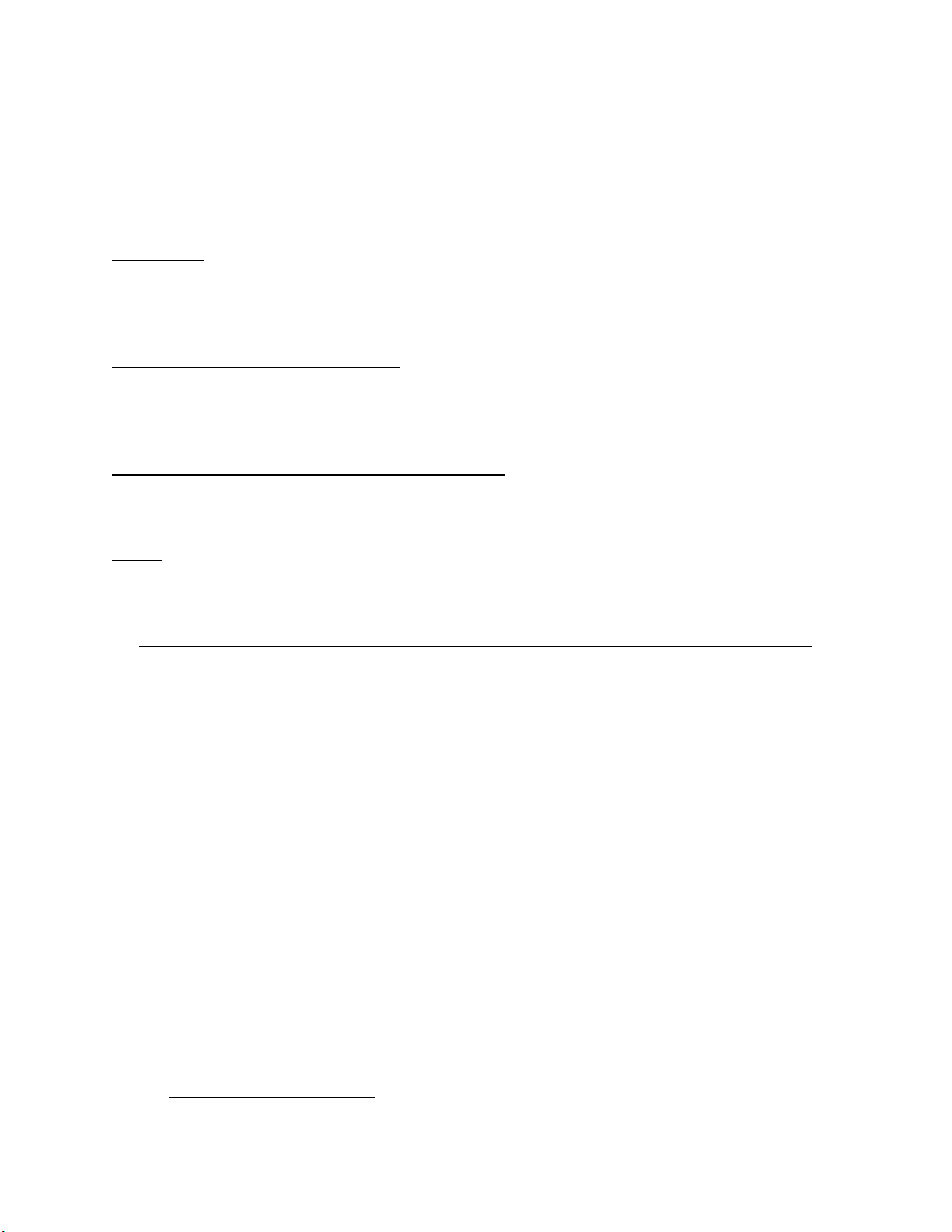
6 cell, 12 volt battery @ 13.25 volts, 200mA
12 cell, 24 volt battery @ 26.50 volts, 200mA
This is measured at exactly 120V incoming.
BATTERY CHARGER PERFORMANCE
Should the charging rate of your Battery charger be lower than the specified rate of charge - do
not condemn the unit too hastily as there are several reasons for this condition.
Battery chargers are manufactured so as to give their rated capacity only when all conditions are
normal. Conditions that affect charger output are line voltage, battery condition and temperature.
Line voltage is very important as should your line voltage be low, the output of the charger will
drop accordingly. In most instances a charger is built for operation on 120 volts AC, and
maximum ampere rating is obtained at this voltage. It has been observed, there is a drop of 1 to 2
amperes for every 1 volt drop in line voltage By line voltage, we mean line voltage under load.
The line must deliver 120 volts while the charger is operating. Very often, line voltage will test
120 volts with no load, but as the charger load is applied, the line voltage drops. This is
particularly true if the circuit to which it is connected is overloaded with other equipment, or
where a long undersized extension cord is being used.
Battery condition, also plays a very important part in the output of a charger. Chargers are
generally designed to deliver their maximum output on a fully discharged battery. If the battery
is partially charged, you will not get maximum output, as the higher battery voltage opposes the
charger voltage and a lower rate results. The output of a charger can vary considerably,
depending on the state of the battery being charged. Cold or sulphated batteries have high
internal resistance and the normal output voltage of the charger cannot force the full rated current
into the battery, because of this high internal resistance. The rate therefore will be low.
Another cause of a low charging rate is a battery whose specific gravity of its electrolyte is down
around 1.100 or below. This low specific gravity will offer a high degree of resistance to the
initial charging rate due to the fact that the conductivity of the electrolyte is very nearly that of
water. As the battery in this condition is charged the specific gravity of the electrolyte will rise
and the charging rate will rise as the conductivity increases.
Should you have the combination of low line voltage and unfavourable battery condition, the
output of any charger will be extremely low. This combination can reduce the output of an
honestly rated charger as much as 75 per cent. It is therefore recommended that, if a charger has
a low DC output, the unit be checked as follows:
1. Discharge a normal, healthy battery to 1.120 or 1.130 sp. gr.
2. Connect the charger and start the charge.
3. Check line voltage while the charger is operating. It should be 120 volts to obtain
maximum DC output.
3