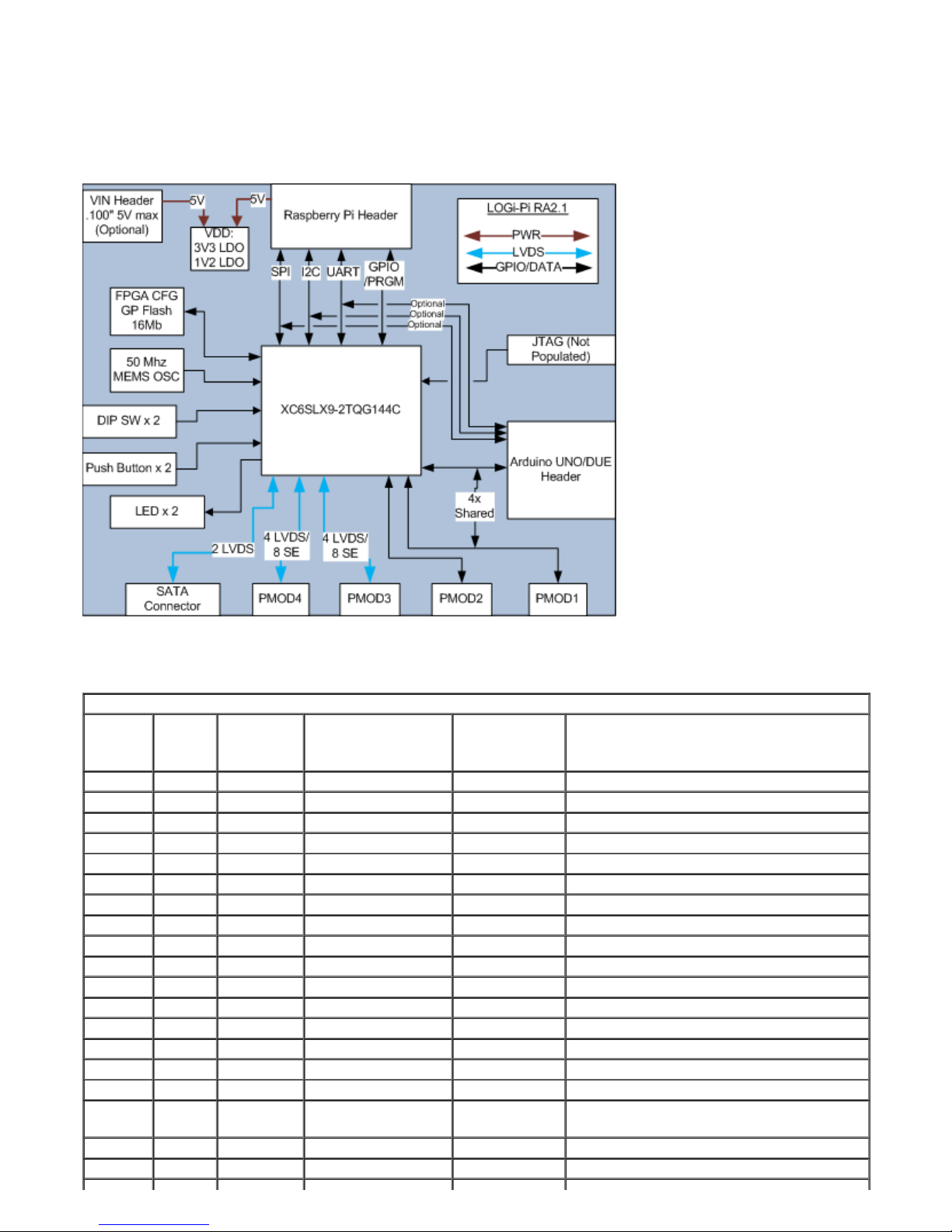
The PMOD connectors are not optimal for differential signals as they are not capable of maintaining the differential
impedance based on the large separation of the signal throughout the length of the connector. It is possible to
minimize this mismatch by replacing the PMOD connectors with low profile .100" vertical headers that will shorten
the path of separation therefore minimizing the impedance mismatch and allow for higher bandwidth interfaces. For
optimal performance using the LVDS signals on PMOD3 and PMOD4 it is recommended that LVDS signals be
directly soldered to the header pads to eliminate the impedance mismatch that occurs throughout the connector.
Push Button Usage
Two push button switches are provided on the LOGi-Pi. The pushbuttons are configured active high and an
discrete 10k ohm pull-up resistor is populated on-board to eliminate the need for configuring and used the on-chip
pull-up resistors. Additionally a DNP capacitor footprint is provided to allow users to install a capacitor for analog
debounce functionality. It is recommended the soft debounce logic be used in HDL, if the debounce functionality is
not enable by use of an installed capacitor,
DIP Switch Usage
A two position DIP switch is used on the LOGi-Pi. It is anticipated that the DIP switch be used for mode control
and other general purpose usage.
LED Usage
Two general purpose LED's are used on the LOGi-Pi. Due to the limited pin availability on the FPGA TQFP
package the LED pins are also shared with two rarely used PWM inputs on the Arduino Shield (RA2.1 only).
JTAG Interface
A unpopulated JTAG header is available on the LOGi-Pi. The JTAG header is contains the Digilent Inc. 6 pin
function pinout and is a .100" 6 pin header. The Digilent Inc JTAG adapters or xinlinx flying lead adapters can be
used to interface with the FPGA through the JTAG connection. The JTAG connection allows for direct
programming FPGA or onboard Flash memory, additionally chipscope can be used for deep debug and analysis.
Programming the FPGA from the Raspberry Pi
The main method of programming the FPGA is to use the LOGi Loader from the Raspberry Pi. The LOGi Loader
is a a program that has been developed to automate the process of loading the FPGA. The user needs to
download the LOGi Loader from the LOGi github repository and install the loader application on the Raspberry Pi
device. Once installed, the LOGi Loader can be invoked from the location of the stored FPGA bit file. The LOGi
loader will load the FPGA with the given bitstream file.
Raspberry Pi SPI to FPGA Interface
The Raspberry Pi to FPGA main communication interface is the PI SPI port. The Max Theoritical SPI clock rate
support on the Pi is "NEEDED VALUE". Though, based our development experience there are some instability
issues that can occur when reaching very high clock rates. The current LOGI drivers implement a 32Mhz clock
reliably. With further work users may be able to increase this clock rate with further driver deveopment.