THine THCV242 User manual

THCV242_ Rev.2.00_E
Copyright©2019 THine Electronics, Inc. THine Electronics, Inc.
1/53
Security E
THCV242
SerDes receiver with bi-directional transceiver
1. General Description
THCV242 is designed to support 1080p60 2Mpixel
uncompressed video data over 15m 100ohm
differential STP or single-end 50ohm Coaxial cable
with 4 in-line connectors between camera and
processor by V-by-One® HS.
THCV242 supports a MIPI CSI-2. Each CSI-2 data
lane can transmit up to 1.2Gbps/lane. Virtual channel
is supported. MIPI 2nd port output supports data
copy and distribution.
One high-speed V-by-One® HS lane can transmit up
to 1080p60fps. The maximum serial data rate is
4Gbps/lane. 2nd input lane supports HDR large
amount of data or camera switch experience.
THCV242 is capable to control and monitor remote
camera module from MPU via GPIO or 1Mbps 2-
wire serial interface.
Several fault and error detection function including
CRC provides hardware functional safety design.
2. Features
MIPI CSI-2 with 1,2 or 4-lane output
MIPI D-PHY supports 80Mbps~1.2Gbps
MIPI Virtual channel supported
Video formats: RAW8/10/12/14/16/20,
YUV422/420, RGB888/666/565, JPEG, User-
defined generic 8-bit
V-by-One® HS 400Mbps~4Gbps x2lane
V-by-One® HS standard version1.5
Video stream switch and copy/distribution
Frame sync remote supply scheme for multiple
camera stream synchronization
Wide range IO voltage from 1.7V to 3.6V
2-wire serial interface 1Mbps bridge function
Remote GPIO/UART control and monitoring
Error detection including CRC and notification
QFN64 9x9mm 0.5mm pitch Exp-pad package
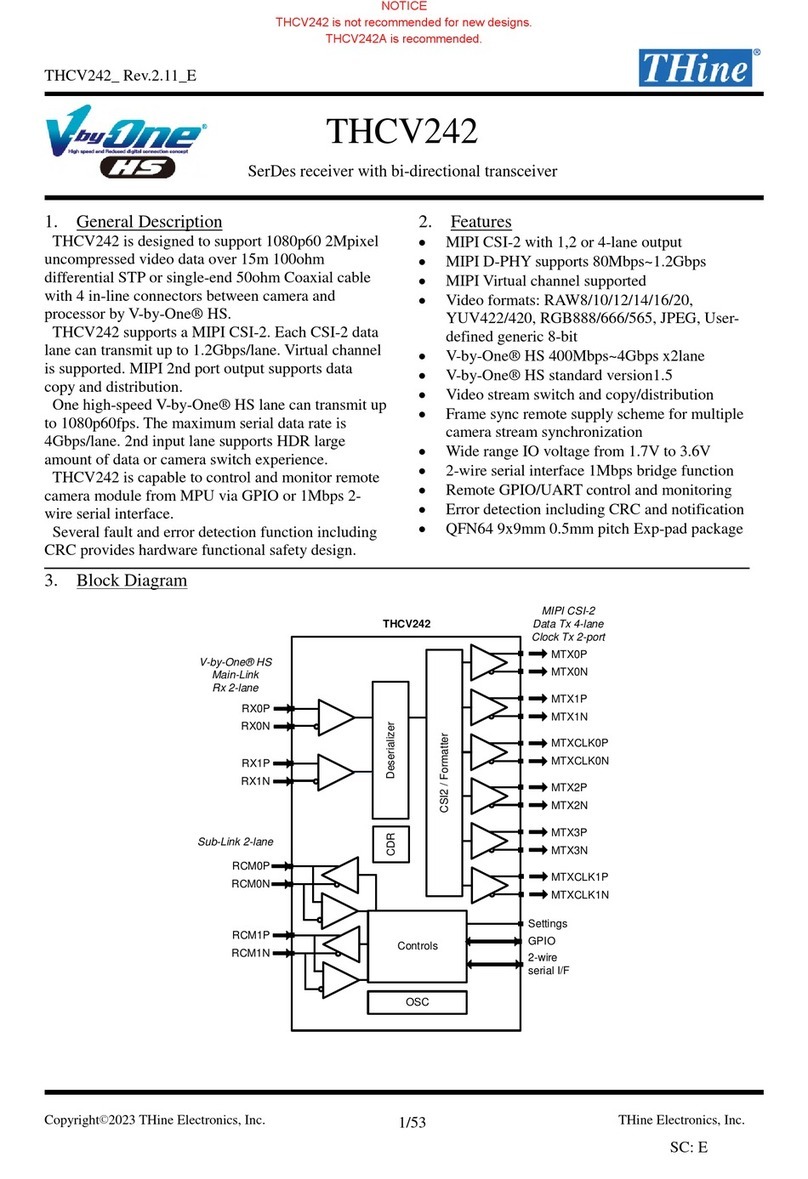
3. Block Diagram
MTX0P
MTX0N
CSI2 / Formatter
Deserializer
CDR
Controls
MTXCLK0P
MTXCLK0N
OSC
MTX1P
MTX1N
Settings
2-wire
serial I/F
RX0P
RX0N
RCM1P
RCM1N
MIPI CSI-2
Data Tx 4-lane
Clock Tx 2-port
THCV242
V-by-One® HS
Main-Link
Rx 2-lane
Sub-Link 2-lane
MTX2P
MTX2N
MTX3P
MTX3N
GPIO
RX1P
RX1N
RCM0P
RCM0N MTXCLK1P
MTXCLK1N

