INDEX
MTU AIS-C
1. INTRODUCTION TO AIS...................................................................................2
1.1. PURPOSE OF AIS................................................................................................. 3
1.2. SHIP TO EARTH INFORMATION.......................................................................... 4
1.3. VESSEL TRAFFIC SYSTEMS VTS ........................................................................... 5
1.4. HOW DOES AIS WORK?...................................................................................... 5
1.5. FREQUENCIES AND AIS TRANSMISSION. ........................................................... 5
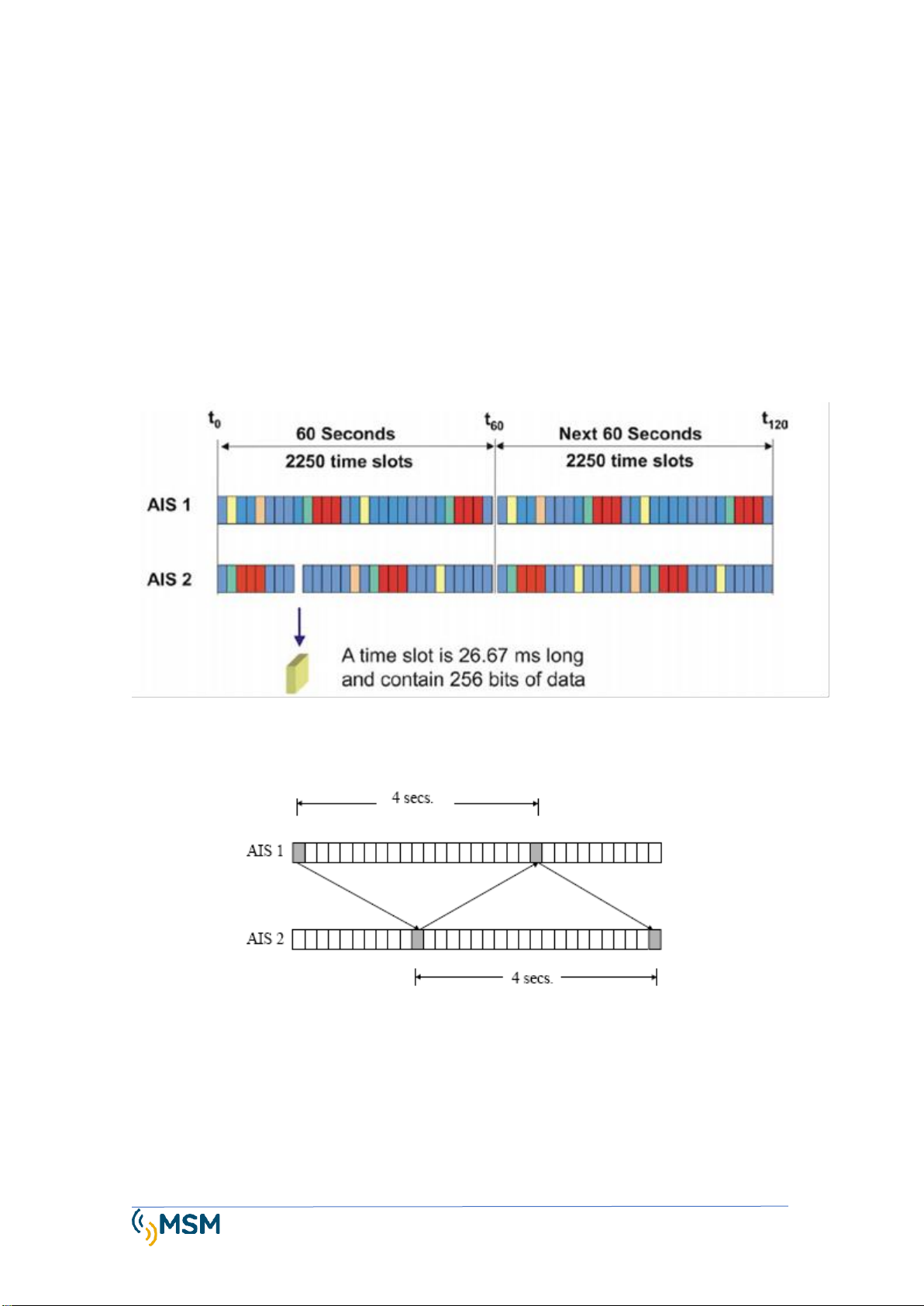
1.6. THE SOTDMA PROTOCOL................................................................................... 6
1.7. DATA REFRESH SPEED........................................................................................ 7
2. DESCRIPTION OF MTU-AIS-C...........................................................................8
2.1. AIS AtoN TYPE 1. ................................................................................................ 8
2.2. AIS AtoN TYPE 3 ................................................................................................. 8
3. GENERAL FEATURES .......................................................................................9
3.1. MAIN FEATURES OF THE SYSTEM .................................................................... 11
3.2. CONNECTOR FEATURES ................................................................................... 11
4. INSTALLATION.............................................................................................. 12
4.1. POWER AND INTERFACE CONNECTOR. "W TYPE"........................................... 13
4.2. SENSOR INTERFACE CONNECTOR. "X TYPE".................................................... 14
4.3. SENSOR INTERFACE CONNECTOR. "Y TYPE".................................................... 15
4.4. VHF ANTENNA CONNECTOR............................................................................ 16
4.5. GPS ANTENNA CONNECTOR ............................................................................ 16
4.6. POWER CONNECTOR (W) ................................................................................ 16
4.7. INSTALLING THE VHF RADIO ANTENNA........................................................... 17
4.8. INSTALLING AND CONNECTING A GPS ANTENNA ........................................... 17
5. CONFIGURATION USING PROATON SOFTWARE ............................................ 18
5.1. PROAtoN INSTALLATION.................................................................................. 18
5.2. CONFIGURATION SCREEN................................................................................ 19
5.3. MTU-AIS CONFIGURATION .............................................................................. 21
5.4. OFFLINE CONFIGURATION............................................................................... 29
6. MTU-AIS REPEATER FUNCTION..................................................................... 30
7. MTU-AIS DIAGNOSTIC .................................................................................. 31