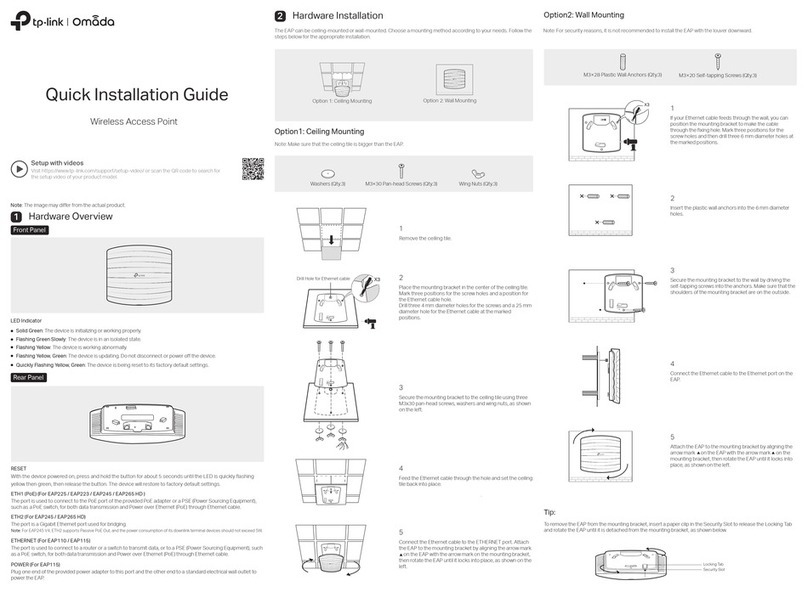
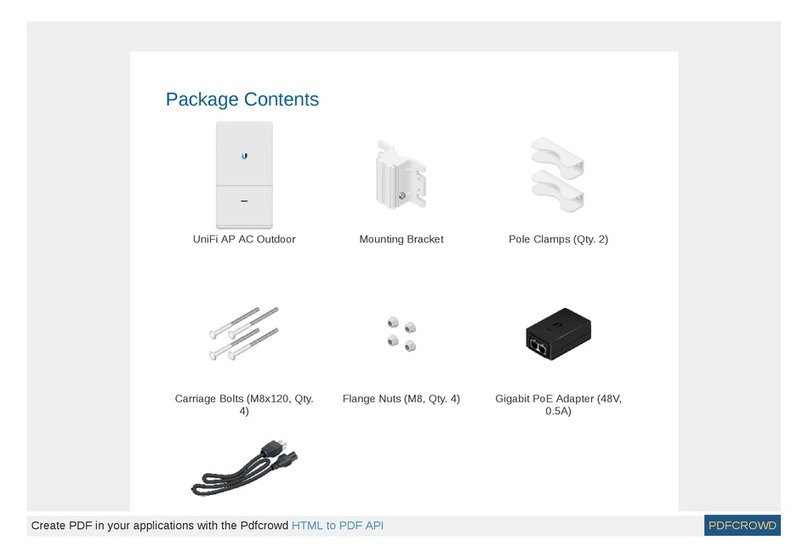
Pg 4 of 26
Contents
1INTRODUCTION .................................................................................... 1
THE PRODUCT ........................................................................................... 1
KEY FEATURES .......................................................................................... 1
2PACKAGE CONTENTS............................................................................. 2
CONTENT OF PACKAGE ................................................................................. 2
SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS FOR CONFIGURATION ...................................................... 2
3CONNECTION ........................................................................................ 3
4BASIC IP NETWORKING........................................................................ 3
WIRELESS LAN BASICS................................................................................ 4
5GETTING STARTED................................................................................ 5
6CONFIGURATION WIZARD .................................................................... 8
7CONFIGURATION MENU ...................................................................... 11
SYSTEM SUMMARY >CONFIGURATION ..............................................................11
SYSTEM SUMMARY >ASSOCIATIONS................................................................12
SYSTEM SUMMARY >STATISTICS ...................................................................12
SYSTEM SUMMARY >SITE SCAN ....................................................................13
BASIC SETTING >SNTP .............................................................................13
BASIC SETTING >LAN SETTING ....................................................................14
BASIC >VLAN SETTING .............................................................................15
WIRELESS >BASIC SETTING ........................................................................16
SECURITY MODE >OPEN-SYSTEM/SHARED KEY ...................................................18
SECURITY MODE >WPA 2-PSK ....................................................................20
WIRELESS >ADVANCE SETTING.....................................................................21
WIRELESS >MAC ACCESS CONTROL...............................................................22
WIRELESS >BANDWIDTH CONTROL ................................................................23
SYSTEM TOOLS >SYSTEM LOG ......................................................................24
SYSTEM TOOLS >SYSTEM ADMIN ...................................................................25
SYSTEM TOOLS >LICENSE KEY......................................................................25
SYSTEM TOOLS >SNMP CONFIGURATION .........................................................26
SYSTEM TOOLS >BACKUP/RESTORE SETTINGS ...................................................27
SYSTEM TOOLS >FIRMWARE UPDATE ..............................................................28
SYSTEM TOOLS >REBOOT ...........................................................................29