THCV242_ Rev.2.00_E
Copyright©2019 THine Electronics, Inc. THine Electronics, Inc.
2/53
Security E
Contents page
1. General Description.........................................................................................................................................1
2. Features ...........................................................................................................................................................1
3. Block Diagram ................................................................................................................................................1
4. Pin Configuration............................................................................................................................................4
5. Pin Description................................................................................................................................................5
6. Functional Description ....................................................................................................................................6
6.1. Functional Overview...............................................................................................................................6
6.2. V-by-One® HS........................................................................................................................................6
V-by-One® HS input setting ...........................................................................................................6
MPRF (Main-Link PRivate Format) ...............................................................................................7
V-by-One® HS standard format......................................................................................................8
Link Status (HTPDN/LOCKN).....................................................................................................12
6.3. Local, Remote and Remote Slave Register Programming ....................................................................14
2-wire serial I/F slave Device ID...................................................................................................14
2-wire serial Read/Write access to local Register..........................................................................15
2-wire serial I/F Watch Dog Timer................................................................................................16
Sub-Link setting ............................................................................................................................17
Sub-Link 2-wire Read/Write access to remote Register................................................................18
6.3.5.1. Sub-Link 2-wire Set and Trigger mode.................................................................................18
6.3.5.2. Sub-Link 2-wire Pass Through mode....................................................................................21
Sub-Link transaction time accuracy Improvement........................................................................24
6.4. GPIO setting..........................................................................................................................................25
Register GPIO ...............................................................................................................................26
Through GPIO...............................................................................................................................27
GPIO as secondary 2-wire port .....................................................................................................28
6.5. MIPI ......................................................................................................................................................29
Deserializer and CSI-2 Formatter..................................................................................................29
6.5.1.1. PLL setting ............................................................................................................................29
6.5.1.2. Video stream switch and copy/distribution............................................................................31
Header/Packet/Sync Pre-processing..............................................................................................32
MIPI output setting........................................................................................................................33
MIPI CSI-2 Virtual Channel..........................................................................................................35
Multiple camera synchronization Frame Vsync supply ................................................................36
6.6. Status monitoring, Interrupt and Error Detection..................................................................................38
Internal Error / status signal monitoring pin output.......................................................................38

THCV242_ Rev.2.00_E
Copyright©2019 THine Electronics, Inc. THine Electronics, Inc.
3/53
Security E
Internal Error / status signal monitoring register...........................................................................41
Interrupt monitoring ......................................................................................................................42
Register Auto Checksum diagnosis...............................................................................................43
6.7. Power On Sequence...............................................................................................................................44
6.8. Lock / Re-Lock Sequence .....................................................................................................................45
7. Absolute Maximum Ratings..........................................................................................................................46
8. Recommended Operating Conditions............................................................................................................46
9. Consumption Current....................................................................................................................................47
10. DC Specifications......................................................................................................................................48
10.1. CMOS DC Specifications..................................................................................................................48
10.2. CML Receiver DC Specifications .....................................................................................................48
10.3. MIPI Transmitter DC Specifications.................................................................................................49
10.4. CML Bi-directional Buffer DC Specifications..................................................................................50
11. AC Specifications......................................................................................................................................51
11.1. GeneralAC Specifications ....................................................................................................................51
11.2. CML Receiver AC Specifications .........................................................................................................51
11.3. MIPI Transmitter AC Specifications .....................................................................................................51
11.4. CML B-directional Buffer AC Specifications .......................................................................................51
11.5. 2-wire serial Slave AC Specifications ...................................................................................................51
12. Package......................................................................................................................................................52
13. Notices and Requests.................................................................................................................................53
MIPI is a licensed trademark of MIPI, Inc. in the U.S. and other jurisdictions.

THCV242_ Rev.2.00_E
Copyright©2019 THine Electronics, Inc. THine Electronics, Inc.
4/53
Security E
4. Pin Configuration
VDDIO1
GPIO7
GPIO6
GPIO5
GPIO4
GPIO3
GPIO2
GPIO1
GPIO0
INT1
INT0
AIN1
AIN0
SDA
SCL
VDDIO1
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
ERR0 49 32 EXTSYNC
ERR1 50 31 PDN
VDDCORE 51 30 VDDPLL
VDDRX 52 29 VDDTX
RX0N 53 28 MTX3P
RX0P 54 27 MTX3N
VSSRX 55 26 MTX1P
RX1N 56 25 MTX1N
RX1P 57 24 MTXCLK0P
VDDRX 58 23 MTXCLK0N
RSVDL0 59 22 MTX0P
RSVDL0 60 21 MTX0N
VSSRX 61 20 MTX2P
RSVDL0 62 19 MTX2N
RSVDL0 63 18 MTXCLK1P
VDDRX 64 17 MTXCLK1N
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
VDDCORE
VDDIO2
RCM0N
RCM0P
RCM1N
RCM1P
RSVDL2
RSVDL2
RSVDL2
RSVDL2
VDDIO2
RSVDT2H2
RSVDT1L2
RSVDL2
VDDCORE
VDDTX
THCV242
(TOP VIEW)
65 EXPGND
●

THCV242_ Rev.2.00_E
Copyright©2019 THine Electronics, Inc. THine Electronics, Inc.
5/53
Security E
5. Pin Description
Pin Name Pin # type* Description
RX0P/N 54, 53 CI V-by-One® HS Input lane0
RX1P/N 57, 56 CI V-by-One® HS Input lane1
RCM0P/N 4, 3 CB
CML Bi-directiona Input/Output (Sub-Link).
RCM1P/N 6, 5 CB
CML Bi-directiona Input/Output (Sub-Link).
MTX0P/N 22, 21 MO MIPIdifferential data outputs lane0
MTX1P/N 26, 25 MO MIPIdifferential data outputs lane1
MTX2P/N 20, 19 MO MIPIdifferential data outputs lane2
MTX3P/N 28, 27 MO MIPIdifferential data outputs lane3
MTXCLK0P/N 24, 23 MO MIPIdifferential clock outputs lane0
MTXCLK1P/N 18, 17 MO MIPIdifferential clock outputs lane1
RSVDT1L2 13 I2 Reserved Pin, Must be tied to ground for normal operation.
RSVDT2H2 12 I2 Reserved pin. Must be tied to VDDIO2 for normal operation.
PDN 31 I1
Power Down (User Power On Reset control must be reuiquired.)
0: Power Down Mode
1: Normal Operation
AIN1 37 I1
AIN0 36 I1
SCL 34 B 2-wire SerialInterface clock line
SDA 35 B 2-wire SerialInterface data line
GPIO0 40 B General Purpose Input/Output
GPIO1 41 B General Purpose Input/Output
GPIO2 42 B General Purpose Input/Output
GPIO3 43 B General Purpose Input/Output
GPIO4 44 B General Purpose Input/Output
GPIO5 45 B General Purpose Input/Output
GPIO6 46 B General Purpose Input/Output
GPIO7 47 B General Purpose Input/Output
INT0 38 O
INT1 39 O
ERR0 49 O Internal Error / status signal monitoring output
ERR1 50 O Internal Error / status signal monitoring output
EXTSYNC 32 B External Sync input/output for multiple camera syncronization
RSVDL0
59, 60, 62, 63 I0 Reserved Pins, Must be tied to ground for normal operation.
RSVDL2
7, 8, 9, 10, 14 I2 Reserved Pins, Must be tied to ground for normal operation.
VDDIO1 33, 48 P Power Supply for CMOS I/O
VDDIO2 2,11 P Power Supply for Sub-Link I/O
VDDCORE 1,15,51 P Power Supply for DigitalCircuit
VDDRX 52,58,64 P Power Supply for Analog Circuit
VSSRX 55,61 G GND for Analog Circuit
VDDTX 16,29 P Power Supply for Analog Circuit
VDDPLL 30 P Power Supply for Analog Circuit
EXPGND 65 G Exposed GND Pad
*type symbol ; MO=MIPIOutput, CI=CML Input, CB=CML Bi-directionalinput/output
I0=1.2V CMOS Input, I1=1.8~3.3V VDDIO1 domain CMOS Input, I2=1.8~3.3V VDDIO2 domain CMOS Input
O=1.8~3.3V VDDIO1 domain CMOS Output, B=1.8~3.3V VDDIO1 domain CMOS Bi-directionalinput/output
P=Power, G=Ground
Device Address Setting for 2-w ire Serial Interface
[AIN1:AIN0]=00: ID=7'h0B
[AIN1:AIN0]=01: ID=7'h34
[AIN1:AIN0]=10: ID=7'h77
[AIN1:AIN0]=11: ID=7'h65
Interrupt signal output.
It must be connected w ith a pull-up resistor.
0 : Interrupt occurred
1 : Steady state

