PICOLAS LDP-AV 16N45-40 User manual
Popular Industrial Electrical manuals by other brands
Murata
Murata GRM0335C1E3R9BA01 Series Reference sheet

ARCAIR
ARCAIR N6000 Automatic System Safety and operating instructions
Murata
Murata GRM31CR61E106MA12 Series Reference sheet
Murata
Murata GQM2195C2A9R1CB01 Series Reference sheet

MFJ
MFJ MFJ-918 quick start guide

Abtech
Abtech HVJB Series Installation, operation & maintenance instructions
Murata
Murata GRM0335C1H8R1DA01 Series Reference sheet

SAF-HOLLAND
SAF-HOLLAND CBX 5415.5 Installation and operation manual

Eaton
Eaton Ulusoy HMH24-04 user manual
Murata
Murata GJM0335C1E4R4BB01 Series Reference sheet

Newlong
Newlong NP-7H NSTRUCTION MANUAL/PARTS LIST

Stahl
Stahl 8575/12 operating instructions
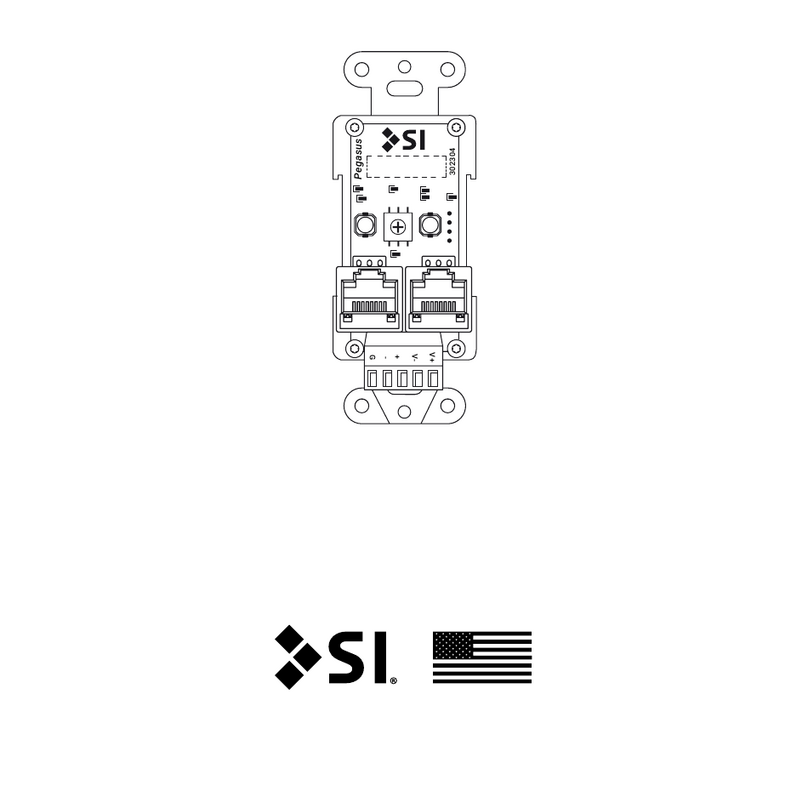
SI
SI Pegasus installation instructions
Murata
Murata GRM1555C1H2R7CA01 Seies Reference sheet
Murata
Murata GRM0225C1E6R4BA03 Series Reference sheet

Cooper Power Systems
Cooper Power Systems VXE15 Installation and operation instructions
S&C
S&C Vista SD manual

Murata
Murata GRM0335C2A7R3CA01 Series Reference sheet









