adafruit learning system PA1010D User manual

Adafruit Mini GPS PA1010D Module
Created by Kattni Rembor
Last updated on 2021-10-22 11:38:03 AM EDT

2
3
7
7
8
8
9
9
9
10
11
11
11
12
14
14
14
14
15
16
16
16
17
17
18
18
18
19
20
21
22
23
23
23
23
27
27
27
27
31
33
33
33
33
Guide Contents
Guide Contents
Overview
Pinouts
GPS Module
Power Pins
I2C Data Pins
Other Pins
UART Serial Data Pins
LEDs
Optional Coin Cell
Arduino I2C Usage
Wiring
Installation
Echo Test Demo
Arduino UART Usage
Wiring
Installation
Echo Test Demo
Hardware UART
CircuitPython & Python Setup
CircuitPython Microcontroller Wiring
I2C Interface
UART Interface
Python Computer Wiring
I2C Interface
UART Interface
USB-to-Serial Cable Interface
Hardware UART Interface
CircuitPython Installation of GPS Library
Python Installation of GPS Library
Python Docs
CircuitPython & Python I2C Usage
CircuitPython Microcontroller Usage
Linux, Computer or Raspberry Pi Usage
Echotest Example
CircuitPython & Python UART Usage
CircuitPython Microcontroller
Linux/Computer/Raspberry Pi with Python
Example Parsing Code
GPS Example Code Explained
Downloads
Files:
Schematic
Fab Print
© Adafruit Industries https://learn.adafruit.com/adafruit-mini-gps-pa1010d-module Page 2 of 35

Overview
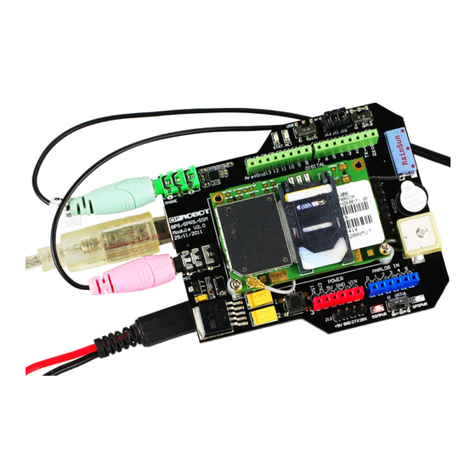
This miniature GPS breakout is only 1" x 1" (~ 25mm x 25mm) but houses a complete GPS/GNSS solution
with both I2C and UART interfaces. There's even an antenna on top so it's plug and play!
Support for GPS, GLONASS, GALILEO, QZSS
-165 dBm sensitivity, up to 10 Hz updates
Up to 210 PRN channels with 99 search channels and 33 simultaneous tracking channels
5V friendly design and only 30mA current draw
Breadboard-able, with 4 mounting holes
UART
and
I2C interfaces, pick whichever you like most!
RTC battery-compatible
PPS output on fix ±20ns jitter
Internal patch antenna
Low-power and standby mode with WAKE pin
© Adafruit Industries https://learn.adafruit.com/adafruit-mini-gps-pa1010d-module Page 3 of 35

The breakout is built around the MTK3333 chipset, a reliable, high-quality GPS module that can handle up
to 33 simultaneous tracking channels, has an excellent high-sensitivity receiver (-165 dBm tracking!), and a
built in antenna. It can do up to 10 location updates a second for high speed, high sensitivity logging or
tracking. Power usage is incredibly low, only 30 mA during navigation.
Best of all, we added all the extra goodies you could ever want: a ultra-low dropout 3.3V regulator so you
can power it with 3.3-5VDC in, 5V level safe inputs on UART and I2C, a footprint for optional CR1220 coin
cell to keep the RTC running and allow warm starts, a green power LED and a tiny red PPS LED. The LED
© Adafruit Industries https://learn.adafruit.com/adafruit-mini-gps-pa1010d-module Page 4 of 35