THCV242_ Rev.2.00_E
Copyright©2019 THine Electronics, Inc. THine Electronics, Inc.
6/53
Security E
6. Functional Description
6.1. Functional Overview
THCV242 can receive CMLvideo signal transmitted over 15m length and encode it to MIPI CSI-2 format. With
High Speed CML SerDes, high reliability and robustness encoding scheme and CDR (Clock and Data Recovery)
architecture, the THCV242 enables to receive RAW/YUV/RGB/JPEG/Generic8bit data through Main-Link by
single 100ohm differential pair or 50ohm Coax cable with minimal external components. In addition, THCV242
has Sub-Link which enables bi-directional transmission of 2-wire serial interface signals, GPIO signals and also
HTPDN/LOCKN signals for Main-Link through the other 1-pair of CML-Line. The THCV242 system is able to
watch remote devices and to control them via 2-wire serial interface or GPIOs. They also can report interrupt
events caused by change of remote device statuses and internal statuses such as CRC error.
6.2. V-by-One® HS
V-by-One® HS input setting
Setting of V-by-One® HS input format can be configurable by 2-wire access to internal register.
Table 1. V-by-One® HS input format setting
bit Register Name width R/W init Description
0x10 10 [7:6] R_MLNK_NHSEL0 2 R/W 2'h2
V-by-One® Main-Link Mode Select (for LINK0)
00 : Reserved
01 : Reserved
10 : V-by-One® HS standard mode
11 : Reserved
0x10 10 [5:4] R_MLNK_COL0 2 R/W 2'h1
V-by-One® Main-Link Byte Mode Select (for LINK0)
00 : Reserved
01 : 8bit (3Byte mode)
10 : 10bit (4Byte mode)
11 : Reserved
0x10 12 [4] R_RGB565_ON_L0 1 R/W 1'b0
Main-Link Input Data Format Setting2
(This register could use only when R_VX1_LANE_FMT0=0x1)
0: RGB888
1: RGB565
0x10 12 [3:0]
R_VX1_LANE_FMT0 4 R/W 4'h0
Main-Link Input Data Format Setting
0: MPRF
1: RGBxxx
2,3,4,5,6: YUV422 (NormalYU1,NormalYU2,NormalYU3,DemuxYU1,DemuxYU2)
7,8,9: RAW8 (NormalR081,NormalR082,DemuxR081)
10,11,12: RAW10 (NormalR101,DemuxR101,DemuxR102)
13,14,15: RAW12 (NormalR121,DemuxR121,DemuxR122)
0x10 14 [7:6] R_VRZ_NHSEL1 2 R/W 2'h2
V-by-One® Main-Link Mode Select (for LINK1)
00 : Reserved
01 : Reserved
10 : V-by-One® HS standard mode
11 : Reserved
0x10 14 [5:4] R_VRZ_COL1 2 R/W 2'h1
V-by-One® Main-Link Byte Mode Select (for LINK1)
00 : Reserved
01 : 8bit (3Byte mode)
10 : 10bit (4Byte mode)
11 : Reserved
Adr

THCV242_ Rev.2.00_E
Copyright©2019 THine Electronics, Inc. THine Electronics, Inc.
7/53
Security E
MPRF (Main-Link PRivate Format)
MPRF format encoding preserves original data packet input to V-by-One® HS transmitter and output the data
packet from THCV242. The counterpart transmitter must have installed MPRF format decoder like THCV241
because MPRF is not standard format.
Input V-by-One® HS Byte Mode is 4Byte Mode.
Video formats: RAW8/10/12/14/16/20, YUV422/420, RGB888/666/565, JPEG, and User-defined generic 8-bit
are all supported with MPRF.
Figure 1. MPRF (Main-Link PRivate Format)
THCV241CMOS Sensor THCV242 Processor
In ECUor
controller
Original
Data packet
(format,
payload, etc.)
Preserved
Data packet
(format,
payload, etc.)
Main-Link
MPRF
format

