CAUTION: DO NOT ATTEMPT TO MODIFY THIS PRODUCT IN ANY WAY AND
NEVER PERFORM CUSTOMIZED INSTALLATIONS WITHOUT
MANUFACTURER'S APPROVAL. UNAUTHORIZED MODIFICATIONS WILL NOT
ONLY VOID THE WARRANTY, BUT MAY LEAD TO YOUR BEING LIABLE FOR
ANY RESULTING PROPERTY DAMAGE OR USER INJURY.
SERVICE WORK SHOULD BE PERFORMED ONLY AFTER YOU ARE
THOROUGHLY FAMILIAR WITH ALL OF THE FOLLOWING SAFETY CHECKS
AND SERVICING GUIDELINES. TO DO OTHERWISE, INCREASES THE RISK OF
POTENTIAL HAZARDS AND INJURY TO THE USER.
WHILE SERVICING, USE AN ISOLATION TRANSFORMER FOR PROTECTION
FROM A.C. LINE SHOCK.
AFTER THE ORIGINAL SERVICE PROBLEM HAS BEEN CORRECTED, A CHECK
SHOULD BE MADE OF THE FOLLOWING.
1. BE SURE THAT ALL COMPONENTS ARE POSITIONED IN SUCH A WAY AS
TO AVOID POSSIBILITY OF ADJACENT COMPONENT SHORTS. THIS IS
ESPECIALLY IMPORTANT ON THOSE MODULES WITCH ARE
TRANSPORTED TO AND FROM THE REPAIR SHOP.
2. NEVER RELEASE A REPAIR UNLESS ALL PROTECTIVE DEVICES SUCH AS
INSULATORS, BARRIERS, COVERS, SHIELDS, STRAIN RELIEFS, POWER
SUPPLY CORDS, AND OTHER HARDWARE HAVE BEEN REINSTALLED PER
ORIGINAL DESIGN. BE SURE THAT THE SAFETY PURPOSE OF THE
POLARIZED LINE PLUG HAS NOT BEEN DEFEATED.
3. SOLDERING MUST BE INSPECTED TO DISCOVER POSSIBLE COLD
SOLDER JOINTS, SOLDER SPLASHES OR SHARP SOLDER POINTS. BE
CERTAIN TO REMOVE ALL LOOSE FOREIGN PARTICLES.
4. CHECK FOR PHYSICAL EVIDENCE DF DAMAGE OR DETERIORATION TO
PARTS AND COMPONENTS, FOR FRAYED LEADS AND DAMAGED
INSULATION (INCLUDING A.C. CORD), AND REPLACE IF NECESSARY
FOLLOW ORIGINAL LAYOUT, LEAD LENGTH AND DRESS.
5. NO LEAD OR COMPONENT SHOULD TOUCH A RECEIVING TUBE OR A
RESISTOR RATED AT 1 WATT OR MORE. LEAD TENSION AROUND
PROTRUDING METAL SURFACES MUST BE AVOIDED.
6. ALL CRITICAL COMPONENTS SUCH AS FUSES. FLAMEPROOF RESISTORS,
CAPACITORS, ETC. MUST BE REPLACED WITH EXACT FACTORY TYPES,
DO NOT USE REPLACEMENT COMPONENTS OTHER THAN THOSE
SPECIFIED OR MAKE UNRECOMMENDED CIRCUIT MODIFICATIONS.
7. AFTER RE-ASSEMBLY OF THE SET, ALWAYS PERFORM AN A.C. LEAKAGE
TEST ON ALL EXPOSED METALLIC PARTS OF THE CABINET, (THE
CHANNEL SELECTOR KNOB, ANTENNA TERMINALS. HANDLE AND
SCREWS) TO BE SURE THE SET IS SAFE TO OPERATE WITHOUT DANGER
OF ELECTRICAL SHOCK. DO NOT USE A LINE ISOLATION TRANSFORMER
DURING THIS TEST, MAKE SURE TO USE AN A.C. VOLTMETER. HAVING
5000 OHMS PER VOLT OR MORE SENSITIVITY, IN THE FOLLOWING
MANNER; CONNECT A 1500 OHMS 10 WATT RESISTOR, PARALLELED BY
A.15 MFD. 150V A.C. TYPE CAPACITOR BETWEEN A KNOWN GOOD EARTH
GROUND (WATER PIPE, CONDUIT, ETC.) AND THE EXPOSED METALLIC
PARTS, ONE AT A TIME. MEASURE THE A.C. VOLTAGE ACROSS THE
COMBINATION OF 1500 OHM RESISTOR AND 15 MFD CAPACITOR.