blinks at about 1Hz when a fix is found and is off when no fix.
Unlike our Ultimate GPS modules, this module does not have the ability to connect an external antenna,
it's designed to be as small as possible for compact projects.
As with all Adafruit breakouts, we've done the work to make this GPS module super easy to use. We've
put it on a breakout board with the required support circuitry and connectors to make it easy to work with,
and is now a trend we've added SparkFun Qwiic (https://adafru.it/Fpw) compatible STEMMA
QT (https://adafru.it/Ft4) JST SH connectors that allow you to get going without needing to solder. Just
use a STEMMA QT adapter cable (https://adafru.it/FA-), plug it into your favorite micro or Blinka supported
SBC and you're ready to rock!
Comes with one fully assembled and tested module, a piece of header you can solder to it for bread-
boarding, and a CR1220 coin cell holder. A CR1220 coin cell is not included, but we have them in the
shop if you'd like to use the GPS's RTC (http://adafru.it/380)
© Adafruit Industries https://learn.adafruit.com/adafruit-mini-gps-pa1010d-module Page 5 of 35

© Adafruit Industries https://learn.adafruit.com/adafruit-mini-gps-pa1010d-module Page 6 of 35

Pinouts
This GPS module can be used with I2C or UART. Let's take a look!
GPS Module
The PA1010D GPS module with built-in antenna is
located in the center of the board. It has all kinds of
features!
Support for GPS, GLONASS, GALILEO, QZSS
-165 dBm sensitivity, up to 10 Hz updates
Up to 210 PRN channels with 99 search channels
and 33 simultaneous tracking channels
UART
and
I2C interfaces, pick whichever you like
most!
PPS output on fix ±20ns jitter
Internal patch antenna
Low-power and standby mode with WAKE pin
Note: Due to the sensitivity of the built in antenna, the
PA1010D Mini GPS module may need a more
unobstructed view of the sky than other GPS modules. If
you are having trouble getting a fix, try moving the
module to a clear spot with the antenna pointing up at the
sky.
© Adafruit Industries https://learn.adafruit.com/adafruit-mini-gps-pa1010d-module Page 7 of 35

Power Pins
VIN - power input, connect to 3-5VDC. It's important
to connect to a
clean and quiet
power supply. GPS's
are very sensitive, so you want a nice and quiet
power supply. Don't connect to a switching supply if
you can avoid it, an LDO will be less noisy! This
module only draws 30mA current during navigation
GND - power and signal ground. Connect to your
power supply and microcontroller ground.
Optional:
3Vo - is the output from the onboard 3.3V regulator.
If you have a need for a clean 3.3V output, you can
use this! It can provide at least 100mA output.
I2C Data Pins
SCL - this is the I2C clock pin, connect to your
microcontroller or computer's I2C clock line.
SDA - this is the I2C data pin, connect to your
microcontroller or computer's I2C data line.
These pins have 10K pullups to Vin. They are level shifted
so you can use 3 or 5V logic
On both sides in the middle are the Sparkfun
Qwiic (https://adafru.it/Fpw) compatible STEMMA
QT (https://adafru.it/Ft4) JST SH connectors, for
using with I2C. Use with any of the STEMMA QT
cables available in the Adafruit shop to connect this
breakout to your project without needing to solder!
© Adafruit Industries https://learn.adafruit.com/adafruit-mini-gps-pa1010d-module Page 8 of 35

Other Pins
RST - When pulled to ground, this will put the chip
in the module into reset. Handy when you want to
start with a completely clean setup.
PPS is a "pulse per second" output. Most of the time
it is at logic low (ground) and then it pulses high
(3.3V) once a second, for 50-100ms, so it should be
easy for a microcontroller to sync up to it
WAKE - This pin works with low power and standby
modes. Check the datasheet for more information!
UART Serial Data Pins
TXO - the pin that transmits data
from
the GPS
module to your microcontroller or computer. It is
3.3V logic level. Data comes out at 9600 baud 8N1
by default
RXI - the pin that you can use to send data
to
the
GPS. This pin is level shifted so you can use 3-5V
logic. By default it expects 9600 baud data by
default.
LEDs
© Adafruit Industries https://learn.adafruit.com/adafruit-mini-gps-pa1010d-module Page 9 of 35

There are two LEDs on the board.
ON - Green power LED. Lit when the board is
powered
PPS - Red PPS LED, blinks at about 1Hz when a fix is
found and is off when no fix.
Optional Coin Cell
The back has a footprint for an optional coin cell battery.
The board ships with a CR1220 coin cell holder that can
be soldered onto the back. CR1220 battery not included.
© Adafruit Industries https://learn.adafruit.com/adafruit-mini-gps-pa1010d-module Page 10 of 35

