Sensoterra Multi-Depth User manual

Multi-Depth
Soil moisture
sensor
USER GUIDE
Grow more, waste less...

Welcome
Welcome on board and thank you for joining us!
In this guide we will help you get started - from
successfully installing your sensor to getting
data out of the ground.
2 | Multi-Depth soil moisture sensor

Contents
Preparation
Overview 4
Download the app 6
Choosing your location 7
Ensuring good
connectivity 8
Choosing soil type 11
Choosing a unit
of measure 13
Installation
Registering the sensor 16
Installing the sensor 17
Ensuring good soil
contact 19
Mounting the antenna 20
Wake up your sensor 22
Data
Accessing the data 23
Understanding
the data 24
Use and
maintenance
Moving a sensor 26
Storage 27
Warranty 28
Support 29
Safety 30
31
2
4
www.sensoterra.com | 3

Preparation
1
What is in the box:
Multi-Depth sensor
Antenna
Antenna extension cable
Flag
Cable ties
Drill bit
Magnet
Overview
Bucket of water
Rubber hammerSmartphone! Electric drill
Spade Wrench size
25mm/1inch
What is not in the box:
4 | Multi-Depth soil moisture sensor4 | Multi-Depth soil moisture sensor

Preparation
1
Download the
Sensoterra app
Download and install
the Sensoterra app
from the App Store or
Google Play on your
smartphone. Create
an account or log-in.
You will need the app
for registering sensors
when you install them in
the eld.
Download the app
6 | Multi-Depth soil moisture sensor6 | Multi-Depth soil moisture sensor

Preparation
1
The eld you like to monitor can consist of geographic
features like slopes and changing soil types. These features
might inuence the soil moisture levels throughout the eld.
Consider placing sensors in different places to get a broad
overview of the eld you monitor.
Choosing your location
Soil type A
Soil type B
Soil type C
www.sensoterra.com | 7www.sensoterra.com | 7
Preparation
1
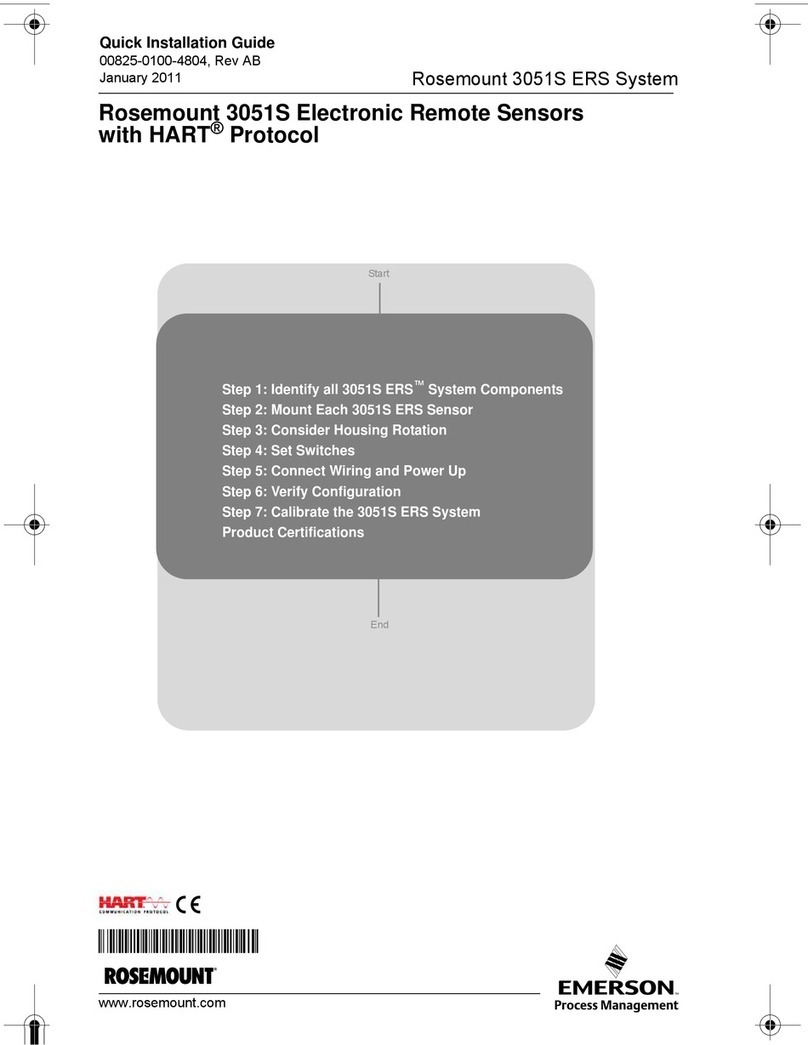
Sensoterra sensors communicate over the LoRa
network. This means the data is rst sent from the
sensor to a gateway, which then forwards the data
to the cloud via an internet connection.
If you are installing your own gateway, the basic
rule is to nd free line of sight from thesensor
antenna to the gateway antenna.
Objects like houses, barns, big trees, big vehicles
in the line between sensor and gatewaycould
obstruct the signal. Try to get the gateway antenna
up as high as possible to get a lookover the elds
and think about the location of the objects when
choosing the locations of the sensors.
Ensuring good connectivity
8 | Multi-Depth soil moisture sensor8 | Multi-Depth soil moisture sensor