REVERSE THE A.C. PLUG AND REPEAT A.C. ANY VOLTAGE
MEASUREMENTS FOR EACH EXPOSED METALLIC PART. VOLTAGE
MEASURED MUST NOT EXCEED 75 VOLTS R.M.S. THIS CORRESPONDS
TO 0.5 MILLIAMP A.C. ANY VALUE EXCEEDING THIS LIMIT CONSTITUTES A
POTENTIAL SHOCK HAZARD AND MUST BE CORRECTED IMMEDIATELY.
THE LIGHTNING FLASH WITH APROWHEAD SYMBOL. WITHIN AN
EQUILATERAL TRIANGLE, IS INTENDED TO ALERT THE SERVICE
PERSONNEL TO THE PRESENCE OF UNINSULATED "DANGEROUS
VOLTAGE" THAT MAY BE OF SUFFICIENT MAGNITUDE TO
CONSTITUTE A RISK OF ELECTRIC SHOCK.
THE EXCLAMATION POINT WITHIN AN EQUILATERAL TRIANGLE IS
INTENDED TO ALERT THE SERVICE PERSONNEL TO THE
PRESENCE OF IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION IN SERVICE
LITERATURE.
SAFETY CHECKS
SUBJECT: FIRE & SHOCK HAZARD
SUBJECT GRAPHIC SYMBOLS
PLACE THIS PROBE
ON EACH EXPOSED
METAL PART
SUBJECT: X-RADIATION
SUBJECT: IMPLOSION
SUBJECT: TIPS ON PROPER INSTALLATION
1. BE SURE PROCEDURES AND INSTRUCTIONS TO ALL SERVICE PERSONNEL
COVER THE SUBJECT OF
2. ONLY FACTORY SPECIFIED C.R.T ANODE CONNECTORS MUST BE USED.
DEGAUSSING SHIELDS ALSO SERVE AS AN X-RAY SHIELD IN COLOR SETS,
ALWAYS RE-INSTALL THEM.
3. IT IS ESSENTIAL THAT SERVICE PERSONNEL HAVE AVAILABLE AN
ACCURATE AND RELIABLE HIGH VOLTAGE METER. THE CALIBRATION OF
THE METER SHOULD BE CHECKED PERIODICALLY AGAINST A
REFERENCE STANDARD, SUCH AS THE ONE AVAILABLE AT YOUR
DISTRIBUTOR.
4. WHEN THE HIGH VOLTAGE CIRCUITRY IS OPERATING PROPERLY, THERE IS
NO POSSIBILITY OF AN
5. WHEN TROUBLESHOOTING AND MAKING TEST MEASUREMENTS IN A
PRODUCT WITH A PROBLEM OF EXCESSIVE HIGH VOLTAGE AVOID BEING
UNNECESSARILY CLOSE TO THE PICTURE TUBE AND THE HIGH VOLTAGE
SUPPLY DO NOT OPERATE THE PRODUCT LONGER THAN IT IS NECESSARY
TO LOCATE THE CAUSE OF EXCESSIVE VOLTAGE.
6. REFER TO HV. B+ AND SHUTDOWN ADJUSTMENT PROCEDURES
DESCRIBED IN THE APPROPRIATE SCHEMATIC AND DIAGRAMS(WHERE
USED).
1. ALL DIRECT VIEWED PICTURE TUBES ARE EQUIPPED WITH AN INTEGRAL
IMPLOSION PROTECTION SYSTEM, BUT CARE SHOULD BE TAKEN TO
AVOID DAMAGE DURING INSTALLATION, AVOID SCRATCHING THE TUBE. IF
SCRATCHED REPLACE IT.