THCV242_ Rev.2.00_E
Copyright©2019 THine Electronics, Inc. THine Electronics, Inc.
8/53
Security E
V-by-One® HS standard format
THCV242 input format capabilities as receiver are shown as follows. D[31:0] indicates V-by-One®HS standard
version1.5 UnPacker packet definition. Data can be transmitted normally only when both transmitter and receiver
are set to the same available format. Some of the THCV242 format may not be supported by particular counterpart
transmitter because THCV242 prepares multiple formats that suit to multiple transmitter devices alternatives.
Table 2. V-by-One® HS input data mapping format 1/4
Format Name RGB888
Vx1HS std. Packer Packet ref. Normal Mode1 Normal Mode2 Normal Mode3 Demux Mode1 Demux Mode2
V-by-One®HS_D[31]
0 0 0 0 Y[7](1st pixel) Cb[7]
V-by-One®HS_D[30]
0 0 0 0 Y[6](1st pixel) Cb[6]
V-by-One®HS_D[29]
0 0 0 0 Y[5](1st pixel) Cb[5]
V-by-One®HS_D[28]
0 0 0 0 Y[4](1st pixel) Cb[4]
V-by-One®HS_D[27]
0 0 0 0 Y[3](1st pixel) Cb[3]
V-by-One®HS_D[26]
0 0 0 0 Y[2](1st pixel) Cb[2]
V-by-One®HS_D[25]
0 0 0 0 Y[1](1st pixel) Cb[1]
V-by-One®HS_D[24]
0 0 0 0 Y[0](1st pixel) Cb[0]
V-by-One®HS_D[23]
B[7] 0 Cb[7]/Cr[7] Y[7] Cb[7] Y[7](1st pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[22]
B[6] 0 Cb[6]/Cr[6] Y[6] Cb[6] Y[6](1st pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[21]
B[5] 0 Cb[5]/Cr[5] Y[5] Cb[5] Y[5](1st pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[20]
B[4] 0 Cb[4]/Cr[4] Y[4] Cb[4] Y[4](1st pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[19]
B[3] 0 Cb[3]/Cr[3] Y[3] Cb[3] Y[3](1st pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[18]
B[2] 0 Cb[2]/Cr[2] Y[2] Cb[2] Y[2](1st pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[17]
B[1] 0 Cb[1]/Cr[1] Y[1] Cb[1] Y[1](1st pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[16]
B[0] 0 Cb[0]/Cr[0] Y[0] Cb[0] Y[0](1st pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[15]
G[7] Y[7] 0 0 Y[7](2nd pixel) Cr[7]
V-by-One®HS_D[14]
G[6] Y[6] 0 0 Y[6](2nd pixel) Cr[6]
V-by-One®HS_D[13]
G[5] Y[5] 0 0 Y[5](2nd pixel) Cr[5]
V-by-One®HS_D[12]
G[4] Y[4] 0 0 Y[4](2nd pixel) Cr[4]
V-by-One®HS_D[11]
G[3] Y[3] 0 0 Y[3](2nd pixel) Cr[3]
V-by-One®HS_D[10]
G[2] Y[2] 0 0 Y[2](2nd pixel) Cr[2]
V-by-One®HS_D[9]
G[1] Y[1] 0 0 Y[1](2nd pixel) Cr[1]
V-by-One®HS_D[8]
G[0] Y[0] 0 0 Y[0](2nd pixel) Cr[0]
V-by-One®HS_D[7]
R[7] Cb[7]/Cr[7] Y[7] Cb[7]/Cr[7] Cr[7] Y[7](2nd pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[6]
R[6] Cb[6]/Cr[6] Y[6] Cb[6]/Cr[6] Cr[6] Y[6](2nd pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[5]
R[5] Cb[5]/Cr[5] Y[5] Cb[5]/Cr[5] Cr[5] Y[5](2nd pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[4]
R[4] Cb[4]/Cr[4] Y[4] Cb[4]/Cr[4] Cr[4] Y[4](2nd pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[3]
R[3] Cb[3]/Cr[3] Y[3] Cb[3]/Cr[3] Cr[3] Y[3](2nd pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[2]
R[2] Cb[2]/Cr[2] Y[2] Cb[2]/Cr[2] Cr[2] Y[2](2nd pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[1]
R[1] Cb[1]/Cr[1] Y[1] Cb[1]/Cr[1] Cr[1] Y[1](2nd pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[0]
R[0] Cb[0]/Cr[0] Y[0] Cb[0]/Cr[0] Cr[0] Y[0](2nd pixel)
YUV422

THCV242_ Rev.2.00_E
Copyright©2019 THine Electronics, Inc. THine Electronics, Inc.
9/53
Security E
Table 3. V-by-One® HS input data mapping format 2/4
Format Name
Vx1HS std. Packer Packet ref. Normal Mode1 Normal Mode2 Demux Mode1
V-by-One®HS_D[31]
0 0 RAW[7] (2nd pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[30]
0 0 RAW[6] (2nd pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[29]
0 0 RAW[5] (2nd pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[28]
0 0 RAW[4] (2nd pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[27]
0 0 RAW[3] (2nd pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[26]
0 0 RAW[2] (2nd pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[25]
0 0 RAW[1] (2nd pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[24]
0 0 RAW[0] (2nd pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[23]
0 RAW[7] (1st pixel) RAW[7] (1st pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[22]
0 RAW[6] (1st pixel) RAW[6] (1st pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[21]
0 RAW[5] (1st pixel) RAW[5] (1st pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[20]
0 RAW[4] (1st pixel) RAW[4] (1st pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[19]
0 RAW[3] (1st pixel) RAW[3] (1st pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[18]
0 RAW[2] (1st pixel) RAW[2] (1st pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[17]
0 RAW[1] (1st pixel) RAW[1] (1st pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[16]
0 RAW[0] (1st pixel) RAW[0] (1st pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[15]
RAW[7] (2nd pixel) 0 RAW[7] (4th pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[14]
RAW[6] (2nd pixel) 0 RAW[6] (4th pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[13]
RAW[5] (2nd pixel) 0 RAW[5] (4th pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[12]
RAW[4] (2nd pixel) 0 RAW[4] (4th pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[11]
RAW[3] (2nd pixel) 0 RAW[3] (4th pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[10]
RAW[2] (2nd pixel) 0 RAW[2] (4th pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[9]
RAW[1] (2nd pixel) 0 RAW[1] (4th pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[8]
RAW[0] (2nd pixel) 0 RAW[0] (4th pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[7]
RAW[7] (1st pixel) RAW[7] (2nd pixel) RAW[7] (3rd pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[6]
RAW[6] (1st pixel) RAW[6] (2nd pixel) RAW[6] (3rd pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[5]
RAW[5] (1st pixel) RAW[5] (2nd pixel) RAW[5] (3rd pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[4]
RAW[4] (1st pixel) RAW[4] (2nd pixel) RAW[4] (3rd pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[3]
RAW[3] (1st pixel) RAW[3] (2nd pixel) RAW[3] (3rd pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[2]
RAW[2] (1st pixel) RAW[2] (2nd pixel) RAW[2] (3rd pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[1]
RAW[1] (1st pixel) RAW[1] (2nd pixel) RAW[1] (3rd pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[0]
RAW[0] (1st pixel) RAW[0] (2nd pixel) RAW[0] (3rd pixel)
RAW8

