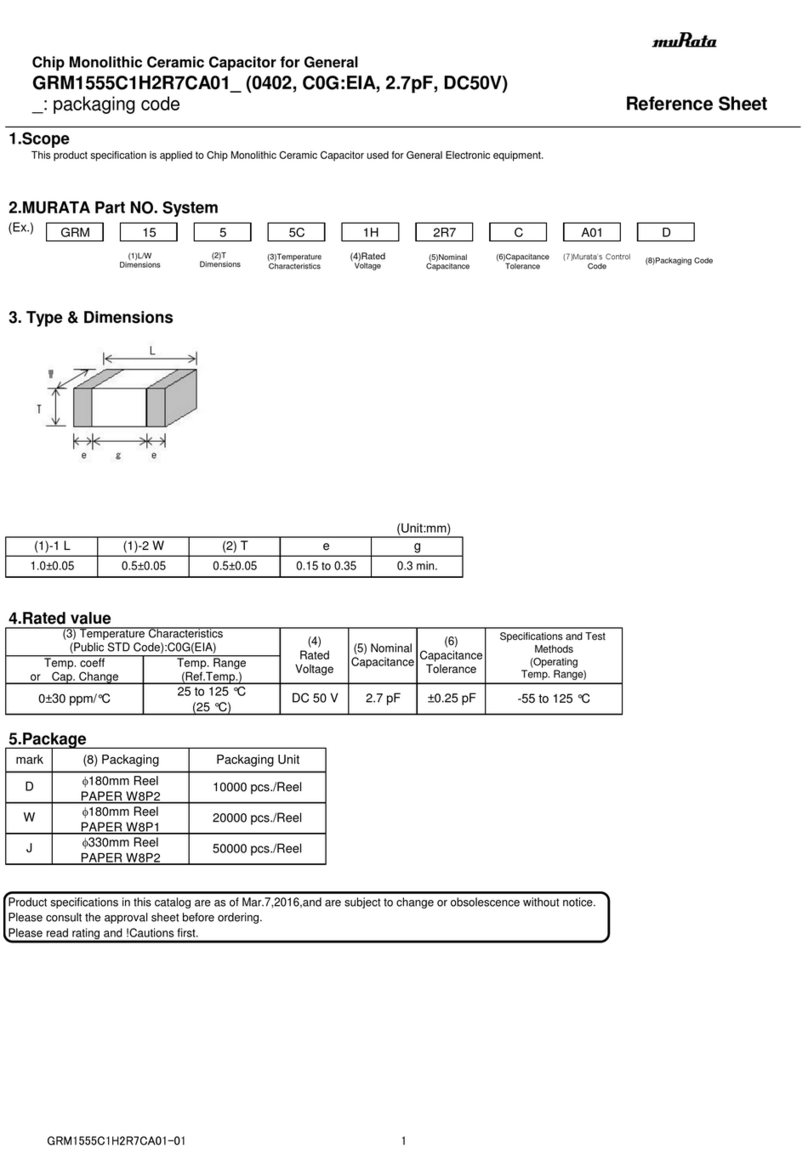
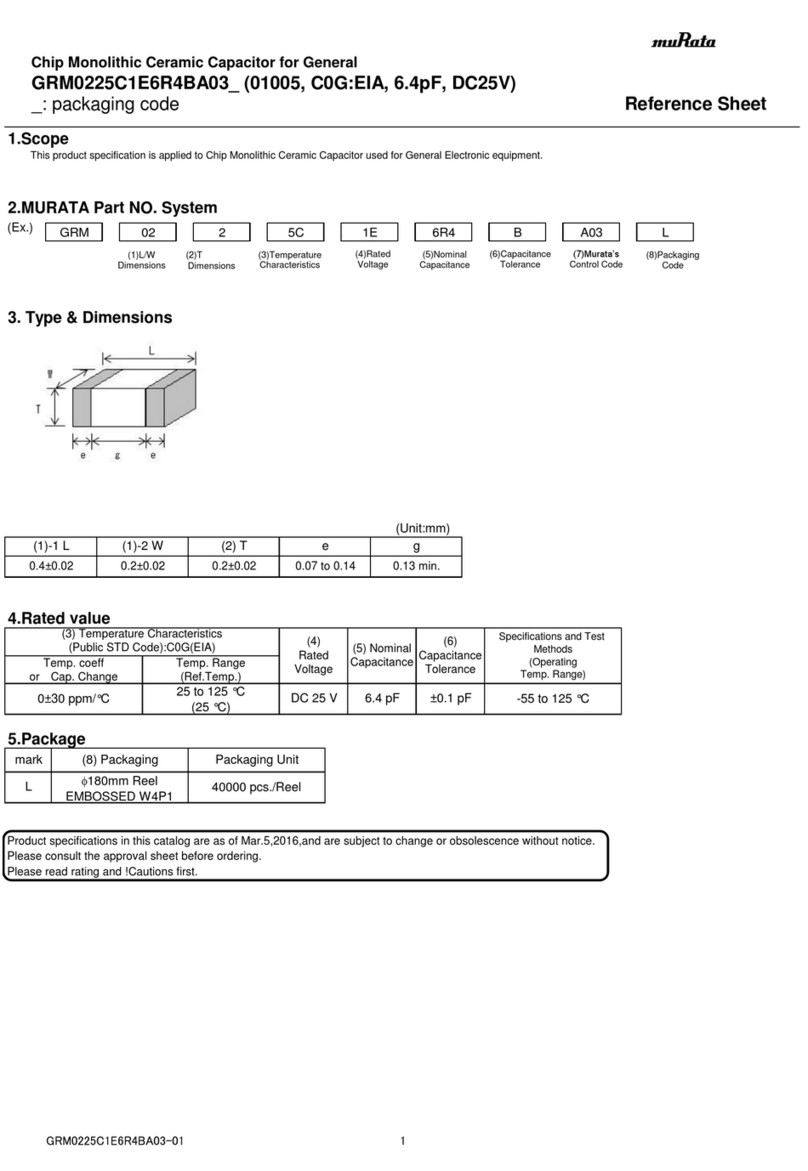
The Interface Solution Experts 7
4-Wire Isolator, Converter, Repeater,
and Splitter in an Aluminum Housing
Calibration
Prior to shipment, every ECT is subjected to rigorous
testing by our team of skilled technicians. Every
product Moore Industries manufactures, sells and
services is guaranteed to meet the strict quality
standards that have become synonymous with our
company name.
Before placing your ECT into service, a bench check
of basic operation is recommended to ensure that the
unit hasn’t sustained any damage during transit, and to
set zero and span points for your application.
Every unit should be:
• CheckedtoverifythattheappropriateECT
model has been ordered for the intended
application.
• Connectedinacalibrationsetup(described
later in this section) and checked for desired
output.
• Adjustedfordesiredzeroandspan.
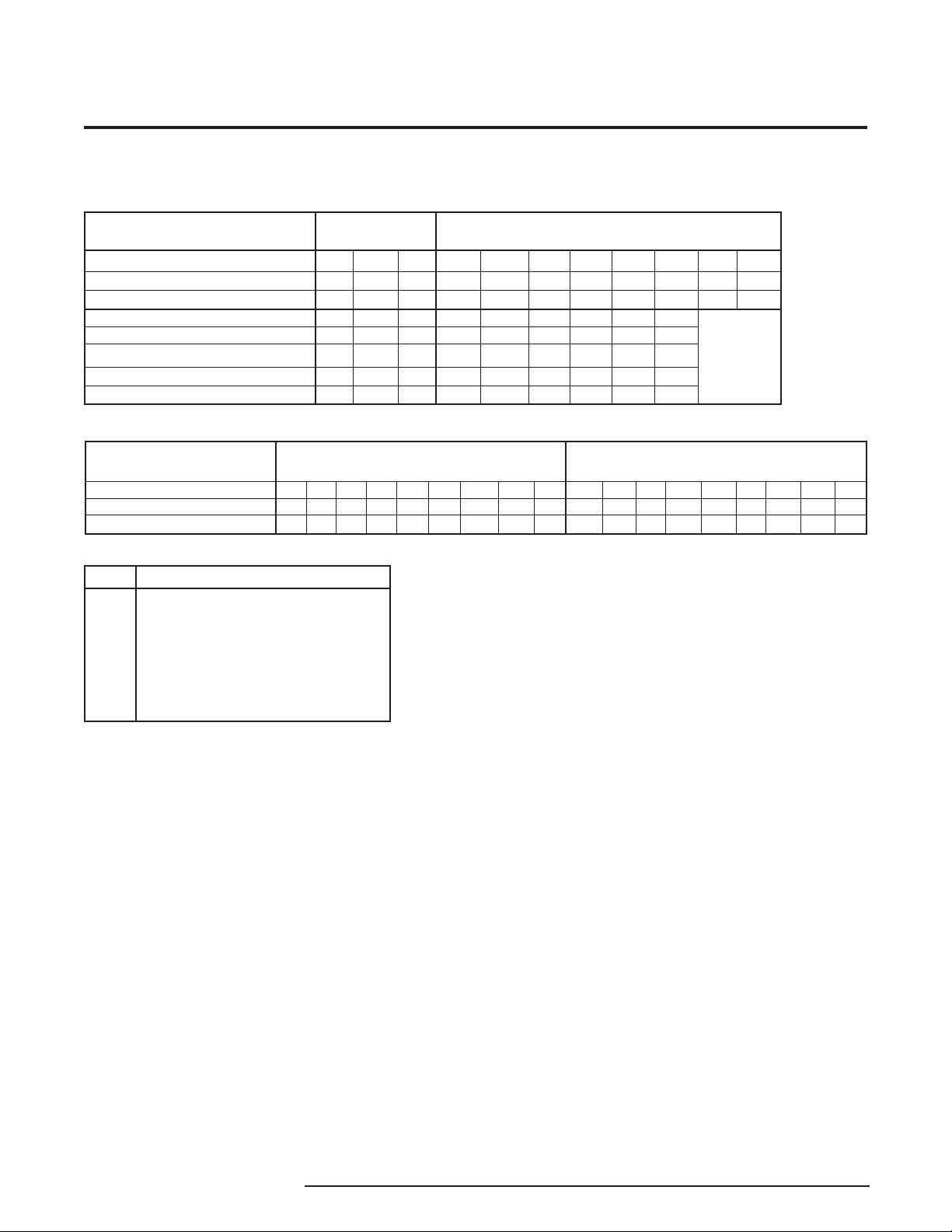
Table 3. Gathering the equipment for 4-wire ECT calibration
Voltage/Current
Calibrator
Power
Supply
Load
