ESI-100 IP-PBX
1 Overview
The purpose of this configuration guide is to describe the steps needed to configure
the ESI-100 PBX for proper operation with Optimum Business Sip Trunking. The
steps below describe the basic configuration required to enable the PBX to use
Optimum Business SIP Trunking for inbound and outbound calling. Please refer to
the ESI-100 PBX documentation to configure advanced PBX features.
2 Prerequisites
Please follow the instructions in the Optimum Business SIP Trunk Set-up Guide. The
set-up guide was left by the Optimum Business technician at installation. If you do
not have the set-up guide, go to optimumbusiness.com/sip to download a copy.
The set-up guide describes the steps needed to configure the LAN side of the
Optimum Business SIP Trunk Adaptor (Edgewater 4552).
This configuration guide provides the configuration steps for both PBX registration
and Static IP or non-registration modes of PBX operation.
The PBX used in the lab comprises of the following:
Table 1 – PBX Information
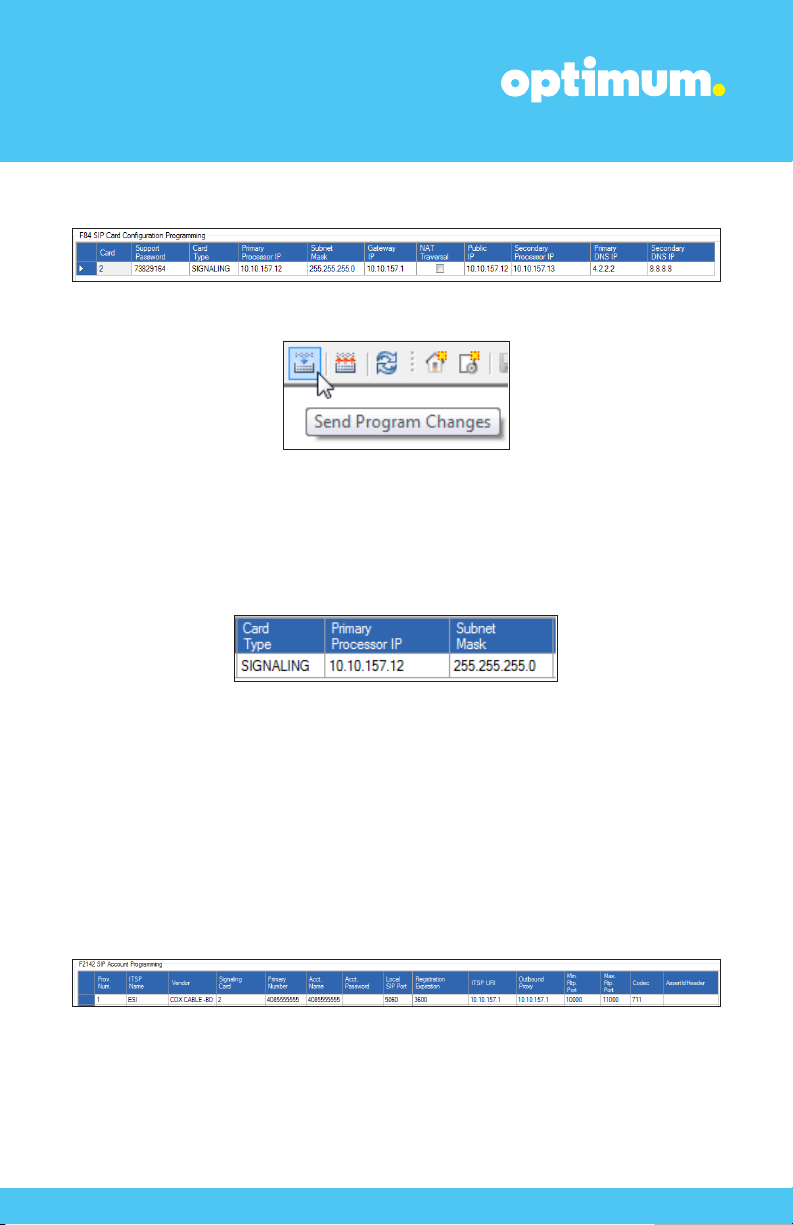
3 ESI-100 Configuration
The configuration described here assumes that the PBX is already configured
and operational with station side phones using assigned extensions or DIDs. This
configuration is based on ESI-100 version 12.5.25.0.
3
Manufacturer: ESI
Model: ESI-100
Software Version: 12.5.25.0
Does the PBX send SIP
Registration messages Ye s
(Yes/No)?
Vendor Contact: www.esi.com