Preparation
1
Terrain
Terrain that is hilly creates signal shadows over the eld.
By placing the gateway at thehighest point of the hills
could reduce the signal shadows. The sensors should be
placed onthe side of the hill that is facing the gateway.
Avoid placing them in the signal shadow or place your
gateway elsewhere.
Gateway
Farm
Shadow
area
Field
www.sensoterra.com | 9www.sensoterra.com | 9
Preparation
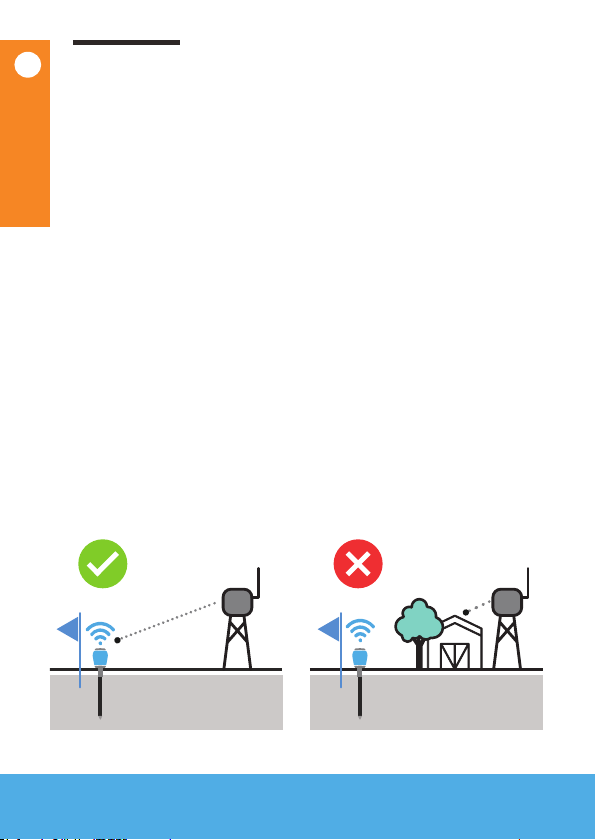
1Crops that block the signal
Crops could create a very dense canopy containing a
lot of water, which might block the signal. There are
multiple antenna extension cable lengths available.
Pick the cable that brings the antenna above the
crop canopy to create a free line of sight.
Cable length counts
Cable length reduces the signal strength. There is
a trade off between bringing the antenna high up
and using a long cable length. In case of objects/
terrain/crop canopy use the cable length to create
a free line of sight to the gateway. If you have a
shallow crop and a at area use a shorter cable.
Always get the most height out of your cable length. Don’t
take the longest cable and roll up the excessive cable.
Excessive
cable length
10 | Multi-Depth soil moisture sensor10 | Multi-Depth soil moisture sensor