Resistor
Multimeter
Screwdriver
Adjustable, calibrated to an accuracy
of ±0.025% (EDC Model CR 103 or
MV 105 or equivalent)
Rotek Model 811A (or equivalent)
recommended for calibrating
AC input units.
Calibrated, 24Vdc, ±10%, nominal
250 ohms (±0.01%) precision
Calibrated to an accuracy of ±0.025%,
minimum (Keithley Model 197,
or Fluke Model 8840 or 8842 or
equivalent)
Standard (Blade-type), head width
3.1mm (0.125 in), maximum
Device Specifications
Calibration Setup
Table 3 lists the equipment you will need to bench
check the ECT. These materials are not supplied by
Moore Industries, but should be available in those
environments suited for calibration and maintenance of
electronic instruments.
Figures 2 through 5 show the calibration setups for
each type of ECT. Moore Industries recommends
that the procedures in this section be carried out
at a technician’s bench or in a similar, lab-type
environment. Do not calibrate the ECT in the field or
installed in the application.
Calibration Procedure
With the unit incorporated into the setup described in
the appropriate Figure (2, 3, 4 or 5):
1. Apply the appropriate power to the ECT.
2. Set the Voltage or Current Calibrator to 100%
span (full scale input) for the type of ECT being
calibrated. For example, 20mA for a
4-20mA input unit or 5V for a 1-5V input unit.
3. Adjust the Span potentiometer (pot) until
the multimeter reads 20mA, plus/minus the
stated accuracy specification. If measuring
the voltage drop across the precision resistor,
adjust the pot until output is 5V, plus/minus the
stated accuracy specification.
4. Set the Calibrator to 0% of the rated span for
the type of ECT being calibrated. For example,
4mA for a 4-20mA input unit or 1V for a 1-5V
input unit.
5. Adjust the Zero pot until the multimeter
reads 4mA, plus/minus the stated accuracy
specification. If measuring the voltage drop
across the precision resistor, adjust the
pot until output is 1V, plus/minus the stated
accuracy specification.
6. Repeat steps 2 through 5 for each channel
until the ECT output or the voltage across the
resistor is stable at both 0 and 100% of rated
input span.