THCV242_ Rev.2.00_E
Copyright©2019 THine Electronics, Inc. THine Electronics, Inc.
10/53
Security E
Table 4. V-by-One® HS input data mapping format 3/4
Format Name
Vx1HS std. Packer Packet ref. Normal Demux Mode1 Demux Mode2
V-by-One®HS_D[31]
0 0 0
V-by-One®HS_D[30]
0 0 0
V-by-One®HS_D[29]
0 0 0
V-by-One®HS_D[28]
0 0 0
V-by-One®HS_D[27]
0 0 0
V-by-One®HS_D[26]
0 0 0
V-by-One®HS_D[25]
0 RAW[1](1st pixel) 0
V-by-One®HS_D[24]
0 RAW[0](1st pixel) 0
V-by-One®HS_D[23]
0 RAW[9](1st pixel) 0
V-by-One®HS_D[22]
0 RAW[8](1st pixel) 0
V-by-One®HS_D[21]
0 RAW[7](1st pixel) RAW[1](1st pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[20]
0 RAW[6](1st pixel) RAW[0](1st pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[19]
0 RAW[5](1st pixel) RAW[9](1st pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[18]
0 RAW[4](1st pixel) RAW[8](1st pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[17]
0 RAW[3](1st pixel) RAW[7](1st pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[16]
0 RAW[2](1st pixel) RAW[6](1st pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[15]
0 0 RAW[5](1st pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[14]
0 0 RAW[4](1st pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[13]
0 0 RAW[3](1st pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[12]
0 0 RAW[2](1st pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[11]
0 0 0
V-by-One®HS_D[10]
0 0 0
V-by-One®HS_D[9]
RAW[1] RAW[1](2nd pixel) RAW[1](2nd pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[8]
RAW[0] RAW[0](2nd pixel) RAW[0](2nd pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[7]
RAW[9] RAW[9](2nd pixel) RAW[9](2nd pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[6]
RAW[8] RAW[8](2nd pixel) RAW[8](2nd pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[5]
RAW[7] RAW[7](2nd pixel) RAW[7](2nd pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[4]
RAW[6] RAW[6](2nd pixel) RAW[6](2nd pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[3]
RAW[5] RAW[5](2nd pixel) RAW[5](2nd pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[2]
RAW[4] RAW[4](2nd pixel) RAW[4](2nd pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[1]
RAW[3] RAW[3](2nd pixel) RAW[3](2nd pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[0]
RAW[2] RAW[2](2nd pixel) RAW[2](2nd pixel)
RAW10

THCV242_ Rev.2.00_E
Copyright©2019 THine Electronics, Inc. THine Electronics, Inc.
11/53
Security E
Table 5. V-by-One® HS input data mapping format 4/4
Format Name
Vx1HS std. Packer Packet ref. Normal Demux Mode1 Demux Mode2
V-by-One®HS_D[31]
0 0 0
V-by-One®HS_D[30]
0 0 0
V-by-One®HS_D[29]
0 0 0
V-by-One®HS_D[28]
0 0 0
V-by-One®HS_D[27]
0 RAW[3](1st pixel) 0
V-by-One®HS_D[26]
0 RAW[2](1st pixel) 0
V-by-One®HS_D[25]
0 RAW[1](1st pixel) 0
V-by-One®HS_D[24]
0 RAW[0](1st pixel) 0
V-by-One®HS_D[23]
0 RAW[11](1st pixel) RAW[3](1st pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[22]
0 RAW[10](1st pixel) RAW[2](1st pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[21]
0 RAW[9](1st pixel) RAW[1](1st pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[20]
0 RAW[8](1st pixel) RAW[0](1st pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[19]
0 RAW[7](1st pixel) RAW[11](1st pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[18]
0 RAW[6](1st pixel) RAW[10](1st pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[17]
0 RAW[5](1st pixel) RAW[9](1st pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[16]
0 RAW[4](1st pixel) RAW[8](1st pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[15]
0 0 RAW[7](1st pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[14]
0 0 RAW[6](1st pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[13]
0 0 RAW[5](1st pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[12]
0 0 RAW[4](1st pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[11]
RAW[3] RAW[3](2nd pixel) RAW[3](2nd pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[10]
RAW[2] RAW[2](2nd pixel) RAW[2](2nd pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[9]
RAW[1] RAW[1](2nd pixel) RAW[1](2nd pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[8]
RAW[0] RAW[0](2nd pixel) RAW[0](2nd pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[7]
RAW[11] RAW[11](2nd pixel) RAW[11](2nd pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[6]
RAW[10] RAW[10](2nd pixel) RAW[10](2nd pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[5]
RAW[9] RAW[9](2nd pixel) RAW[9](2nd pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[4]
RAW[8] RAW[8](2nd pixel) RAW[8](2nd pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[3]
RAW[7] RAW[7](2nd pixel) RAW[7](2nd pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[2]
RAW[6] RAW[6](2nd pixel) RAW[6](2nd pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[1]
RAW[5] RAW[5](2nd pixel) RAW[5](2nd pixel)
V-by-One®HS_D[0]
RAW[4] RAW[4](2nd pixel) RAW[4](2nd pixel)
RAW12

