A Interference
For a successful wireless installation, it is critical to
understand that the wireless network is influenced by the
same environmental factors that affect other wireless systems.
Interference from radio emitters, various electronic devices,
and solid objects may degrade or stop communication.
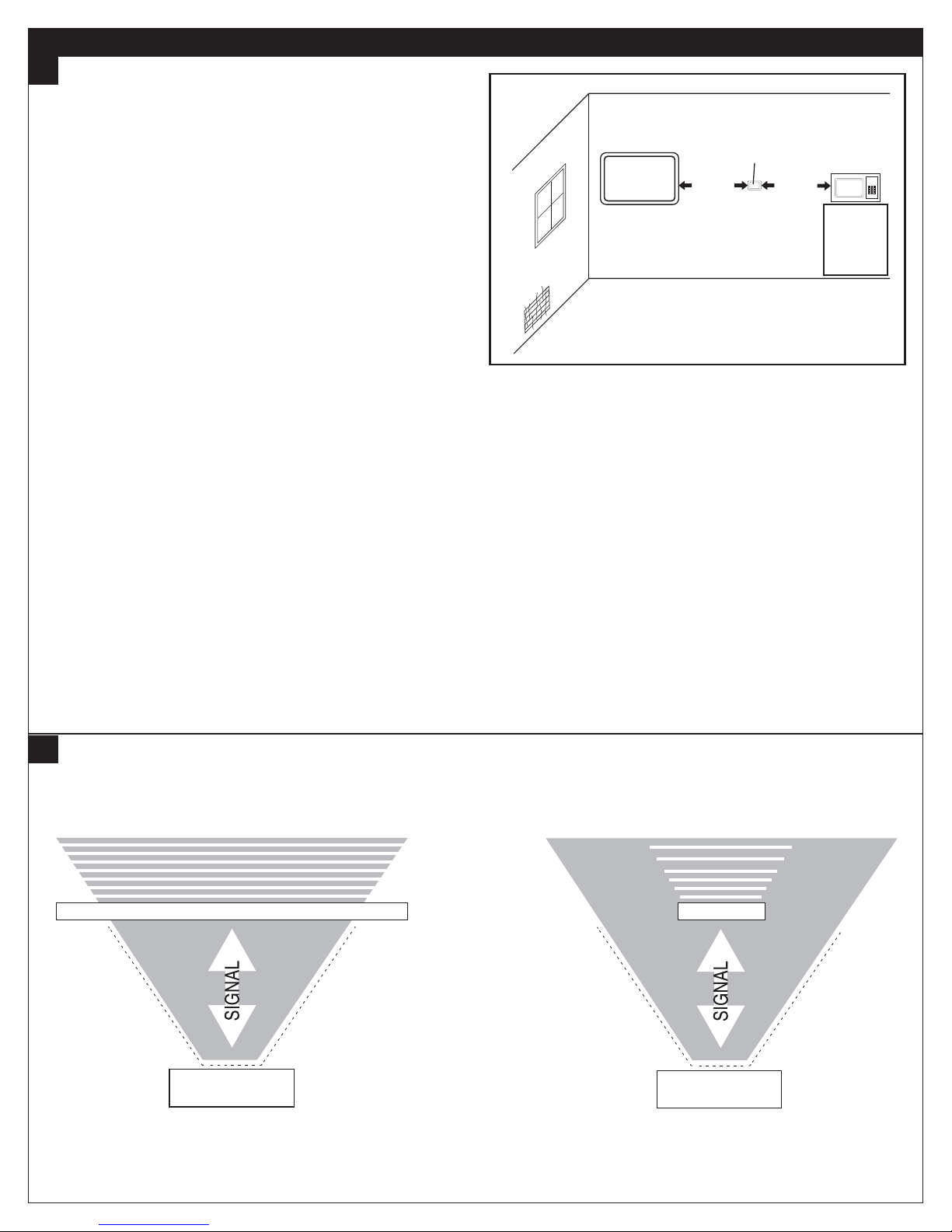
Wireless competition
Too many wireless devices can saturate the
environment.
• Do not place Nexia Wireless devices, wireless routers,
or repeaters within 5 ft. of each other.
• Do not place radios of any type within 5 ft. of each
other. This includes not only these wireless controls
and sensors, but also wireless phones, security
systems, cameras, cell phones, stereo receivers, TV's,
baby monitors, cable boxes, HAM equipment, wireless
remotes, game systems, microwave ovens, etc.
Multipath Distortion
The RF signal will arrive at the receiver antenna by
many different paths all simultaneously.
• The arrival of the same signal by way of multiple paths
can lead to interference and a distorted signal. This
is often referred to as "multipath distortion" and leads
to "dead spots" around the home or room where the
range will be less than expected.
• Relocating a device can often address multipath
distortion issues.
> 5 FEET > 5 FEET
Control
or
Sensor
TV
Microwave
Avoiding Signal
Competition
Wireless Signal Interference
B Obstructions
Obstructions in the path of the signal degrade or reflect the signal.
Front
Device
Wall
Decreased
Signal
Front
Obstruction
Decreased
Signal
Device



