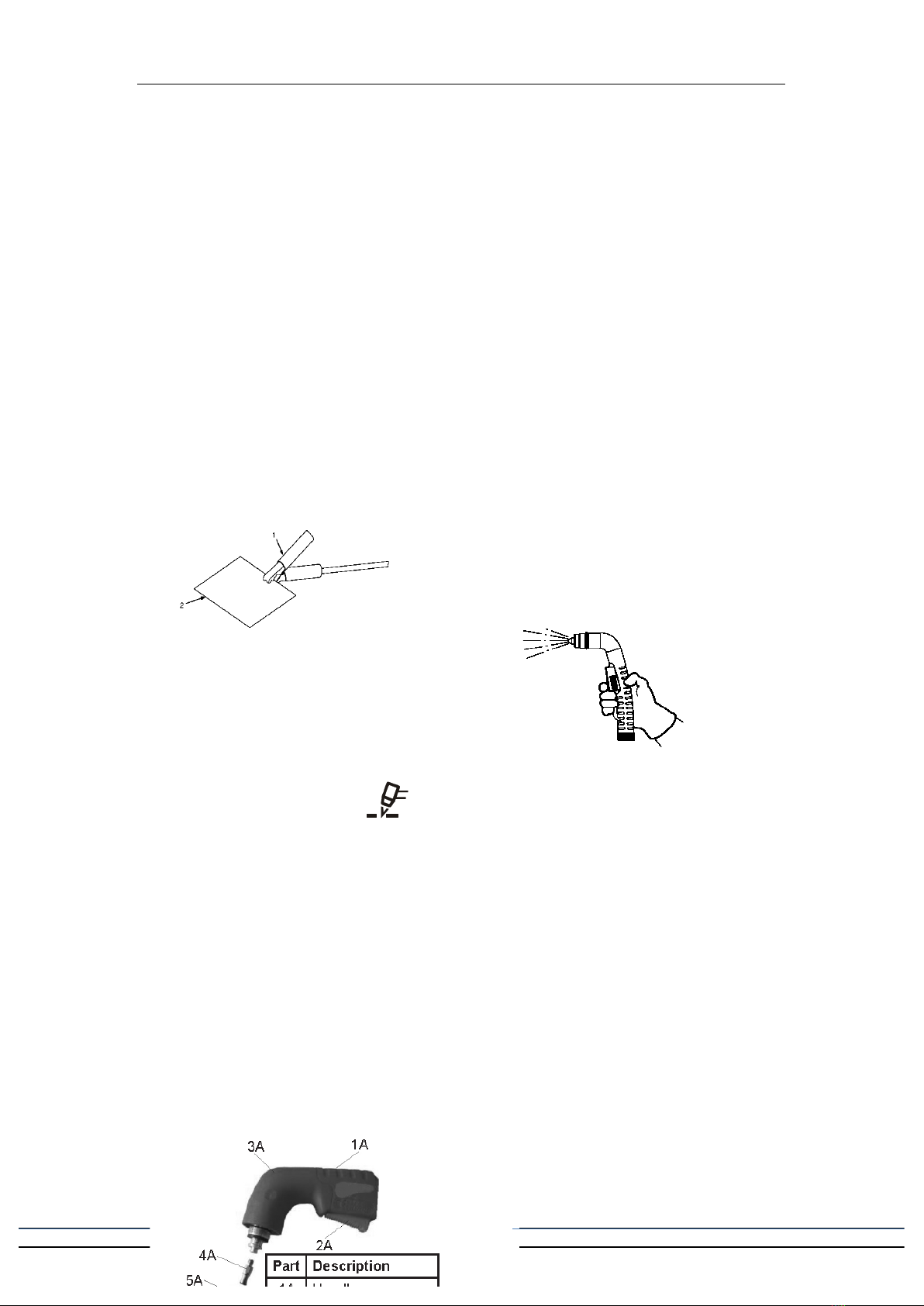
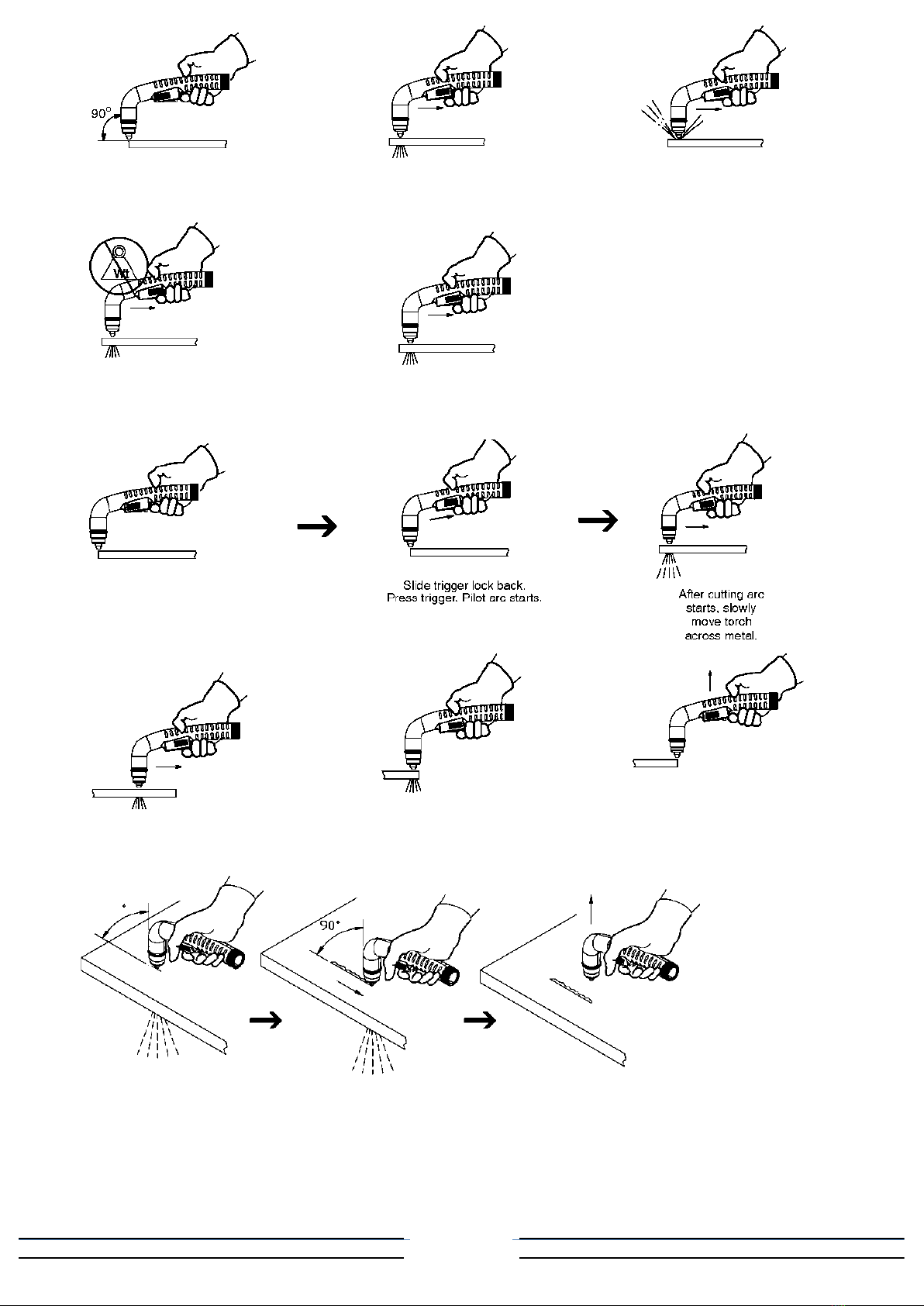
damp or wet location.
4. Avoid unintentional starting. Make
sure you are prepared to begin work
before turning on the tool.
5. Never leave the tool unattended
when it is plugged into an electrical
outlet. Turn off the tool, and unplug it
from its electrical outlet before leaving.
6. Always unplug the tool from its
electrical outlet before performing
and inspection, maintenance, or
cleaning procedures.
7. Prevent eye injury and burns.
Wearing and using the approved
personal safety clothing and safety
devices reduce the risk for injury.
a. Wear the approved safety impact
eye goggles with a welding helmet
featuring at least a number 10
shade lens rating.
b. Leather leggings, fire resistant
shoes or boots should be worn
when using this product. Do not
wear pants with cuffs, shirts with
open pockets, or any clothing that
can catch and hold molten metal
or sparks.
c. Keep clothing free of grease, oil,
solvents, or any flammable
substances. Wear dry, insulating
gloves and protective clothing.
d. Wear an approved head covering
to protect the head and neck. Use
aprons, cape, sleeves, shoulder
covers, and bibs designed and
approved for welding and cutting
procedures.
e. When welding/cutting overhead or
in confined spaces, wear flame
resistant ear plugs or ear muffs to
keep sparks out of ears.
8. Prevent accidental fires. Remove
any combustible material from the
work area.
a. When possible, move the work to
a location well away from
combustible; protect the
combustibles with a cover made of
fire resistant material.
b. Remove or make safe all
combustible materials for a radius
of 35 feet (10 meters) around the
work area. Use a fire resistant
material to cover or block all open
doorways, windows, cracks, and
other openings.
c. Enclose the work area with
portable fire resistant screens.
Protect combustible walls, ceilings,
floors, etc., from sparks and heat
with fire resistant covers.
d. If working on a metal wall, ceiling,
etc., prevent ignition of
combustibles on the other side by
mobbing the combustibles to a
safe location. If relocation of
combustibles is not possible,
designate someone to serve as a
fire watch, equipped with a fire
extinguisher, during the cutting or
welding process and for at least
one half hour after the cutting or
welding is completed.
e. Do not weld or cut on materials
having a combustible coating or
combustible internal structure, as
in walls or ceilings, without an
approved method for eliminating
the hazard.
f. Do not dispose of hot slag in
containers holding combustible
materials. Keep a fire extinguisher
nearby and know how to use it.
g. After welding or cutting, make a
thorough examination for evidence
of fire. Be aware that easily visible
smoke or flame may not be
present for some time after the fire