Arduino I2C Usage
Wiring
If you have a STEMMA QT breakout cable (https://adafru.it/FA-), then you can wire like this:
RED to 3.3
BLACK to GND
BLUE to SDA
YELLOW to SCL
If you want to solder pins to the header connectors and use a breadboard, then wire like this:
VIN to 3.3
GND to GND
SDA to SDA
SCL to SCL
Installation
The Adafruit GPS Library includes support for the Mini GPS PA1010D module. You can install it from the
Arduino IDE via the Library Manager:
© Adafruit Industries https://learn.adafruit.com/adafruit-mini-gps-pa1010d-module Page 11 of 35

Click the Manage Libraries... menu item, search for Adafruit GPS, and select the Adafruit GPS Library:
Echo Test Demo
We can test basic functionality using one of the examples from the library. This won't do any parsing. It
simply dumps the raw data sentences as received from the GPS module.
Open up File -> Examples -> Adafruit GPS Library -> GPS_I2C_EchoTest and upload to your Arduino
board with the GPS module connected.
Once the sketch is uploaded, open up the Serial Monitor ( Tools -> Serial Monitor) at 115200 baud. You
should see something like this:
If you see this, then you are successfully talking to the GPS module. Once it obtains a lock on the GPS
satellites, which can takes several minutes, there will be more information in the sentences. To see that
information in a more user friendly format, try running the GPS_I2C_Parsing example from the library.
© Adafruit Industries https://learn.adafruit.com/adafruit-mini-gps-pa1010d-module Page 12 of 35

© Adafruit Industries https://learn.adafruit.com/adafruit-mini-gps-pa1010d-module Page 13 of 35

Arduino UART Usage
Wiring
Note that the breakout has pins on two sides. Be sure to use the side with the UART pins. They are
labeled TXO and RXI. We'll demonstrate using SoftwareSerial on the Metro 328. Here's the wiring:
3.3 to VIN
GND to GND
8 to TXO
7 to RXI
Installation
See the Arduino I2C Usage section for details about installing the Adafruit GPS Library. The same library
is used for UART.
Echo Test Demo
We can test basic functionality using one of the examples from the library. This won't do any parsing. It
simply dumps the raw data sentences as received from the GPS module.
Open up File -> Examples -> Adafruit GPS Library -> GPS_SoftwareSerial_EchoTest and upload to your
Arduino board with the GPS module connected.
Once the sketch is uploaded, open up the Serial Monitor ( Tools -> Serial Monitor) at 115200 baud. You
should see something like this:
© Adafruit Industries https://learn.adafruit.com/adafruit-mini-gps-pa1010d-module Page 14 of 35

If you see this, then you are successfully talking to the GPS module. Once it obtains a lock on the GPS
satellites, which can takes several minutes, there will be more information in the sentences. To see that
information in a more user friendly format, try running the GPS_SoftwareSerial_Parsing example from the
library.
Hardware UART
The above example demonstrated UART usage via SoftwareSerial. If you have a board with an available
hardware UART, you can use that also. Simply connect to the TX/RX pins for the hardware UART for your
particular board and then see the examples in the Adafruit GPS Library with HardwareSerial in the name.
© Adafruit Industries https://learn.adafruit.com/adafruit-mini-gps-pa1010d-module Page 15 of 35

CircuitPython & Python Setup
It's easy to use the Adafruit Mini GPS PA1010D breakout with Python or CircuitPython and the Adafruit
CircuitPython GPS (https://adafru.it/BuR) module. This library allows you to write Python code that reads
the date, time, location and more from the breakout.
You can use this sensor with any CircuitPython microcontroller board or with a computer that has GPIO
and Python thanks to Adafruit_Blinka, our CircuitPython-for-Python compatibility
library (https://adafru.it/BSN).
CircuitPython Microcontroller Wiring
The Adafruit Mini GPS PA1010D can be wired up in multiple ways. We recommend I2C as it is the
simplest. There are two ways you can connect the GPS to a microcontroller using I2C.
I2C Interface
Here is an example of the module connected to a Feather M0 Express for I2C using the STEMMA
connector and a STEMMA cable:
Feather 3V to STEMMA red wire (VIN)
Feather GND to STEMMA black wire (GND)
Feather SDA to STEMMA blue wire (SDA)
Feather SCL to STEMMA yellow wire (SCL)
Here is an example of the module connected to a Feather M0 Express for I2C using jumper wires:
© Adafruit Industries https://learn.adafruit.com/adafruit-mini-gps-pa1010d-module Page 16 of 35

