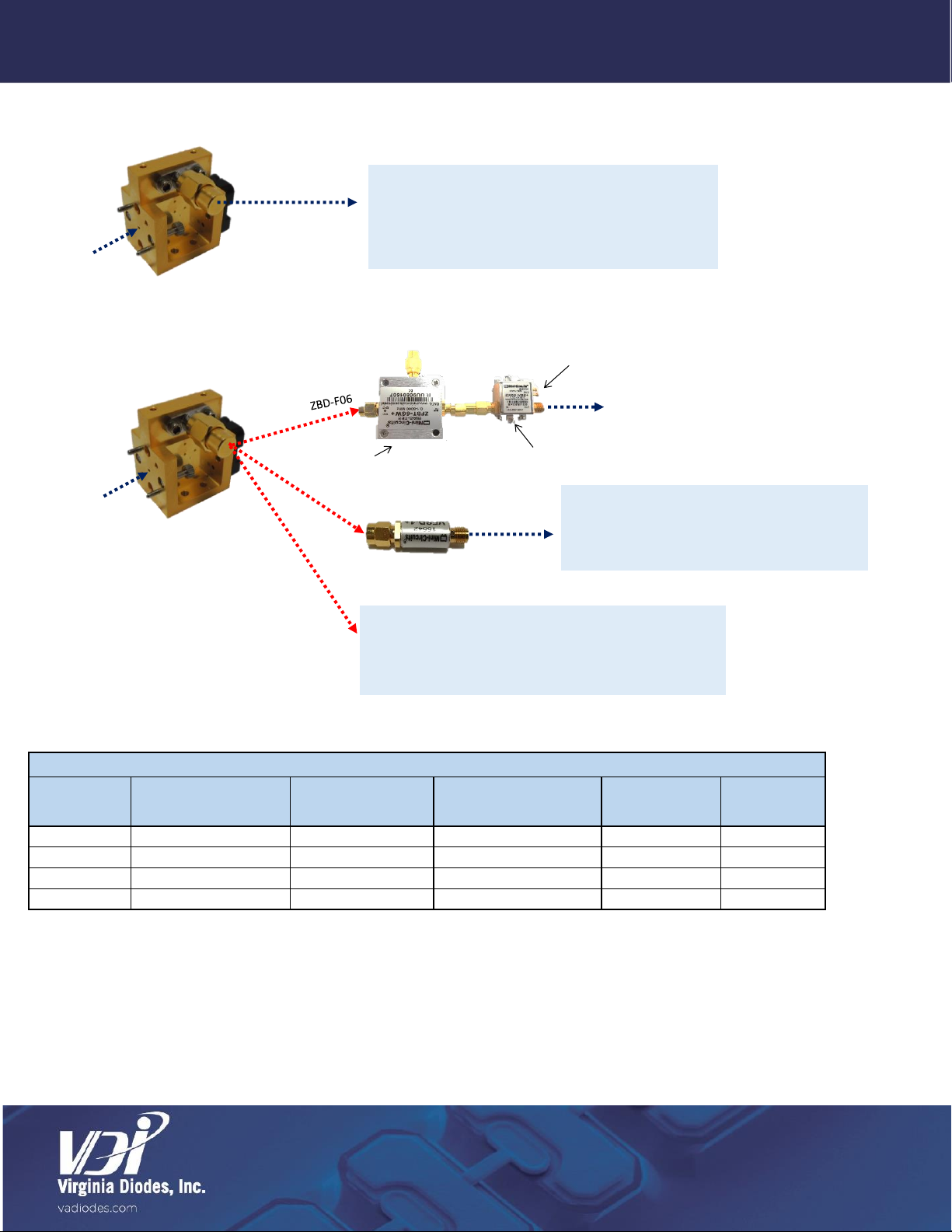
Zero-Bias Detectors (ZBD)
Virginia Diodes offers zero biased, Schottky diode detectors for a variety of millimeter wave and
terahertz applications. These detectors provide high responsivity and extremely fast response time. VDI
detectors offer full waveguide band coverage and are available from WR15 (50-75 GHz) to WR0.65
(1100-1700 GHz). Higher frequency custom detectors are available upon request.
Safety and Operational Guidelines
Read all instructions and information in this product manual before connecting the product to external equipment.
Operational procedures must be followed for proper function. If you have questions, contact VDI before operating the
product.
The internal components of every detector can be damaged by Electro Static Discharge (ESD). Any operator using or
handling the device should wear a grounded wrist strap specifically designed to guard against ESD. The work
environment including test benches should also be properly grounded.