Preparation
1
For more information visit the soil calibration
section on www.sensoterra.com
Choosing soil type
When installing the sensor in the app there is an
option to pick soil type. It is important to choose
the closest soil type available. This will improve
the accuracy of the measurement from the sensor.
Sensoterra calibrates the sensor measurements
for many different soil types to make the data you
view in the app and customer site and the push
notications you set up more useful.
www.sensoterra.com | 11www.sensoterra.com | 11
Preparation
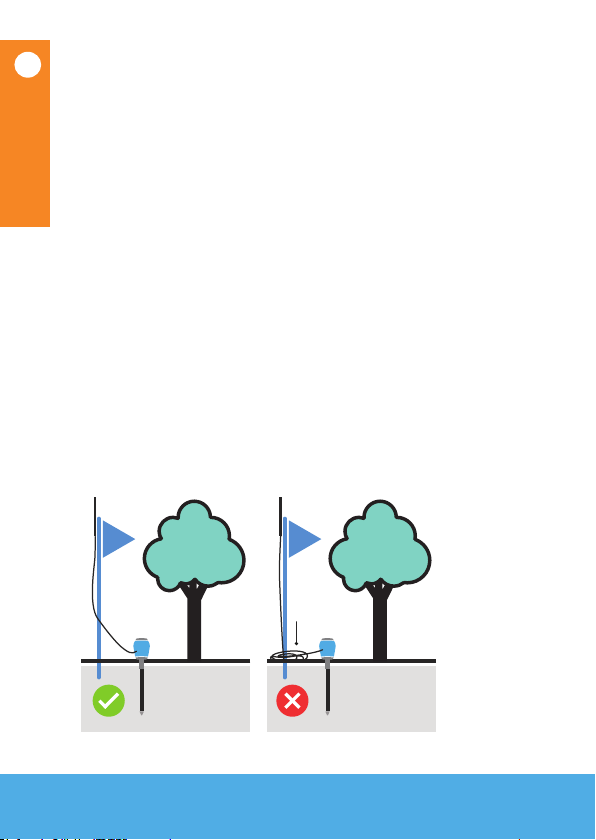
1Use the soil triangle to determine which
calibration is closest to your soil type:
10
90
100 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10
90
100
20 0
30 70
40 60
50 50
60 40
70 30
80 20
90 10
100
clay
clay loa
m
sand %
clay %
silt %
loam (green
-
house soil
)
clay loam silt
peat
loamy sand
sand
sand
(planting soil)
sand
(dunes soil 2)
sand
(dunes soil 1)
sand
(tree soil)
We continuously add new calibrations,
please visit our soil calibration section on
www.sensoterra.com for the latest information.
12 | Multi-Depth soil moisture sensor12 | Multi-Depth soil moisture sensor

Preparation
1
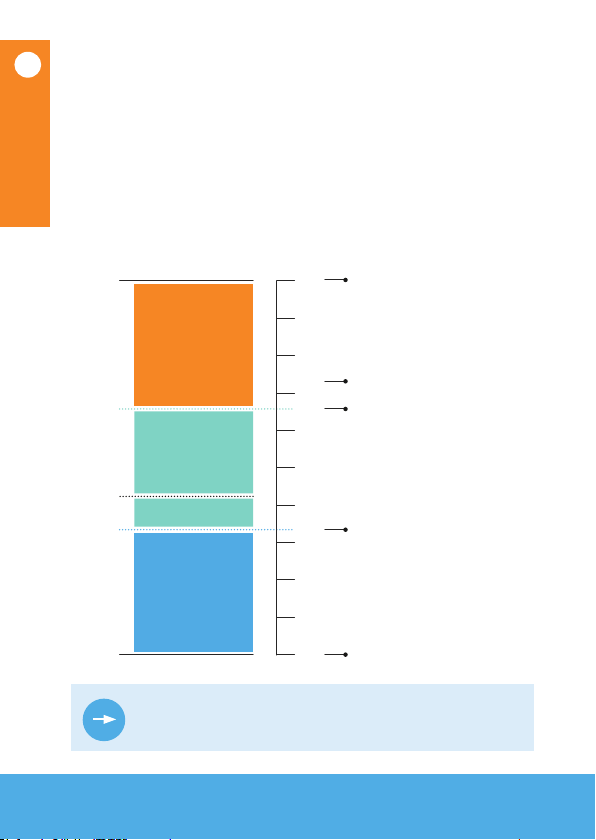
The Sensoterra app and monitor can show data in two ways:
Volumetric Moisture Contentand Sensoterra Index.
Volumetric Moisture Content
The volumetric soil moisture content of the soil is expressed
in the app as Volumetric (%).Volumetric soil moisture data
provides a percent value of the soil moisture content of the
soil.It is simply the ratio of water volume to soil volume.
The volumetric soil moisture percentagesallow for careful
management of soil moisture levels in your soil.
Choosing a unit of measure
Example:
22%
63%
Saturation
point*
* Saturation point = maximum volume of water that the soil can hold
83%
28%
53%
55%
2%
10%
40%
PEAT
KEY: CLAY
4%
17%
38%
SAND LOAMY SAND
Too dry
Healthy
Too wet
Solid soil
fraction
www.sensoterra.com | 13www.sensoterra.com | 13
Preparation
1
For more on units of measurement:
support.sensoterra.com
Sensoterra Index scale (SI)
Sensoterra Index scale is based on pF data and focuses on
the ‘Too Dry’, ‘Too Wet’, and the ‘Plant available water”
(or Healthy) zones and spreads the three zones over a 0 to
10 scale. The 0 and 10 values represent oven-dry soil and
complete saturation of the soil, respectively. The Sensoterra
Index is a simplied soil moisture score that allows you to
determine soil health at a glance, as well as making it easy
comparing data from sensors in different soils.
Complete saturation (pF0)
Field capacity (pF2)
The maximum amount of
water the soil can hold
Permanent wilting
point ±2 (pF4.2)
Wilting point (pF2.5–pF3)
The point at which plants
begin to wilt permanently
through drought
Oven dry soil (pF7)
pF7 0
1
2
3
3.3
6.6
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
pF4
Limiting
Healthy
Too Wet
Too Dr y
Productive
pF2.5
pF2
pF0
Sensoterr a Index
pF Values
14 | Multi-Depth soil moisture sensor14 | Multi-Depth soil moisture sensor

