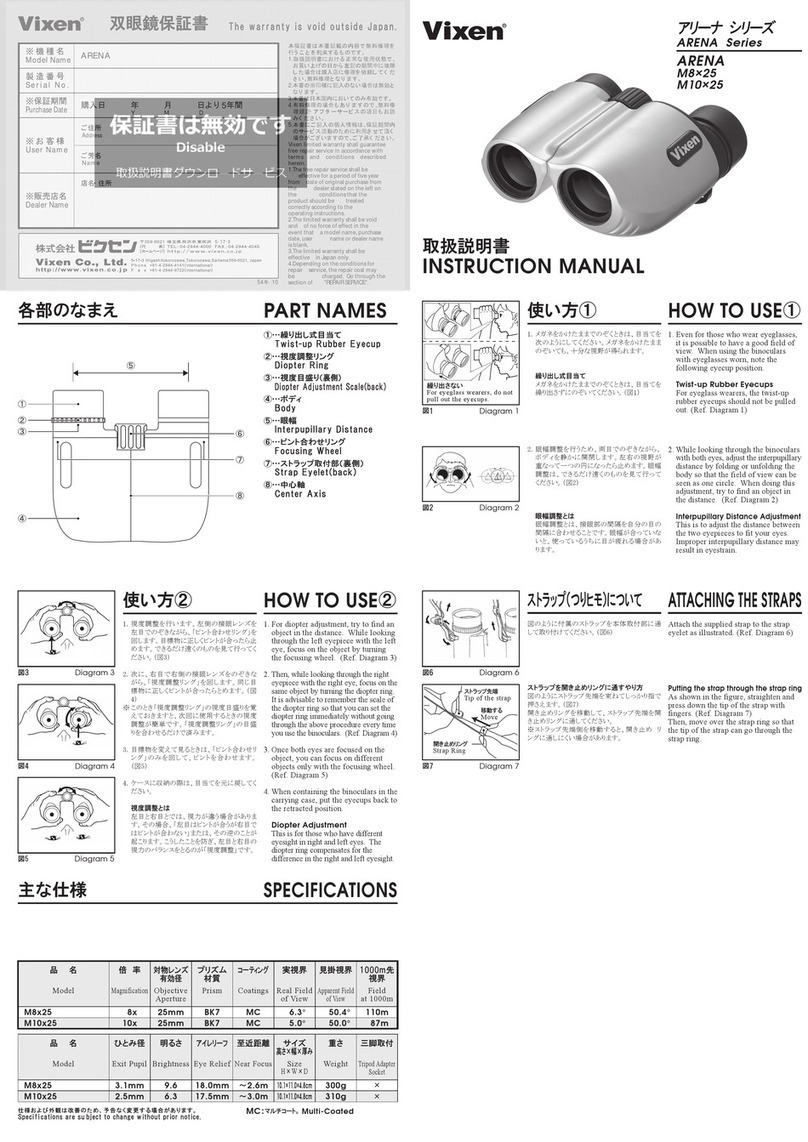
Reticle:
The vertical scale of this reticle, (visible through the
right half of the binocular), allows you to calculate
distance from your position to an object, provided its
height is known. You may also calculate the height
of an object if you know its distance from you. De-
tailed instructions follow in this manual.
Compass Illumination:
The PENTAX Marine binocular features a compass
illuminator that functions with available ambient
light. Light enters through a small white diuser
disc on top of the compass housing to illuminate the
compass scale. Bright ambient light levels make the
scale appear bright and low light levels make the
scale appear dim. In order to adequately view the
compass scale in ambient light, make certain not to
cover the diuser disc.
Using the Compass Illuminator Lamp:
The PENTAX Marine binocular is equipped with a
built-in LED compass illuminator for use at night
and in low light conditions. The
compass housing is located on
the top right side of the binocu-
lar. When the ambient light level
does not permit you to see the
compass scale clearly, depress
the black power buon on top of the compass hous-
ing to power the lamp. The lamp is illuminated only
while the buon is depressed. If the illuminator
lamp is dim or does not come on, replace the baer-
ies. If fresh baeries do not provide illumination, the
unit may require service.
Changing Baeries:
Both baeries should always be changed at the same
time. To change baeries, use a thin coin to unscrew
the baery chamber cover, by turning it counter-
clockwise. Remove the old bat-
teries. Insert both new baeries
properly seated with “+” facing
up. Replace the baery chamber
cover by turning it in a clock-
wise direction; making certain it
is properly sealed (to prevent penetration of outside
moisture). If the binocular is not to be used for an
extended time, remove the baeries. This keeps the
binocular safe from baery leakage during storage.
Baery type: (2) LR43 (1.5v alkaline)
Equivalent types: AG12, G12, 386, CX186 - (1.5v)
IMPORTANT:
AFTER DIRECT EXPOSURE TO SALTWATER OR
SALT-SPRAY, RINSE THE BINOCULAR THOR-
OUGHLY WITH FRESH WATER AND WIPE DRY.
AVOID EXTENDED EXPOSURE TO BRIGHT DI-
RECT SUNLIGHT AND SEVERE TEMPERATURE
FLUCTUATIONS. IF USED IN VERY COLD TEM-
PERATURES, GRADUALLY EXPOSE THE UNIT
TO WARMER TEMPERATURES IN ORDER TO
AVOID CONDENSATION BUILD-UP.
Ranging Reticle:
This reticle features vertical and horizontal scales.
Each minor division on the horizontal scale and ver-
tical scale indicates 5 mils and each major division
indicates 10 mils.
Equivalents:
5 mils = .3 degrees
10 mils = .6 degrees
1 degree = 17.8 mils
1 degree = 60 minutes
360 degrees = 6400 mils
Using the Reticle to Measure Azimuth:
Azimuth is dened as the angle (usually in degrees)
between a reference plane and a point. In navigation,
the reference plane is typically true North which is
dened as 0 degrees North. In rotating your view-
ing position clockwise to a point due East (from true
North), the azimuth is 90 degrees; due South the
azimuth is 180 degrees, due West the azimuth is 270
degrees, and due North is referenced as 360 degrees
on the compass scale.
The PENTAX Marine’s mil reticle can measure the
azimuth angle, altitude (elevation) angle, and can
help you calculate distance from the viewer to the
object, and the size of an object based on known
distance from the viewer.
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
I
1
7
0
1
8
0
1
9
0
80
60
40
20
0 20 60 80