4. Installation
4.1 The pump must be secured to a horizontal, plane and solid foundation by bolts
through the holes in the base plate.
When installing the pump, follow the procedure below in order to avoid damaging the
pump.
4.2 Outdoor installation: When the pump is installed outside, please provide
a suitable cover to protect it from weather and forst. Please do not allow any
foreign objects fall into the motor fan cover.
~ 6 ~
Step Action
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
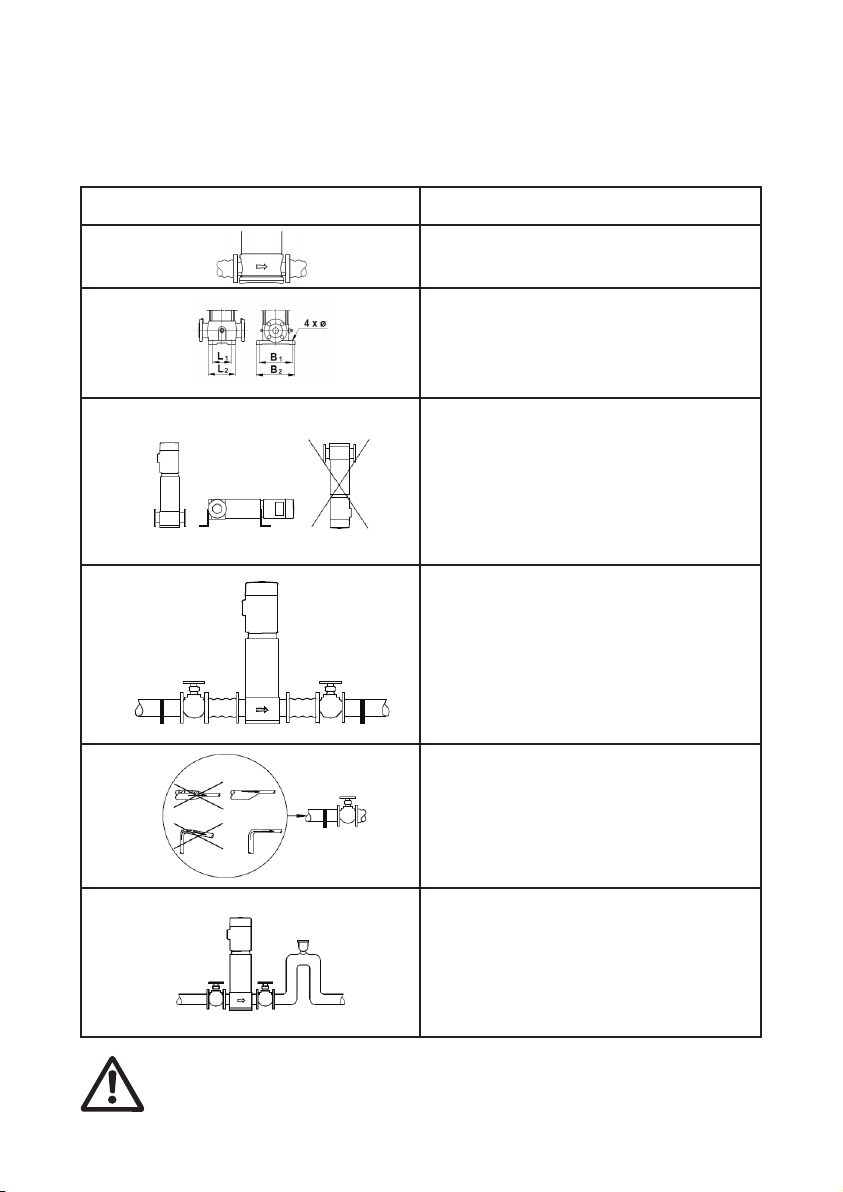
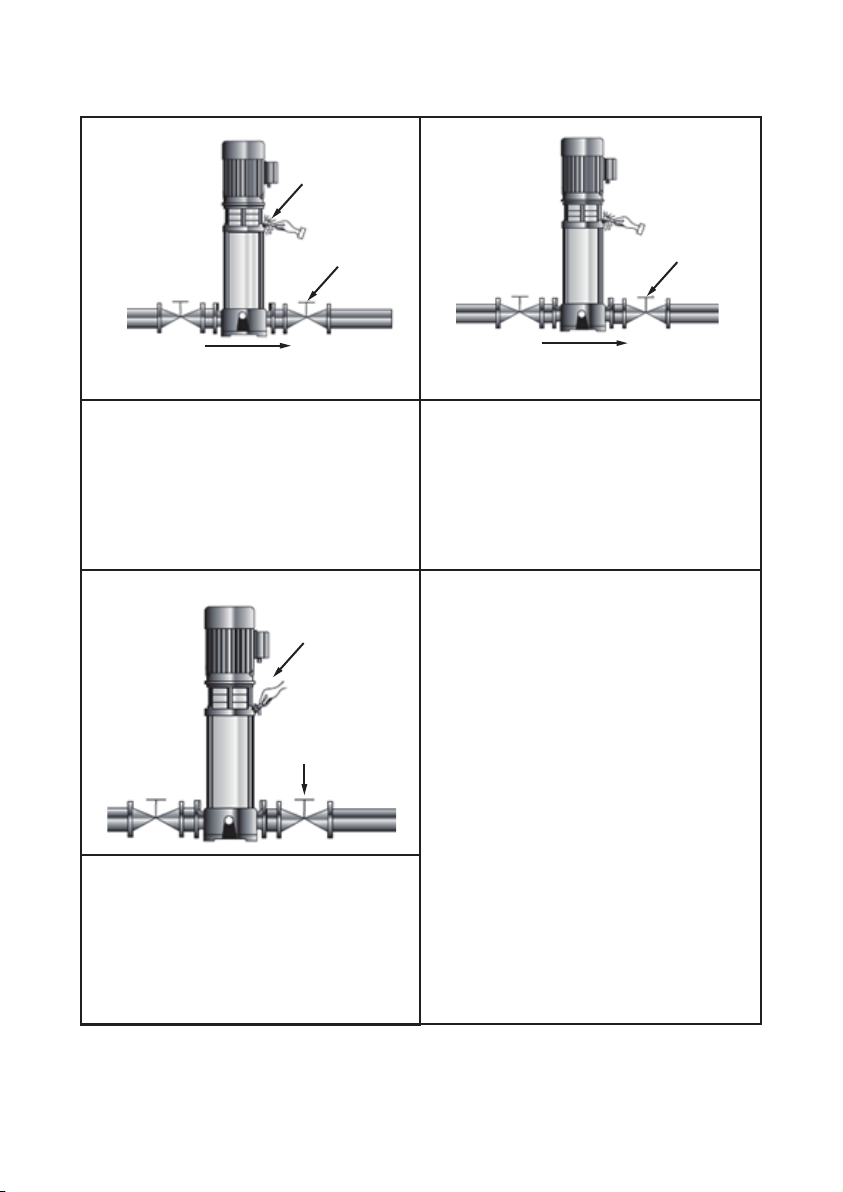
Arrows on the pump base show the
direction of flow of liquid through the pump.
This information is in:
• port-to-port lengths
• dimensions of the base
• pipework connections
• diameter and position of foundation bolts.
The pump can be installed vertically or
horizontally (TPR, TPRN 120 and 150, 75
kW, only vertically). However, the motor must
neither fall below the horizontal plane nor be
installed upside down.
Ensure that an adequate supply of cool air
reaches the motor cooling fan.
Motors above 4 kW must be supported.
To minimize possible noise from the pump,
we advise you to fit expansion joints on either
side of the pump.
Fit isolating valves on either side of the pump
to avoid draining the system if the pump
needs to be removed for cleaning, repair or
replacement.
Always protect the pump against backflow by
means of a non-return valve (foot valve).
Install the pipes so that air locks do not
occur, especially on the suction side of the
pump.
Fit a vacuum valve close to the pump if the
installation has one of these characteristics:
• The discharge pipe slopes downwards
away from the pump.
• There is a risk of siphon effect.
• Protection against backflow of unclean
liquids is needed.