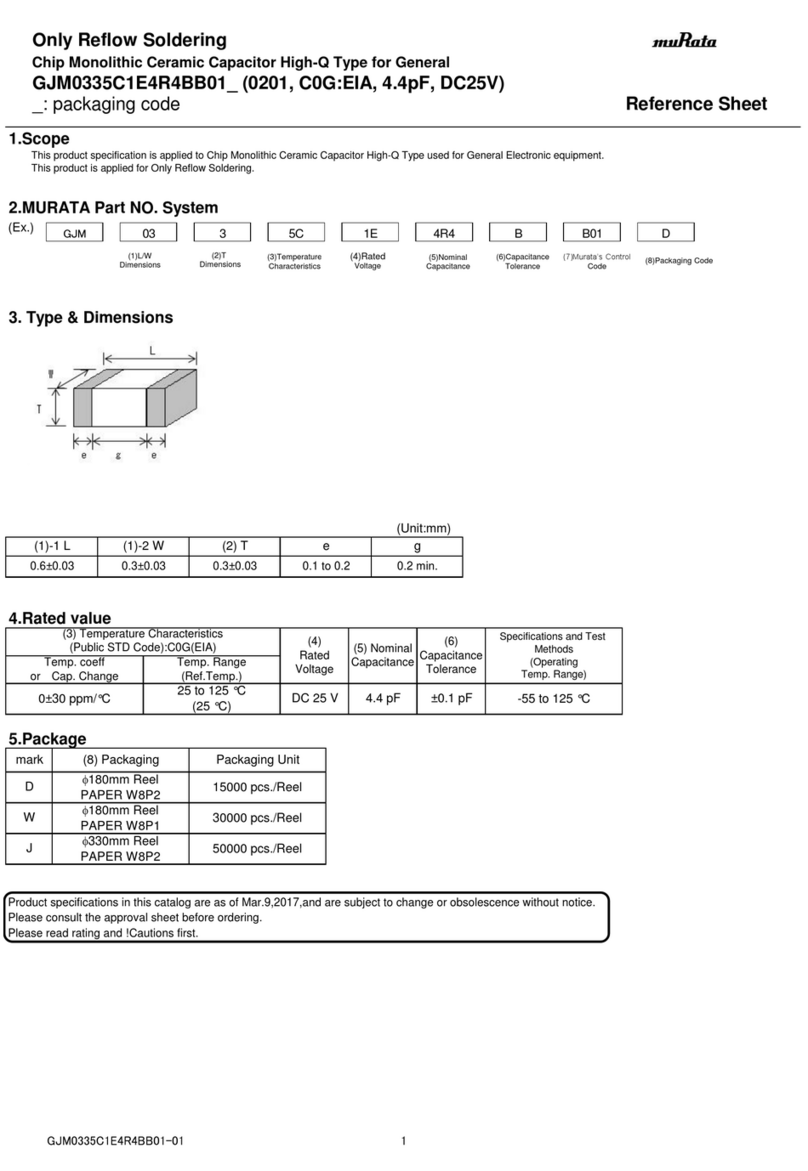
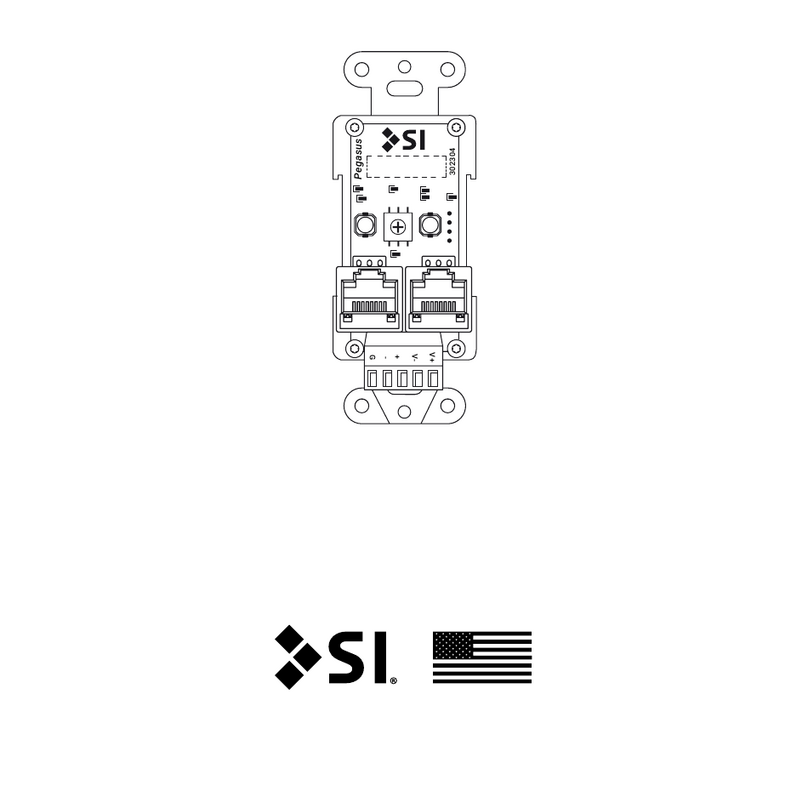
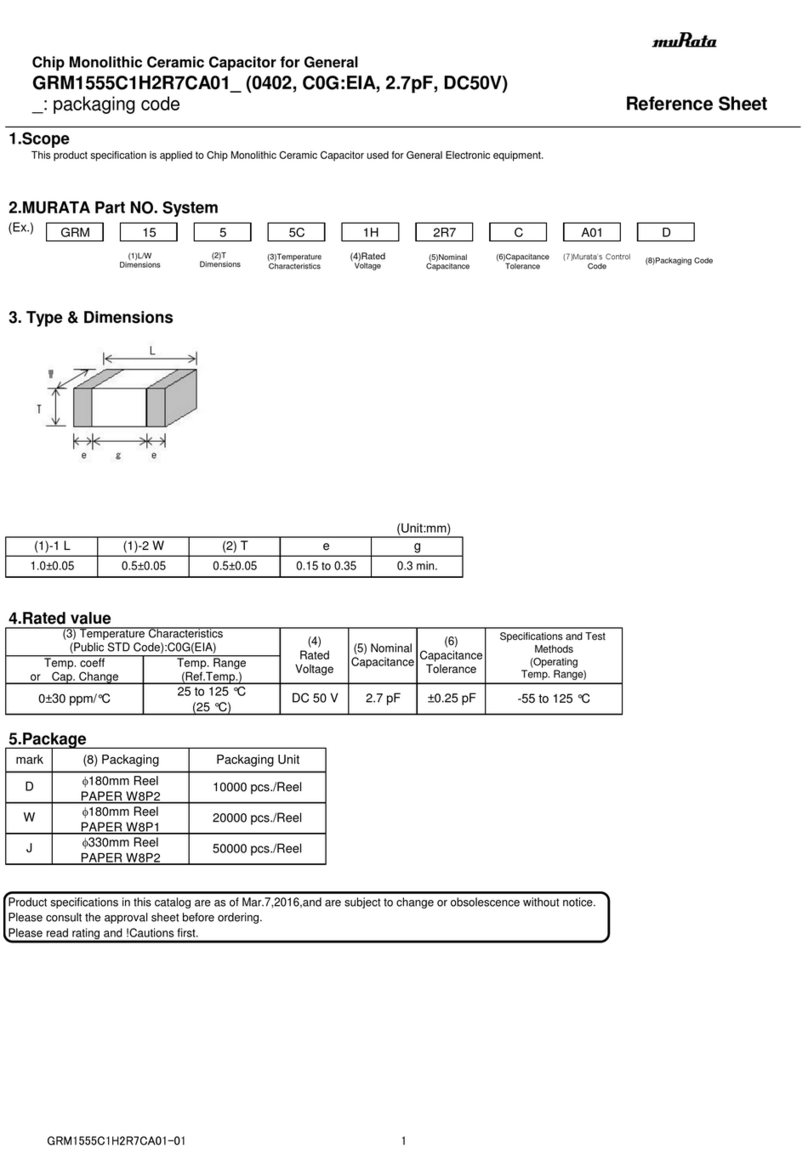
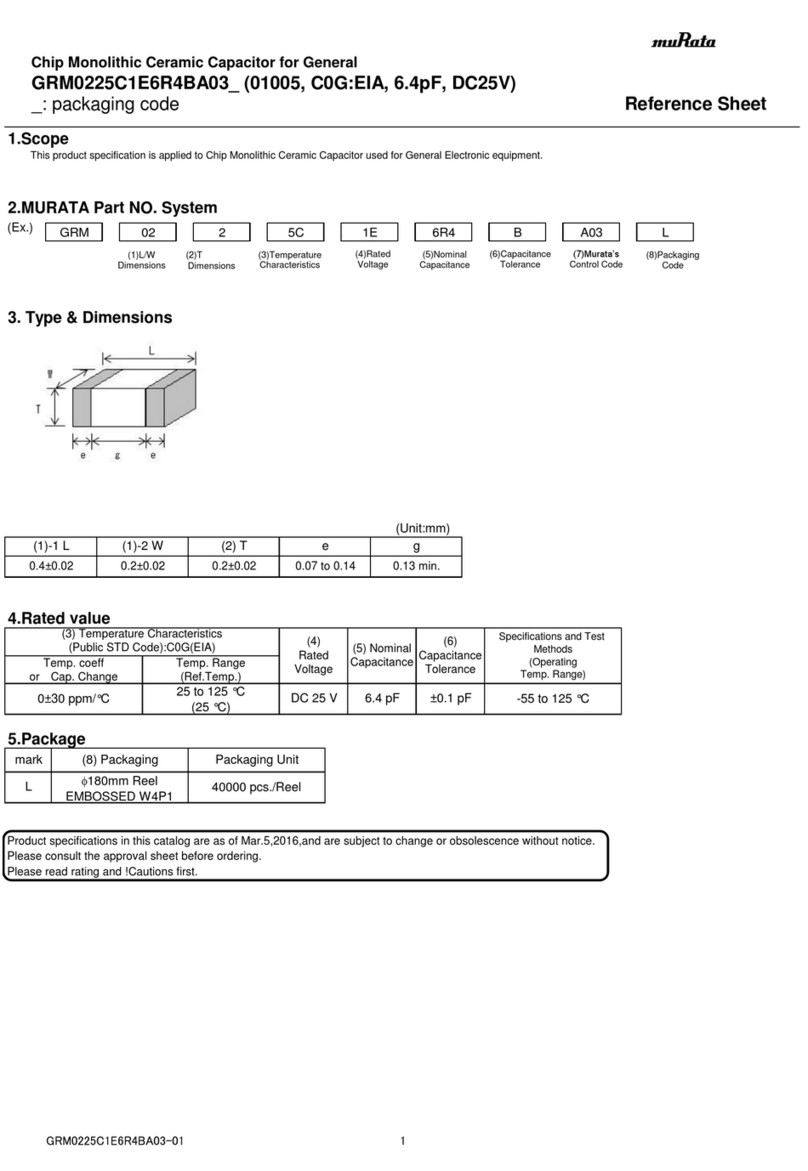
Page | 2
Contents
1.0 Overview...................................................................................................................... 3
2.0 Controls and Indicators –Front Panel............................................................................... 6
2.1 GNSS Status....................................................................................................................... 7
2.2 GNSS Detailed Status.......................................................................................................... 7
2.3 Channel Status ................................................................................................................... 7