2. USE ONLY RECOMMENDED FACTORY REPLACEMENT TUBES.
1. NEVER INSTALL ANY PRODUCT IN A CLOSED-IN RECESS. CUBBYHOLE OR
CLOSELY FITTING SHELF SPACE, OVER OR CLOSE TO HEAT DUCT, OR IN
THE PATH OF HEATED AIR FLOW.
2. AVOID CONDITIONS OF HIGH HUMIDITY SUCH AS: OUTDOOR PATIO
INSTALLATIONS WHERE DEW IS A FACTOR, NEAR STEAM RADIATORS
WHERE STEAM LEAKAGE IS A FACTOR, ETC.
3. AVOID PLACEMENT WHERE DRAPERIES MAY OBSTRUCT REAR VENTING.
THE CUSTOMER SHOULD ALSO AVOID THE USE OF DECORATIVE
SCARVES OR OTHER COVERINGS WHICH MIGHT OBSTRUCT VENTILATION.
4. WALL AND SHELF MOUNTED INSTALLATIONS USING A COMMERCIAL
MOUNTING KIT, MUST FOLLOW THE FACTORY APPROVED MOUNTING
INSTRUCTIONS. A PRODUCT MOUNTED TO A SHELF OR PLATFORM MUST
RETAIN ITS ORIGINAL FEET (OR THE EQUIVALENT THICKNESS IN SPACERS)
TO PROVIDE ADEQUATE AIR FLOW ACROSS THE BOTTOM. BOLTS OR
SCREWS USED FOR FASTENERS MUST NOT TOUCH ANY PARTS OR
WIRING. PERFORM LEAKAGE TEST ON CUSTOMIZED INSTALLATIONS.
5. CAUTION CUSTOMERS AGAINST THE MOUNTING OF A PRODUCT ON
SLOPING SHELF OR A TILTED POSITION, UNLESS THE PRODUCT IS
PROPERLY SECURED.
6. A PRODUCT ON A ROLL-ABOUT CART SHOULD BE STABLE ON ITS
MOUNTING TO THE CART CAUTION THE CUSTOMER ON THE HAZARDS OF
TRYING TO ROLL A CART WITH SMALL CASTERS ACROSS THRESHOLDS
OR DEEP PILE CARPETS.
7. CAUTION CUSTOMERS AGAINST THE USE OF A CART OR STAND WHICH
HAS NOT BEEN LISTED BY UNDERWRITERS LABORATORIES, INC. FOR USE
WITH THEIR SPECIFIC MODEL OF TELEVISION RECEIVER OR
GENERICALLY APPROVED FOR USE WITH TV'S OF THE SAME OR LARGER
SCREEN SIZE.
8. CAUTION CUSTOMERS AGAINST THE USE OF EXTENSION CORDS. EXPLAIN
THAT A FOREST OF EXTENSIONS SPROUTING FROM A SINGLE OUTLET
CAN LEAD TO DISASTROUS CONSEQUENCES TO HOME AND FAMILY.
X-RADIATION. THE ONLY POTENTIAL SOURCE OF
X-RAYS IN CURRENT T.V. RECEIVERS IS THE PICTURE TUBE. HOWEVER,
THIS TUBE DOES NOT EMIT X-RYS WHEN THE HIGH VOLTAGE IS AT THE
FACTORY SPECIFIED LEVEL. THE PROPER VALUE IS GIVEN IN THE
APPLICABLE SCHEMATIC. OPERATION AT HIGHER VOLTAGES MAY CAUSE A
FAILURE OF THE PICTURE TUBE OR HIGH VOLTAGE SUPPLY AND, UNDER
CERTAIN CIRCUMSTANCES, MAY PRODUCE RADIATION IN EXCESS OF
DESIRABLE LEVELS.