Preparation
1
Volumetric Moisture Content Example
This example shows two graphs compared by their
volumetric moisture content. It looks like the sandy
soil is very dry.
Sensoterra Index scale (SI)Example
The same graphs compared by Sensoterra Index. It now
becomes clear, that relative to the soil type, both soils are
in their healthy zones with SI values above 3.3.
Planting soil
Planting soil
Sand
Sand
www.sensoterra.com | 15www.sensoterra.com | 15

To register your sensor, rst select a suitable
location in the eld where you want to install your
sensor. Once you arethere, open the app and
select “add a new device”. The GPS location will
be stored so you can easily nd the sensor again.
Follow the guidelines in the app.
Registering the sensor
QR code
16 | Multi-Depth soil moisture sensor16 | Multi-Depth soil moisture sensor
Installation
2

Installing the sensor
Soft soil
The blank metal points on the sensor stem are the
measurements points. These need to be in full contactwith
the soil for a good measurement. Wetting the sensor
before installationcould help as a lubricant.
Install the sensor in the soil. If the soil is soft, you can push
the sensor fully into the ground. Ifthe soil is too hard for
you to push the sensor all the way, use a rubber hammer
until thebottom of the head is ush with the soil.
If using a
hammer
The hammer
vibrations may cause the
top soil to loosen and create
gaps between the soil
and the probe. To prevent
this from happening:
Try to hit the probe
as straight on the
top as possible.
Hold the probe just below
the head to damp the
vibrations of the probe.
www.sensoterra.com | 17www.sensoterra.com | 17
Installation
2
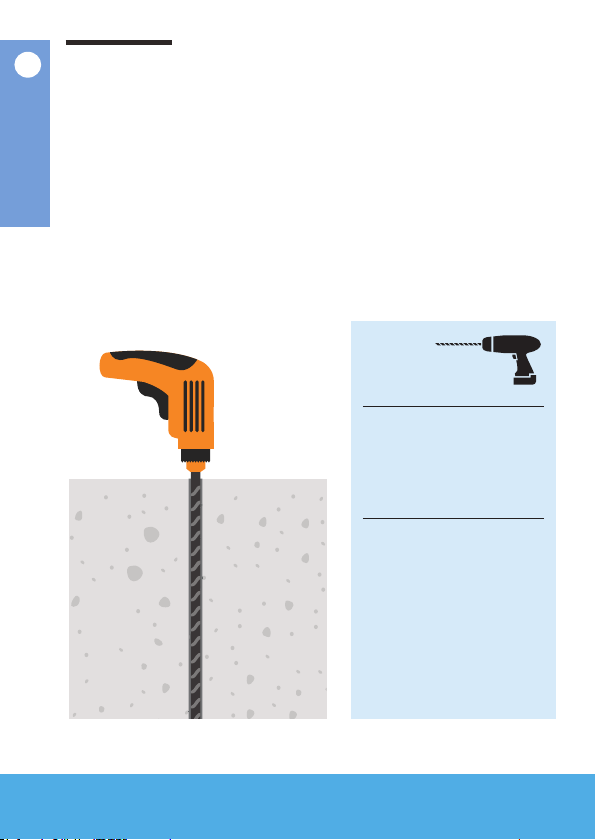
Installing the sensor
Hard soil
If the soil is hard and you experience so much resistance
that the sensor starts vibrating, use a long drill bit topre-
drill a hole for the sensor. After you have pre-drilled the
hole, you can push/hammer thesensor into the hole.
Using a drill
Drill a straight hole
directly into the soil.
Rotate the drill slowly to
avoid the wobbly effect
of the long thin drill.
Hammer or push the
probe as straight as
possible in the created
hole. If the probe is
accidentally pushed
sideways (creating
movement or gaps in the
soil) remove the probe
and drill a new hole.
18 | Multi-Depth soil moisture sensor18 | Multi-Depth soil moisture sensor
Installation
2