THCV242_ Rev.2.00_E
Copyright©2019 THine Electronics, Inc. THine Electronics, Inc.
12/53
Security E
Link Status (HTPDN/LOCKN)
Hot-Plug Function
HTPDN indicates Main-Link connect condition between Transmitter and Receiver. HTPDN of Transmitter side
is high when Receiver is not active or not connected. Then Transmitter can enter into power down mode. HTPDN
is set to Low by the Receiver when Receiver is active and connects to the Transmitter, and then Transmitter must
start up and transmit CDR training pattern for link training. HTPDN is open drain output at the receiver side.
Transmitter side needs Pull-up resistor.
There is an application option to omit HTPDN connection between Transmitter and Receiver. In this case,
HTPDN at Transmitter side should always be at Low.
Lock Detect Function
LOCKN indicates whether CDR PLL of Main-Link is in lock status or not. LOCKN at Transmitter input is set
to High bypull-up resistor when Receiver is not active or in CDR PLLtraining. LOCKN is set to Low by Receiver
when CDR lock is completed.After that the CDR training mode finishes and then Transmitter shifts to the normal
mode. LOCKN of Receiver is open drain. Transmitter side needs pull-up resistor.
When an application omits HTPDN, LOCKN signal should only be considered with HTPDN pulled low by
Receiver.
Vcc
(Tx side)
HTPDN
LOCKN
V-by-One®
HS Tx
30kΩ
ERRy
(HTPDN)
ERRx
(LOCKN)
30kΩ
Vcc
(Tx side)
HTPDN
LOCKN
V-by-One®
HS Tx
HTPDN
ERRx
(LOCKN)
30kΩ
With HTPDN connect Without HTPDN connect
THCV242 THCV242
Figure 2. Physical wire connection for wired Hot-plug and Lock detect scheme
It will need same GND potential reference between transmitter and receiver device to connect HTPDN and
LOCKN pins directly like above. HTPDN and LOCKN can also be transmitted via Sub-Link without physical
wire connection.Assignment can be configurable by 2-wire access to internal register.

THCV242_ Rev.2.00_E
Copyright©2019 THine Electronics, Inc. THine Electronics, Inc.
13/53
Security E
Table 6. HTPDN/LOCKN register
Addr(h) bit Register Name width R/W Description Default
0x0019 [7:4] ReservedL 4 RW
Must be set 0 4'd0
[3:2] R_LOCKN_LN1_SEL 2 RW
Sub-Link Lane1 LOCKN/HTPDN scheme of releted Main-Link select
0:LOCKN1
1:LOCKN0 | LOCKN1
2:Reserved
3:1'b0 (Forced LOCKN/HTPDN=Low)
*LOCKN1=LOCKNsignal of V-by-One(R) HS Lane1=RX1P/RX1N
*HTPDNof the same lane as above set LOCKN lane is used
2'd0
[1:0] R_LOCKN_LN0_SEL 2 RW
Sub-Link Lane0 LOCKN/HTPDN scheme of releted Main-Link select
0:LOCKN0
1:LOCKN0 | LOCKN1
2:Reserved
3:1'b0 (Forced LOCKN/HTPDN=Low)
*LOCKN0=LOCKNsignal of V-by-One(R) HS Lane0=RX0P/RX0N
*HTPDNof the same lane as above set LOCKN lane is used
2'd0

THCV242_ Rev.2.00_E
Copyright©2019 THine Electronics, Inc. THine Electronics, Inc.
14/53
Security E
6.3. Local, Remote and Remote Slave Register Programming
2-wire serial I/F slave Device ID
To use basic functions, initialization, GPIO (General Purpose Input/Output), fault/error detection, and interrupt
function, 2-wire serial I/F enables to access registers. AIN<1:0> pin determines 2-wire slave Device ID setting.
Table 7. 2-wire serial I/F Device ID select byAIN pin
As an additional method, 2-wire slave Device ID setting can be changed from default value by register setting.
Table 8. 2-wire serial I/F Device ID select by register setting
AIN1 37 I1
AIN0 36 I1
Device Address Setting for 2-wire Serial Interface
[AIN1:AIN0]=00: ID=7'h0B
[AIN1:AIN0]=01: ID=7'h34
[AIN1:AIN0]=10: ID=7'h77
[AIN1:AIN0]=11: ID=7'h65
Addr(h) bit Register Name width R/W Description Default
0x0030 [7:0] R_2WIRE_SADR 8 RW
2WIRE slave device address setting
[7]2WIRE slave device address control
0: 2WIRE slv device addr. is set by AIN<1:0> pin
1: 2WIRE slv device addr. is set by following register [6:0]
[6:0]2WIRE slave device address value for register control
8'd0

THCV242_ Rev.2.00_E
Copyright©2019 THine Electronics, Inc. THine Electronics, Inc.
15/53
Security E
2-wire serial Read/Write access to local Register
HOST MPU can directly access THCV242 local register by 2-wire serial I/F.
Figure 3. Host to THCV242 local register access configuration
Figure 4. 2-wire serial I/F write to THCV242 local register protocol
Figure 5. 2-wire serial I/F read to THCV242 local register protocol
Sub-Link
Master
THCV242
Sub-Link Block
Register
2-wire
Slave Host
MPU
SCL
AIN<1:0> = User Select
SDA
S Register address MSBDevice ID W A
S
P
A
A
W
Start condition
Stop condition
ACK
NACK
Write command indicator
Access from 2-wire serial interface Master
Access from 2-wire serial interface Slave
Register address LSBA A Write data #1 A ... A P
S Register address MSBDevice ID W A
S
P
A
A
W
R
Start condition
Stop condition
ACK
NACK
Read command indicator
Write command indicator
Access from 2-wire serial interface Master
Access from 2-wire serial interface Slave
Repeated start condition
Sr
Register address LSBA A Read data #1 A ... PDevice ID R ASr A

THCV242_ Rev.2.00_E
Copyright©2019 THine Electronics, Inc. THine Electronics, Inc.
16/53
Security E
2-wire serial I/F Watch Dog Timer
2-wire Watch Dog Timer (WDT) is installed to monitor status.
Table 9. 2-wire WDT setting
Addr(h) bit Register Name width R/W Description Default
0x003B [7:5] reserved 3 -
- -
[4] R_2WIRE_WD_EN 1 RW
2WIRE WDT Enable
0:Disable
1:Enable 1'b1
[3:1] reserved 3 -
- -
[0] R_2WIRE_WD_OFFSET 1 RW
2WIRE_WDT_OffsetTime
1:11'd2047
0:11'd1023 1'd1
0x003C [7:0] R_2WIRE_WD_TIM 8 RW
2WIRE WDT_time=64×{R_2WIRE_WD_TIM<7:0>+1}×{2WIRE_WDT_OffsetTime}×tOSC 8'd255