Feather 3V to module VIN
Feather GND to module GND
Feather SCL to module SCL
Feather SDA to module SDA
UART Interface
Here is an example of the module connected to a Feather M0 Express using UART:
Feather 3V to module VIN
Feather GND to module GND
Feather TX to module RXI
Feather RX to module TXO
Python Computer Wiring
Since there's
dozens
of Linux computers/boards you can use we will show wiring for Raspberry Pi. For
other platforms, please visit the guide for CircuitPython on Linux to see whether your platform is
supported (https://adafru.it/BSN).
© Adafruit Industries https://learn.adafruit.com/adafruit-mini-gps-pa1010d-module Page 17 of 35

I2C Interface
Here's the Raspberry Pi wired with I2C using the STEMMA connector and a STEMMA cable:
Pi 3V to STEMMA red wire (VIN)
Pi GND to STEMMA black wire (GND)
Pi SDA to STEMMA blue wire (SDA)
Pi SCL to STEMMA yellow wire (SCL)
Here's the Raspberry Pi wired with I2C using jumper wires:
Pi 3V to module VIN
Pi GND to module GND
Pi SCL to module SCL
Pi SDA to module SDA
UART Interface
For UART, you have two options: An external USB-to-serial converter or the built-in UART on the Pi's
TX/RX pins.
USB-to-Serial Cable Interface
Here's an example of wiring up the USB-to-TTL serial converter (https://adafru.it/dDd), and the FTDI serial
TTL-232 USB cable (https://adafru.it/dNN) (also available in USB-C (https://adafru.it/H3d)):
© Adafruit Industries https://learn.adafruit.com/adafruit-mini-gps-pa1010d-module Page 18 of 35

For USB to TTL serial cable:
USB 3V (red wire) to module VIN
USB GND (black wire) to module GND
USB TX (green wire) to module RXI
USB RX (white wire) to module TXO
For FTDI serial TTL cable - the FTDI cable pinout matches
the pinout on the UART side of the PA1010D Mini GPS
Module. Connect the cable so that the wires align as
follows:
FTDI black wire to module GND
FTDI brown wire to module PPS
FTDI red wire to module VIN
FTDI orange wire to module RXI
FTDI yellow wire to module TXO
FTDI green wire to module WAKE
Hardware UART Interface
Here's an example using the Pi's built-in UART:
For single board computers other than the Raspberry Pi, the serial port may be tied to the
console or not be available to the user. Please see the board documentation to see how the
serial port may be used.
© Adafruit Industries https://learn.adafruit.com/adafruit-mini-gps-pa1010d-module Page 19 of 35

Pi 3V to module VIN
Pi GND to module GND
Pi TX to module RXI
Pi RX to module TXO
If you want to use the built-in UART, you'll need to disable the serial console and enable the serial port
hardware in raspi-config. See the UART/Serial section of the CircuitPython on Raspberry Pi
guide (https://adafru.it/CEk) for detailed instructions on how to do this.
CircuitPython Installation of GPS Library
Next you'll need to install the Adafruit CircuitPython GPS (https://adafru.it/BuR) library on your
CircuitPython board.
First make sure you are running the latest version of Adafruit CircuitPython (https://adafru.it/Em8) for your
board.
Next you'll need to install the necessary libraries to use the hardware. Carefully follow the steps to find
and install these libraries from Adafruit's CircuitPython library bundle (https://adafru.it/ENC). For example,
the Welcome to CircuitPython guide has a great page on how to install the library
bundle (https://adafru.it/ABU).
To install the libraries, you'll need to copy the following files from the bundle to the lib folder on your
CIRCUITPY drive:
adafruit_gps.mpy
adafruit_bus_device
Before continuing make sure your board's lib folder has the adafruit_gps.mpy and adafruit_bus_device
files and folders copied over.
© Adafruit Industries https://learn.adafruit.com/adafruit-mini-gps-pa1010d-module Page 20 of 35
Table of contents