X-RADIATION PROBLEM. EVERY TIME A COLOR
CHASSIS IS SERVICED, THE BRIGHTNESS SHOULD BE RUN UP AND DOWN
WHILE MONITORING THE HIGH VOLTAGE WITH A METER TO BE CERTAIN
THAT THE HIGH VOLTAGE DOES NOT EXCEED THE SPECIFIED VALUE AND
THAT IT IS REGULATING CORRECTLY. WE SUGGEST THAT YOU AND YOUR
SERVICE ORGANIZATION REVIEW TEST PROCEDURES SO THAT VOLTAGE
REGULATION IS ALWAYS CHECKED AS A STANDARD SERVICING
PROCEDURE AND THAT THE HIGH VOLTAGE READING BE RECORDED ON
EACH CUSTOMER'S INVOICE.
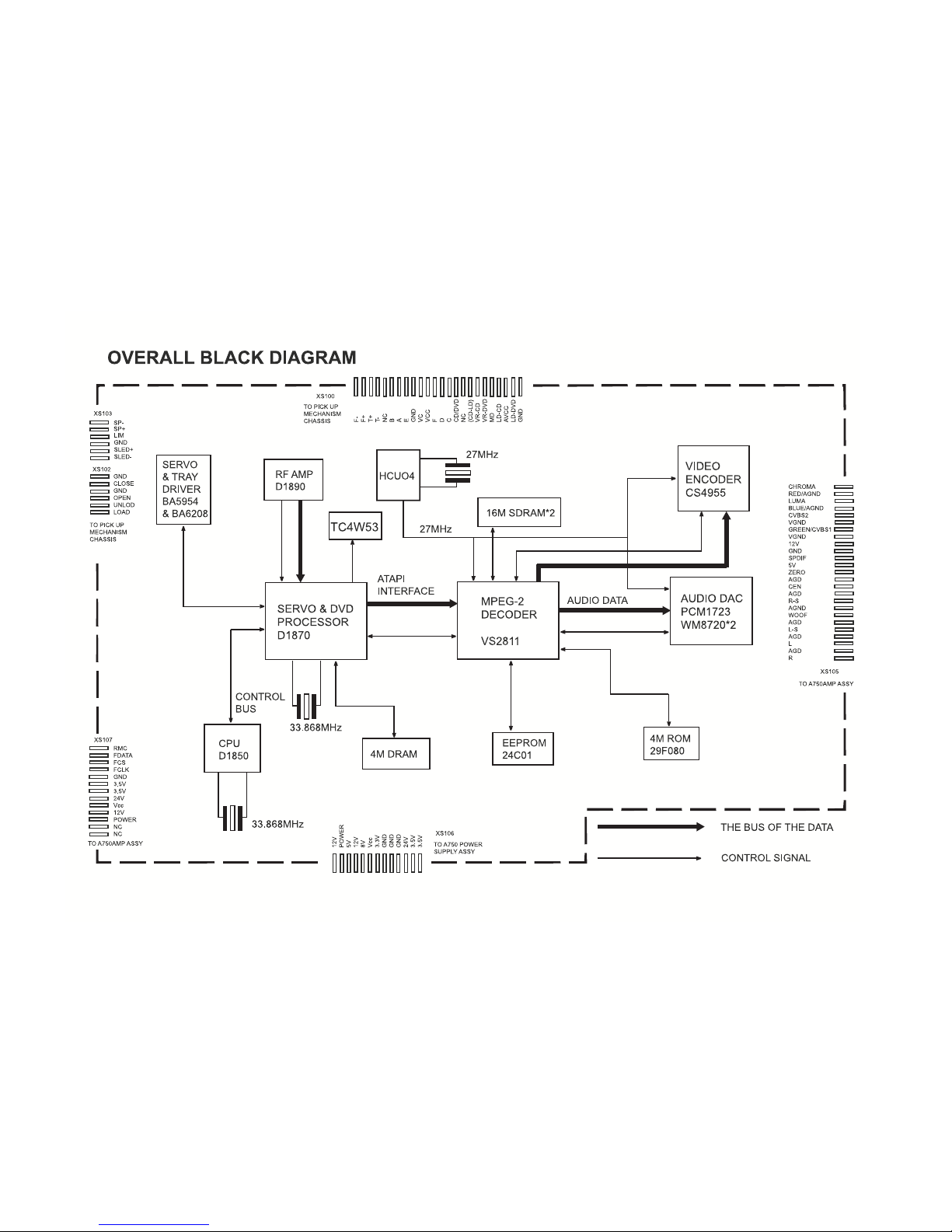
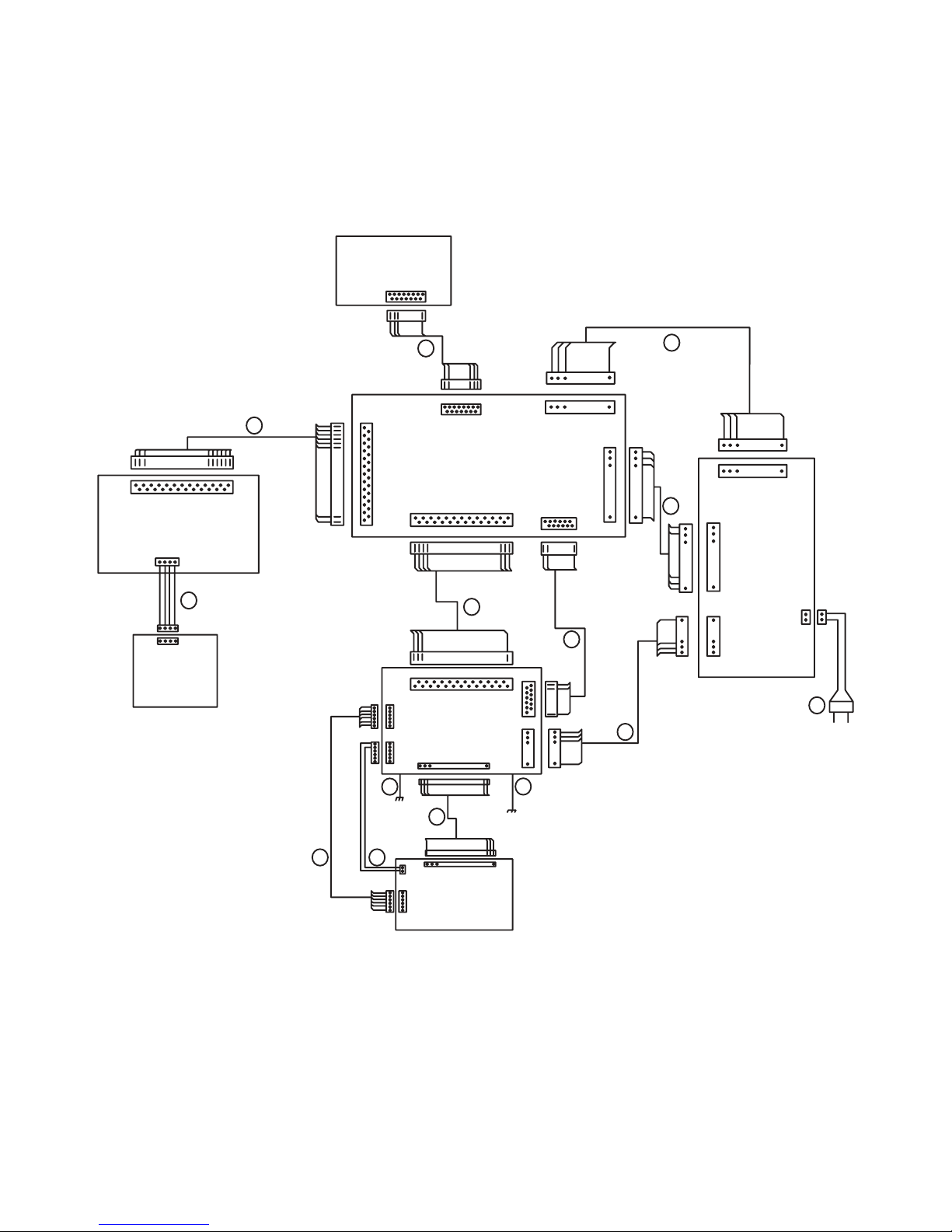
PRODUCT SAFETY SERVICING GUIDELINES FOR VIDEO PRODUCTS
GOOD EARTH GROUND
SUCH AS THE WATER
PIPE, CONDUIT, ETC.
2