THCV242_ Rev.2.00_E
Copyright©2019 THine Electronics, Inc. THine Electronics, Inc.
17/53
Security E
Sub-Link setting
THCV242 has Sub-Link which enables bi-directional transmission of 2-wire serial interface signals, GPIO
signals and also HTPDN/LOCKN signals for Main-Link. THCV242 is Sub-Link Master and connectable to Sub-
Link Slave device such as THCV241.
Sub-Link Polling interval is controllable from about 20us to 800us, that may have relationships on fault/error
detection, interrupt, or other UART / GPIO transfer time designed on application. SSR (Sub-Link Status Read)
interval determines recovery quickness from 2-wire serial remote communication completion. SSR interval
effects only on Sub-Link Master “2-wire Set&Trigger mode1” (R_SLINK_MODE setting).
Table 10. Sub-Link Master protocol basic setting
To use GPIO (General Purpose Input/Output) pin, fault/error detection and interrupt function, “2-wire
Set&Trigger mode1”, “2-wire Pass Through mode1” enables remote register access. THCV242, Sub-Link Master
device has 2-wire serial slave block and can connect to HOST MPU. On the other hand, the counterpart Sub-Link
Slave device has 2-wire serial master block and can connect to remote side 2-wire serial slave devices.
HOST MPU can access register of Sub-Link Master device, Sub-Link Slave device and remote side 2-wire serial
slave devices.
Addr(h) bit Register Name width R/W Description Default
0x0004 [7:3] reserved 5 -
- -
[2:0] R_SLINK_MODE 3 RW
Sub-Link basic protocol setting as Sub-Link Master
1: 2-wire Set&Trigger (Normal) mode1
3: 2-wire Pass Through mode1
0,2,4,5,6,7: Reserved
3'd1
0x0010 [7:4] R_SLINK_EN 4 RW
Sub-Link Enable
[7] Reserved
[6] Reserved
[5] 0:Lane1 Disable, 1:Lane1 Enable
[4] 0:Lane0 Disable, 1:Lane0 Enable
4'd0
[3:0] R_SLINK_POL_EN 4 RW
Sub-Link Polling Enable
[3] Reserved
[2] Reserved
[1] 0:Lane1 Disable, 1:Lane1 Enable
[0] 0:Lane0 Disable, 1:Lane0 Enable
4'hF
0x0011 [7:4] R_SLINK_SSR_EN 4 RW
Sub-Link SSR Enable
[7] Reserved
[6] Reserved
[5] 0:Lane1 Disable, 1:Lane1 Enable
[4] 0:Lane0 Disable, 1:Lane0 Enable
4'hF
[3:0] R_SLINK_WD_EN 4 RW
Sub-Link WDT Enable
[3] Reserved
[2] Reserved
[1] 0:Lane1 Disable, 1:Lane1 Enable
[0] 0:Lane0 Disable, 1:Lane0 Enable
4'hF
0x001A [7:5] reserved 3 -
--
[4] R_SLINK_POL_OFSET_EN 1 RW
Sub-Link Polling Offset Enable
0:Disable
1:Enable, Polling time phase of each lanes are shifted as below
lane1 offset from lane0: Sub-Link Poling interval x 1/4
1'b0
[3:2] reserved 2 -
- -
[1:0] R_SLINK_POL_TIM_UP 2 RW
Sub-LinkPolling interval setting (min. 0x018, about 20us) 2'd0
0x001B [7:0] R_SLINK_POL_TIM_DN 8 RW
Sub-Link Polling interval time=64×(256×R_SLINK_POL_TIM_UP<1:0>
+R_SLINK_POL_TIM_DN<7:0>+1)×tOSC
*No Polling when R_SLINK_POL_TIM_UP=0 and R_SLINK_POL_TIM_DN=0
8'd124
0x001C [7:2] reserved 6 -
--
[1:0] R_SLINK_SSR_TIM_UP 2 RW
Sub-Link SSR interval setting 2'd0
0x001D [7:0] R_SLINK_SSR_TIM_DN 8 RW
Sub-Link SSR interval time=64×(256×R_SLINK_SSR_TIM_UP<1:0>
+R_SLINK_SSR_TIM_DN<7:0>+1)×tOSC
*No SSR when R_SLINK_SSR_TIM_UP=0 and R_SLINK_SSR_TIM_DN=0
8'd249

THCV242_ Rev.2.00_E
Copyright©2019 THine Electronics, Inc. THine Electronics, Inc.
18/53
Security E
Sub-Link 2-wire Read/Write access to remote Register
6.3.5.1. Sub-Link 2-wire Set and Trigger mode
HOST MPU can access to Sub-Link Slave’s register via THCV242 as Sub-Link Master only by THCV242
internal local register control and monitoring on 2-wire Set&Trigger mode1.
Figure 6. Host MPU to Sub-Link Slave Register via THCV242 access configuration
HOST MPU can access to remote side 2-wire serial slave register via THCV242 as Sub-Link Master only by
THCV242 internal local register control and monitoring on 2-wire Set&Trigger mode1.
Figure 7. Host MPU to remote 2-wire slave devices via THCV242 access configuration
Sub-Link Block
2-wire
Slave
Sub-Link
Master
THCV242 as Sub-Link MasterSub-Link Slave Device
Sub-Link Block
Sub-Link
Slave
2-wire
Master
Sub-Link
line
AIN<1:0> = User Select
Interrupt signal
(MSSEL=1)
Host
MPU
SCL
SDA
INT
Register
Register
Triggered access by Sub-Link Master
Access from/to HOST
Sub-Link Block
2-wire
Slave
Sub-Link
Master
THCV242 as Sub-Link MasterSub-Link Slave Device
Sub-Link Block
Sub-Link
Slave
2-wire
Master
Sub-Link
line
2-wire
Slave
Device#b
・
・
2-wire
Slave
Device#a
AIN<1:0> = User Select
(MSSEL=1)
Interrupt signal
Host
MPU
SCL
SDA
INT
RegisterRegister
SCL
SDA
Triggered access by Sub-Link Master
Access from/to HOST