VDI assumes the customer is familiar with microwave, millimeter wave, and VDI products in general. The user and
customer are expected to understand all safety guidelines, health hazards, and general advisories that may exist and
are associated with the use of this device. VDI is not responsible for any human hazards that may exist or may occur
while using this device.
Virginia Diodes, Inc. (VDI) accepts no liability for damage or injury resulting from or caused by:
•Improper use, disassembly or use for purposes other than those for which the product was designed;
•Use outside common safety, health or general advisories pertaining to microwave, millimeter wave, and VDI products;
•Repairs carried out by persons other than VDI or its assigned agents.
Waveguide Inspection / Test Port Care
•Inspect waveguide flanges for debris prior to making connections.
•Making a connection with metal debris between the waveguide flanges can damage the waveguide interface and prevent
repeatable connections.
•If debris is present, clean the flange with pre-dampened lint free wipes or swabs (e.g. TexWipe TX1065). If these are not
available, lint free cloths lightly dampened with ethanol may be used (e.g. TexWipe TX604).
•When device is not in use, cover appropriate waveguide flanges with provided dust cap or protective waveguide tape.
•Waveguide screws should be torqued between 20-50 cNm, greater values can damage the interface.
•Use a torque of 90 cNm when making coaxial connections. Avoid sharp bends in cables.
General Operating Practices and Recommendations
•Check with VDI before any use is attempted beyond those described in this manual, including uses that may exceed
limitations stated here or commonly accepted standards of practice.
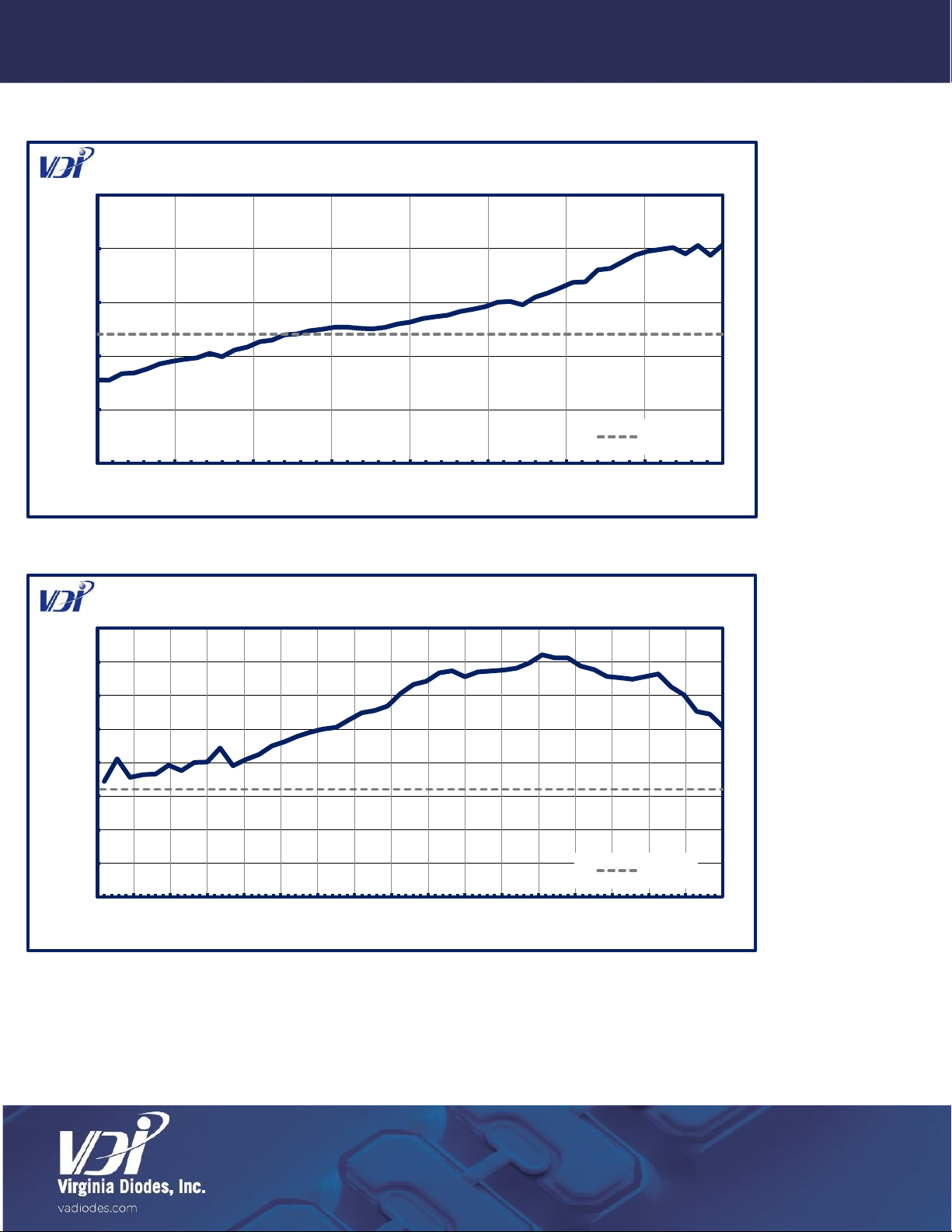
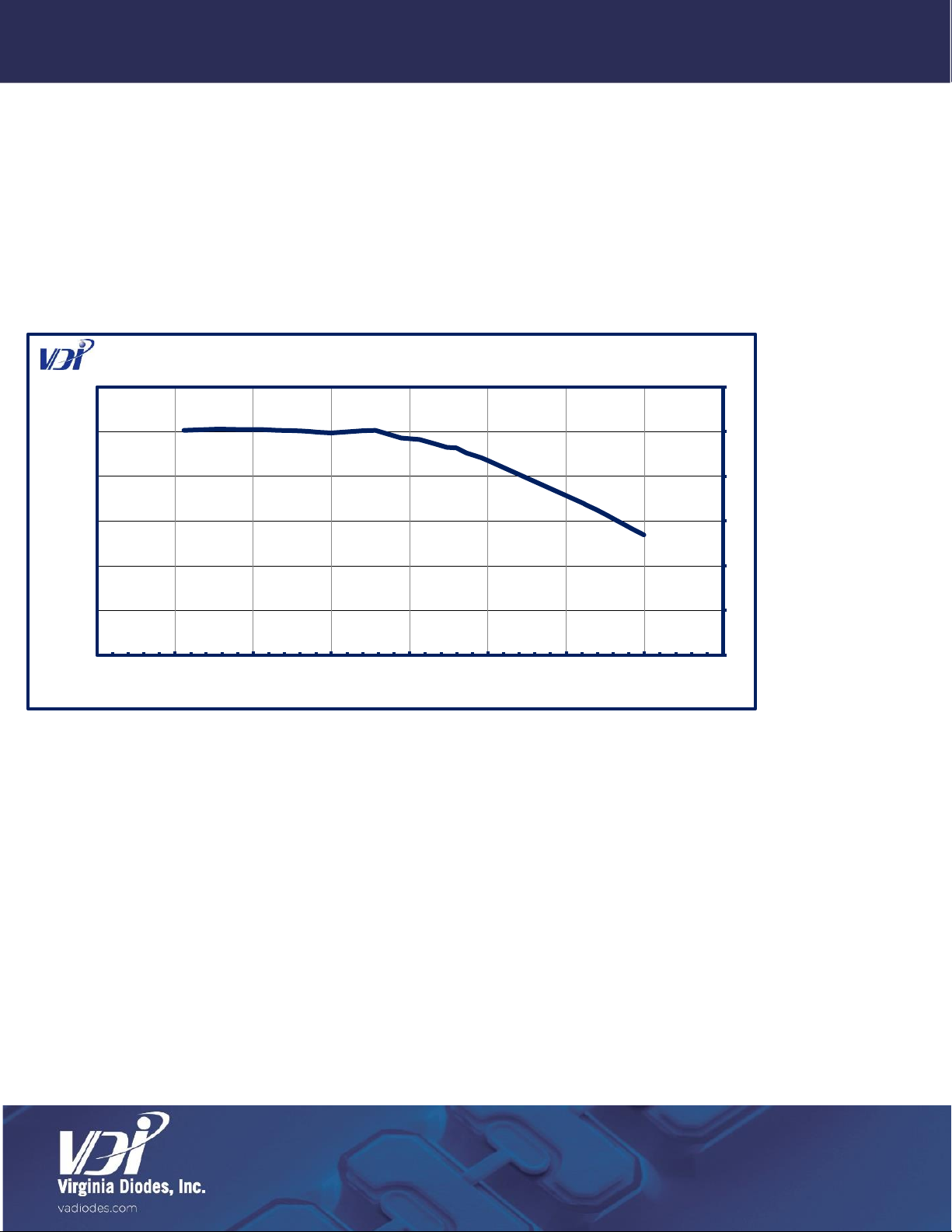
•Specifications listed in this document reflect the latest specifications. For ZBDs shipped prior to July 3, 2019, please refer
to individualized data sheets.