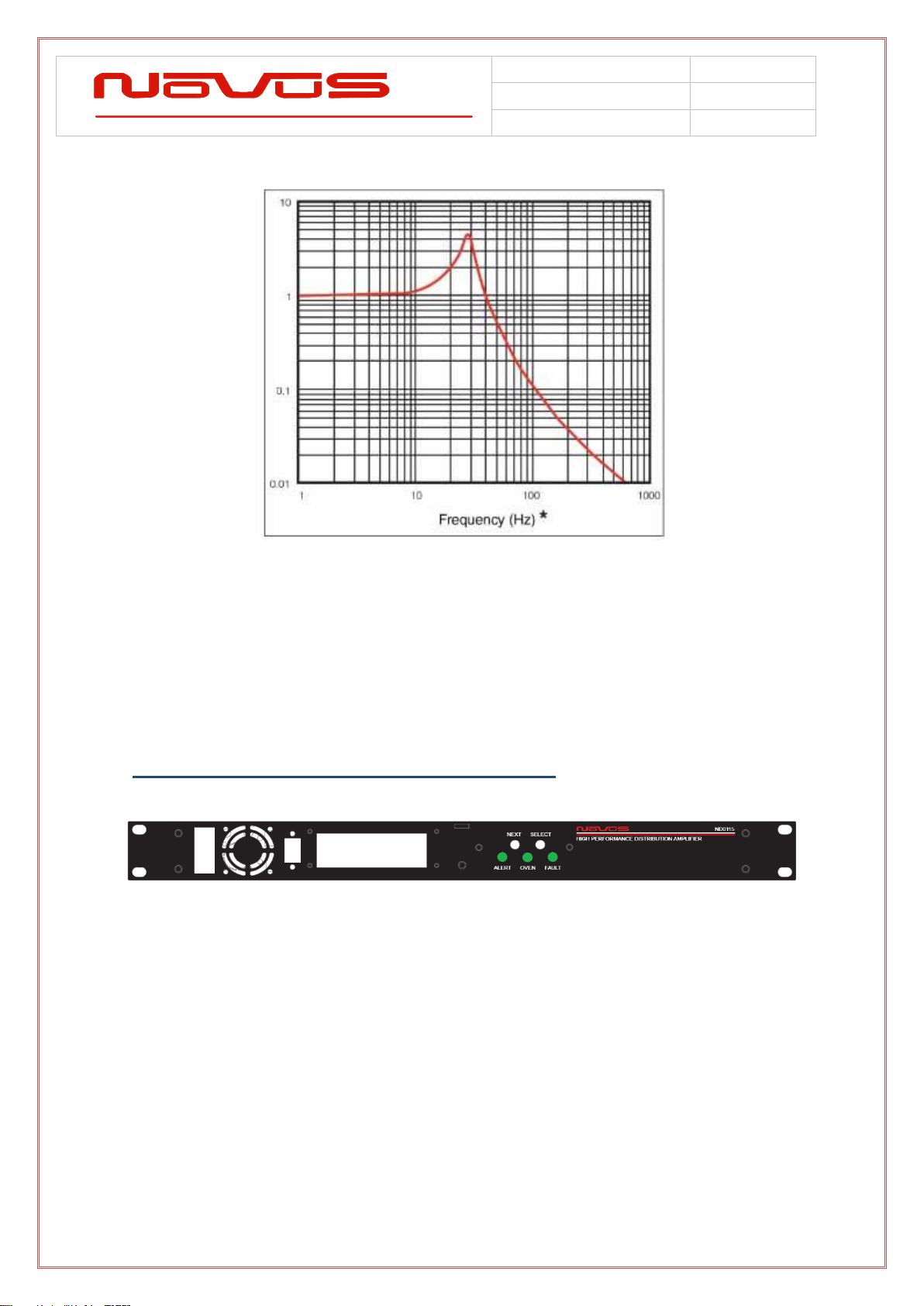
2.4 Status LEDs........................................................................................................................ 8
2.5 Alert Threshold................................................................................................................... 9
2.6 Latch Channel Values.........................................................................................................11
2.7 PPS Status ........................................................................................................................11
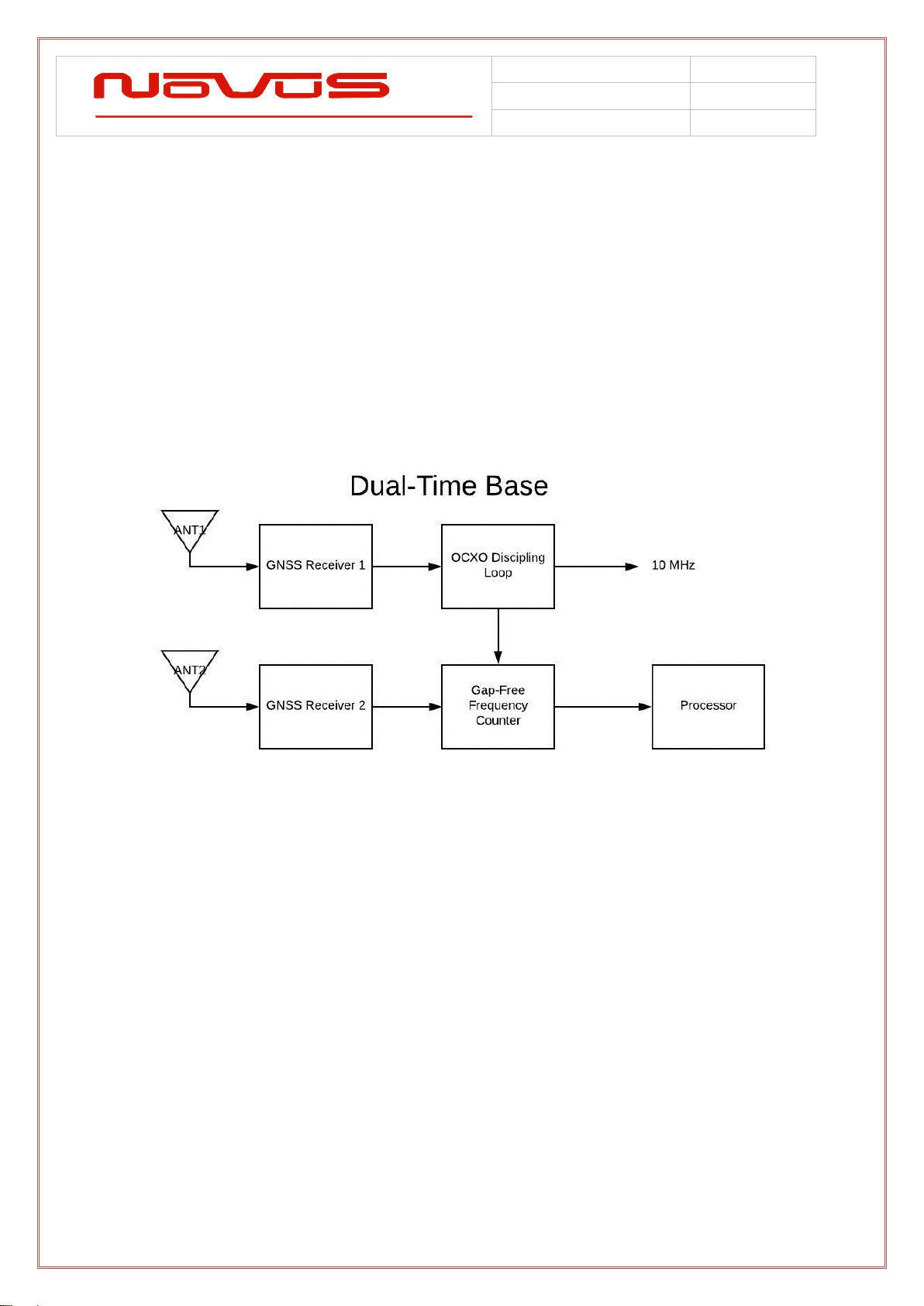
2.8 GPS Select (Dual Time Base Feature) .................................................................................13
2.9 Save Configuration ............................................................................................................14
2.10 Fault Status.....................................................................................................................14
2.11 UTC Mode .......................................................................................................................15
2.12 GMT Offset......................................................................................................................15
2.13 Power Switch...................................................................................................................16
3.0 Rear Panel .................................................................................................................. 16
3.1 Channel Outputs - BNC ......................................................................................................16
3.2 Antenna Input A/B - SMA ...................................................................................................16
3.3 DC Input...........................................................................................................................17
3.4 AC Input ...........................................................................................................................17
4.0 GNSS Receiver............................................................................................................. 17
5.0 Antenna...................................................................................................................... 19
6.0 Programming Guide (RS232 Port) .................................................................................. 20
6.1 RS232 / Status / Command ................................................................................................21
Specifications .................................................................................................................... 22
Performance .........................................................................................................................22
Environmental and Mechanical .............................................................................................22
LIMITED HARDWARE WARRANTY ....................................................................................... 23