THCV242_ Rev.2.00_E
Copyright©2019 THine Electronics, Inc. THine Electronics, Inc.
19/53
Security E
In principle, when Sub-Link bridges 2-wire serial interface communication from Sub-Link Master to Sub-Link
Slave or remote side 2-wire serial slave devices, time lag occurs between HOST MPU side 2-wire serial access
and Sub-Link Slave internal bus access or remote side 2-wire serial access.
R_2WIRE_CLKSEN (Sub-Link Master side register, 0x0042 bit0) selects whether 2-wire serial slave of Sub-
Link Master perform clock stretching.
When R_2WIRE_CLKSEN = 1, Sub-Link Master device waits HOSTMPU until Sub-Link Slave register access
or remote side 2-wire serial slave register access complete by clock stretching.
When R_2WIRE_CLKSEN = 0, Sub-Link Master device informs HOST MPU that Sub-Link Slave register
access or remote side 2-wire serial register access has completed by interruption (detectable on INT pin) without
clock stretching.
Figure 8. Sub-Link Master 2-wire slave clock stretching operation
2-wire Write A
...
SD1
(SCL)
SD0
(SDA)
Access start to Sub-Link Slave’s register or
Remote side 2-wire serial Slave’s register
...
Stop
Condition
2-wire Write A
...
SD1
(SCL)
SD0
(SDA)
Access start to Sub-Link Slave’s register or
Remote side 2-wire serial Slave’s register
...
Stop
Condition
Clock Stretching
INT Interruption
R_2WIRE_CLKSEN=1 (Clock Stretching Enable)
R_2WIRE_CLKSEN=0 (No Clock Stretching)
Sub-Link communication time + Sub-Link Slave side internal bus access process time
or
Sub-Link communication time + Remote side 2-wire serial Access Time
Sub-Link Slave register Access or
Remote side 2-wire serial register
Access completion

THCV242_ Rev.2.00_E
Copyright©2019 THine Electronics, Inc. THine Electronics, Inc.
20/53
Security E
Table 11. 2-wire serial I/F Set& Trigger mode remote access control and monitoring local registers
Addr(h) bit Register Name width R/W Description Default
0x00D0 [7:0] R_2WIRE_DATA0 8 RW
2-wire serial I/F remote write/read data #0 8'd0
0x00D1 [7:0] R_2WIRE_DATA1 8 RW 2-wire serial I/F remote write/read data #1 8'd0
0x00D2 [7:0] R_2WIRE_DATA2 8 RW 2-wire serial I/F remote write/read data #2 8'd0
0x00D3 [7:0] R_2WIRE_DATA3 8 RW 2-wire serial I/F remote write/read data #3 8'd0
0x00D4 [7:0] R_2WIRE_DATA4 8 RW 2-wire serial I/F remote write/read data #4 8'd0
0x00D5 [7:0] R_2WIRE_DATA5 8 RW 2-wire serial I/F remote write/read data #5 8'd0
0x00D6 [7:0] R_2WIRE_DATA6 8 RW 2-wire serial I/F remote write/read data #6 8'd0
0x00D7 [7:0] R_2WIRE_DATA7 8 RW 2-wire serial I/F remote write/read data #7 8'd0
0x00D8 [7:0] R_2WIRE_DATA8 8 RW 2-wire serial I/F remote write/read data #8 8'd0
0x00D9 [7:0] R_2WIRE_DATA9 8 RW 2-wire serial I/F remote write/read data #9 8'd0
0x00DA [7:0] R_2WIRE_DATA10 8 RW 2-wire serial I/F remote write/read data #10 8'd0
0x00DB [7:0] R_2WIRE_DATA11 8 RW 2-wire serial I/F remote write/read data #11 8'd0
0x00DC [7:0] R_2WIRE_DATA12 8 RW 2-wire serial I/F remote write/read data #12 8'd0
0x00DD [7:0] R_2WIRE_DATA13 8 RW 2-wire serial I/F remote write/read data #13 8'd0
0x00DE [7:0] R_2WIRE_DATA14 8 RW 2-wire serial I/F remote write/read data #14 8'd0
0x00DF [7:0] R_2WIRE_DATA15 8 RW 2-wire serial I/F remote write/read data #15 8'd0
0x00E0 [7:1] R_2WIRE_DEVADR 7 RW
2-wire serial I/F remote access target device address.
if target=self addr.; access to Sub-Link Slave inside register,
else; access to remote side 2-wire serial Slave devices externally connected to Sub-Link slave
7'h00
[0] R_2WIRE_WR 1 RW
2-wire serial I/F remote access write or read select
0:Write
1:Read 1'b0
0x00E1 [7] reserved 1 -
- -
[6:4] R_2WIRE_WADR_BYTE 3 RW
2-wire serial I/F remote device's Sub Address (Word Address, register address) Byte width select.
address Byte width=R_2WIRE_WADR_BYTE<2:0>+1
0 : 1Byte= 8bit Sub addr.(refgister addr.)
1 : 2Byte=16bit Sub addr.(refgister addr.)
4 : 5Byte=40bit Sub addr.(refgister addr.), etc.
3'd0
[3:0] R_2WIRE_DATA_BYTE 4 RW
2-wire serial I/F remote access data Byte number
Byte Number = R_2WIRE_DATA_BYTE + 1 (e.g. 0x2 for 3byte burst)
[write rule] R_2WIRE_WADR_BYTE+R_2WIRE_DATA_BYTE < 'd16
[read rule] R_2WIRE_DATA_BYTE<'d16
4'd0
0x00E2 [7:1] reserved 7 -
- -
[0] R_2WIRE_CLKSEN 1 RW
2-wire serial I/F local response clock stretching Enable
0: Sub-Link Master (2-wire slave) No clock stretching
1: Sub-Link Master (2-wire slave) clock stretching Enable
*2-wire Pass Through mode forces clock stretching Enable
1'b0
0x00E3 [7:2] reserved 6 -
- -
[1:0] R_2WIRE_RD_LANE_SEL 2 RW
Sub-Link transaction read lane select
0: Lane0 Sub-Link read
1: Lane1 Sub-Link read
2,3: Reserved
2'd0
0x00E4 [7:2] reserved 4 -
- -
[1:0] R_2WIRE_WR_LANE_SEL 4 RW
Sub-Link transaction write lane select
[1] 0: Lane1 Disable, 1:Lane1 Enable
[0] 0: Lane0 Disable, 1:Lane0 Enable
*Only active when R_SLINK_MODE=4'd0 or 4'd1
4'hF
0x00E5 [7:1] reserved 7 -
- -
[0] R_2WIRE_START 1 W
2-wire serial I/F remote access start trigger -
Table of contents
Other THine Receiver manuals