Ensuring good soil contact
Using soil & water mix
Gently push the sensor
sideways to check if there
is air around the stem. If
there is, the sensormight
have poor soil contact.
This can be solved by
digging out the top
20-30 cm of soilaround
the sensor. Mix the dug
up soil with water and
pour it into the hole. This
will allow thesoil to ow
around the sensor and
ensure proper contact.
www.sensoterra.com | 19www.sensoterra.com | 19
Installation
2
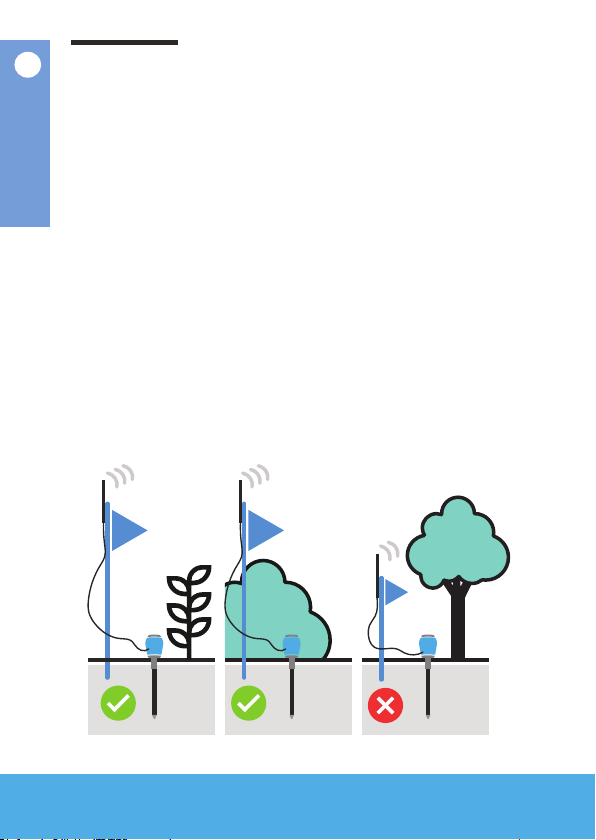
1. Place the ag next to
the sensor. This will
be used as a pole for
the antenna, to keep it
well above ground.
2. Attach the antenna
cable to the antenna
connector on the
sensor, then connect
the antenna in the
opposite end.
3. Mount the antenna
securely on the ag
with cable ties.
4. If the crops are
growing higher than
the ag, mount the
antenna higher than
the expected height
of the crop or even in
the canopy.
Mounting the antenna
20 | Multi-Depth soil moisture sensor20 | Multi-Depth soil moisture sensor
Installation
2
Table of contents
Other Sensoterra Accessories manuals
Popular Accessories manuals by other brands

VOLTCRAFT
VOLTCRAFT VC-201C operating instructions

Westfalia
Westfalia 76 82 34 instruction manual

Gared Sports
Gared Sports Ultra Champ I Installation, operation and maintenance instructions

Philips
Philips LFH7177/03 quick start guide

Trane
Trane Air-Fi WCS-SB Installation, operation and maintenance

FTS
FTS DTS-12 user manual