distributed by
7
1 General
1.1 Standards and regulations
There are dierent international standards for electrical machines, e.g.
• the international“IEC” standard or
• the North American“NEMA”-standard and others.
The motors covered by this catalogue are designed and manufactured according to the latest IEC standards.
Furthermore they full the relevant regulations of the European Community (“EC Regulations”).
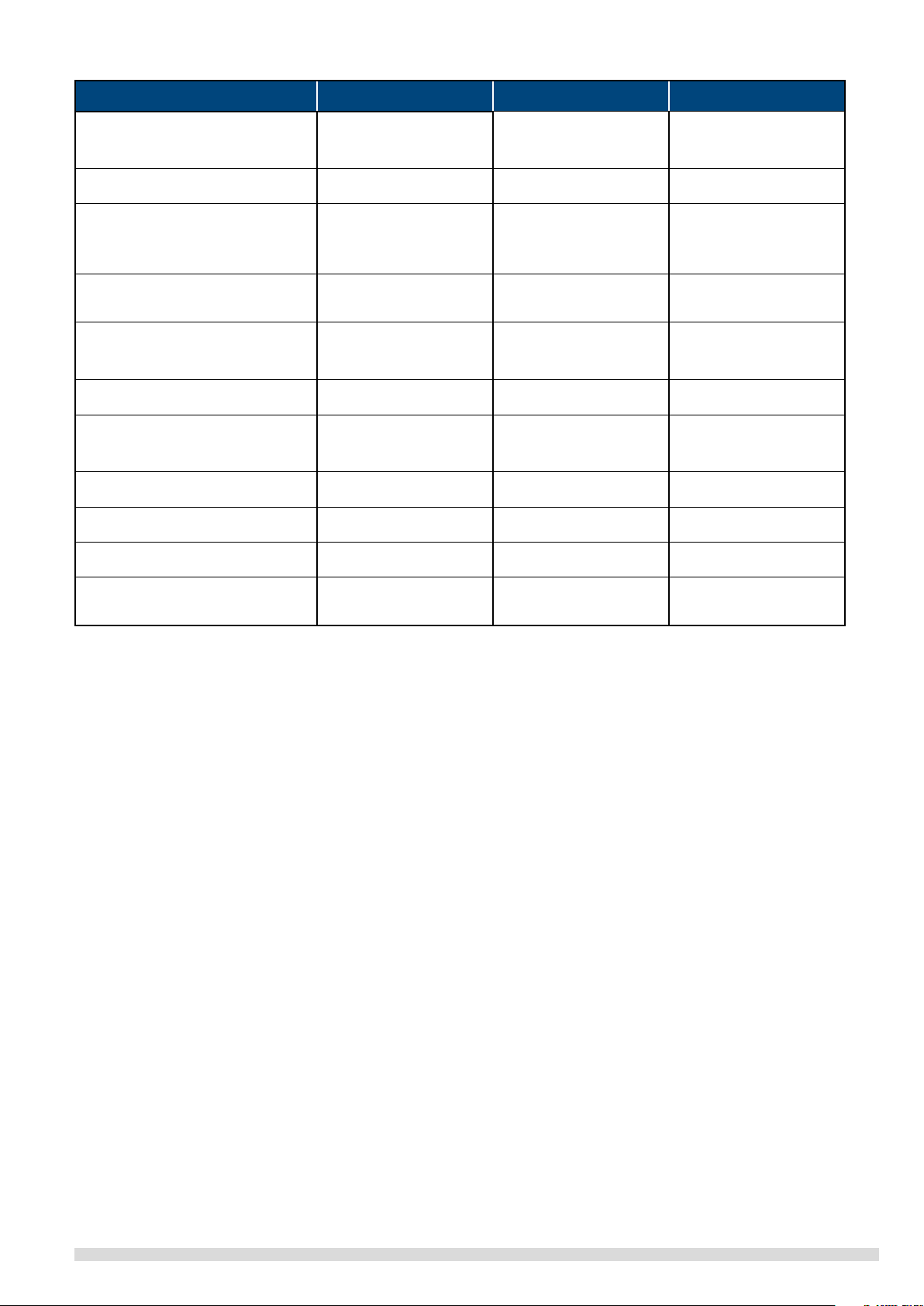
List of national and international standards and regulations applied:
Title International IEC Europe EN/Directive Germany DIN/VDE
Rotating electrical machines – Part 1:
Rating and performance 60034-1 60034-1 DIN EN 60034-1
VDE 0530 Part 1
Rotating electrical machines – Part 2-1:
Standard methods for determining losses
and eciency from tests
60034-2-1 60034-2-1 DIN EN 60 034-2
VDE 0530 Part 2
Rotating electrical machines –
Part 5: Degrees of protection provided by
the integral design of rotating electrical
machines (IP code) – Classication
60034-5 60034-5 DIN EN 60 034-5
VDE 0530 Part 5
Rotating electrical machines –
Part 6: Methods of cooling (IC Code 60034-6 60034-6 DIN EN 60034-6
VDE 0530 Part 6
Rotating electrical machines –
Part 7: Classication of types of
construction, mounting arrangements and
terminal box position (IM Code
60034-7 60034-7 DIN EN 60034-7
VDE 0530 Part 7
Rotating electrical machines –
Part 8: Terminal markings and direction of
rotation
60034-8 60034-8 DIN EN 60034-8
VDE 0530 Part 8
Rotating electrical machines –
Part 9: Noise limits 60034-9 60034-9 DIN EN 60034-9
VDE 0530 Part 9
Rotating electrical machines –
Part 11: Thermal protection 60034-11 60034-11
Thermistors, PTC - - DIN 44081:1980-6
Rotating electrical machines –
Part 12: Starting performance of single-
speed three-phase cage induction motors
60034-12 60034-12 DIN EN 60034-12
VDE 0530 Part 12
Rotating electrical machines –
Part 14: Mechanical vibration of certain
machines with shaft heights 56 mm and hi-
gher – Measurement, evaluation and limits
of vibration severity
60034-14 60034-14 DIN EN 60034-14
VDE 0530 Part 14
Cage induction motors when fed from
converters-Application guide TS 60034-17 - -
Mechanical vibration; balancing shaft and
tment key convention - - DIN ISO 8821
Mechanical vibration – Balance quality
requirements for rotors in a constant (rigid)
state – Part 1: Specication and verication
of balance tolerances
- - DIN ISO 1940-1:
2004-04